Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Polygons and Construction
Încărcat de
Joann Ng0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
46 vizualizări15 paginiangles
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentangles
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
46 vizualizări15 paginiPolygons and Construction
Încărcat de
Joann Ngangles
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 15
POLYGONS AND CONSTRUCTION
1. A regular polygon has interior angles of 135 each.
(a) Find the number of sides of the polygon.
(b) What is the special name given to this polygon?
Ans: (a) [ 2 ]
(b) [ 1 ]
2. PQRSTU is a hexagon. Find
a) the sum of all its interior angles
b) the value of x .
Ans: (a) ___________ [2]
(b) ___________ [3]
3 The diagram shows a pentagon PQRST. QR is produced to U.
Given that the sum of interior angles of a pentagon is 540
o
, find the value of x
o
.
Hence calculate the value of SRU .
[3]
4. Each exterior angle in a regular polygon is 30. How many sides does the polygon have?
Ans: [2]
P
T
Q
R
U
S
150
(x 10)
110
115
(3x 5)
5. Given that ABCDEF is a regular hexagon. Find the values of x , y and z .
Ans: x ___________________
o
[1]
y
___________________
o
[1]
z
___________________
o
[2]
y
x
A
B
E
C
D
F
z
6. Three interior angles of an n-gon are 153
0
, 144
0
and 100
0
. If the remaining interior angles
are each equal to 149
0
, find the value of n. [3]
7. (a) Name the polygon below.
(b) An interior angle of a polygon is (32x 2) and its corresponding exterior
angle is (3x + 7). Find the value of x.
Answer (a) ... [1]
(b) ... [2]
8. A polygon has n sides. If one of its interior angles is 84 and the other remaining interior angles are
each equal to 156 , find the value of n. [3]
9. The sizes of 3 interior angles of a 9-sided polygon are 116, 108 and 130 respectively. The size of
each remaining interior angle of the polygon is x.
(a) Calculate the value of x.
(b) Hence, find the size of the largest exterior angle of the polygon,
Ans: (a) x =_______________[2]
(b)________________ [1]
10. In a hexagon, 2 of the interior angles are 135 each and another 2 of the exterior angles are
50 each. The remaining interior angles are x each. Find the value of x.
Answer:
x =
o
[3]
11. In the isosceles triangle ABC, AB = 5 cm and BC = CA = 6 cm.
(a) Construct the triangle ABC in the space below.
(b) Construct the perpendicular bisector of the line AB
(c) Hence, find the area of the triangle ABC
Answer: (c) cm
2
[1]
A
B
12. (a) Construct such that AB = 5 cm, BC = 6.5 cm, CA = 7.8 cm. [2]
(b) Construct the angle bisector of ACB which cuts AB at P. [2]
(c) Measure and write down the length of AP.
13. Answer the whole of this question on a sheet of plain paper.
(a) Construct the triangle ABC in which BC = 10 cm, BCA = 110
o
and AC = 5 cm. [2]
(b) Measure and write down the size of ABC . [1]
(c) Construct
(i) the perpendicular bisector of BC, [1]
(ii) the angle bisector of BAC . [1]
14. (a) Construct and label triangle ABC, where AB = 7.9 cm, BAC 48 and
AC = 4.8 cm. [2]
(b) Measure and write down the length of BC. [1]
(c) Measure and write down the size of ACB . [1]
(d) Construct and label line X, which is equidistant from points B and C of the triangle.
[1]
(e) Construct and label line Y, which splits BAC into 2 equal parts. [1]
15. Answer the whole of this question on a piece of plain A4 paper.
(a) Using compass and ruler, draw and label ABC in which AB = 14 cm, CAB = 60
o
and
AC = 12 cm. [2]
(b) On your diagram,
(i) construct the angle bisector of ABC, [2]
(ii) construct the perpendicular bisector of AB, [2]
(iii) mark clearly, P, the point where the two bisectors intersect each other, [1]
(iv) measure PAB. [1]
16. In quadrilateral PQRS, PQ = 8 cm, QR = 8.5 cm, RS = 6.5 cm, PS = 5 cm and QS = 7 cm.
Showing your construction lines clearly, construct
(a) the quadrilateral PQRS using the given line PQ. [2]
(b)(i) the angle bisector of PQR , [1]
(ii) the perpendicular bisector of the line PQ. [1]
Answer: (a) and (b)
P Q
17. (a) Construct a quadrilateral ABCD such that AB = 9.4 cm, BC = 10.0 cm, AD = 6 cm,
CD = 10.6 cm and DAB = 80. Use the line AB given below and label your diagram clearly. [4]
(b) Construct the perpendicular bisector of AB and the angle bisector of DAB.
Label the point of intersection of the perpendicular bisector and the angle bisector as X.[3]
(c) Write down the length of AX. [1]
18. Complete this question on the blank piece of paper provided.
Construct a triangle ABC such that AB = 10cm, AC = 6.5cm and
70 BAC .
[ 2 ]
(a) Measure the length of BC.
[ 1 ]
(b) Draw the perpendicular bisector of AC, showing your construction
workings clearly.
[ 2 ]
(c) Label the point G, which is the point of intersection of the
perpendicular bisector drawn in (b) and the line AC.
[ 1 ]
(d) Measure the length of BG.
[ 1 ]
(e) Hence or otherwise, find the area of the triangle ABC. [ 2 ]
19. (a) Construct a quadrilateral ABCD such that AB = 6 cm, BC = 9.6 cm,
CD = 10 cm, AD = 10.4 cm and angle ABC = 80. [3]
(b) Construct the perpendicular bisector of the line AD and the angle bisector of angle BCD.
[2]
(c) Given that these 2 bisectors meet at T, mark clearly the point T. [1]
(d) Hence, measure and write down the length of BT. [1]
20. Construct a quadrilateral PQRS such that PQ = 8 cm, QR = 6 cm, 100 PSR ,
RS = 5 cm and PS = 7 cm. [2]
(a) Construct the perpendicular bisector of QR.
(b) Construct the angle bisector of QPS .
(c) M is the point of intersection of the 2 lines constructed in parts (a) and (b).
(i) Measure PMQ .
(ii) What is the length of PM ?
Answer (a) On diagram [1]
(b) On diagram [1]
(c)(i) PMQ = ... [1]
(ii) PM = ..cm [1]
P Q
P 7 cm S
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Secondary 1 AlgebraDocument55 paginiSecondary 1 AlgebraJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimation and ApproximationDocument13 paginiEstimation and ApproximationJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimation and ApproximationDocument13 paginiEstimation and ApproximationJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Not A Toy Sample PDFDocument37 paginiNot A Toy Sample PDFMartha Paola CorralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 04Document19 paginiCH 04Charmaine Bernados BrucalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compound Interest R P: Mathematical FormulaeDocument21 paginiCompound Interest R P: Mathematical FormulaeJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 (A) Solve The Inequality (B) Hence, State The (I) (Ii)Document13 pagini1 (A) Solve The Inequality (B) Hence, State The (I) (Ii)Joann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prac 1 P1Document20 paginiPrac 1 P1Joann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnglesDocument23 paginiAnglesJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angles and Parallel LinesDocument15 paginiAngles and Parallel LinesJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer: $Document18 paginiAnswer: $Joann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0580 s11 Ms 11 PDFDocument3 pagini0580 s11 Ms 11 PDFJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect ProportionDocument15 paginiDirect and Indirect ProportionJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Area and VolumeDocument33 paginiArea and VolumeJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- F170 User ManualDocument6 paginiF170 User ManualJoann NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roxas City For Revision Research 7 Q1 MELC 23 Week2Document10 paginiRoxas City For Revision Research 7 Q1 MELC 23 Week2Rachele DolleteÎncă nu există evaluări
- NIQS BESMM 4 BillDocument85 paginiNIQS BESMM 4 BillAliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Out Fire SurpressDocument69 paginiHand Out Fire SurpressSeptiawanWandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regional Manager Business Development in Atlanta GA Resume Jay GriffithDocument2 paginiRegional Manager Business Development in Atlanta GA Resume Jay GriffithJayGriffithÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Universe?Document19 paginiWhat Is Universe?Ruben M. VerdidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elpodereso Case AnalysisDocument3 paginiElpodereso Case AnalysisUsama17100% (2)
- Draft JV Agreement (La Mesa Gardens Condominiums - Amparo Property)Document13 paginiDraft JV Agreement (La Mesa Gardens Condominiums - Amparo Property)Patrick PenachosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epreuve Anglais EG@2022Document12 paginiEpreuve Anglais EG@2022Tresor SokoudjouÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE MELCs Grade 3Document4 paginiPE MELCs Grade 3MARISSA BERNALDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- I I I I: Peroxid.Q!Document2 paginiI I I I: Peroxid.Q!Diego PradelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report FinalDocument48 paginiReport FinalSantosh ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Please Refer Tender Document and Annexures For More DetailsDocument1 paginăPlease Refer Tender Document and Annexures For More DetailsNAYANMANI NAMASUDRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stone As A Building Material: LateriteDocument13 paginiStone As A Building Material: LateriteSatyajeet ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aakriti 1Document92 paginiAakriti 1raghav bansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document8 paginiChapter 2Fahmia MidtimbangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Walking in Space - Lyrics and Chord PatternDocument2 paginiWalking in Space - Lyrics and Chord Patternjohn smithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kosher Leche Descremada Dairy America Usa Planta TiptonDocument2 paginiKosher Leche Descremada Dairy America Usa Planta Tiptontania SaezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Spin Inversion: A Danger To Your HealthDocument4 paginiElectronic Spin Inversion: A Danger To Your Healthambertje12Încă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Chem Lab #3Document4 paginiAnalytical Chem Lab #3kent galangÎncă nu există evaluări
- EdisDocument227 paginiEdisThong Chan100% (1)
- Bcci ScandalDocument6 paginiBcci ScandalNausaf AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building and Structural Construction N6 T1 2024 T2Document9 paginiBuilding and Structural Construction N6 T1 2024 T2FranceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume 1Document2 paginiResume 1Aidie HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genomic Tools For Crop ImprovementDocument41 paginiGenomic Tools For Crop ImprovementNeeru RedhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airport & Harbour Engg-AssignmentDocument3 paginiAirport & Harbour Engg-AssignmentAshok Kumar RajanavarÎncă nu există evaluări
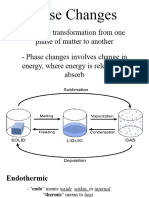
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 Lesson 5 Endothermic and Exotheric Reaction and Heating and Cooling CurveDocument19 paginiGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 Lesson 5 Endothermic and Exotheric Reaction and Heating and Cooling CurveJolo Allexice R. PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Review CompilationDocument9 paginiMath Review CompilationJessa Laika CastardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production of Bioethanol From Empty Fruit Bunch (Efb) of Oil PalmDocument26 paginiProduction of Bioethanol From Empty Fruit Bunch (Efb) of Oil PalmcelestavionaÎncă nu există evaluări