Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Wo 2013104043 A 1
Încărcat de
Mladen MuskinjaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Wo 2013104043 A 1
Încărcat de
Mladen MuskinjaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
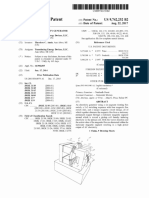
Electric energy generation system with feedback
WO 2013104043 A1
Abstract
The present invention relates to electric energy generation equipment comprising
a basic circuit formed by a rectifier (10), for example, an AC/DC converter con
nected in series to an inverter (12), for example, a DC/AC converter, and a bank
of batteries (13) connected in series between the rectifier (10) and the invert
er (12). An electron capturing element (14), which can be either a free space el
ectron capturing element or, alternatively, an earth electron capturing element,
is connected in series to the basic circuit formed by the rectifier (10), the i
nverter (12) and the battery assembly (13). The bank of batteries (13) powers th
e basic circuit because it is connected to the system. Consequently, the inverte
r (12) converts direct current into alternating current and supplies this curren
t to the electron capturing element (14). After receiving the electric current f
rom the inverter (12), the electron capturing element (14) starts capturing elec
trons from the alternating current and powering the rectifier (10), which conver
ts the alternating current into a direct current in order to recharge the bank o
f batteries (13) and power the inverter (12) which powers the electron capturing
element, closing the feedback loop, and also providing electric energy for cons
umption by external loads.
Description translated from Portuguese (Portugal)
Descriptive Report of Patent for "SYSTEM
Self powered FOR ELECTRICITY GENERATION ".
Technical Field
The present invention relates to a device for generating electricity, in particu
lar a self-powered equipment for generating electricity.
Description of the Related Art
Numerous projects are the mechanisms for the generation of electricity based on
electromagnetism, but they are all fundamentally related to the use of electrome
chanical devices and magnets, which, by their technical limitations of generatin
g capacity and ecological implications, unfeasible using scale economic projects
hitherto known.
Obietivos the Invention
The present invention aims to contribute to the generation of sustainable energy
, proposing a device capable of producing abundant electricity from a power cons
umption smallest initially provided by energy storage (battery bank), and later
by the equipment itself, that generates electricity for consumption and external
loads for your auto feed.
The above objective and other objectives are achieved by the present invention t
hrough an apparatus that includes a basic circuit of a typical uninterruptible p
ower supply of energy, known as the UPS device formed by a rectifier (AC DC conv
erter) connected to a device inverter (inverter DC / AC) and connected to them,
energy storage devices (battery bank); taking on this basic circuit one trap ele
ctrons from space (equipment as defined in Brazilian patent application No. BR10
20120008378 of 13.01.2012) or, alternatively, a trap electrons earth (equipment
as defined in Brazilian patent application No. BR1020120008386 of 13.01.2012) th
at the device receiving power inverter (inverter DC / AC), will generate electri
city and power the device rectifier (AC / DC converter) that will power the devi
ce inverter (inverter DC / AC), which will keep feeding the trap electrons, endi
ng the cycle of self-feeding, and also providing electricity to consumption of e
xternal loads.
The self-powered system for generating electricity from the present invention ca
n be fixed or mobile. It is fixed when using electron captors earth, connected t
o ground grid. He is mobile when using electron captors free space that capture
electrons through their isolated nuclei.
The self-powered system for generating electricity from the present invention ca
n have a variety of modalities constructive - but all within the same inventive
concept - since there are a variety of combinations made with the basic componen
ts (rectifier, inverter and batteries), the systems Uninterruptible power supply
known as UPS, which may be used in constructing the apparatus of the present in
vention. Constructive modalities include single phase, two phase or three phase,
any voltage and power.
Brief Description of the Drawings
The present invention will be hereinafter described with the aid of drawings, bu
t which are not absolutely limiting where it can be observed other details and a
dvantages of the present invention.
The figures show:
Figure 1 - shows a basic circuit system for self-powered electricity generation
of the present invention;
Figure 2 - shows a first embodiment of the constructive system for self-powered
electricity generation of the present invention;
Figure 3 - shows a second embodiment of constructive self-powered system for gen
erating electricity from the invention of the present invention;
Figure 4 - shows a third embodiment of the constructive system for self-powered
electricity generation of the present invention; Figure 5 - shows a fourth modal
ity of constructive self-powered system for generating electricity from the pres
ent invention;
Figure 6 - shows a fifth embodiment of constructive self-powered system for gene
rating electricity from the present invention.
Detailed Description of the Invention
There are different ways of closing self-feeding cycle depending on the circuit
structure. Such constructive arrangements are shown in figures 2 to 6, wherein t
he structure is maintained main circuit, which is an open and closed circuit gen
erating electricity instantaneously.
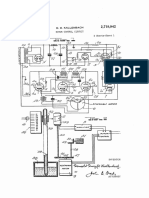
As shown in Figure 1, the self-powered system for generating electricity compris
es a basic circuit consisting of a rectifier (AC DC converter) 10 which is conne
cted in series with an inverter (DC / AC) 12 3 a bank of batteries that are conn
ected in series between the rectifier 10 and the inverter 12. A trap electrons 1
4 - which can be a trap electrons from space (equipment as defined in Brazilian
patent application No. BR1020120008378, from 13.01.2012) or, alternatively, a tr
ap electrons earth (equipment defined in the patent Brazilian No. BR102012000838
6 of 13.1.2012) - is connected in series to the basic circuit formed by the rect
ifier 10, the inverter 12 and the battery pack 13.
When turned on the system, the battery bank 13 provides power to the basic circu
it. Consequently, the inverter 12 converts direct current into alternating curre
nt and provides such a current to trap electrons 1. The trap electrons 14, after
receiving electric current from the inverter 12, passes to capture electrons in
alternating current and feed the rectifier 10 which converts alternating curren
t into direct current to recharge the battery bank 13 and feed the inverter 12,
which will keep feeding the trap electrons, ending the cycle of self-feeding, an
d also providing electricity for consumption of external loads.
Thus particular, the rectifier 10 and the inverter 12, which initially received
electrical current from the battery bank 13, started to use the current generate
d by the sensor of electrons. Thus, the supply of power from the battery bank 13
is switched to the power supply from the electron sensor 14, that is, the elect
ron sensor 14 is supplying power, the feeding system itself, and providing in ou
tput port 18, electricity consumption for external loads.
As can be seen in Figure 2, another embodiment of the system for self-powered el
ectric power generation equipment comprising a circuit that includes a base of a
typical uninterruptible power supply of energy, known as UPS formed by a batter
y charger (AC converter CC ) 21 connected to a drive device (inverter DC / AC) 2
3 and attached to them, devices accumulator (battery bank) 22 - this being the b
asic circuit together with other devices and connected to a trap electrons space
27 free (equipment as defined in Brazilian patent application No. BR10201200083
78 of 13.01.2012) or, alternatively, a trap electrons land 27 (equipment as defi
ned in Brazilian patent application No. BR1020120008386 of 13.01.2012), comprisi
ng Thus, the battery charger (AC converter CC) 21 is connected in series with th
e bank of batteries 22 connected in series with the inverter 23, which is connec
ted in series with the phase transfer switch 24.1 at the connection point, which
is connected at the connection point 24.1 the point 24.3 the connection itself
phase transfer switch 24, connected in series to trap electrons 27 electrons, in
parallel with the battery charger (AC / DC converter) 21, and this is parallel
to the surge suppressor 25 defusing to the bonding points 24.1 and 24.3 of phase
transfer switch 24 to connect the bonding points 24.3 and 24.2, and the connect
ion point 24.2 is connected in series with the filter 26, which is in series wit
h the surge suppressor 25, which is in parallel to the battery charger (AC / DC
converter) 21, the battery bank 22, the inverter 23 and the connection point 24.
1, which are in series with the transfer switch phase 24, which is in series wit
h the connection point 24.3 and the electron trap electrons 27 which is in serie
s with the output phase 28. In a constructive alternative for use in emergency s
ituations where the system is no longer self-powered, the system may comprise a
power input of an external power source, the interconnection point 29 to provide
power to surge suppressor 25, which provides power to feed exit point 28 to fee
d external loads.
The bank of 22 batteries supply power to the inverter 23 and inverter 23 convert
s the DC current into alternating current, which goes to feed the transfer switc
h 24. The transfer switch (24) is connected to the filter 26 and the sensor 27 e
lectrons.
After being fed, the sensor 27 is electron capture electrons in alternating curr
ent and feed the battery charger (AC / DC converter) 21, the filter 26 which is
connected to the surge suppressor 25, which is connected to the transfer switch
24, which feeds the sensor 27, which feeds the battery charger (AC DC converter)
21, which is feeding the batteries and switching occurs by the transfer switch
24 when the surge suppressor 25 is powered, disarms the transfer switch 24 cutti
ng off the supply of power from the batteries to the input of the supply of elec
tric current electron sensor 27.
When the electron sensor 27 is turned off, the transfer switch 24 back to the in
itial situation (point 24.1 and 24.3 on the point system to function as self-fee
ding.
The electron sensor 27 provides power to the transfer switch 24 without interrup
tion of power because the transfer switch 24 has been switched by the surge supp
ressor 25 which provides power supply for the system itself, that is, closing th
e cycle of self-feeding and supplying energy to the point of exit 28, which feed
s the external loads.
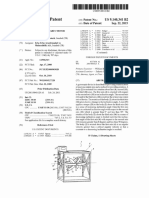
As shown in Figure 3, another embodiment of the self-powered system for generati
ng electricity comprises a device that includes a basic circuit of a typical uni
nterruptible power supply energy, known as UPS, consisting of a battery charger
(AC / DC converter ) 31 connected to a drive device (inverter DC / AC) 35 and at
tached to them, devices accumulator (battery bank) 32, and this basic circuit to
gether with other devices and connected to a trap electrons space 37 free (equip
ment as defined in Brazilian patent application No. BR1020120008378 of 13.01.201
2 or, alternatively, a trap electrons land 37 (equipment as defined in Brazilian
patent application No. BR1020120008386 of 13.01.2012) comprising thus a bank of
batteries 32 connected in series with the DC / DC converter 33, which is connec
ted in series with the phase transfer switch 34 34.1 connection point which is c
onnected in series to the connection point 34.3, which is in series with the inv
erter 35, which is connected in series with the sensor of 37 electrons, and 38 t
hree-phase output, which is in parallel with the battery charger (AC / DC conver
ter) 31, the rectifier 36 is in parallel to the battery charger ( AC / DC conver
ter) 31 and in series with the phase transfer switch 34, the connection point 34
.2, which is in series with the connection point 34.3, in parallel with 34.1 con
nection point, the connection point 34.3 is in series with the inverter DC / AC
35, which is connected in series with the sensor of 37 electrons, which is in pa
rallel to the battery charger (AC / DC converter) 31, the battery bank 32, the s
tandby DC converter / CC 33 and the point of attachment to 34.1.
In a constructive alternative for use in emergency situations where the system i
s no longer self-powered, the system may comprise a power input of an external p
ower source, the interconnection point 39 connected to the rectifier 36 which pr
ovide electrical power to the transfer switch three phase 34, the inverter DC /
AC 35, which is providing electricity at exit 38, which is also the power point
of the external load.
The battery bank 32 provides power to the DC / DC converter 33, to feed the tran
sfer switch 34.
At this time, the transfer switch 34 does not switch because current receiving p
oints 34.1 and 34.2 and simultaneously transferred to the electric current feedi
ng point 34.3 inverter DC / AC 35, which when fed, converts the DC current in st
ream alternating, and provides AC for trap electrons 37.
The rectifier 36 supplies power to the transfer switch 34 and the transfer switc
h 34 receives power from the batteries and inverter 33 that feeds the inverter D
C / AC 35. At this time, the inverter DC / AC 35 goes to feed the sensor of 37 e
lectrons, leaving the supply of energy from the batteries to the power supply fo
r sensor, which shall provide power feeding the system itself.
Thus, the sensor 37 starts to capture electrons in alternating current and passe
s to feed the battery charger (AC / DC converter) 31. The battery charger (AC /
DC converter) 31 continues to supply power to the inverter (33), continuing the
flow of energy
As can be seen in Figure 4, another embodiment of the system for self-powered el
ectricity generation equipment that comprises a basic circuit of a typical unint
erruptible power supply energy, known as UPS, consisting of a battery charger (A
C / DC converter ) (A) connected to a drive device (inverter DC / AC) 42 and att
ached to them, devices accumulator (battery bank) 41, and this basic circuit tog
ether with other devices and connected to an electron captor free space 44 (equi
pment as defined in Brazilian patent application No. BR1020120008378 of 13.01.20
12) or, alternatively, a trap electrons land 44 (equipment as defined in Brazili
an patent application No. BR1020120008386 of 13.01.2012) comprising Thus, a batt
ery charger (A) connected to a battery bank 41, which is connected in series wit
h inverter 42 at point (B) which is in series to the point (C) of inverter 42 wh
ich is in series with the electron sensor 44, which is in series with the phase
transfer switch 43 via the output connection point 45 three-phase load, the phas
e transfer switch 43 is in series with inverter 42 which is connected in series
the (AC / DC converter) in paragraph (A) the battery bank 41.
In a constructive alternative for use in emergency situations, in which the syst
em ceases to be self-powered, the system may include a power input of an externa
l power source, the interconnection point 46, and providing electricity output 4
5, which is also the feeding point of the external loads.
The battery bank 41 provides power to the inverter 42 which converts the direct
current into alternating current and feeds the sensor of 44 electrons.
The transfer switch closes when the batteries need recharging.
The sensor 44 captures electrons with alternating current, which feeds the trans
fer switch in one of his 43 points output load receiving alternating current, wh
ich becomes the input power. The transfer switch 43 feeds the inverter 42 and in
verter 42 feeds the batteries, charging them and closing the cycle of self-feedi
ng and providing power at the output 45, which is in series with the power input
, which is also the power point of external loads.
As can be seen in Figure 5, another embodiment of the system for self-powered el
ectric power generation equipment comprising a circuit that includes a base of a
typical uninterruptible power supply of energy, known as UPS, comprising a batt
ery charger (AC converter / CC) 51 connected to a drive device (inverter DC / AC
) 53 and attached to them, devices accumulator (battery bank) 52, and this basic
circuit together with other devices and connected to an electron captor free sp
ace 56 (equipment as defined in Brazilian patent application No. BR1020120008378
of 13.01.2012) or, alternatively, a trap electrons land 56 (equipment as define
d in Brazilian patent application No. BR1020120008386 of 13.01.2012) comprising
Thus, a battery charger 51 which is connected in series with a battery bank 52,
which is connected in series with the inverter 53, which is connected in series
with the transformer 55 at its point C, which is in series with its point (B) wh
ich is in series with the electron sensor 56, which is in series with the batter
y charger 51 which is connected at the exit point load 58, with the entry point
59, which is in series with the phase transfer switch 54 in section 54.1, which
is closed with 54.3 connection point, which is in series with the point (A) of t
he transformer 55 which exits at point (B), the points (A) and 54.3 as well as t
he parallel points 54.1 and 54.2, are all parallel to the battery 51, the batter
y bank 52, the inverter 53 and to the point (C) of the transformer 55.
In a constructive alternative for use in emergency situations, in which the syst
em ceases to be self-powered, the system may include a power input of an externa
l power source, the interconnection point 59, that this interconnected key trans
fer 54 which delivers power on the output 58, which is the feeding point of the
external loads.
The battery bank 52 which provides power to the inverter 53, which converts the
direct current into alternating current, feeding point (C) of the transformer, w
hich comes out in paragraph (B) and paragraph (A) of the transformer.
Paragraph (B) of the transformer feeds the trap that captures electrons 56 elect
rons in alternating current and feeds the battery charger 51, which feeds the ba
ttery bank 52.
The battery charger 51 is connected in parallel with the transfer switch 54 via
connection points 54.1 and 54.3, feeding point (A) of the transformer, which com
es out in Section B. The point (A) of the transformer and the key transfer point
s 54.3 and 54.1 are in parallel to the battery charger 51, the battery 52 and th
e inverter 53 and to the point (C) of the transformer 55.
The transfer switch 54, with the absence of electric current had always been lin
ked in Section 54.2 and 54.3, when the transfer switch 54 is supplied with elect
ric current, ever occurred to switching off the point with 54.2 and connecting t
he connection point that is 54.1 closed the connection point 54.3.
The battery bank 52 only provides power to the inverter 53 when the transfer swi
tch 54 is turned point point 54.3 to 54.2, that is, when the transfer switch 54
is not energized. The inverter 53, to receive electrical current from the batter
ies 52, transforms into alternating current that passes through the transformer
55 point (C) to the point (B), feeding the sensor of 56 electrons, capturing, ge
nerating alternating electric current that leaves the exit point 58 to the load
input point 59. The entry point 59 is in series with the battery charger 51, and
entry point 59 that provides the electrical current transfer switch 54 that swi
tches the point 54.1 with 54.3 point, with this switching power supply leaves th
e assembly batteries, to supply energy electron sensor 56, which goes to supply
power feeding system itself, closing the self-feeding cycle, which provides powe
r at the output 58, which is the feeding point of the external loads.
As can be seen in Figure 6, another embodiment constructive system for self-powe
red electric power generation equipment comprising a circuit that includes a bas
e of a typical uninterruptible power supply of energy, known as the UPS device f
ormed by a rectifier (AC converter / CC) 61 connected to a drive device (inverte
r DC / AC) 63 and attached to them, devices accumulator (battery bank 62, and th
is basic circuit together with other devices and connected to a trap electrons s
pace 64 (equipment as defined in Brazilian patent application No. BR102012000837
8 of 13.01.2012), or, alternatively, a trap electrons earth 64 (equipment as def
ined in Brazilian patent application No. BR1020120008386 of 13.01.2012) comprisi
ng Thus, delta converter (AC / DC) 61, which is connected in series to a battery
bank 62, which is connected in series with the inverter (DC / AC) 63, which is
in series with the electron sensor 64 which is connected in series with the delt
a converter (DC / DC) 61 whose part (AC) is in series with the alternating curre
nt (AC) inverter 63 via a connection point 65 which is in parallel with part (DC
) converter delta 61 with the battery bank 62 and Part (DC) inverter 63. In a co
nstructive alternative for use in emergency situations, in which the system ceas
es to be self-powered The system may comprise a power input of an external power
source, the interconnection point 66 connected to the delta converter 61, the o
utput 67 supplying power, which is the feeding point loads.
The battery bank 62 provides power to the inverter 63, which converts the direct
current into alternating current, powering the sensor of 64 electrons. The sens
or 64 starts to capture electrons in alternating current feeding the delta conve
rter 61 via an exit point load 67.
The part of the alternating three-phase delta converter 61 is fed with an altern
ating drive part 63 through connection point 65, which is connected in parallel
to the delta continuous DC converter 61, which feeds the battery bank 62 and wit
h the continuous portion the inverter 63, closing the cycle of self-feeding and
supplying power at the output 67, which is the feeding point loads.
Having described examples of preferred embodiments, it should be understood that
the scope of the present invention encompasses other possible form of construct
ion equipment using the electron sensors connected to a basic circuit of a typic
al uninterruptible power supply of energy, known as UPS, comprising a device rec
tifier (AC / DC converter) 10, connected to one inverter (inverter DC / AC) 12,
and attached to them, energy storage devices (battery bank).
Claims translated from Portuguese (Portugal)
CLAIMS
1 "self powered SYSTEM FOR ELECTRICITY GENERATION" characterized by a device
that includes a basic circuit of a typical uninterruptible power supply energy,
known as UPS, formed by a device rectifier (AC / DC converter) (10), connected
to a device inverter (inverter DC / AC) (12) and connected to them, energy stora
ge devices (battery bank) (13) - typical circuit of an uninterruptible power sup
ply energy, known as UPS - having switched this basic circuit one trap electrons
from space (1) (equipment as defined in Brazilian patent application No. BR1020
120008378 of 13.01.2012), or, alternatively, a trap electrons of the earth (14)
(defined in the application equipment Brazilian Patent No. BR1020120008386 of 13
.01.2012), which receive electrical energy from the basic circuit will generate
electric power and feed the basic circuit that will keep feeding the trap electr
ons (14), closing the cycle of self-feeding and also available at the output por
t (18), electricity consumption for external loads.
2. System for self-powered electricity generation characterized by a device
that includes a basic circuit of a typical uninterruptible power supply energy,
known as UPS, consisting of a battery charger (AC DC converter) (21), connected
to one inverter (inverter DC / AC) (23) and attached to them, devices accumulato
r (battery bank) (22), and this basic circuit together with other devices and co
nnected to a trap electrons in the free space (27) comprising thus the battery c
harger (AC / DC converter) (21) is connected in series to the battery bank (22)
connected in series with the inverter (23), which is connected in series with th
e transfer switch phase at the connection point (24.1) which is connected to the
connection point (24.1) at a connection point (24.3) of the proper phase transf
er switch (24) connected in series to trap electrons (27) in parallel with batte
ry charger (AC / DC converter) (21), and this is in parallel to the surge suppre
ssor (25), to disarm the connection points (24.1) and (24.3) of the three-phase
transfer switch (24) and connecting the bonding points (24.3) and (24.2), and th
e connection point (24.2) is connected in series with the filter (26) which is i
n series with the surge suppressor (25) which is parallel the battery charger (A
C / DC converter) (21), the battery bank (22), the inverter (23) and the connect
ion point (24.1), which are in series with the phase transfer switch (24), which
is in series with the connection point (24.3) and the electron sensor (27) whic
h is in series with the output phase (28), will generate electricity and feed th
e basic circuit, which will keep the power trap electrons (27), closing the cycl
e of self-feeding, and also available at the output port (28), electricity consu
mption for external loads.
3. System for self-powered electricity generation characterized by a device
that includes a basic circuit of a typical uninterruptible power supply energy,
known as UPS, consisting of a battery charger (AC / DC converter) (31), connecte
d to a device the inverter (inverter DC / AC) (35) and attached to them, devices
accumulator (battery bank) (32), and this basic circuit together with other dev
ices and connected to a trap electrons in the free space (37 ) comprising thus a
battery bank (32) connected in series with the standby converter DC / DC (33) w
hich is connected in series with the phase transfer switch (34) at the connectio
n point (34) .1 which is connected in series to the connection point (34.3) whic
h is in series with the inverter (35), which is connected in series with the ele
ctron sensor (37) and three phase output (38) which is parallel with battery cha
rger (AC / DC converter) (31), the rectifier (36) is in parallel to the battery
charger (AC / DC converter) (31), and in series with the phase transfer switch (
34), the connection point (34.2) which is in series with the connection point (3
4.3) and parallel to the connection point (34.1), the connection point (34.3) is
in series with the inverter DC / AC ( 35), which is connected in series with th
e sensor of electrons (37), which is in parallel to the battery charger (AC / DC
converter) (31), the battery bank (32), the tri standby converter DC / DC (33)
and the connection point (34.1), will generate electricity and feed the basic ci
rcuit that will keep feeding the trap electrons (37), closing the cycle of self-
feeding, and also available at the output port (38), electric power consumption
for external loads.
4. Self-powered system for generating electrical energy characterized by a d
evice that includes a basic circuit of a typical uninterruptible power supply en
ergy, known as UPS, consisting of a battery charger (AC / DC converter) (A), con
nected to a device Inverter (inverter DC / AC) (42) and connected to them, energ
y storage devices (battery bank) (41), and this basic circuit plus other devices
and connected to a trap electrons from space (44 ), comprising thus a battery c
harger (A) connected to a battery bank (41) which is connected in series with th
e inverter (42) in section (B), which is in series to the point (C) of the inver
ter (42), which is in series with the electron sensor (44) which is in series wi
th the phase transfer switch (43) through the connection point of the output pha
se of the load (45), the transfer switch triphasic (43) is in series with the in
verter (42), which is connected in series with (AC / DC converter) in paragraph
(A) the battery bank (41), will generate electricity and feed the basic circuit,
which will keep feeding the trap electrons (44), closing the cycle of self-feed
ing, and also available at the output port (45), electricity consumption for ext
ernal loads.
5. System for self-powered electricity generation characterized by a device
that includes a basic circuit of a typical uninterruptible power supply energy,
known as UPS, consisting of a battery charger (AC / DC converter) (51), connecte
d to a device Inverter (inverter DC / AC) (53) and connected to them, energy sto
rage devices (battery bank) (52), and this basic circuit plus other devices and
connected to a trap electrons from space (56 ) comprising thus a battery charger
(51) which is connected in series with a battery bank (52) which is connected i
n series with the inverter (53) which is connected in series with the transforme
r (55) at its point (C), which is in series with its point (B) which is in serie
s with the electron sensor (56) which is in series with the battery charger (51)
, which is connected at the point of output load (58), the entry point (59) whic
h is in series with the phase transfer switch (54) at point (54.1) which is clos
ed with the connection point (54.3) which is series with the point (A) of the tr
ansformer (55) out under point (B), the points (A) and (54.3) as well as paralle
l points (54.1) and (54.2) are all parallel to the loader battery (51), the batt
ery bank (52), the inverter (53) and point (C) of the transformer (55), will gen
erate electricity and feed the basic circuit that will keep feeding the trap ele
ctrons ( 56), closing the cycle of self-feeding, and also available at the outpu
t port (58), electricity consumption for external loads.
6. System for self-powered electricity generation characterized by a device
that includes a basic circuit of a typical uninterruptible power supply energy,
known as UPS, formed by a device rectifier (AC / DC converter) (61), connected t
o one inverter (inverter DC / AC) (63) and attached to them, devices accumulator
(battery bank) (62), and this basic circuit together with other devices and con
nected to a trap electrons in the free space (64) comprising thus a delta conver
ter (AC DC), (61) which is connected in series to a battery bank (62) which is c
onnected in series with the inverter (DC / AC) (63), which is series with the el
ectron sensor (64) which is connected in series with the delta converter (AC / D
C) (61) whose part (AC) is in series with the alternating current (AC) inverter
(63), through a connection point (65), which is in parallel with the part (DC) c
onverter delta (61), with the battery bank (62) and the part (DC) inverter (63),
will generate electricity and feed the basic circuit that will keep feeding the
trap electrons (64), closing the cycle of self-feeding, and also available at t
he output port (67), electricity consumption for external loads.
7. System for self-powered electricity generation according to any one of cl
aims 1 to 6, characterized by the fact that it is configured for use with DC - D
C.
8. Self-powered system for generating electricity, according to any of claim
s 1-6, characterized in that it is configured for use with AC - CA.
9. Self-powered system for generating electricity, according to any of claim
s 1-6, characterized in that it is configured for use in electrical networks of
low, medium and high voltages.
10. System for self-powered electricity generation according to any one of c
laims 1 to 6, characterized by the fact that it is configured for use on electri
cal monophasic, biphasic, triphasic or at any power.
11. System according to any one of claims 1 to 6, characterized by the fact
that the sensor used is the electron trap electrons in the free space.
12. System according to any one of claims 1 to 6, characterized by the fact
that the sensor used is the electron trap electrons land.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Edwin Gray Electronic Circuit PDFDocument6 paginiEdwin Gray Electronic Circuit PDFAvram StefanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy DevicesDocument6 paginiEnergy DevicesXavi Granados ContrerasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gray 4595975Document7 paginiGray 4595975MANNAJANELAGUNAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation On Induction Motor Driven Water Pump Fed by Solar Photovoltaic Array Using Boost ConverterDocument20 paginiSimulation On Induction Motor Driven Water Pump Fed by Solar Photovoltaic Array Using Boost ConverterJohnny Edward KingsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- EP1022840B1Document14 paginiEP1022840B1duffy5555Încă nu există evaluări
- Paper SaraDocument9 paginiPaper SaraSara ElbadaouiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TT Brown's Electrokinetic Generator PatentDocument7 paginiTT Brown's Electrokinetic Generator PatentJason Warden0% (1)
- Dynamic Modeling, Design of A Wind/fuel Cell/ultra-Capacitor-Based Hybrid Power Generation SystemDocument16 paginiDynamic Modeling, Design of A Wind/fuel Cell/ultra-Capacitor-Based Hybrid Power Generation SystemYellaturi Siva Kishore ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Generation by Railway Track PDFDocument10 paginiPower Generation by Railway Track PDFVinoth KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generation of Energy Usig MagnetsDocument26 paginiGeneration of Energy Usig MagnetsSridhar PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design, Control, and Simulation of A Novel Power Conversion SystemDocument6 paginiDesign, Control, and Simulation of A Novel Power Conversion SystemDeepan RedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Flow and Management of A Hybrid wind/PV/fuel Cell Generation SystemDocument17 paginiEnergy Flow and Management of A Hybrid wind/PV/fuel Cell Generation SystemPriya SingÎncă nu există evaluări
- U.S. Patent 2,719,942, Entitled "Motor Control System", To Kallenbach, Oct. 4, 1955.Document6 paginiU.S. Patent 2,719,942, Entitled "Motor Control System", To Kallenbach, Oct. 4, 1955.Anonymous a7S1qyXÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actual Wind EnergyDocument11 paginiActual Wind EnergyAbhishek V DeshpandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adaptive Piezoelectric Energy HarvestingDocument20 paginiAdaptive Piezoelectric Energy HarvestingSyam MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control of Hybrid Battery/Ultra-capacitor Energy Storage For Stand-Alone Photovoltaic SystemDocument6 paginiControl of Hybrid Battery/Ultra-capacitor Energy Storage For Stand-Alone Photovoltaic Systemaaaa aaaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- US568176 - TeslaDocument4 paginiUS568176 - TesladaveklodavekloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition of Electrical TermDocument2 paginiDefinition of Electrical TermLuis Carlos100% (1)
- Estudo CapacitorDocument9 paginiEstudo Capacitorsajo1000Încă nu există evaluări
- Novel Control for Direct Interface Converters in DC and AC Power SuppliesDocument10 paginiNovel Control for Direct Interface Converters in DC and AC Power SuppliesSherif M. DabourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Three Phase Solar-Based 4.5kw Ac Power Inverter StationDocument6 paginiDesign of Three Phase Solar-Based 4.5kw Ac Power Inverter StationAJER JOURNALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi-Functional Bidirectional ACDC T-TypeDocument6 paginiMulti-Functional Bidirectional ACDC T-TypeDheereshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stand Alone Self ExcitedDocument6 paginiStand Alone Self ExcitedSamundra GurungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling of A Standalone Photovoltaic System With Charge Controller For Battery Energy Storage SystemDocument10 paginiModelling of A Standalone Photovoltaic System With Charge Controller For Battery Energy Storage SystemHari KiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 082 ICCEP 07 Capri Italy Altas Sharaf (PV Array Simulink)Document5 pagini082 ICCEP 07 Capri Italy Altas Sharaf (PV Array Simulink)ronniedakingpouÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Nonisolated Three-Port DC-DC Converter and Three-Domain Control Method For PV-Battery Power SystemsDocument11 paginiA Nonisolated Three-Port DC-DC Converter and Three-Domain Control Method For PV-Battery Power SystemsChristian EmenikeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stabilization of Wind Energy Conversion System With Hydrogen Generator by Using EDLC Energy Storage SystemDocument9 paginiStabilization of Wind Energy Conversion System With Hydrogen Generator by Using EDLC Energy Storage SystemPriyanka GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- STATCOMDocument17 paginiSTATCOMAbdel-Rahman Saifedin ArandasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wo 2013104039 A 1Document8 paginiWo 2013104039 A 1Mladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Novel Quasi-Z-Source Inverter Topology With Special Coupled Inductors For Input Current Ripples CancellationDocument8 paginiA Novel Quasi-Z-Source Inverter Topology With Special Coupled Inductors For Input Current Ripples CancellationSherif M. DabourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motionless Electromagnetic GeneratorDocument9 paginiMotionless Electromagnetic GeneratorViswa TejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Injection of Photovoltaic Arrays Power and Power Quality Improvement by Universal Power Quality Conditioning SystemDocument12 paginiInjection of Photovoltaic Arrays Power and Power Quality Improvement by Universal Power Quality Conditioning Systemtariq76Încă nu există evaluări
- Circuito de ControlDocument3 paginiCircuito de ControlEmer nelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPPT Controller Based Solar Power Generation UsingDocument9 paginiMPPT Controller Based Solar Power Generation UsingHarith HaikalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of A Solar MPPT Charger Using Cuk Converter For Standalone ApplicationDocument6 paginiSimulation of A Solar MPPT Charger Using Cuk Converter For Standalone ApplicationcashnuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self-Oscillating Power Factor Correction CircuitDocument15 paginiSelf-Oscillating Power Factor Correction CircuitDumitru ScortanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switched-Capacitor-Cell-Based Voltage Multipliers and DC-AC InvertersDocument12 paginiSwitched-Capacitor-Cell-Based Voltage Multipliers and DC-AC Invertersvinay kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimized Hydrogen and Electricity Generation From Wind: June 2003 - NREL/TP-500-34364Document12 paginiOptimized Hydrogen and Electricity Generation From Wind: June 2003 - NREL/TP-500-34364Sabin LalÎncă nu există evaluări
- IET Power Electronics - 2019 - Bosso - Isolated Bidirectional DC To Three Phase AC Converter For Integration of RenewableDocument11 paginiIET Power Electronics - 2019 - Bosso - Isolated Bidirectional DC To Three Phase AC Converter For Integration of RenewableUppili RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of A CC-VSI For Active Filtering and Photovoltaic Energy Conversion With A 1-To-1 MPPT ControllerDocument6 paginiApplication of A CC-VSI For Active Filtering and Photovoltaic Energy Conversion With A 1-To-1 MPPT Controllerbeton2008Încă nu există evaluări
- Report Content - Digital Water MeterDocument44 paginiReport Content - Digital Water MeteramiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nec 2017 Article690Document130 paginiNec 2017 Article690Director PQR CON18-74EC100% (2)
- Patente Del Señor Edwin H. Colpitts 1918 US1624537Document5 paginiPatente Del Señor Edwin H. Colpitts 1918 US1624537Adrian GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kabeya Muya Power Electronic DSDocument4 paginiKabeya Muya Power Electronic DSMoïse KabeyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photovoltaic Water Pumping System With Three-Level NPC InverterDocument10 paginiPhotovoltaic Water Pumping System With Three-Level NPC InverterTI Journals PublishingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control of Hybrid System Using Multi-Input Inverter and Maximum Power Point TrackingDocument8 paginiControl of Hybrid System Using Multi-Input Inverter and Maximum Power Point TrackingInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Încă nu există evaluări
- Arun IeeeDocument9 paginiArun IeeebalasingarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Novel Buck Boost InverterDocument8 paginiA Novel Buck Boost InverterskrtamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short-Circuit CurrentsDocument3 paginiShort-Circuit CurrentsAhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Device For Improving The Immunity of AC Contactors During Voltage DipsDocument5 paginiA Device For Improving The Immunity of AC Contactors During Voltage DipsRAPRATSINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Improvement of Distribution Systems Using DSTATCOM Voltage ControlDocument5 paginiDynamic Improvement of Distribution Systems Using DSTATCOM Voltage ControlVinod Kumar VudathaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Hybrid Ac-Dc Microgrid and Its ControlDocument9 paginiA Hybrid Ac-Dc Microgrid and Its ControlTouseef HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- US3018394Document5 paginiUS3018394kartikkeyyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProjectDocument30 paginiProjectmitesh goyal100% (1)
- Photovoltaic-Grid Integrated System: Sameer Khader, Abdel-Karim DaudDocument6 paginiPhotovoltaic-Grid Integrated System: Sameer Khader, Abdel-Karim Daudtariq76Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsDocument40 paginiBasic Electronics Terms and DefinitionsIrish Balaba67% (3)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDe la EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesDe la EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDe la EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDe la EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- More Thoughts On The Uwe Jarck DeviceDocument5 paginiMore Thoughts On The Uwe Jarck DeviceMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drawing Pages of JP2016174482 A PatentDocument1 paginăDrawing Pages of JP2016174482 A PatentMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Espacenet DocumentDocument1 paginăEspacenet DocumentMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119826 A1Document7 paginiUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119826 A1Mladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sand2012 0304Document64 paginiSand2012 0304Emma GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Energy Systems (Johnson)Document449 paginiWind Energy Systems (Johnson)Mario Shawn Hayden Jr100% (1)
- Mushroom Production GuideDocument123 paginiMushroom Production GuideMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Us7224077 PDFDocument6 paginiUs7224077 PDFMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book Cultivation Merged MushroomDocument278 paginiBook Cultivation Merged MushroomHussain1006100% (2)
- JPS54159538A Original Document 20200712174721Document4 paginiJPS54159538A Original Document 20200712174721Mladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0148513 A1Document18 paginiUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0148513 A1Mladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Course Button Mushrooms (Agaricus Bisporus) : Daily Program On Delphy Mushroom FarmDocument2 paginiAdvanced Course Button Mushrooms (Agaricus Bisporus) : Daily Program On Delphy Mushroom FarmMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1974008662Document4 pagini1974008662Mladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Us7224077 PDFDocument6 paginiUs7224077 PDFMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Course Mushrooms: HAS Training and ConsultancyDocument2 paginiOnline Course Mushrooms: HAS Training and ConsultancyMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR-14D Operating Instructions: 144 X 144 X 50 MMDocument2 paginiPR-14D Operating Instructions: 144 X 144 X 50 MMMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- US8047090B2 Original Document 20200618185937Document9 paginiUS8047090B2 Original Document 20200618185937Mladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FR2876163A1Document8 paginiFR2876163A1Mladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PatentsDocument7 paginiPatentsMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wo2012140458a3 PDFDocument3 paginiWo2012140458a3 PDFMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetic Electricity Generator DesignDocument14 paginiMagnetic Electricity Generator DesignMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wo2012140458a3 PDFDocument3 paginiWo2012140458a3 PDFMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application PDFDocument3 paginiApplication PDFMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application PDFDocument6 paginiApplication PDFMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wo2012140458a3 PDFDocument3 paginiWo2012140458a3 PDFMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application PDFDocument2 paginiApplication PDFMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Double-Channel: Submersible PumpsDocument4 paginiDouble-Channel: Submersible PumpsMladen Muskinja0% (1)
- Us 1560428Document5 paginiUs 1560428Mladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application PDFDocument2 paginiApplication PDFMladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- US9140341B2 Original Document 20200618185302Document32 paginiUS9140341B2 Original Document 20200618185302Mladen MuskinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam Exam Exam Exam::::: Cisco Cisco Cisco Cisco 640-802 640-802 640-802 640-802Document17 paginiExam Exam Exam Exam::::: Cisco Cisco Cisco Cisco 640-802 640-802 640-802 640-802dmbowie89Încă nu există evaluări
- Mobira MD59 Modifications For Radio Amateur Use: (Draft Version)Document4 paginiMobira MD59 Modifications For Radio Amateur Use: (Draft Version)DefaultAnomolyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1998-03 The Computer Paper - Ontario EditionDocument144 pagini1998-03 The Computer Paper - Ontario EditionthecomputerpaperÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTS Fault Code GuideDocument7 paginiBTS Fault Code Guidefimmy1Încă nu există evaluări
- CSS 7 AssessmentDocument1 paginăCSS 7 AssessmentMelanie PradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Article Internet of ThingsDocument179 paginiResearch Article Internet of ThingsHussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes and Effect of Harmonics in Power System IJSETR-VOL-3-IsSUE-2-214-220Document7 paginiCauses and Effect of Harmonics in Power System IJSETR-VOL-3-IsSUE-2-214-220emmanuel akaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP EliteBook 840 G1 QuickSpecsDocument63 paginiHP EliteBook 840 G1 QuickSpecsrute silvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windows PowerShell CmdletDocument6 paginiWindows PowerShell CmdletPrithwish GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unimotor Technical DataDocument108 paginiUnimotor Technical DataEugen BlagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A02 - Cool DB2 10 For ZOS FeaturesDocument29 paginiA02 - Cool DB2 10 For ZOS Featuresahm_mo2001Încă nu există evaluări
- Maintain Training FacilitiesDocument4 paginiMaintain Training FacilitiesRuth ValÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fast Dormancy and Enhanced Cell FACH V1 - OLNDocument49 paginiFast Dormancy and Enhanced Cell FACH V1 - OLNMatthew BarnettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab On TCP SpoofingDocument2 paginiLab On TCP SpoofingBenjamin HolmesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZTE CDROM found and accessed successfullyDocument4 paginiZTE CDROM found and accessed successfullyAdi HaryantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nvis 5586A FinalDocument191 paginiNvis 5586A FinalSaiKumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Manual - CR-100 - EN PDFDocument16 paginiUser Manual - CR-100 - EN PDFEnache DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Vitae Name:: Career ObjectiveDocument2 paginiCurriculum Vitae Name:: Career ObjectiveRiyaz BasheerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 62TEDACCODocument0 pagini62TEDACCOKatie DavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hanau - Wide Vue InstDocument39 paginiHanau - Wide Vue InstRahul JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ags 688Document2 paginiAgs 688dsimovic100% (1)
- Computer Fundamentals & Office ApplicationsDocument216 paginiComputer Fundamentals & Office ApplicationsJMadskilzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset Technology On Temporary Fault or Remain Tripped OtherwiseDocument4 paginiThree Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset Technology On Temporary Fault or Remain Tripped OtherwisePritesh Singh50% (2)
- Innovair Oasis Mini Split 2nd Gen 9K 24K Troubleshooting Guide EnglishDocument8 paginiInnovair Oasis Mini Split 2nd Gen 9K 24K Troubleshooting Guide Englishsergio123451Încă nu există evaluări
- ResumeDocument2 paginiResumeapi-397601484Încă nu există evaluări
- Centero VR910 DatasheetDocument1 paginăCentero VR910 DatasheetraytangclÎncă nu există evaluări
- JORDAHL® JTA-CE OverviewDocument24 paginiJORDAHL® JTA-CE Overviewaristo_onan2546Încă nu există evaluări
- Wireless DC Moor Speed and Direction ControlDocument2 paginiWireless DC Moor Speed and Direction ControlJoseph JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computing TextbookDocument502 paginiComputing Textbookfor FreeTrailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nagios Fan For Hyper-VDocument28 paginiNagios Fan For Hyper-Vnia8aprihansahÎncă nu există evaluări