Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Defuzzification Methods Explained
Încărcat de
kaylarobertsTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Defuzzification Methods Explained
Încărcat de
kaylarobertsDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
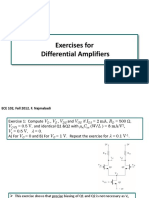
Lecture 05
Defuzzification
!"
v Defuzzification means the fuzzy-to-crisp
conversions.
The fuzzy results generated cannot be used to the applications.
It is necessary to convert the fuzzy quantities into crisp quantities
for further processing.
v Defuzzification has the capability to
reduce a fuzzy set to a crisp single-valued quantity or as a set.
Outline
v Lambda Cuts
for Fuzzy Sets
for Fuzzy Relations
v Defuzzification Methods
Maxima method
Centroid method
Weighted average method
Middle-of-maxima method
First-of-maxima or last-of-maxima
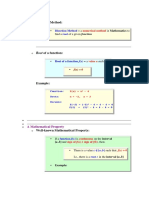
Lambda Cuts for Fuzzy Sets
v Consider a fuzzy set
Its lambda cut denoted by
is a crisp set:
the value of lambda cut set is x, when the membership value
corresponding to x is greater than or equal to the specified .
This lambda cut set can also be called as alpha cut
set.
A
%
(0 1) A
Lambda Cuts for Fuzzy Sets
v Properties of Lambda Cut Sets
The standard set of operations on fuzzy sets is similar to the
standard set operations on lambda cut sets.
Lambda Cuts for Fuzzy Relations
v Considering a fuzzy relation
A fuzzy relation can be converted into a crisp relation
by depending the lambda cut relation of the fuzzy
relation as:
v Properties of Lambda Cut Relations
R
%
Lambda Cuts: Examples
Example 1. Two fuzzy sets P and Q are
defined on x as follows:
Find the following cut sets
Lambda Cuts: Examples
Solution. Given
We have
Then we can calculate
Lambda Cuts: Examples
Solution. Given
We have
Then we can calculate
Lambda Cuts: Examples
Solution. Given
We have
Then we can calculate
Lambda Cuts: Examples
Solution. Given
We have
Then we can calculate
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.2
0.4
Lambda Cuts: Examples
Solution. Given
We have
Then we can calculate
0 0 0 0
Lambda Cuts: Examples
Example 2. The fuzzy sets A and B are
defined in the universe X = {0, 1, 2, 3}, with the
following membership functions:
Define the intervals along x-axis corresponding
to the cut sets for each fuzzy set A and B
for following values of = 0.2, 0.5, 0.6.
2
Lambda Cuts: Examples
Solution. The membership degrees for each elements:
Then
That is,
2 ( 3) x +
2 ( 5) x x + 1/ 3 4 / 7 3/ 4
B
B
Lambda Cuts: Examples
Example 3. For the fuzzy relation:
find the cut relations for the following values
of = 0+, 0.2, 0.9, 0.5.
Lambda Cuts: Examples
Solution. Given
we have
Outline
v Lambda Cuts
for Fuzzy Sets
for Fuzzy Relations
v Defuzzification Methods
Maxima method
Centroid method
Weighted average method
Middle-of-maxima method
First-of-maxima or last-of-maxima
Defuzzification Methods
v The output of an entire fuzzy process can be
union of two or more fuzzy sets.
v Definition 1. Defuzzification is a process to select a
representative element from the fuzzy output inferred
from the fuzzy rule-based system.
v There are various methods used for defuzzifying
the fuzzy output functions:
Maxima method
Centroid method
Weighted average method
Middle-of-maxima method
First-of-maxima or last-of-maxima
!
Defuzzification Methods
(1) Maxima
Defuzzification Methods
*
( ) ( ), for all
C C
z z z Z
% %
( ) z
z
*
z
0
(2) Centroid method
Defuzzification Methods
*
( )
, for all
( )
C
C
z zdz
z z Z
z dz
%
%
( ) z
z
*
z
0
(3) Weighted average method
This method can be used only for symmetrical
output membership functions
Weighting each membership function in the obtained
output by its largest membership value
Defuzzification Methods
(4) Middle-of-maxima method
The present of the maximum membership need not
be unique!
i.e., the maximum membership need not be a single point, it
can be a range.
Defuzzification Methods
(5) First-of-Maxima
Last-of-Maxima
Defuzzification Methods
max
0
z
Defuzzification: Examples
Example 4. For the given membership function
as shown, determine the defuzzified output
value using different defuzzification methods.
z
0.7
0.5
1
1 2 3 4 5 6
1
A
%
z
0.5
1
1 2 3 4 5 6
2
A
%
Defuzzification: Examples
z
0.7
0.5
1
1 2 3 4 5 6
1
A
%
z
0.5
1
1 2 3 4 5 6
2
A
%
0 0
z
0.7
0.5
1
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2
A A U
% %
0
a
b
c
d
e
f
0.35 0 2
0.7 2 2.7
( ) 2 2.7 3
1 3 4
0.5 3 4 6
z z
z
z z z
z
z z
<
<
= <
<
Defuzzification: Examples
(2) Centroid method
(1) Maxima method
Not applicable since there is no a single maximum
point.
0.35 0 2
0.7 2 2.7
( ) 2 2.7 3
1 3 4
0.5 3 4 6
z z
z
z z z
z
z z
<
<
= <
<
0.7
0.5
1
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2
A A U
% %
0
a
b
c
d
e
f
*
( )
( )
C
C
z zdz
z
z dz
%
%
z
Defuzzification: Examples
0.35 0 2
0.7 2 2.7
( ) 2 2.7 3
1 3 4
0.5 3 4 6
x x
x
x x x
x
x x
<
<
= <
<
(3) Weighted average method
Not applicable since the membership functions
are not symmetrical.
(4) Middle-of-maxima method
4
x
0.7
0.5
1
1 2 3 5 6 0
d
e
*
3 4
3.5
2
z
+
= =
Review Questions
1. Define defuzzification process.
2. What is the necessity to convert the fuzzy quantities into
crisp quantities?
3. State the method lambda cuts employed for the conversion of
the fuzzy set into crisp.
4. How is lambda cut method employed for a fuzzy relation?
5. How does the maximum method convert the fuzzy quantity
to crisp quantity?
6. In what way does the Centroid method perform the
defuzzification process?
7. Compare the methods employed for defuzzification process
on the basis of accuracy and time consumption.
Exercise Problems
1. Two fuzzy sets A and B both defined on x are as
follows:
Find
Exercise Problems
2. The fuzzy set A , B , C are all defined on the universe
X = [0, 5] with the following membership functions:
(a) Sketch the membership functions
(b) Define the intervals along x-axis corresponding to the
cut sets for each of the fuzzy sets A , B , C for the
following values of . = 0.2, = 0.5, = 0.9.
Exercise Problems
3. For fuzzy relation R
Find cut relations for the following values of
( ) 0.4 ( ) 0.7 a b = =
Exercise Problems
4. By using maxima and centroid methods, convert fuzzy
output to a crisp value z! for the following graph
z
0.5
1
1 2 3 4 5 6 0
1
A
%
2
A
%
Exercise Problems
5. Convert fuzzy value z to precise value z! for the
following graph by using weighted average method
and middle-ofmaxima method.
The membership functions in the above graph are symmetrical functions.
z
0.5
1
1 2 3 4 5 6
0
7 8 9 10
1
A
%
2
A
%
3
A
%
0.75
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Life Plan TemplateDocument2 paginiLife Plan Templateunderwood@eject.co.za100% (1)
- Alder - Multivariate CalculusDocument198 paginiAlder - Multivariate Calculuscantor2000Încă nu există evaluări
- Model Gen ManDocument9 paginiModel Gen ManArnab Jyoti BaruahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poset & LatticeDocument15 paginiPoset & LatticeDab ErqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13 Vector FunctionsDocument44 paginiChapter 13 Vector Functionsdharmendra choudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch03 DSPDocument149 paginiCh03 DSPSalman Shah100% (1)
- Fast matrix multiplication with Strassen's algorithmDocument4 paginiFast matrix multiplication with Strassen's algorithmMahesh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Encoded Problems (StatsFinals)Document4 paginiEncoded Problems (StatsFinals)HueyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ERP in Rolls-RoyceDocument16 paginiERP in Rolls-RoyceGabriela Montiel100% (3)
- ERP in Rolls-RoyceDocument16 paginiERP in Rolls-RoyceGabriela Montiel100% (3)
- Nelder-Mead Optimization AlgorithmDocument5 paginiNelder-Mead Optimization AlgorithmKartika NugraheniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euler Method in Numerical Analysis PDFDocument2 paginiEuler Method in Numerical Analysis PDFDawn0% (1)
- Math 10Document5 paginiMath 10Zhaine Cerado100% (3)
- Solutions 9: Demo 1: KKT Conditions With Inequality ConstraintsDocument11 paginiSolutions 9: Demo 1: KKT Conditions With Inequality ConstraintsxAlexis19xÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multirate Signal Processing: I. Selesnick EL 713 Lecture NotesDocument32 paginiMultirate Signal Processing: I. Selesnick EL 713 Lecture Notesboopathi123Încă nu există evaluări
- 5 A &B Delta Modulation and Adaptive Delta ModulationDocument5 pagini5 A &B Delta Modulation and Adaptive Delta Modulationkingibzz82Încă nu există evaluări
- Exam With Model AnswersDocument4 paginiExam With Model Answersjjia048Încă nu există evaluări
- 2013 BME210 HW4 SolutionDocument9 pagini2013 BME210 HW4 SolutionFaraz JalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual for Industrial Automation Diploma Electronics EngineeringDocument56 paginiLab Manual for Industrial Automation Diploma Electronics EngineeringEr Amarsinh RÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITCE436 Lab3 07Document9 paginiITCE436 Lab3 07Noor AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors TutorialDocument11 paginiEigenvalues and Eigenvectors TutorialMebeek DagnewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2Document9 paginiLecture 2fujinlim98Încă nu există evaluări
- Soal Tugas 3Document4 paginiSoal Tugas 3Auliya Nusyura Al IslamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VectorisationDocument11 paginiVectorisationIlie StefanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 15 Trigonomeertric FunctionsDocument32 paginiModule 15 Trigonomeertric Functionsbakaraz7523027Încă nu există evaluări
- Exercise Chapter 2Document10 paginiExercise Chapter 2NurAtieqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lattice Diagram For ReflectionDocument11 paginiLattice Diagram For ReflectionEarnest ArujÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Statistics Assignment 5 Manish Chauhan (09-1128)Document14 paginiBusiness Statistics Assignment 5 Manish Chauhan (09-1128)manishÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE102 F11 Summary HighlightsDocument24 paginiECE102 F11 Summary HighlightsLolÎncă nu există evaluări
- NWC SolutionDocument22 paginiNWC SolutionThái ĐoànÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRT DivDocument8 paginiSRT Divdeepika0821843Încă nu există evaluări
- MIT6 094IAP10 Assn01Document12 paginiMIT6 094IAP10 Assn01Rosh OtojanovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yousaf Esa Lab Report 3 ME-41 CDocument9 paginiYousaf Esa Lab Report 3 ME-41 CTallal RajpootÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Random Signals and NoiseDocument7 paginiFinal Exam Random Signals and NoiseqwentionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution To The Drill Problems of Chapter 05 (Engineering Electromagnetics, Hayt, A.Buck 7th Ed) BEE 4A, 4B & 4C D5.1 (A)Document1 paginăSolution To The Drill Problems of Chapter 05 (Engineering Electromagnetics, Hayt, A.Buck 7th Ed) BEE 4A, 4B & 4C D5.1 (A)SHELPTSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alg. Dijkstra MatlabDocument1 paginăAlg. Dijkstra Matlabpunct_0Încă nu există evaluări
- 09 Sinusoidal Steady State AnalysisDocument31 pagini09 Sinusoidal Steady State AnalysisRon CabsÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCMUT Final 2009Document9 paginiHCMUT Final 2009Aep CisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab GADocument32 paginiMatlab GASusana De León AldacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Divided Difference Interpolation FormulaDocument31 paginiNewton's Divided Difference Interpolation FormulaAnuraj N VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Mode and Complex ModeDocument2 paginiReal Mode and Complex ModeTao Lai100% (2)
- PV Lab ReportDocument6 paginiPV Lab ReportBen HeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW1Document8 paginiHW1Anonymous fXSlye100% (1)
- Defuzzification Techniques: Debasis Samanta (IIT Kharagpur)Document54 paginiDefuzzification Techniques: Debasis Samanta (IIT Kharagpur)Foram PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factorial Experiment Analysis and InterpretationDocument7 paginiFactorial Experiment Analysis and Interpretation48Raut AparnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Notes For Calculus 3: Lia VasDocument14 paginiMatlab Notes For Calculus 3: Lia VasTaha Alhatmi100% (1)
- Waveform Synthesis Using Laplace TransformDocument3 paginiWaveform Synthesis Using Laplace Transformkvamsee112Încă nu există evaluări
- Minimum Spanning TreesDocument24 paginiMinimum Spanning TreesTestÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 2 Solutions - Network SecurityDocument9 paginiCH 2 Solutions - Network Securitykarthikc_625Încă nu există evaluări
- Discuss The Methodology of Operations ResearchDocument5 paginiDiscuss The Methodology of Operations Researchankitoye0% (1)
- ImplementationDocument14 paginiImplementationTamilSelvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Linear Algebra Biswa Nath Datta PART II Ch7 11Document392 paginiNumerical Linear Algebra Biswa Nath Datta PART II Ch7 11priya0978Încă nu există evaluări
- All The MATH You'll Ever Need: By: Marichu Augusto MangubatDocument19 paginiAll The MATH You'll Ever Need: By: Marichu Augusto Mangubatmarichu mangubatÎncă nu există evaluări
- (123doc) Xu Ly Tin Hieu So Bai3aDocument24 pagini(123doc) Xu Ly Tin Hieu So Bai3aThành VỹÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE102 - F12 ProSet 7 PDFDocument37 paginiECE102 - F12 ProSet 7 PDFlokeshwarrvrjcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Computing Laboratory ManualDocument54 paginiTechnical Computing Laboratory ManualKarlo UntalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alberty-Matlab Implementation of Fem in ElasticityDocument25 paginiAlberty-Matlab Implementation of Fem in ElasticityRick HunterÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1L LP Transformation TricksDocument12 pagini1L LP Transformation TrickscaspersoongÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECDSA Advantages Over OthersDocument7 paginiECDSA Advantages Over Othersyesswap10Încă nu există evaluări
- VHDL Code For FilterDocument2 paginiVHDL Code For FilterArkadip GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATLAB Basics in 40 CharactersDocument50 paginiMATLAB Basics in 40 CharactersOleg ZenderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hw4 Mfe Au14 SolutionDocument7 paginiHw4 Mfe Au14 SolutionWenn ZhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discrete Optimization Specialization: Workshop 0Document2 paginiDiscrete Optimization Specialization: Workshop 0gsbabilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jacobi MethodDocument2 paginiJacobi MethodJuancho SotilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defuzzification 141012012422 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument34 paginiDefuzzification 141012012422 Conversion Gate02 PDFNgaa SiemensÎncă nu există evaluări
- GLPK Implementation For Minimum Bounded Degree Spanning TreeDocument7 paginiGLPK Implementation For Minimum Bounded Degree Spanning TreePaolo BozzelliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuzzification: by Considering Quantities As Uncertain: Imprecision Ambiguity VaguenessDocument60 paginiFuzzification: by Considering Quantities As Uncertain: Imprecision Ambiguity VaguenessJay Kumar RanjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument187 paginiEnterprise Resource PlanningkaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ERP2Document138 paginiERP2kaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- PastaDocument1 paginăPastakaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- AJAX: Creating Web Pages With A Synchronous Javascript and XMLDocument408 paginiAJAX: Creating Web Pages With A Synchronous Javascript and XMLmary100% (2)
- Reason For ReengineeringDocument5 paginiReason For ReengineeringkaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single PhaseDocument1 paginăSingle PhasekaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Round Robin 1Document3 paginiRound Robin 1kaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Serial Iz AbilityDocument20 paginiSerial Iz AbilitykaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perl Programs: #Display The Names Which Starts With A and Ends With RDocument2 paginiPerl Programs: #Display The Names Which Starts With A and Ends With RkaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cat2 Memory ManagementDocument8 paginiCat2 Memory ManagementkaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- OverviewDocument8 paginiOverviewkaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ckmetrics 1Document7 paginiCkmetrics 1kaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntrodDocument31 paginiIntrodkaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- DCCN Forozon PptsDocument22 paginiDCCN Forozon Pptskalyani777Încă nu există evaluări
- Refactoring 1Document4 paginiRefactoring 1kaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Query OptimiationDocument39 paginiQuery OptimiationkaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concurrency Control Mechanisms Ensure Database ConsistencyDocument54 paginiConcurrency Control Mechanisms Ensure Database ConsistencykaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - Design QualitiesDocument17 paginiUnit - Design QualitieskaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apriori (Compatibility Mode) - 2Document23 paginiApriori (Compatibility Mode) - 2kaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Vector Spaces and Linear DependenceDocument5 paginiIntroduction to Vector Spaces and Linear DependencekaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logical Database Design and The Relational ModelDocument52 paginiLogical Database Design and The Relational ModelkaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit I: Fundamentals (Part2)Document20 paginiUnit I: Fundamentals (Part2)kaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating SystemsDocument24 paginiOperating SystemskaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 59 HowThingsWorkDocument5 pagini59 HowThingsWorkKaranVeer Singh ThindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class2 FinalDocument52 paginiClass2 FinalkaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class1 FINALDocument55 paginiClass1 FINALkaylarobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- NFA To DFADocument18 paginiNFA To DFAmmparechaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dilla University Numerical Analysis ModuleDocument184 paginiDilla University Numerical Analysis ModuleYonas Chaka83% (6)
- Matrices and Determinants Chapter Covers Systems of Equations, Operations, Inverses & ApplicationsDocument100 paginiMatrices and Determinants Chapter Covers Systems of Equations, Operations, Inverses & ApplicationsamirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orthogonal polynomials exercisesDocument4 paginiOrthogonal polynomials exercisesFabio Ferraz de CarvalhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TableMix - Group MDocument12 paginiTableMix - Group MDang Phan HaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Analysis 2000. Vol.2Document355 paginiNumerical Analysis 2000. Vol.2api-3851953100% (1)
- Sudoku Using Constraint SatisfactionDocument12 paginiSudoku Using Constraint SatisfactionTyler DerdunÎncă nu există evaluări
- 26 PDFDocument134 pagini26 PDFDarwin MojicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2: NOR and Nand GatesDocument26 paginiExperiment 2: NOR and Nand GatesReinmark Nathaniel MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-2.3 Local Search Algo and Optimization ProblemsDocument18 paginiUnit-2.3 Local Search Algo and Optimization Problemsmani111111Încă nu există evaluări
- MIT15 093J F09 Rec04Document4 paginiMIT15 093J F09 Rec04santiago gonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 - A.BHARGAVI (182001)Document4 paginiAssignment 1 - A.BHARGAVI (182001)A BHARGAVIÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE159 Computer Aided Power System DesignDocument1 paginăEE159 Computer Aided Power System DesignrameshsmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integer Programming: The Branch & Bound MethodDocument19 paginiInteger Programming: The Branch & Bound Methodimran_chaudhry100% (1)
- Assignment 5 Sec11Document2 paginiAssignment 5 Sec11The Hawk UnofficialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout, Assignment Msc. Math, 2ND Sem, 2023 BatchDocument5 paginiHandout, Assignment Msc. Math, 2ND Sem, 2023 BatchMD dilshadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sundown Rent A CarDocument14 paginiSundown Rent A Carvisu0090% (1)
- 06 Jacobi Gauss SeidelDocument65 pagini06 Jacobi Gauss Seidelfredy picoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bisection MethodDocument15 paginiBisection MethodSohar AlkindiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics 7 Module 1 Lesson 2 Polynomials Pre-Requisite Concepts: Constants, Variables, Algebraic ExpressionsDocument3 paginiMathematics 7 Module 1 Lesson 2 Polynomials Pre-Requisite Concepts: Constants, Variables, Algebraic Expressionsdorris09Încă nu există evaluări
- LUfbsub - Bas: Forward and Back Substitution in Visual BasicDocument2 paginiLUfbsub - Bas: Forward and Back Substitution in Visual BasicrodwellheadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cubic Spline Interpolation: MATH 375, Numerical AnalysisDocument65 paginiCubic Spline Interpolation: MATH 375, Numerical AnalysisJain PradeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcse 0041Document5 paginiMcse 0041Rajat ManchandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sofiya Yus - QUEUE LAB 1 Q2Document4 paginiSofiya Yus - QUEUE LAB 1 Q2Sofiya YusÎncă nu există evaluări
- WMSU Grade 7 Math ReviewDocument3 paginiWMSU Grade 7 Math ReviewAliyah NabuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defuzzification Techniques: Debasis Samanta (IIT Kharagpur)Document54 paginiDefuzzification Techniques: Debasis Samanta (IIT Kharagpur)Foram PatelÎncă nu există evaluări