Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Phases: Nursing Care
Încărcat de
Kathryn LauditTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Phases: Nursing Care
Încărcat de
Kathryn LauditDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Phases[edit]
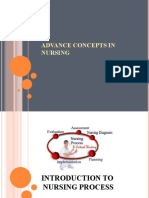
The nursing process is goal-oriented method of caring that provides a framework to nursing care. It
involves six major steps:
A
Assess (what data is collected?)
D
Diagnose (what is the problem?)
O
Outcome Identification - (Was originally a part of the Planning phase, but has recently been
added as a new step in the complete process).
P
Plan (how to manage the problem)
I
Implement (putting plan into action)
R
Rationale (Scientific reason of the implementations)
E
Evaluate (did the plan work?)
According to some theorists, this six-steps description of the nursing
process is outdated and misrepresents nursing as linear and atomic.
[7]
Assessing phase[edit]
Main article: Nursing assessment
The nurse completes an holistic nursing assessment of the needs of
the individual/family/community, regardless of the reason for the
encounter. The nurse collects subjective data and objective data using
a nursing framework, such as MarjoryGordon's functional health
patterns.
Models for data collection[edit]
Nursing assessments provide the starting point for determining nursing
diagnoses. It is vital that a recognized nursing assessment framework
is used in practice to identify the patient's* problems, risks and
outcomes for enhancing health. The use of an evidence-based nursing
framework such as Gordon's Functional Health Pattern Assessment
should guide assessments that support nurses in determination of
NANDA-I nursing diagnoses. For accurate determination of nursing
diagnoses, a useful, evidence-based assessment framework is best
practice.
Methods[edit]
Client Interview
Physical Examination
Obtaining a health history (including dietary data)
Family history/report
Diagnostic Data
Observation
Diagnosing phase[edit]
Main article: Nursing diagnosis
Nursing diagnoses represent the nurse's clinical judgment about actual
or potential health problems/life process occurring with the individual,
family, group or community. The accuracy of the nursing diagnosis is
validated when a nurse is able to clearly identify and link to the defining
characteristics, related factors and/or risk factors found within the
patients assessment. Multiple nursing diagnoses may be made for one
client.
Planning phase[edit]
Main article: Nursing care plan
In agreement with the client, the nurse addresses each of the problems
identified in the diagnosing phase. When there are multiple nursing
diagnoses to be addressed, the nurse prioritizes which diagnoses will
receive the most attention first according to their severity and potential
for causing more serious harm. For each problem a measurable
goal/outcome is set. For each goal/outcome, the nurse selects nursing
interventions that will help achieve the goal/outcome. A common
method of formulating the expected outcomes is to use the evidence-
based Nursing Outcomes Classification to allow for the use of
standardized language which improves consistency of terminology,
definition and outcome measures. The interventions used in
the Nursing Interventions Classification again allow for the use of
standardized language which improves consistency of terminology,
definition and ability to identify nursing activities, which can also be
linked to nursing workload and staffing indices. The result of this phase
is a nursing care plan.
Implementing phase[edit]
The nurse implements the nursing care plan, performing the
determined interventions that were selected to help meet the
goals/outcomes that were established. Delegated tasks and the
monitoring of them is included here as well.
Evaluating phase[edit]
The nurse evaluates the progress toward the goals/outcomes identified
in the previous phases. If progress towards the goal is slow, or if
regression has occurred, the nurse must change the plan of care
accordingly. Conversely, if the goal has been achieved then the care
can cease. New problems may be identified at this stage, and thus the
process will start all over again.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nursing ProcessDocument20 paginiNursing Processwideyatma100% (2)
- Nrs 110 Lecture 1 Care Plan WorkshopDocument45 paginiNrs 110 Lecture 1 Care Plan Workshopalphabennydelta4468100% (2)
- Nursing ProcessDocument5 paginiNursing ProcessStacy CamposÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursingprocess Assessing 111105015609 Phpapp01Document71 paginiNursingprocess Assessing 111105015609 Phpapp01ALmik HussinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 001 - Nida Najiyah - NURSING PROCESS AS A SCIENTIFIC METHOD IN PROBLEM SOLVING - Id.enDocument7 pagini001 - Nida Najiyah - NURSING PROCESS AS A SCIENTIFIC METHOD IN PROBLEM SOLVING - Id.enChristine HevinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessing LEARNING OUTCOMES After Completing This Chapter, You WillDocument27 paginiAssessing LEARNING OUTCOMES After Completing This Chapter, You Willtwy113Încă nu există evaluări
- Key Concepts, Chapter 15, Evaluating: Critically About How Best To Evaluate The Patient's Progress Toward Valued HealthDocument4 paginiKey Concepts, Chapter 15, Evaluating: Critically About How Best To Evaluate The Patient's Progress Toward Valued HealthmsbunnileeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories, Models in ObgDocument83 paginiTheories, Models in ObgSyama Aneesh100% (1)
- FU M1 CU4 LEC Critical Thinking and Assessment Foundation of Quality Nursing CareDocument8 paginiFU M1 CU4 LEC Critical Thinking and Assessment Foundation of Quality Nursing CareAthena Gonzales100% (1)
- Module 1 REVIEW OF THE NURSING PROCESS 1Document3 paginiModule 1 REVIEW OF THE NURSING PROCESS 1hamisi100% (2)
- Nursing ProcessDocument15 paginiNursing ProcessCreole Kaye RubiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HA - Nursing Process April2016Document45 paginiHA - Nursing Process April2016M Ronela Paglinawan MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing ProcessDocument4 paginiNursing ProcessAngelrica TumbadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defining The Nursing ProcessDocument6 paginiDefining The Nursing ProcessBrandy RaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- FUNA RLE AssessmentDocument15 paginiFUNA RLE AssessmentVinzii DrtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Interventions, Implementation and EvaluationDocument9 paginiNursing Interventions, Implementation and EvaluationSintya KeytimuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proses KeperawatanDocument13 paginiProses Keperawatangeape ayuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument12 paginiNursing Care PlanGladys Tamayo100% (1)
- Unit 1 (C) Nursing ProcessDocument43 paginiUnit 1 (C) Nursing ProcessSumaira NoreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSING PROCESS LectureDocument56 paginiNURSING PROCESS LectureSamantha SunglaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundies II Exam 1 Blue PrintDocument24 paginiFundies II Exam 1 Blue PrintStephanieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Nursing ProcessDocument64 paginiUnit 2 Nursing ProcessAshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 Nursing ProcessDocument34 paginiModule 5 Nursing Processscrewdriver100% (5)
- Planning: By: Ayugi Winnyfred Patience. Bsc. MidwiferyDocument15 paginiPlanning: By: Ayugi Winnyfred Patience. Bsc. MidwiferyAYO NELSONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steps in Making A Family Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiSteps in Making A Family Nursing Care PlanMary LouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asessment of Marilynn e DoengesDocument26 paginiAsessment of Marilynn e DoengesMuhammad PanduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Assurance: Components of Quality Assurance - Tools in Quality AssuranceDocument25 paginiQuality Assurance: Components of Quality Assurance - Tools in Quality AssuranceBlaiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing ProcessDocument26 paginiNursing Processprema100% (3)
- 2nd SEMDocument3 pagini2nd SEMMj Kenneth IlayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing ProcessDocument3 paginiNursing ProcessAlisa MiradiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 5 Steps of The Nursing ProcessDocument1 paginăThe 5 Steps of The Nursing ProcessKathryn LauditÎncă nu există evaluări
- NIC and NOCDocument4 paginiNIC and NOCFernando Oliveira0% (1)
- White CH 1-6Document76 paginiWhite CH 1-6Rozmine MerchantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 - Nursing ProcessDocument10 paginiModule 1 - Nursing ProcessZyrene RiveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety Pi CoverpageDocument3 paginiSafety Pi Coverpageapi-291660325Încă nu există evaluări
- Block One Nursing ProcessDocument2 paginiBlock One Nursing ProcessdavidvpnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Process Unit-4Document27 paginiNursing Process Unit-4Rashid HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steps in Writing A Nursing Care PlanDocument5 paginiSteps in Writing A Nursing Care PlanbrendaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EvaluationDocument22 paginiEvaluationKharisma AprilliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Process OUTPUTDocument5 paginiNursing Process OUTPUTfima_njÎncă nu există evaluări
- Six Phases of The Nursing ProcessDocument4 paginiSix Phases of The Nursing ProcessJan Jamison Zulueta100% (3)
- T2 - The Nursing Process and PharmacologyDocument7 paginiT2 - The Nursing Process and PharmacologyTRISHA MAE BATAUSAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Audit-Definition, History, Purposes, Methods, Characteristics, ProcessDocument3 paginiNursing Audit-Definition, History, Purposes, Methods, Characteristics, ProcessGladys YaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Process and DocumentationDocument52 paginiNursing Process and Documentationgeorgeloto12100% (2)
- Critical Pathway: Clinical Pathways Have Four Main Components (Hill, 1994, Hill 1998)Document5 paginiCritical Pathway: Clinical Pathways Have Four Main Components (Hill, 1994, Hill 1998)pooja singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals in NursingDocument17 paginiFundamentals in Nursingreymar.martinez88Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Process - Planning: Prepared and Presented byDocument23 paginiNursing Process - Planning: Prepared and Presented byAnuchithraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Document 172Document31 paginiDocument 172Reniella HidalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slide 7 - Patient - Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document27 paginiSlide 7 - Patient - Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Gilang Cahyo Kumolo100% (2)
- Health AssessmentDocument3 paginiHealth AssessmentCres Padua QuinzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 7 Concept IntegrationDocument14 paginiModule 7 Concept Integrationmuriel bautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planning LEARNING OUTCOMES After Completing This Chapter, You WillDocument25 paginiPlanning LEARNING OUTCOMES After Completing This Chapter, You Willtwy113Încă nu există evaluări
- The Nursing Process OverviewDocument26 paginiThe Nursing Process OverviewAYO NELSONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qsir Measuring Quality CareDocument4 paginiQsir Measuring Quality CareAli H. MhmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing EvaluationDocument9 paginiNursing Evaluationnayla.vtcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Nursing Care Plan DiagramDocument2 paginiFamily Nursing Care Plan DiagramAlexander DontonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audit As A Quality Control Tool ReportDocument30 paginiAudit As A Quality Control Tool ReportJenno Ray Senal67% (3)
- The Care Process: Assessment, planning, implementation and evaluation in healthcareDe la EverandThe Care Process: Assessment, planning, implementation and evaluation in healthcareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Write-Up - Beck Institute - Worksheet-Packet - 2020-18-23Document6 paginiCase Write-Up - Beck Institute - Worksheet-Packet - 2020-18-23Carmen-Ioana RotaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Depersonalization ReportDocument4 paginiDepersonalization ReportLeslie Vine DelosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- European Psychiatry: A. Castagnini, P. Fusar-PoliDocument10 paginiEuropean Psychiatry: A. Castagnini, P. Fusar-PoliQwerty QwertyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stahl' Essential Psychopharmacology 273Document1 paginăStahl' Essential Psychopharmacology 273Muhammad AzkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 3 - Data Analysis - SRS PDFDocument19 paginiGroup 3 - Data Analysis - SRS PDFzekarias amsaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Poppelreuter Figure Visual PerceptualDocument4 paginiThe Poppelreuter Figure Visual PerceptualIcaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Food Addiction Treatment Background PW FINAL 10-19-14Document90 pagini01 Food Addiction Treatment Background PW FINAL 10-19-14mariaaga100% (4)
- Module 1-Introduction To Clincal ChemistryDocument4 paginiModule 1-Introduction To Clincal ChemistryAllyah Ross DuqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSPE Sample LetterDocument5 paginiMSPE Sample Letterjohn dereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal - Effectiveness of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Patients With Treatment Resistant SchizophreniaDocument22 paginiJournal - Effectiveness of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Patients With Treatment Resistant SchizophreniaAntikka PrasetyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is AutismDocument22 paginiWhat Is AutismDebbie Ann CabreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- TB1 Chapter 15 - Web Quiz 2Document4 paginiTB1 Chapter 15 - Web Quiz 2MonicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Mental Status ExamDocument7 paginiThe Mental Status ExamAnonymous ewPKlLWtfhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case History ReportDocument27 paginiCase History Reportdivya100% (2)
- 2guideline For Mental Health Management in Primary Health Care. December 2020Document146 pagini2guideline For Mental Health Management in Primary Health Care. December 2020Soo PlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DXR Clinician Quick ReferenceDocument2 paginiDXR Clinician Quick Referencebjpalmer100% (3)
- Application of Betty NeumanDocument17 paginiApplication of Betty NeumanAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- Morgellons Dr. WymoreDocument2 paginiMorgellons Dr. WymoreSpace_Hulker100% (2)
- 6t70 ATRADocument6 pagini6t70 ATRAfulltransmission100% (1)
- PH Psy 223 Syllabus SP 17 Complete HC Update 1Document4 paginiPH Psy 223 Syllabus SP 17 Complete HC Update 1Jamal louisÎncă nu există evaluări
- TrammellsoappedsDocument9 paginiTrammellsoappedsapi-284269118100% (1)
- Nur 205 1 Exam 1 Study GuideDocument10 paginiNur 205 1 Exam 1 Study Guidesylphlike5Încă nu există evaluări
- Inbde GuideDocument28 paginiInbde GuideJordan BolivarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self Assessment Toolkit (NABH)Document47 paginiSelf Assessment Toolkit (NABH)poonam@ims100% (6)
- Mental RetardationDocument35 paginiMental RetardationCharles Dean UgaldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penilaian Preceptorship (Mini-Cex, Dops, Longcase, Soca) 2020Document49 paginiPenilaian Preceptorship (Mini-Cex, Dops, Longcase, Soca) 2020Dian tri febrianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fountain 2016Document23 paginiFountain 2016Alfred RodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Fungal Infections - (2015) PDFDocument298 paginiDiagnosis and Treatment of Fungal Infections - (2015) PDFgaedprietlz25100% (1)