Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
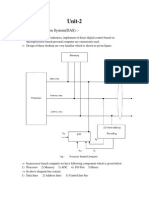
Microcontroller
Încărcat de
Bryan Adversalo0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
80 vizualizări3 paginimicrocontroller
Titlu original
microcontroller
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentmicrocontroller
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
80 vizualizări3 paginiMicrocontroller
Încărcat de
Bryan Adversalomicrocontroller
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
Lecture 12 - 1 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
Lecture 12 - System Buses: Interfacing
Processors and Peripherals
N System interconnection structures may support these transfers:
Memory to processor: the processor reads instructions and data from
memory
Processor to memory: the processor writes data to memory
I/O to processor: the processor reads data from I/O device
Processor to I/O: the processor writes data to I/O device
I/O to or from memory: I/O module allowed to exchange data directly with
memory without going through the processor - Direct Memory Access (DMA)
Reference: Computer Organization & Architecture (5th Ed), William Stallings
Lecture 12 - 2 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
Signals found on a bus
N Address lines
N Data lines
N Control lines:
Memory write: data on the bus written into the addressed location
Memory read: data from the addressed location placed on the bus
I/O write: data on the bus output to the addressed I/O port
I/O read: data from the addressed I/O port placed on the bus
Bus REQ: indicates a module needs to gain control of the bus
Bus GRANT: indicates that requesting module has been granted control of
the bus
Interrupt REQ: indicates that an interrupt is pending
Interrupt ACK: Acknowledges that pending interrupt has been recognized
Reset: Initializes everything connected to the bus
Clock: on a synchronous bus, everything is synchronized to this signal
Lecture 12 - 3 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
Traditional Bus Architecture
N Speed of expansion bus is limited.
Lecture 12 - 4 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
High-Performance Bus Architecture
(e.g. PCI Bus)
N Separate out fast local bus (PCI bus) and slower I/O expansion bus (ISA
bus)
Lecture 12 - 5 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
I/O Devices
N Very diverse data rate:
Lecture 12 - 6 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
Techniques for Inputting a Block of Data
Lecture 12 - 7 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
Polling and Interrupt
N Both are methods to notify processor that I/O device needs attention
N Polling
simple, but slow
processor check status of I/O device regularly to see if it needs attention
similar to checking a telephone without bells!
N Interrupt
fast, but more complicated
processor is notified by I/O device (interrupted) when device needs attention
similar to a telephone with bells
Lecture 12 - 8 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
Direct Memory Access
N Interrupt & programmed I/O requires processor to transfer data
between memory and I/O module.
N Processor is tied up in performing the transfer by executing a number
of instructions - SLOW!!!
N I/O module can contain autonomous hardware to perform transfer
DMA
N DMA is stealing bus cycles from processor - a technique known as
cycle stealing
Lecture 12 - 9 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
Direct Memory Access (cont)
N DMA is initiated by a processor. The following information must be sent
by the processor to the DMA module:
Tell DMA module whether a read or write is required
Send to the DMA module the address of the I/O device involved in the
transfer
The starting location in memory to read from or write to - DMA module will
store this locally in the address register
The number of word to read or write - DMA module will store this in the data
count register
N Once DMA is initiated, the processor can continue with other work.
N Since processor has cache memory, it can work concurrently with
transfer between I/O device and memory. (But there is extra work needed
to ensure cache coherency)
Lecture 12 - 10 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
Lecture 12 - 11 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing Lecture 12 - 12 pykc/gac - 4-Dec-01 ISE1 / EE2 Computing
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.De la EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.Încă nu există evaluări
- L21-24 IO OrganisationDocument23 paginiL21-24 IO OrganisationThiruvengadam RengasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9: Input/Output: The Architecture of Computer Hardware and Systems SoftwareDocument40 paginiChapter 9: Input/Output: The Architecture of Computer Hardware and Systems SoftwareWaqas AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intellignt Instrumentation NotesDocument13 paginiIntellignt Instrumentation NotesBarun DhimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bahir Dar University Faculty of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument35 paginiBahir Dar University Faculty of Electrical and Computer EngineeringBESFATÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parallel Data TransfersDocument5 paginiParallel Data TransfersWanjira KigokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8255PPIDocument60 pagini8255PPIVedant BohraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interfacing ConceptsDocument17 paginiInterfacing Conceptsanon_61073984100% (1)
- Unit-2: Data Acquisition System (DAS)Document10 paginiUnit-2: Data Acquisition System (DAS)Barun DhimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework: - Reading - Machine Projects - LabsDocument21 paginiHomework: - Reading - Machine Projects - Labsloveygupta007Încă nu există evaluări
- B.ram Lecture 1 2Document11 paginiB.ram Lecture 1 2Yamini GollepallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSS Quarterly Exam 1Document18 paginiCSS Quarterly Exam 1seph bronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Serial Communications: A Serial Connection Sends Information Over TheDocument9 paginiSerial Communications: A Serial Connection Sends Information Over Theteferi GetachewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interfacing Examples: ECP2036 Microprocessor Systems and InterfacingDocument20 paginiInterfacing Examples: ECP2036 Microprocessor Systems and InterfacingAnonymous LKInG4giPpÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8251 and 8255 USARTDocument86 pagini8251 and 8255 USARTmoazzam hussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- FPGA-Based Multi Protocol Data Acquisition System With High Speed USB InterfaceDocument4 paginiFPGA-Based Multi Protocol Data Acquisition System With High Speed USB InterfaceVibin MammenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitsubishi Training 20130226Document4 paginiMitsubishi Training 20130226fellskevÎncă nu există evaluări
- CA Classes-266-270Document5 paginiCA Classes-266-270SrinivasaRaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance CP IIDocument50 paginiAdvance CP IIRavi KhimaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 4:: Computer Interconnection Structures, Bus Interconnection, PCIDocument16 paginiWeek 4:: Computer Interconnection Structures, Bus Interconnection, PCIRegji IndonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 PDFDocument40 pagini4 PDFjeeturathiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Processing Unit: Lecture PlanDocument15 paginiBasic Processing Unit: Lecture PlanCharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Parallel PortsDocument11 paginiIntroduction To Parallel PortsJanet Cui TibudanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arc Chap5Document38 paginiArc Chap5Natnael BerhanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- PC Interfacing Fourth Level Lecture TWO: Parallel (Centronic) Port InterfaceDocument9 paginiPC Interfacing Fourth Level Lecture TWO: Parallel (Centronic) Port Interfaceأسامة المياحيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architecture IIDocument158 paginiArchitecture IIGafeer FableÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP8085 Lab ManualDocument179 paginiMP8085 Lab ManualEvan3333Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts in Serial I/O Interfacing I/O DevicesDocument33 paginiBasic Concepts in Serial I/O Interfacing I/O DevicessubendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 7 (Input Output Organisation) (MFRDT)Document29 paginiWeek 7 (Input Output Organisation) (MFRDT)Mohamed Abdirashid AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8257 DMA Controller:: To Fetch The Instruction To Decode The Instruction and To Execute The InstructionDocument25 pagini8257 DMA Controller:: To Fetch The Instruction To Decode The Instruction and To Execute The Instructionsatyanarayana12Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12: I/O SubsystemDocument10 paginiChapter 12: I/O SubsystemHadjer BouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types Profibus CommunicationDocument23 paginiTypes Profibus CommunicationAhmed ElsayedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yaskawa Electric America: Introduction To DevicenetDocument17 paginiYaskawa Electric America: Introduction To DevicenetPaul VolzÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProfimDocument5 paginiProfimFernando ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PD - POCSAG Decoder User Documentation Version 1.02 June 1995Document9 paginiPD - POCSAG Decoder User Documentation Version 1.02 June 1995jamesyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5Document5 paginiUnit 5kisu kingÎncă nu există evaluări
- DMADocument5 paginiDMAPrabir K DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siminar (1) FinalDocument11 paginiSiminar (1) FinalNora MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard I/O Interfances Reference: Call Hamacher, "Computer Organization"Document10 paginiStandard I/O Interfances Reference: Call Hamacher, "Computer Organization"JochumÎncă nu există evaluări
- GLA UNIVERSITY Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, IndiaDocument31 paginiGLA UNIVERSITY Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, IndiaANSHY SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 3 Computer Function InterconnectionDocument30 paginiChap 3 Computer Function InterconnectionNguyễn Thanh LiêmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coa Assignment-4: Akshit Aggarwal CS63 171294Document7 paginiCoa Assignment-4: Akshit Aggarwal CS63 171294Rajput RishavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Input-Output Modules: Detection Mechanism. Functions of I/O ModuleDocument8 paginiInput-Output Modules: Detection Mechanism. Functions of I/O ModuleSubash GautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument12 paginiComputer Organization and Architecturechand1894Încă nu există evaluări
- Allen Bradley PLCDocument32 paginiAllen Bradley PLCchayan_m_shahÎncă nu există evaluări
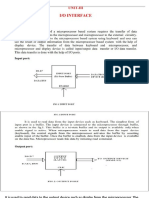
- Peripheral/Computer Connections: Lec Tarannum Zaki, Dept. of CSE, MISTDocument52 paginiPeripheral/Computer Connections: Lec Tarannum Zaki, Dept. of CSE, MISTDurba Binte KalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accessing I/O Devices: Generic Model of IO ModuleDocument14 paginiAccessing I/O Devices: Generic Model of IO ModuleAdarsha BhattaraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Input Output Organization in Computer Organization and Architecture 2022Document14 paginiInput Output Organization in Computer Organization and Architecture 2022sravan123Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3Document71 paginiUnit 3Vishesh ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4Document30 paginiUnit 4Subathra Devi MourouganeÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMECS2010 pp1196-1199 PDFDocument4 paginiIMECS2010 pp1196-1199 PDFksajjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Profibus: Tim Linnell (Eurotherm LTD)Document23 paginiProfibus: Tim Linnell (Eurotherm LTD)sina20795100% (2)
- Module3 Specialpurposeprogrammabledevicesandtheirinterfacing 141020230225 Conversion Gate02Document65 paginiModule3 Specialpurposeprogrammabledevicesandtheirinterfacing 141020230225 Conversion Gate02zelalem2022Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Operating SystemDocument20 paginiUnit 5 Operating SystemPoornima.BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-I: 8-Bit MicroprocessorsDocument55 paginiUnit-I: 8-Bit MicroprocessorsAASTHA KIETÎncă nu există evaluări
- proDNC EDocument24 paginiproDNC EFaizan HamiedÎncă nu există evaluări
- IO SystemDocument32 paginiIO Systemnanekaraditya06Încă nu există evaluări
- Max Session-IDocument28 paginiMax Session-IelrajilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Ee301Document14 paginiLab Ee301ah chong100% (1)
- Introduction To Power SupplyDocument7 paginiIntroduction To Power SupplydennycollinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power TransfomerDocument63 paginiPower Transfomerah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 6 Diode RectifierDocument36 paginiLecture 6 Diode Rectifierah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction Power Supply Rev7 22Document19 paginiIntroduction Power Supply Rev7 22Resy ApolinarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 (1) OkDocument14 paginiChapter 5 (1) Okah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction Power Supply Rev7 22Document19 paginiIntroduction Power Supply Rev7 22Resy ApolinarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sram DramDocument24 paginiSram DramVishal VishwakarmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 3Document66 paginiPart 3ah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7805Document20 pagini7805Niculae NoicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5590power SupplyDocument14 pagini5590power Supplyah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7805 Datasheet FairchildDocument29 pagini7805 Datasheet FairchildsumitseghalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cent-112-6 OkDocument69 paginiCent-112-6 Okah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual MemoryDocument19 paginiVirtual Memoryah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual MemoryDocument19 paginiVirtual Memoryah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shift Register and Its TypesDocument22 paginiShift Register and Its TypeschoprahridyeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sram DramDocument24 paginiSram DramVishal VishwakarmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 3Document66 paginiPart 3ah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shift Register and Its TypesDocument22 paginiShift Register and Its TypeschoprahridyeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Main Memory: Computer Architecture COE 501Document18 paginiMain Memory: Computer Architecture COE 501ah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Registers in The Central Processor: b3 b2 b1 b0Document5 paginiRegisters in The Central Processor: b3 b2 b1 b0ah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Registers in The Central Processor: b3 b2 b1 b0Document5 paginiRegisters in The Central Processor: b3 b2 b1 b0ah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Main Memory: Computer Architecture COE 501Document18 paginiMain Memory: Computer Architecture COE 501ah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE 380 Computer Operating Systems: Instructor: Insup LeeDocument66 paginiCSE 380 Computer Operating Systems: Instructor: Insup Leeah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE 380 Computer Operating Systems: Instructor: Insup LeeDocument66 paginiCSE 380 Computer Operating Systems: Instructor: Insup Leeah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disk-Based Storage Oct. 23, 2008: "The Course That Gives CMU Its Zip!"Document38 paginiDisk-Based Storage Oct. 23, 2008: "The Course That Gives CMU Its Zip!"ah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disk-Based Storage Oct. 23, 2008: "The Course That Gives CMU Its Zip!"Document38 paginiDisk-Based Storage Oct. 23, 2008: "The Course That Gives CMU Its Zip!"ah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory Element (ROM RAM)Document25 paginiMemory Element (ROM RAM)ah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory Element (ROM RAM)Document25 paginiMemory Element (ROM RAM)ah chongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use Virtual Memory To Build A File SystemDocument24 paginiUse Virtual Memory To Build A File Systemah chongÎncă nu există evaluări