Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CHH Drug Study Week 2
Încărcat de
maryxtine24Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CHH Drug Study Week 2
Încărcat de
maryxtine24Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
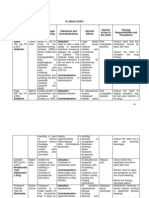
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Mannitol Pharmacologic Class:
Osmotic Diuretic
Therapeutic Class:
Diuretic
Test dose for marked oliguria or
suspected inadequate kidney
function.
Oliguria
To prevent oliguria or acute renal
impairment.
Edema; ascites caused by renal,
hepatic, or cardiac failure.
To reduce intraocular or
intracranial pressure
Diuresis in drug intoxication
Irrigation solution during
transurethral resection prostate
20% 150ml IV bolus every
4 hours
Assess patients condition before therapy and
regularly thereafter to monitor drugs
effectiveness.
Monitor vital signs, central venous pressure, and
fluid intake and output hourly.
Monitor weight and kidney function, as well as
serum and urine sodium and potassium levels.
Tell patient that he may feel thirsty or have a
dry mouth, and emphasize the importance of
drinking only the amount of fluid provided.
Instruct patient to immediately report pain in
chest, back, or legs, or shortness of breath.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Osmetrol Chemical Effect:
Increases osmotic pressure
of glomerular filtrate,
inhibiting tubular
reabsorption of water and
electrolytes. This elevates
blood osmolality, enhancing
water and sodium flow into
extracellular fluid.
Therapeutic Effect:
Increases water excretion,
decreases intracranial or
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to the drug or any of
its components, and in those with
anuria, severe pulmonary congestion,
frank pulmonary edema,severe heart
failure, severe dehydration, metabolic
edema, progressive renal disease or
dysfunction, or active intracranial
bleeding except during craniotomy.
CNS: headache, confusion,
seizures
CV: Circulatory overload,
heart failure, tachycardia,
chest pain
EENT: blurred vision,
rhinitis
GI: thirst, nausea, vomiting,
diarrhea
GU: urine retention
Metabolic: water
intoxication, cellular
dehydration, electrolyte
Patient maintains adequate hydration
throughout the therapy.
Adequate balance of patients fluid output noted.
Decrease evidence of elevated intracranial
pressure
Moderate to minimal drainage from patients JP
drain at right frontoparietal area.
intraocular pressure,
prevents or treats kidney
dysfunction, and promotes
excretion of drug
overdosage.
imbalance
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
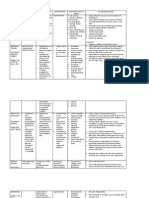
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Citicoline Pharmacologic Class:
CNS Stimulant
Therapeutic Class:
Peripheral Vasodilators,
Cerebral Activators,
Nootropics
Citicoline is indicated in CVD in
acute recovery phase in severe s/sx
of cerebrovascular insufficiency
and in-cranial traumatism and their
sequellae. Citicoline in CVA,
stimulates brain function
1gm IVTT Monitor patients neurologic status.
Note for any signs of slurring of speech.
Titer medication when discontinuing.
Citicoline may be taken with or without food. Take
it with or between meals.
The supplement should not be taken in the late
afternoon or at night because it can cause
difficulty sleeping.
Citicoline therapy should be started within 24
hours of a stroke.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Zynapse It is a CNS Stimulant or a
Nootropics. It acts by increasing
the blood flow and O2
consumption of the brain and
involved in the biosynthesis
action. In simplest terms,
Citicoline promotes brain
metabolism.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to the drug or any of
its components.
Contraindicated in patients with
hypertonia of the parasympathetic
nervous system.
Use cautiously in patients with
renal and hepatic damage.
Fleeting and
discrete
hypotension effect,
increased
parasympathetic
effects, low blood
pressure
Itching or hives,
swelling in face or
hands, chest
tightness, tingling
in mouth and
throat.
Patient maintains adequate hydration throughout
the therapy.
Adequate balance of patients fluid output noted.
Decrease evidence of elevated intracranial
pressure
Moderate to minimal drainage from patients JP
drain at right frontoparietal area.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
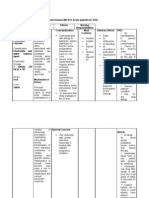
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Omeprazole Pharmacologic Class:
substituted benzimidazole
Therapeutic Class:
proton pump inhibitor
Pregnancy Risk Category: C
Erosive esophagitis, symptomatic,
poorly responsive
gastroesophageal reflux disease
(GERD)
GERD without esophagitis
Pathologic hypersecretory
conditions (such as Zollinger-
Ellison syndrome)
Duodenal Ulcer (short-term
therapy)
Gastric Ulcer
H. pylori eradication to reduce risk
of duodenal ulcer recurrence as
part of triple therapy with
clarithromycin and amoxicillin
Heartburn on 2 or more days per
week
Posterior laryngitis
40mg IF adverse GI reaction occurs, monitor hydration
status.
Give tablets or capsules 30 mins before meals;
powder for oral suspension 1 hour before meals.
Only use water to mix with powder for
suspension, do not use any other liquids or food.
Inform patient that OTC drugs may require 1-4
days for full effect, although some patients may
get complete relief of symptoms within 24 hours.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Omepron Chemical Effect:
Inhibits acid (proton) pump
and binds to hydrogen-
potassium adenosine
triphosphatase on secretory
surface of gastric parietal
cells to block formation of
gastric acid.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to the drug, any of
its components.
Use cautiously for pregnancy and
lactation.
In children ages 2-16 years, drug
may be used to treat GERD, erosive
esophagitis, and for maintenance of
CNS: dizziness,
headache
GI: abdominal pain,
constipation, diarrhea,
flatulence, nausea,
vomiting
Musculoskeletal: back
pain
Patient maintains adequate hydration throughout
the therapy.
Normal acid-base balance based on patients
laboratory results
Normal abdominal sounds upon auscultating
Therapeutic Effcet:
It relieves symptoms caused
by excessive gastric acid.
healing in erosive esophagitis
(tablets and capsules only).
Respiratory: cough
Skin: rash
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Metronidazole Pharmacologic Class:
nitroimidazole
Therapeutic Class:
Antibacterial, antiprotozoal,
amebicide
Pregnancy Risk Category: B
Amebic hepatic abscess
Intestinal Amebiasis
Trichomoniasis
Refractory trichomoniasis
Bacterial infections caused by
anaerobic microorganisms
To prevent postoperative infection
in contaminated colorectal surgery
Inflammatory papules and pustules
of acne rosacea
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Bacterial vaginosis
Active Crohn disease
500mg IV Assess patients infection before and regularly
thereafter to monitor drug effectiveness.
Watch carefully for edema, especially in patients
also receiving corticosteroids, because Flagyl I.V.
RTU may cause sodium retention.
Record number of stools when used in amebiasis.
I.V. infusion may cause thrombophlebitis at site;
observe closely.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Dazomet Chemical Effect:
Direct-acting trichomonacide
and amebicide that works at
both intestinal and
extraintestinal sites.
Therapeutic Effect:
Hinders growth of selected
organims, including most
anaerobic and protozoa.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to the drug or other
nitroimidazole derivatives.
Use cautiously in patients receiving
hepatotoxic drugs and in patients
with history or blood dyscrasia or
CNS disorder, retinal or visual field
changes, hepatic disease, or
alcholism.
CNS: ataxia, confusion,
depression,
drowsiness, fatigue
headache,
incoordination
insomnia, irritability,
seizures, vertigo,
weakness.
CV: edema, flattened T
wave, flushing,
thrombophlebitis.
Patient is still closely monitored from infection.
Patient maintains adequate hydration throughout
the therapy.
Patient and Family state understanding of drug
therapy.
EENT: eye tearing.
GI: abdominal
cramping, anorexia,
constipation, diarrhea,
dry mouth, metallic
taste, nausea, vomiting.
GU: cystitis, darkened
urine, dry vagina and
vulva, dyspareunia.
Hematologic:
neutropenia,
thrombocytopenia,
transient leucopenia.
Skin: burning and
stinging, contact
dermatitis, dry skin,
local allergic reaction
or irritation.
Other: decreased
libido, glossitis,
gynecomastia,
overgrowth of
nonsusceptible
organisms.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Phenobarbital Pharmacologic Class:
barbiturate
Therapeutic Class:
anticonvulsant, sedative-
hypnotic
Pregnancy Risk Category: D
All forms of epilepsy except
absence seizures; febrile seizures in
children.
Status epilepticus
Sedation
Insomnia
Preoperative sedation
Prevention and treatment of
hyperbilirubinemia
To lower serum bilirubin or serum
lipid levels in the treatment of
chronic cholestasis.
500mg IV Assess patients infection before and regularly
thereafter to monitor drug effectiveness.
Watch carefully for edema, especially in patients
also receiving corticosteroids, because Flagyl I.V.
RTU may cause sodium retention.
Record number of stools when used in amebiasis.
I.V. infusion may cause thrombophlebitis at site;
observe closely.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Luminal Chemical Effect:
Direct-acting trichomonacide
and amebicide that works at
both intestinal and
extraintestinal sites.
Therapeutic Effect:
Hinders growth of selected
organims, including most
anaerobic and protozoa.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to barbiturates and
in those with hepatic dysfunction,
respiratory disease with dyspnea or
obstruction, nephritis, or a history
of manifest or latent porphyria.
Use cautiously in debilitated
patients and in patients with acute
or chronic pain, depression, suicidal
tendencies, history of drug abuse,
altered blood pressure, CV disease,
shock, or uremia
CNS: drowsiness,
hangover, lethargy.
CV: bradycardia,
hypotension,
thrombophlebitis
GI: nausea, vomiting
Hematologic:
exacerbation or
porphyria.
Respiratory: apnea,
respiratory depression.
Skin: erythema
multiforme, rash.
Patient is free from seizure activity
Patient has no injury from drug-induced adverse
CNS reactions.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Amlodipine Pharmacologic Class:
Calcium channel blocker
Therapeutic Class:
Antianginal,
antihypertensive
Pregnancy Risk Category: C
Chronic stable angina; vasospasic
angina
Hypertension
10mg tab Assess patients blood pressure or angina before
therapy and regularly thereafter.
Monitor patient carefully for pain.
Be alert for adverse reaction
Assess patients and familys knowledge of drug
therapy
Tell patient that S.L. nitroglycerin may be taken as
needed for acute angina. If patient continues
nitrate therapy during adjustment of amlodipine
dosage, urge continued compliance.
Advise patient to continue taking drug even after
feeling better.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Norvasc Chemical Effect:
Inhibits calcium ion reflux
across cardiac and smooth-
muscle cells, thus decreasing
myocardial contractility and
oxygen demand. Also dilates
coronary arteries and
arterioles.
Therapeutic Effect:
Reduces blood pressure and
prevents angina.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug.
Use cautiously in patients taking
other peripheral vasodilators
(especially those with severe aortic
stenosis) and in those with heart
failure.
In patients with severe hepatic
disease, use cautiously and in
reduced dosage because drug is
metabolized by liver.
CNS: fatigue, headache,
somnolence.
CV: dizziness, edema,
flushing, palpitations.
GI: abdominal pain,
dyspepsia, nausea.
Patients blood pressure became normal.
Patients vital signs were within normal rage.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Telmisartan Pharmacologic Class:
Angiotensin II receptor
antagonist
Therapeutic Class:
Antihypertensive
Pregnancy Risk Category: C
Hypertension 10mg tab If hypotension occurs, place patient in supine
position and give normal saline solution I.V. if
needed.
Inform patient that drug may be taken without
regard to meals.
Inform woman of childbearing age of
consequences of second- and third-trimester
exposure to drug.
Instruct patient with heart failure to notify
prescriber about decreased urine output.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Micardis Chemical Effect:
Blocks the vasoconstrictive
and aldosterone-secreting
effects of angiotensin II by
selectively blocking the
binding of angiotensin II to
the AT1 receptor in many
tissues, such as vascular
smooth muscle and adrenal
glands.
Therapeutic Effect:
Lowers blood pressure.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug or any of its
components.
Use cautiously in patients with
renal and hepatic insufficiency and
in those with an activated rennin-
angiotensin system.
CNS: dizziness, fatigue,
headache, pain
CV: chest pain,
hypertension,
peripheral edema.
EENT: pharyngitis,
sinusitis.
GI: abdominal pain,
dyspepsia, nausea,
diarrhea
GU: UTI
Patients blood pressure became normal.
Patients vital signs were within normal rage.
Patient has no hypotension and maintains
adequate tissue perfusion.
Patient sustains no injury from underlying
disease.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Piperacillin
+Tazobactam
Pharmacologic Class: Beta
Lactamase Inhibitor,
extended spectrum penicillin
Therapeutic Class: antibiotic
Pregnancy Risk category : B
Treatment of moderate to severe
appendicitis, uncomplicated and
complicated skin and skin structure
infections, endometritis, pelvic
inflammatory disease, or
nosocomial or community-acquired
pneumonia caused by piperacillin-
resistant, piperacillin/tazobactam-
susceptible, beta-lactamase-
producing bacteria.
2.25grams IV every 8
hours
Obtain history of hypersensitivity to penicillins,
cephalosporins, or other drugs prior to
administration.
Lab tests: C&S prior to first dose of the drug; start
drug pending results.
Monitor hematologic status with prolonged
therapy (Hct and Hgb, CBC with differential and
platelet count).
Monitor patient carefully during the first 30 min
after initiation of the infusion for signs of
hypersensitivity.
Report rash, itching, or other signs of
hypersensitivity immediately.
Report loose stools or diarrhea as these may
indicate pseudomembranous colitis
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Tazocin It blocks the bacteria's cell
wall growth, which kills the
bacteria. Tazobactam
inhibits the action of
bacterial beta-lactamases. It
is added to the extended
spectrum beta-lactam
antibiotic piperacillin. It
Caution should be exercised in
patients with history of asthma; hay
fever; or kidney, liver, or
gastrointestinal disease (especially
colitis), during pregnancy and
breastfeeding.
Repeated electrolyte estimations
may be needed especially in
It may lead to increase
risk of fever, rashes in
patients with cystic
fibrosis, bleeding,
super infections,
convulsions, kidney
failure.
Allergic Reactions-
Patient is still closely monitored from infection.
Patient maintains adequate hydration throughout
the therapy.
Patient and Family state understanding of drug
therapy.
broadens the spectrum of
piperacillin by making it
effective against organisms
that express beta-lactamase
and would normally degrade
piperacillin.
patients with low potassium levels.
Monitor blood functions regularly.
Diarrhea, severe
allergic reactions, skin
rashes, itching,
occasionally platelet
mediated bleeding,
rigors, malaise,
inflammation in
stomach.
Local- Injection-site
reactions such as pain,
swelling, redness,
indurations and vein
inflammation.
GI- Inflammation of
stomach, hairy tongue,
inflammation of colon,
nausea and vomiting,
blood in stool.
GU- Urine retention,
painful urination.
Blood- Decrease in
white blood cells.
Lab- Increase in liver
enzymes, blood urea
nitrogen, and presence
of red blood cells in
urine.
Misc- Chills, facial
swelling, mucosal
bleeding, tightness in
throat.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Paracetamol Pharmacologic Class:
para-aminophenol derivative
Therapeutic Class: nonopiod
analgesic, antipyretic
Pregnancy Risk category : B
Mild pain or fever
Osteoarthritis
650mg tablet every 6
hours
Assess patients pain or temperature before and
during therapy.
Assess patients drug history, and calculate total
daily dosage accordingly.
Give oral form early in the morning and the
second dose early in the afternoon to avoid
nocturia.
Teach patient to monitor fluid volume by
measuring weight, intake, and output daily.
Enourage patient to avoid high-sodium foods and
to choose high-potassium foods.
Teach patient to recognize and report signs and
symptoms of fluid and electrolyte imbalance..
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Tylenol Chemical Effect:
Blocks pain impulses, probably
by inhibiting prostaglandin or
pain receptor sensitizers. May
relieve fever by acting in
hypothalamic heat-regulating
center.
Therapeutic Effect:
Relieves pain and reduces fever.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug.
Use cautiously in patients with
a history of chronic alcohol
abuse because hepatotoxicity
may occur after therapeutic
doses.
Hematologic: hemolytic
anemia, leucopenia,
neutopenia,
pancytopenia,
thrombocytopenia.
Hepatic: liver damage
(with toxic doses),
jaundice.
Metabolic: hypoglycemia
Patients temperature is already within normal
range and is thermoregulated
Slight grade 1 pitting edema noted from patient.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Tramadol
hydrochloride
Pharmacologic Class: opioid
agonist
Therapeutic Class: analgesic
Pregnancy Risk Category: C
To treat moderate to moderately
severe pain
25mg IVTT every 8
hours
Reassess level of pain at least 30 minutes after
administration.
Monitor patient closely for evidence of serotonin
syndrome, such as agitation, hallucinations, coma,
tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia,
hyperreflexia, incoordination, nausea, vomiting, or
diarrhea.
Monitor CV and respiratory status. Withhold dose
and notify prescriber if respirations decrease or
rate is below 12 breaths/minute.
Monitor bowel and bladder function. Anticipate
need for laxative.
For better analgesic effect, give drugs before onset
of intense pain.
Monitor patients at risk for seizures. Drug may
reduce seizure threshold.
In the case of an overdose, naloxone may also
increase risk of seizures.
Withdrawal symptoms may occur if drug is
stopped abruptly. Reduce dosage gradually.
For ambulatory patients: Be careful in rising and
walking. Avoid driving and other potentially
hazardous activities that require mental alertness
until drugs CNS effects are known.
Avoid giving tramadol to patients with acute
abdominal conditions because it may mask
evidence and disrupt assessment of the abdomen.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Siverol Unknown. A centrally acting
synthetic analgesic
compound not chemically
related to opioids. Thought
to bind to opioid receptors
and inhibit reuptake of
norepinephrine and
serotonin.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug or other opioids,
in breastfeeding women, and in those
with acute intoxication from alcohol,
hypnotics, centrally acting analgesics,
opioids, or psychotropic drugs. Serious
hypersensitivity reactions can occur,
usually after the first dose. Patients
with history of anaphylactic reaction to
codeine and other opioids may be at
increased risk.
Use cautiously in patients at risk for
seizures or respiratory depression; in
patients with increased intracranial
pressure or head injury, acute
abdominal conditions, or renal or
hepatic impairment; or in patients with
physical dependence on opioids.
CNS: dizziness, vertigo,
headache, somnolence,
CNS stimulation,
seizures, malaise
CV: vasodilation, chest
pain, orthostatic
hypotension
EENT: visual
disturbances, blurred
vision, nasal or sinus
congestion, sore throat,
vision changes
ENDO: hot flashes
GI: nausea, vomiting,
constipation,
dyspepsia, dry mouth,
diarrhea, abdominal
pain, anorexia,
flatulence, indigestion,
GU: urine retention,
urinary frequency,
menopausal
symptoms, proteinuria
Musculoskeletal:
hypertonia, arthralgia;
back, limb, or neck pain
Respiratory:
Patients blood pressure became normal.
Patients vital signs were within normal rage.
Patient has no hypotension and maintains
adequate tissue perfusion.
Patient sustains no injury from underlying
disease.
respiratory depression
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Enoxaparin
sodium
Pharmacologic Class: low
molecular weight heparin
derivative
Therapeutic Class:
anticoagulant
Pregnancy Risk Category: B
To prevent deep vein thrombosis
(DVT) following hip replacement
surgery or knee replacement
surgery
To prevent DVT following
abdominal surgery
To prevent ischemic complications
of unstable angina and non-ST
segment elevation MI (NSTEMI)
Acute DVT with or without
pulmonary embolism
Immobile patients during an acute
illness
4000 international units
subcutaneous every 24
hours
Obtain coagulation parameters before therapy.
Monitor effectiveness by evaluating patient for
evidence of pulmonary embolism or DVT.
Monitor platelet count regularly as well as
other coagulation studies.
Dont expel air from prefilled syringes.
Never give IM. Dont massage site after
subcutaneous injection and rotate sites.
Inform patient to tell prescriber about drug use
when planning to undergo any surgery.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Clexane Chemical Effect:
Accelerates formation of
antithrombin IIIB-thrombin
complex and deactivates
thrombin, preventing
conversion of fibrinogen to
fibrin.
Therapeutic Effect:
Prevents pulmonary
embolism and DVT.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug or any of its
components, to heparin, or pork
products; in those with active major
bleeding or thrombocytopenia; and
in those who have antiplatelet
antibodies in presence of drug.
Not recommended for
thromboprophylaxis in patients
with prosthetic heart valves.
Use cautiously in patients with
postoperative indwelling catheters
and in patients who have epidural
or spinal anesthesia. Epidural and
spinal hematomas may result in
long term or permanent paralysis.
Also use cautiously in patients with
a history of heparin-induced
thrombocytopenia; in patients with
conditions that increase their risk
for hemorrhage, and in patients
with congenital bleeding disorders,
ulcer disease, angiodysplastic GI
disease, hemorrhagic stroke, or
recent spinal, eye, or brain injury.
CNS: confusion, fever,
pain
CV: edema, pulmonary
edema
GI: nausea
Hematologic: anemia,
bleeding complications,
hemorrhage,
thrombocytopenia
Skin: ecchymosis,
hematoma, irritation,
pain, or erythema at
injection site, rash,
urticaria
Other: angioedema,
anaphylaxis
Patient doesnt develop pulomonary embolism
or deep vein thrombosis.
Patient has no bleeding complications during
therapy.
Patient and family state understanding of drug
therapy.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Furosemide Electrolytic and water
balance agent; loop diuretic
Treatment of edema associated
with CHF, cirrhosis of liver, and
kidney disease, including
nephrotic syndrome. May be
used for management of
hypertension, alone or in
combination with other
antihypertensive agents, and for
treatment of hypercalcemia. Has
been used concomitantly with
mannitol for treatment of severe
cerebral edema, particularly in
meningitis.
20mg IV now
Closely monitor BP and vital signs
Observe older adults closely during period of
brisk diuresis. Sudden alteration in fluid and
electrolyte balance may precipitate significant
adverse reactions.
Lab tests: Obtain frequent blood count, serum
and urine electrolytes, CO2, BUN, blood sugar,
and uric acid values during first few months of
therapy and periodically thereafter.
Monitor for S&S of hypokalemia .
Monitor I&O ratio and pattern. Weigh patient
daily under standard conditions.
Monitor urine and blood glucose & HbA1C
closely in diabetics and patients with
decompensated hepatic cirrhosis. Drug may
cause hyperglycemia.
Consult physician regarding allowable salt and
fluid intake.
Advise patient to take drug with food and to
take drug in the morning to prevent need to
urinate at night.
Advise patient to immediately report ringing in
the ears, severe abdominal pain, sore throat and
fever; these symptoms may indicate toxicity.
Report muscle cramps or weakness to physician.
Make position changes slowly because high
doses of antihypertensive drugs taken
concurrently may produce episodes of dizziness
or imbalance.
Avoid replacing fluid losses with large amounts
of water.
Avoid prolonged exposure to direct sun
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Lasix Rapid-acting potent
sulfonamide loop
diuretic and
antihypertensive.
Exact mode of action not
clearly defined;
decreases renal vascular
resistance and may
increase renal blood
flow.
Inhibits reabsorption of
sodium and chloride
primarily in loop of
Henle and also in
History of hypersensitivity to
furosemide or sulfonamides;
increasing oliguria, anuria, fluid and
electrolyte depletion states; hepatic
coma; pregnancy (category C),
lactation.
CV: Postural hypotension,
dizziness with excessive
diuresis, acute hypotensive
episodes, circulatory
collapse.
Metabolic: Hypovolemia,
dehydration, hyponatremia,
hypokalemia,
hypochloremia metabolic
alkalosis, hypomagnesemia,
hypocalcemia (tetany),
hyperglycemia, glycosuria,
elevated BUN,
hyperuricemia;
GI:Nausea, vomiting, oral
and gastric burning,
anorexia, diarrhea,
Patient is free from edema
Adequate urine output noted from patient
proximal and distal renal
tubules; an
antihypertensive that
decreases edema and
intravascular volume.
Reportedly less ototoxic
than ethacrynic acid.
constipation, abdominal
cramping, acute
pancreatitis, jaundice.
Urogenital:Allergic
interstitial nephritis,
irreversible renal failure
Hematologic:Anemia,
leukopenia,
thrombocytopenic
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Atorvastatin Pharmacologic Class: HMG-
CoA reductase Inhibitor
Therapeutic Class: antilipemic
Pregnancy Risk Category: X
Adjunct to diet in treatment
of elevated total cholesterol,
serum triglycerides, and LDL
cholesterol in patients with
primary hypercholesterolemia
(types IIa and IIb) and mixed
dyslipidemia, and homozygous
familial hypercholesterolemia
To reduce risk of MI, stroke,
angina and revascularization
procedures in patients with no
evidence of CAD but with
multiple risk factor
80 mg tab 1 tab daily
Monitor patients lipid and liver function levels at
baseline and periodically thereafter.
Monitor patient for signs of rhabdomyolysis,
especially if taking more than one class of lipid
lowering drugs. Check CK level when patient
complains of muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness.
Use drug only after diet and other nondrug treatments
prove ineffective. Patient should follow a low-
cholesterol diet before and during therapy.
Drug can be given anyime during the day with or
without food. Warn patient to avoid alcohol.
Teach patient about proper diet, weight control, and
exercises, and explain their role in controlling
elevated lipid levels.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Lipitor Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase,
the enzyme that catalyzes the
first step in the cholesterol
synthesis pathway, resulting in
a decrease in serum
cholesterol, serum LDLs
(associated with increased risk
of CAD), and increases serum
HDLs (associated with
decreased risk of CAD);
increases hepatic LDL
recapture sites, enhances
reuptake and catabolism
of LDL; lowers triglyceride
levels.
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug and in
those with active liver disease
or conditions linked with
unexplained persistent
increases in transaminase
levels. Also contraindicated in
patients with serious, acute
conditions that suggest
myopathy and in those at risk
for renal failure.
In pregnant or breastfeeding
women and in women who may
become pregnant, drug is
contraindicated.
CNS: asthenia, fever,
headache, malaise
CV: chest pain
EENT: pharyngitis,
sinusitis
GI: abdominal pain,
constipation, diarrhea,
dyspepsia, flatulence
Musculoskeletal:
arthralgia, back pain,
myalgia, rhabdomyolysis
Skin: rash, erythema
multiforme, Stevens-
Johnson syndrome, toxic
epidermal necrolysis
Other: anaphylaxis,
angioedema
Slight decrease of LDL cholesterol level on
patients laboratory results and still for
continuous monitoring.
Patient and family state understanding of drug
therapy.
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Amiodarone Pharmacologic Class:
benzofuran derivative
Therapeutic Class: Ventricular
antiarrhythmic
Pregnancy Risk Category: D
Recurrent ventricular
fibrillation, unstable
ventricular tachycardia, atrial
fibrillation, angina, and
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Supraventricular arrhythmia
200 mg tab TID Assess CV status before therapy and regularly
thereafter to determine effectiveness.
Review pulmonary, liver, and thyroid function test
before therapy and regularly thereafter.
Drug may pose life-threatening risks for patients
already at risk for sudden death. It may cause fatal
pulmonary and hepatic toxicity and should be
used only with life-threatening, recurrent
ventricular arrhythmias unresponsive to other
antiarrhythmics or when other drugs cant be
tolerated.
Give with meals to decrease GI intolerance.
May use methylcellulose ophthalmic solution to
minimize corneal microdeposits.
Use sun screen to prevent photosensitivity
reaction.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Cordarone Amiodarone prolongs the
duration of the action
potential of all cardiac
fibers. The refractory
period is prolonged in all
cardiac tissues.
Amiodarone increases the
cardiac refractory period
without influencing
resting membrane
potential. These
electrophysiologic effects
are reflected in a
decreased sinus rate of 15
to 20%, increased PR and
QT intervals of about
10%, the development of
U-waves, and changes in
T-wave contour. These
changes should not
require discontinuation of
Amiodarone as they are
evidence of its
pharmacological action,
although Amiodarone can
cause marked sinus
bradycardia or sinus
Contraindicated in patients
hypersensitive to drug and in
those with severe sinus node
disease, bradycardia, 2
nd
or
3
rd
degree Av block(unless
pacemaker is present), or
bradycardia induced syncope.
Use cautiously in patients
receiving other
antiarrhythmics and in
patients with pulmonary or
thyroid disease because use
may result in fatal toxicity.
Some IV Cordarone
preparations contain benzyl
alcohol, which may cause
gasping syndrome in
neonates younger than 1
month. Monitor for symptoms
of sudden onset of gasping
respiration, hypotension,
bradycardia, and CV collapse.
In pregnant women, use only
when benefits outweigh the
risks to patient and fetus. In
breast-feeding women, drug
is contraindicated. In
CNS: abnormal gait, ataxia,
dizziness, extrapyramidal
symptoms, fatigue,
headache, malaise,
paresthesia, peipheral
neuropathy
CV: arrhythmia,
bradycardia, heart block,
heart failure, hypotension,
sinus arrest
EENT: corneal
microdeposits, vision
disturbances
GI: anorexia, constipation,
nausea, vomiting
Hepatic: hepatic
dysfunction
Metabolic:
hyperthyroidism,
hypothyroidism
Musculoskeletal: muscle
weakness
Respiratory: SEVERE
PULMOBNARY TOXICITY
(alveolitis, pneumonitis)
Skin: blue-gray skin,
photosensitivity
Rare episodes of cardiac arrythmia noted from
patient
Vital signs are within normal range
arrest and heart block. On
rare occasions, QT
prolongation has been
associated with
worsening of arrhythmia
children, safety hasnt been
established. IV Cordarone
leaches plasticizers from
administration tubing, which
can adversely affect male
reproductive tract
development in a fetus, infant,
or toddler.
Other: gynecomastia
Chong Hua Hospital
Don Mariano Cui St. J. Llorente St., Cebu City, Philippines 6000
Education, Training, & Research Tel. # 255-8000 loc. 7465
Drug Study Format
Generic Name Classification Indication Dosage Nursing Responsibilities
Dobutamine
hydrochloride
Pharmacologic Class:
Beta1, agonist, adrenergic
Therapeutic Class:
Inotropic
Pregnancy Risk Category: C
Short term treatment of
cardiac decompensation
caused by depressed
contractility such as during
refractory heart failure;
adjunct in cardiac surgery.
4ml/hr
.
As needed, correct hypovolemia before starting
therapy by giving volume expanders as
prescribed.
Monitor ECG and blood pressure continuously
during administration.
Monitor fluid intake and output.
Assess electrolyte levels, Stay especially alert for
hypokalemia.
Digoxin may be given before giving this drug
because drug increases AV node conduction,
patients with atrial fibrillation may develop rapid
ventricular rate.
Instruct pt to report angina pain, headache, leg
cramps and shortness of breath.
Trade Name Mechanism of Action Contraindication
Adverse Effects Actual Patient Response
Dobutrex Stimulates beta1 adrenergic
receptors of heart, causing a
positive inotropic effect that
increases myocardial
contractility and stroke
volume. Also reduces
peripheral vascular
resistance, decreases
ventricular filling pressure,
and promotes
atrioventricular conduction.
Hypersensitivity to drug,
Idiopathic hypertrophic
subaortic stenosis.
CNS: headache,
CV: Hypertension,
hypotension, tachycardia,
premature ventricular
contractions
GI: Nausea, vomiting
Metabolic: Hypokalemia
Respiratory: asthma
attacks
Patient regains adequate cardiac output exhibited
by stable vital signs, normal urine output, and
clear mental condition.
Patient and family state understanding of drug
therapy.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Elimination - Nursing Test QuestionsDocument68 paginiElimination - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1100% (1)
- Specimen 1 ValuationDocument17 paginiSpecimen 1 ValuationLight BearerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesDe la EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Project Cash FlowsDocument2 paginiProject Cash FlowsAdarsh Chhajed20% (5)
- Analytical Methods To Measure The Constants of Fats and OilsDocument5 paginiAnalytical Methods To Measure The Constants of Fats and OilsPenicillium Notatum67% (3)
- CHH Drug Study Week 3Document21 paginiCHH Drug Study Week 3maryxtine24Încă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicDocument7 paginiGeneric Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- San Beda College College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument10 paginiSan Beda College College of Nursing Drug StudyDeca TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrugsDocument11 paginiDrugsElisa Libo-onÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismDocument9 paginiDrug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismRene John FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument9 paginiDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 paginiComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument9 paginiDrug Studykcbabee0333% (3)
- Hepatic FailureDocument37 paginiHepatic FailureWinston Dela FuenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 paginiDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument9 paginiDrug StudyOdarp PradzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudiesDocument16 paginiDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 paginiDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument12 paginiDrug StudyFelecidario TaerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument6 paginiDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study 68-75Document8 paginiDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument6 paginiDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pagini5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omeprazole medication guide: Generic name, uses, side effectsDocument4 paginiOmeprazole medication guide: Generic name, uses, side effectsKathleenDawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. ObjectiveDocument4 paginiSubjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objectivechaoz09Încă nu există evaluări
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 paginiName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 paginiGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection with CefuroximeDocument5 paginiTreatment of Urinary Tract Infection with CefuroximeOamaga NajlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paracetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyDocument9 paginiParacetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemotherapy DrugsDocument43 paginiChemotherapy Drugsbrigette_lagat100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument6 paginiDrug StudyRyan BancoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument6 paginiDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument14 paginiDrug StudyKatrina EstoconingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sim 4Document4 paginiSim 4Ding EmilyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP DrugDocument13 paginiNCP DrugMhar CamposanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument10 paginiRani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyIv'z TandocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ditropan Drug CardDocument2 paginiDitropan Drug CardBenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cavite State University drug study on mefenamic acidDocument3 paginiCavite State University drug study on mefenamic acidAngelica Cassandra VillenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument5 paginiDrug StudyKC IgnacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- OB Drug StudyDocument19 paginiOB Drug StudyKismet Summons100% (8)
- Drug Study For Mefenamic Acid, Tramadol and CefuroximeDocument7 paginiDrug Study For Mefenamic Acid, Tramadol and CefuroximeChristian Karl B. LlanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument11 paginiDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study FinalDocument5 paginiDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefDocument10 paginiVentolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefmidskiescreamzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 paginiCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 paginăCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUG and IVF StudyDocument4 paginiDRUG and IVF StudyJohanna Camelle Insong MonteronÎncă nu există evaluări
- VIII. Drug StudyDocument11 paginiVIII. Drug StudyCharlayne AnneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventDocument6 paginiAmlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventErickson Caisido GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibDocument4 paginiTramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibEric de JulianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paracetamol Antipyretic and Analgesic GuideDocument7 paginiParacetamol Antipyretic and Analgesic GuideAnne Monique Moran OngjocoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mefenamic Acid: CefuroximeDocument9 paginiMefenamic Acid: CefuroximeGregory LitangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug analysis guide for trimetazidine and phenytoinDocument9 paginiDrug analysis guide for trimetazidine and phenytoinJoannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- 1 DrugsDocument2 pagini1 DrugsPatricia Lucero100% (2)
- 8copd DrugtabncpDocument18 pagini8copd DrugtabncpMaristelaMolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beta Karoten: (BAY Ta KARE Oh Teen)Document9 paginiBeta Karoten: (BAY Ta KARE Oh Teen)Nisa'ul KhoiriyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relief of gas and bloatingDocument6 paginiRelief of gas and bloatingMichael John Gambong SalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral meds: Drug dosages, mechanisms, effectsDocument15 paginiOral meds: Drug dosages, mechanisms, effectsitsmechachaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 paginiCVA Drug StudyKarel LuÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUG STUDY AND SOAPIE SUBMITTEDDocument17 paginiDRUG STUDY AND SOAPIE SUBMITTEDYasi EcheniqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top Trials in Gastroenterology & HepatologyDe la EverandTop Trials in Gastroenterology & HepatologyEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (7)
- Gas Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDocument7 paginiGas Exchange in Plants and AnimalsMarvin MelisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Florence Nightingale: The Lady with the LampDocument18 paginiFlorence Nightingale: The Lady with the LampsrinivasanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating Systems: Chapter 3: DeadlocksDocument46 paginiOperating Systems: Chapter 3: DeadlocksManoel Katlib100% (1)
- Matlab For SolidworksDocument18 paginiMatlab For SolidworksAle' AmoudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unchained MelodeeDocument93 paginiUnchained MelodeeRafael Cornholio RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPECIFIC GRAVITY - DENSITY OF HYDRAULIC CEMENT (IS - 4031-Part 11-1988)Document6 paginiSPECIFIC GRAVITY - DENSITY OF HYDRAULIC CEMENT (IS - 4031-Part 11-1988)Pritha DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- JJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 6Document30 paginiJJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 6Adib AzharÎncă nu există evaluări
- BASIC IMMUNOLOGY TERMSDocument2 paginiBASIC IMMUNOLOGY TERMSAnnicoldjohn LariozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation & Testing of Fire Protection SystemsDocument7 paginiInstallation & Testing of Fire Protection Systemssunny_84tÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutics | Water Solubility and Dissolution RateDocument11 paginiPharmaceutics | Water Solubility and Dissolution RateAnnisa AgustinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chefs at HomeDocument4 paginiChefs at Homezbdv2kyzv7Încă nu există evaluări
- Nsf-Ansi 55 PDFDocument56 paginiNsf-Ansi 55 PDFJawwad AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- P198 Software and Atlases For Evaluating Thermal Bridges 0Document10 paginiP198 Software and Atlases For Evaluating Thermal Bridges 0cm08909Încă nu există evaluări
- Instrukcja Pellets Fuzzy Logic - ENGDocument53 paginiInstrukcja Pellets Fuzzy Logic - ENGxilef84Încă nu există evaluări
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Triclosan Based On Diazotization Reaction: Response Surface Optimization Using Box - Behnken DesignDocument1 paginăSpectrophotometric Determination of Triclosan Based On Diazotization Reaction: Response Surface Optimization Using Box - Behnken DesignFitra NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Painting, DrawingDocument22 paginiPainting, DrawingMithilesh_Kuma_7083Încă nu există evaluări
- Name: Amir Bin Rossaifuddin Id: 2016307153 Group: Emd2M2ADocument2 paginiName: Amir Bin Rossaifuddin Id: 2016307153 Group: Emd2M2AamirossaifuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINS 2624 Quiz 2 Attempt 2 PDFDocument3 paginiFINS 2624 Quiz 2 Attempt 2 PDFsagarox7Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 14 The Communist Manifesto As International Relations TheoryDocument12 paginiChapter 14 The Communist Manifesto As International Relations TheoryLaurindo Paulo Ribeiro TchinhamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2023-05-11 St. Mary's County TimesDocument40 pagini2023-05-11 St. Mary's County TimesSouthern Maryland OnlineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aac Block Adhesive: Product DescriptionDocument2 paginiAac Block Adhesive: Product DescriptionmaznahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macroeconomics II: Search and Matching: Luiz BrotherhoodDocument18 paginiMacroeconomics II: Search and Matching: Luiz BrotherhoodMartin GutovskieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/13Document20 paginiCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/13Justin OngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Aspects of Food Emulsification and HomogenizationDocument325 paginiEngineering Aspects of Food Emulsification and Homogenizationfurkanturker61Încă nu există evaluări
- Chinkon Kishin - Origens Shintoístas Do Okiyome e Do Espiritismo Na MahikariDocument2 paginiChinkon Kishin - Origens Shintoístas Do Okiyome e Do Espiritismo Na MahikariGauthier Alex Freitas de Abreu0% (1)
- Mast Bending Stress Calculation: Antenna 1Document6 paginiMast Bending Stress Calculation: Antenna 1Vinay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări