Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Basic Mechanical Engineering
Încărcat de
Sadasiva Rao TDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Basic Mechanical Engineering
Încărcat de
Sadasiva Rao TDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lab: BME
(ME-107-F)
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
PreparedBy Ce!"ed By
Mr#$%&'(Par)ar Mr# $%&'( Ba(*da
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATOR+ (ME-107-F)
ME-107F : BASICS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LAB
L T P Sessional 25 Marks
- - 2 Exam 25 Marks
Total 50 Marks
Duration of Exam 3 Hrs.
Notes :
(i) t least !0 ex"eriments are to "erforme# $% stu#ents in t&e semester.
(ii) t least ' ex"eriments s&oul# $e "erforme# from t&e a$o(e list) remainin* t&ree ex"eriments
ma% eit&er $e "erforme# from t&e a$o(e list or #esi*ne# an# set $% t&e +on+erne# institution as
"er t&e s+o"e of t&e s%lla$us.
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
!. To stu#% t&e ,o+&ran an# -a$+o+k . /il+ox $oilers.
2. To stu#% t&e 0orkin* an# fun+tion of mountin*s an# a++essories in $oilers.
3. To stu#% T0o-Stroke . 1our-Stroke Diesel En*ines.
2. To Stu#% T0o-Stroke . 1our-Stroke Petrol En*ines.
5. To stu#% t&e (a"our +om"ression 3efri*eration S%stem an# #etermination of its ,.4.P.
5. To stu#% t&e fun+tionin* of /in#o0 3oom ir ,on#itioner.
'. To stu#% t&e +onstru+tional features an# 0orkin* of Pelton /&eel Tur$ine6 1ran+is Tur$ine
an# 7a"lan Tur$ine.
8. To +al+ulate t&e Me+&ani+al #(anta*e6 9elo+it% 3atio an# Effi+ien+% of Sin*le Start6 Dou$le
Start an# Tri"le Start /orm /&eel.
:. To +al+ulate Me+&ani+al #(anta*e6 9elo+it% 3atio an# Effi+ien+% of Sin*le Pur+&ase an#
Dou$le "ur+&ase 0in+& +ra$ an# "lot *ra"&s.
!0. To fin# t&e "er+enta*e error $et0een o$ser(e# an# +al+ulate# (alues of stresses in t&e
mem$er of a ;i$ ,rane.
!!. To stu#% sim"le s+re0 <a+k an# +om"oun# s+re0 <a+k an# #etermine t&eir effi+ien+%.
!2. To fin# t&e Me+&ani+al #(anta*e6 9elo+it% 3atio an# Effi+ien+% of a Differential /&eel .
xle.
!3. To "erform tensile test6 "lot t&e stress6-strain #ia*ram an# e(aluate t&e tensile "ro"erties of a
*i(en metalli+ s"e+imen.
L',- *. E/per'0e&-,:
1. To study the workng and constructon detas of Cochran and Babcock &
Wcox Boer.
2. To study the workng and functon of mountngs and accessores n boers.
3. To study Two stroke & Four stroke Dese Engnes.
4. To study Two-stroke & Four-stroke Petro Engnes.
5. To study the vapour compresson Refrgeraton System and determnaton of
ts C.O.P.
6. To study the functonng of Wndow Room Ar Condtoner.
7. To study the Constructona features and workng of Peton Whee Turbne,
Francs Turbne and Kapan Turbne.
8. To study the constructon & workng of centrfuga pump.
9. To study the workng of snge pate cutch.
10.To study dfferent type of gears used for power transmsson.
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL
ENGINEERING LABORATOR+
PRACTICAL MAN1AL
FOR
T* ,-%dy -e 2*r"'&) a&d !*&,-r%!-'*& de-a'(, *. C*!ra&
a&d Bab!*!" 3 4'(!*/ B*'(er
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 3 TECHNOLOG+
BAHAL-157056
BHI4ANI(HAR+ANA)
E/per'0e&- N*: 1
AIM:-To study the workng and constructon detas of Cochran and Babcock
& Wcox Boer.
Appara-%,: - Mode of Cochran and Babcock & Wcox Boer.
Te*ry:-
B*'(er: - A steam boer s a cosed vesse n whch steam s produced from
water by combuston of fue.
C(a,,'.'!a-'*& *. B*'(er:
Boers are cassfed on the bass of foowng-
1# A!!*rd'&) -* !*&-e&-, '& -e T%be:
a) F're -%be b*'(er: In fre tube boers, the fue gases pass through the
tube and water surround them.
B)#4a-er -%be b*'(er: In water tube boer, water fows nsde the tubes
and the hot fue gases fow outsde the tubes.
5# A!!*rd'&) -* -e pre,,%re *. ,-ea0:
A)#L*2 pre,,%re b*'(er: A boer whch generates steam at a pressure of
beow 80 bars s caed ow pressure boer. Exampe-Cochran boer,
Lancashre boer etc.
B)#H') pre,,%re b*'(er: A boer whch generates steam at a pressure
hgher then 80 bar s caed hgh pressure boer. Exampe- Babcock and
Wcox boer etc.
7#A!!*rd'&) -* 0e-*d *. !'r!%(a-'*& *. 2a-er:
A)#Na-%ra( C'r!%(a-'*&: In natura crcuaton boer, crcuaton of water
due to gravty or the crcuaton of water takes pace by natura convecton
current produced by the appcaton of heat, exampe-Babcock and Wcox
boer, Lancashre boer etc.
B)#F*r!ed C'r!%(a-'*&: In the forced crcuaton boer, crcuaton of water
by a pump to ncrease the crcuaton. Exampe-Lamont boer etc.
8# A!!*rd'&) -* -e P*,'-'*& *. -e .%r&a!e:
A)#I&-er&a((y .'red b*'(er,: In ths, the furnace s ocated nsde the boer
she. Exampe-Cochran, Locomotve and Lancashre boers.
B)#E/-er&a((y .'red b*'(er,: In ths, the furnace s ocated outsde the
boer she. Exampe-Babcock and Wcox boer etc.
9# A!!*rd'&) -* -e a/', *. ,e((:
A)#:er-'!a( b*'(er,: If the axs of the she of boer s vertca so the boer
s caed as vertca boer.
B)#H*r';*&-a( b*'(er,: If the axs of the she of boer s horzonta so the
boer s caed as Horzonta boers.
C)#I&!('&ed b*'(er,: If the axs of the she of boer s Incned so the boer
s caed as Incned boer.
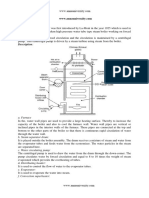
COCHRAN BOILER:
Cochran boer s a vertca, muttubuar fre tube,
nternay fred, natura crcuaton boer.
C*&,-r%!-'*&:
Fgure shows a Cochran boer. It conssts of a vertca
cyndrca she havng a hemspherca top and furnace s aso hemspherca
n shape. The fre grate s arranged n the furnace and the ash pt s provded
beow the grate. A fre door s attached on the fre box. Ad|acent to the fre
box, the boer has a combuston chamber whch s ned wth fre brcks.
Smoke or fre tubes are provded wth combuston chamber. These tubes are
equa n ength and arranged n a group wth wde space n between them.
The ends of these smoke tubes are ftted n the smoke box. The chmney s
provded at the top of the smoke box for dscharge of the gases to the
atmosphere. The furnace s surrounded by water on a sdes except at the
openng for the fre door and the combuston chamber. The smoke tubes are
aso competey surrounded by water.
Dfferent boer mountngs and accessores are ocated at ther proper pace.
4*r"'&):
The hot gas produced from the burnng of the fue on the grate
rses up through the fue ppe and reaches the combuston chamber. The fue
gases from the combuston pass through the fre tubes and the smoke box
and fnay are dscharged through the chmney. The fue gases durng ther
trave from fre box to the chmney gves heat to the surroundng water to
generate steam.
$pe!'.'!a-'*& *. C*!ra& B*'(er:
Dameter of the drum 0.9m to 2.75m
Steam pressure 6.5bar up to 15bar
Heatng surface 120m
2
Maxmum evaporatve capacty 4000Kg/hr of steam
Heght of the she 5.79m
No of tubes 165
Externa dameter of fue tube 62.5mm
Effcency 70to 75%
BABCOC< AND 4ILCO= BOILER:
Babcock and Wcox boer s a
horzonta she, muttubuar, water tube, externay fred, natura crcuaton
boer.
C*&,-r%!-'*&: Fgure shows the detas of a Babcock and Wcox water tube
boer. It conssts of a drum mounted at the top and connected by upper
header and down take header. A arge number of water tubes connect the
uptake and down take headers. The water tubes are ncned at an ange of 5
to 15 degrees to promote water crcuaton. The heatng surface of the unt s
the outer surface of the tubes and haf of the cyndrca surface of the water
drum whch s exposed to fue gases.
Beow the uptake header the furnace of the boer s arranged. The coa s fed
to the chan grate stoker through the fre door. There s a brdge wa
defector whch defects the combuston gases upwards. Baffes are arranged
across the water tubes to act as defectors for the fue gases and to provde
them wth gas passes. Here, two baffes are arranged whch provde three
passes of the fue gases. A chmney s provded for the ext of the gases. A
damper s paced at the net of the chmney to reguate the draught. There
are superheatng tubes for producng superheated steam. Connectons are
provded for other mountng and accessores.
4*r"'&):
The hot combuston gases produced by burnng of fue on the grater rse
upwards and are defected by the brdge wa defector to pass over the front
porton of water tubes and drum. By ths way they compete the frst pass.
Wth the provson of baffes they are defected downwards and compete the
second pass. Agan, wth the provson of baffes they rse upwards and
compete the thrd pass and fnay come out through the chmney. Durng
ther trave they gve heat to water and steam s formed. The fow path of
the combuston gases s shown by the arrows outsde the tubes. The
crcuaton of water n the boer s due to natura crcuaton set-up by
convectve currents (due to gravty). Feed water s supped by a feed check
vave.
The hottest water and stem rse from the tubes to the uptake header and
then through the rser t enters the boer drum. The steam vapours escape
through the upper haf of the drum. The cod water fows from the drum to
the rear header and thus the cyce s competed.
To get superheated steam, the steam accumuated n the steam space s
aowed to enter nto the super heater tubes whch are paced above the
water tubes. The fue gases passng over the fue tubes produce superheated
steam. The steam thus superheated s fnay supped to the user through a
steam stop vave.
$pe!'.'!a-'*& *. Bab!*!" a&d 4'(!*/ B*'(er:
Dameter of the drum 1.22 m to 1.83 m
Length of the drum 6.096 to 9.144 m
Sze of water tubes 7.62 to 10.16 cm
Sze of super heater tube 3.84 to n5.71 cm
Workng pressure 100bar
Steamng capacty 40,000Kg/hr
(Maxmum)
Effcency 60 to 80%
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL
ENGINEERING LABORATOR+
PRACTICAL MAN1AL
FOR
T* ,-%dy -e 2*r"'&) a&d .%&!-'*& *. 0*%&-'&), a&d
a!!e,,*r'e, '& b*'(er,
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 3 TECHNOLOG+
BAHAL-157056
BHI4ANI(HAR+ANA)
E/per'0e&- N*: 5
AIM: - To study the workng and functon of mountngs and accessores n boers.
Appara-%,: - Mode of mountngs and accessores parts n boers.
Te*ry:-
B*'(er: - A steam boer s a cosed vesse n whch steam s produced from water
by combuston of fue.
BOILER MO1NTING$: -
The components whch are ftted on the surface of the boer for compete safety
and contro of steam generaton process are known as boer mountngs. The
foowng are the varous mportant mountngs of a boer.
Pre,,%re Ga%)e- It s usuay mounted on the front top of the boer she. It s
mounted on each boer to show the pressure of the steam. Its da s graduated to
read the pressure n Kograms per sq. centmeter. Bourdons pressure gauge s
commony used as shown n Fg. The essenta eements of ths gauge are the
eptca sprng tube whch s made of bronze and s sod drawn. One end of ths
tube s attached by nes to a toothed quadrant and the other end s connected to a
steam space.
$a.e-y :a(>e,- They are needed to bow off the steam when pressure of the steam
n the boer exceeds the workng pressure. These are paced on the top of the
boer. There are four types of safety vaves:
1. Dead weght safety vave
2. Lever safety vave
3. Sprng oaded safety vave
4. Low water hgh steam safety vave
$pr'&) (*aded ,a.e-y >a(>e- A sprng oaded safety vave s many used for
ocomotves and marne boers. In ths type the vave s oaded by means of a
sprng, nstead of dead weght. A sprng oaded safety vave s as shown n the Fg.
It conssts of two vaves, restng on ther seats. Vave seats are mounted on the
upper ends of two haow vave chests, whch are connected by a brdge. The ower
end of these vaves chests have common passage whch may be connected to the
boer. There s a ever whch has two pvots, one of whch s ntegra wth t and the
other s pn |onted to the ever. Ths pvot rests on the vaves and forces them to
rest on ther respectve seats wth the hep of a heca sprng.
Feed Ce!" :a(>e- A feed check vave s shown n Fg. The functon of the feed
check vave s to aow the suppy of water to the boer at hgh pressure
contnuousy and to prevent the back fow the boer when the pump pressure s ess
than boer pressure or
when pump fas. Feed check vave s ftted to the she sghty beow the norma
water eve of the boer.
F%,'b(e P(%)- It s ftted to the crown pate of the furnace of the fre. The functon
of fusbe pug s to extngush the fre n the fre box, when water eve n the boer
comes down the mt and t prevents from bastng the boer, metng the tube and
over heatng the fre-box crown pate. A fusbe pug s shown n fg. It s ocated n
water space of the boer. The fusbe meta s protected from drect contact of water
by gun meta pug and copper pug. When water eve comes down, the fusbe
meta mets due to hgh heat and copper pug drops down and s hed by gun meta
rbs. Steam comes n contact wth fre and dstngushes t. Thus t prevents boer
from damages.
B(*2 O.. C*!"- The bow off cock as shown n fg., s ftted to the bottom of a
boer drum and conssts of a conca pug ftted to body or casng. The casng s
packed, wth asbestos packng, n groves round the top and bottom of the pug. The
asbestos packng s made tght and pug bears on the packng. Bow off cock has to
prncpe functon are:
1. To empty the boer whenever requred.
2. To dscharge the mud, scae or sedmentaton whch are accumuated
at the bottom of the boer.
4a-er Le>e( I&d'!a-*r- It s an mportant fttng, whch ndcates the water eve
nsde the boer to an observer. It s a safety devce, up on whch the correct
workng of the boer depends. Ths fttng may be seen n froth of the boer, and
are generay two n number. The upper end of the vave opens n steam space
whe the ower end opens n the water. The vave conssts of a strong gass tube.
The end of the tube pass through stuffng boxes formed n the hoow castng. These
castng are fanged and boted to the boer. It has three cocks; two of them contro
the passage between the boer and gass tube, whe the thrd one (the dran cock)
remans cosed.
$-ea0 $-*p :a(>e- A vave paced drecty on a boer and connected to the steam
ppe whch carres steam to the engne or turbne s caed stop vave or |uncton
vave. It s the argest vave on the steam boer. It s, usuay, ftted to the hghest
part of the she by means of a fange as shown n fg.
The prncpa functons of a stop vave are:
1. To contro the fow of steam from the boer to the man steam ppe.
2. To shut off the steam competey when requred.
The body of the stop vave s made of cast ron or cast stee. The vave seat and the
nut through whch the vave spnde works, are made of brass or gun meta.
BOILER ACCE$$ORIE$:
The appances nstaed to ncrease the effcency of the boer are known as the
boer accessores. The commony used accessores are:
E!*&*0',er- Economser s a one type of heat exchange whch exchanges the
some parts of the waste heat of fue gas to the feed water. It s paced between the
ext of the furnace and entry nto the chmney. Generay economser s paced after
the feed pump because n economser water may transfer nto vapour partay,
whch creates a prmng probem n feed pump water nto the boer drum. If
economser s used before feed pump t mts the temperature rse of water. As
economser s shown n fg.
It conssts of vertca cast ron tubes attached wth scraper. The functon of scraper
s to remove the root deposted on the tube, mechancay.
$-ea0 I&?e!-*r- An n|ector s a devce whch s used to ft and force water nto a
boer .e. operatng at hgh pressure. It conssts of a group of nozzes, so arranged
that steam expandng n these nozzes mparts ts knetc energy to a mass of water.
There are many advantages of usng n|ector such as they occupy mnmum space,
have ow nta costs and mantenance cost. Though the steam requred to operate
the n|ector s much more than that n the feed pump for an equvaent duty; the
n|ector has the advantage that practcay the whoe of the heat of the steam s
returned back to the boer.
$%per Hea-er- An eement of steam generatng unt n whch the steam s super
heated, s known s super heater. A super heater s used to ncrease the
temperature of saturated steam at constant pressure. It s usuay paced n the
path of hot fue gases and heat of the fue gases s frst used to superheat the
steam as shown n fgure. The steam enters n the down-steam tube and eaves at
the front header. The overheatng of super heater tube s prevented by the use of a
baanced damper whch contros the fue gas. Steam consumpton of turbne s
reduced by about 1% for each 5.5C of superheat.
Feed P%0p- The functon of the feed pump s to pump the feed water to the boer.
The pumps may be rotary or recprocatng. The rotary pump s generay of hgh
speed centrfuga type. They are drven by sma steam turbne or by eectrc motor
and are used when arge quantty of water s to be supped to boer. The
recprocatng pumps may be snge or doube actng. The most commony used form
of ndependent recprocatng feed pump s that n whch the steam cynder s
drecty connected to the rod or to the pston of the water cynder.
A'r Pre-ea-er- The functon of ar pre-heater s to ncrease the temperature of ar
before t enters the furnace. It s nstaed between the economser and the
chmney. The ar requred for the purpose of combuston s drawn through the ar
pre-heater and ts temperature s rased when passed through ducts. The preheated
ar gves hgher furnace temperature whch resuts n more heat transfer to the
water and reduces the fue consumpton. There are three types of pre-heaters:
1. Tubuar type 2. Pate type 3. Regeneratve type
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL
ENGINEERING LABORATOR+
PRACTICAL MAN1AL
FOR
T* ,-%dy T2*-,-r*"e 3 F*%r-,-r*"e d'e,e( E&)'&e,
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 3 TECHNOLOG+
BAHAL-157056
BHI4ANI (HAR+ANA)
E/per'0e&- N*:7
AIM: - To study Two stroke & Four stroke Dese Engnes.
APPARAT1$ 1$ED: - Mode of Two-stroke & Four-stroke Dese Engnes.
THEOR+-
C+CLE- When seres of events are repeated n order, t competes one cyce. Cyce
s generay cassfed as Four stroke cyce and Two stroke cyce.
a) F*%r ,-r*"e !y!(e- In Four stroke cyce, four operatons are requred to
compete one cyce. These four operatons are sucton, compresson, power
and exhaust.
b) T2* ,-r*"e !y!(e- In a two stroke cyce, the seres of events of the workng
cyce s competed n two strokes of the pston and one revouton of the
crankshaft. The four operatons .e. sucton, compresson, power and exhaust
are competed durng two strokes of the pston.
ENGINE- A power producng machne s caed an engne.
HEAT ENGINE- An engne whch converts heat energy nto mechanca energy s
caed a heat engne.
Type, *. ea- e&)'&e @
a) E/-er&a( C*0b%,-'*& e&)'&e-The engne n whch the combuston of fue
takes pace outsde the cynder s caed an externa combuston engne.
b) I&-er&a( C*0b%,-'*& e&)'&e- The engne n whch the combuston of fue
takes pace nsde the cynder s caed an nterna combuston engne.
FO1R $TRO<E DIE$EL ENGINE
Four-stroke cyce Dese engne or Compresson gnton engne or constant pressure
cyce engne s meant for heavy duty appcatons, ke heavy motor vehces,
statonary power pants, shps and bg ndustra unts, tran ocomotve , tractor and
bus appcaton. In ths the ar compressed n the engne cynder and fue s n|ects
through n|ector.
4*r"'&) *. -e .*%r ,-r*"e D'e,e( e&)'&e-
a) $%!-'*& $-r*"e-The net vave opens durng ths stroke and ony ar s
sucked nto the engne cynder. The exhaust vave remans cosed. When the
pston reaches Bottom Dead Centre (BDC), the sucton stroke s competed
as shown n Fg. (1) and net vave aso coses.
b) C*0pre,,'*& $-r*"e- The pston moves from Bottom Dead Centre (BDC) to
Top Dead Centre (TDC) poston. Both the vaves reman cosed. The ar
drawn durng sucton stroke s compressed.
c) E/pa&,'*& *r P*2er *r 4*r"'&) $-r*"e- |ust before the pston competes
ts compresson stroke, the dese n|ected gets gnted and the rapd
exposon takes pace. The expanson of hot gases pushes the pston down to
BDC poston. Both the vave remans cosed and the usefu work s obtaned
from the engne.
d) E/a%,- $-r*"e- The pston moves from BDC to TDC, the exhaust vave
opens and the net vave remans cosed. The pston pushes the exhaust
gases out through the exhaust vave to the atmosphere t t reaches the TDC
poston and the cyce s competed.
T4O $TRO<E DIE$EL (C#I# ENGINE-)
The workng prncpe of a two stroke dese engne s dscussed beow:
1
,-
,-r*"e : To start wth et us assume the pston to be at ts B.D.C. poston (Fg.
a). The arrangement of the ports s such that the pston performs the two |obs
smutaneousy.
As the pston starts rsng from ts B.D.C. poston, f coses the transfer port and the
exhaust port. The ar whch s aready there n the cynder s compressed (Fg. b).
At the same tme wth the upward movement of the pston, vacuum s created n
the crank case. As soon as the net port s uncovered, the fresh ar s sucked n the
crank case. The chargng s contnued unt the crank case and the space n the
cynder beneath the pston s fed (Fg. c) wth the ar. At the end of the stroke, the
pston reaches the T.D.C. Poston.
5
&d
,-r*"e : Sghty before the competon of the compresson stroke, a very
fne sprays of dese n|ected nto the compressed ar. The fue gntes
spontaneousy.
Pressure s exerted on the crown of the pston due to the combuston of the
ar and the pston s pushed n the downward drecton producng some
usefu power (Fg. c). The downward movement of the pston w frst cose
the net port and then t w compress the ar aready sucked n the crank
case.
|ust the end of power stroke, the pston uncovers the exhaust port and the
transfer port smutaneousy. The expanded gases start escapng through the
exhaust port and at the same tme transfer port (Fg. d) and thus the cyce s
repeated agan.
The fresh ar comng nto the cynder aso heps n exhaustng the burnt
gases out of the cynder through the exhaust port (Fg. d). Ths s known as
scavengng.
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL
ENGINEERING LABORATOR+
PRACTICAL MAN1AL
FOR
T* ,-%dy T2*-,-r*"e 3 F*%r-,-r*"e Pe-r*( E&)'&e,
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 3 TECHNOLOG+
BAHAL-157056
BHI4ANI(HAR+ANA)
E/per'0e&- N*: 8
AIM: - T* ,-%dy T2*-,-r*"e 3 F*%r-,-r*"e Pe-r*( E&)'&e,#
APPART1$ 1$ED: - Mode of Two-stroke & Four-stroke petro Engnes.
THEOR+-
C+CLE- When seres of events are repeated n order, t competes one cyce. Cyce
s generay cassfed as Four stroke cyce and Two stroke cyce.
F*%r ,-r*"e !y!(e- In Four stroke cyce, four operatons are requred to compete
one cyce. These four operatons are sucton, compresson, power and exhaust.
T2* ,-r*"e !y!(e,- In a two stroke cyce, the seres of events of the workng cyce
s competed n two strokes of the pston and one revouton of the crankshaft. The
four operatons .e. sucton, compresson, power and exhaust are competed durng
two strokes of the pston.
ENGINE- A power producng machne s caed an engne.
HEAT ENGINE- An engne whch converts heat energy nto mechanca energy s
caed a heat engne.
Type, *. ea- e&)'&e @
a) E/-er&a( C*0b%,-'*& e&)'&e-The engne n whch the combuston of fue
takes pace outsde the cynder s caed an externa combuston engne.
b) I&-er&a( C*0b%,-'*& e&)'&e- The engne n whch the combuston of fue
takes pace nsde the cynder s caed an nterna combuston engne.
FO1R $TRO<E PETROL ENGINE-
In four stroke petro engne or spark gnton engne a the events of the cyce .e.
sucton, compresson, expanson and exhaust take pace n two revoutons of the
crank shaft I.e. 720 of the crank rotaton. Thus each stroke s of 180 crank shaft
rotaton. Therefore the cyce of operaton for an dea four stroke engne conssts of
the foowng four strokes:
a) $%!-'*& $-r*"e- The pston moves from Top Dead Centre (TDC) to Bottom
Dead Centre (BDC). The net vave opens and a fresh charge of fue and ar
mxture enters the cynder. The exhaust vave remans cosed. When the
pston reaches Bottom Dead Centre (BDC), the net vave aso cosed.
b) C*0pre,,'*& $-r*"e- The pston moves from Bottom Dead Centre (BDC) to
Top Dead Centre (TDC) poston. Both the vaves reman cosed. The charge
drawn durng sucton stroke s compressed n ths stroke.
c) E/pa&,'*& *r P*2er *r 4*r"'&) $-r*"e- |ust before the pston competes
ts compresson stroke, the charge s gnted by the spark pug and the rapd
exposon takes pace. The expanson of hot gases pushes the pston down to
BDC poston. Both the vave remans cosed and the usefu work s obtaned
from the engne.
d) E/a%,- $-r*"e- The pston moves from BDC to TDC, the exhaust vave
opens and the net vave remans cosed. The pston pushes the exhaust
gases out through the exhaust vave to the atmosphere t t reaches the TDC
poston and the cyce s competed.
T4O $TRO<E PETROL ($#I#) ENGINE-
In two stroke cyce petro engne, there are two strokes of the pston and one
revouton of the crankshaft to compete one cyce. In two stroke engnes ports are
used nstead of vave .e. sucton port, transfer port and exhaust port. These ports
are covered and uncovered by the up and down movement of the pston. The top of
the pston s defected to avod mxng of fresh charge wth exhaust gases. The
exhaust gases are expeed out from the engne cynder by the fresh charge of fue
enterng the cynder. The mxture of ar and petro s gnted by an spark produced
at the spark pug. The two stroke of the engne are-
F'r,- $-r*"e- Assumng the pston to be at the BDC poston. The net port s
converted by the pston whereas the transfer port and exhaust port are uncovered.
The pston moves from BDC to TDC. The ar petro mxture enters the cynder. On
the upward movement of the pston, frst of a the transfer port s converted and
then mmedatey, the exhaust port s covered. Smutaneousy the sucton port aso
gets uncovered, the upward movement of the pston heps to compress the ar fue
mxture at the top and creates parta vacuum at the bottom n the crankcase whch
gets fed wth ar fue mxture by the atmospherc pressure. At the end of the
stroke, the pston reaches the TDC poston competng the compresson stroke as
shown n Fg. (a) and (b).
$e!*&d $-r*"e- |ust before the competon of the compresson stroke, the
compressed charge s gnted n the combuston chamber, by means of an eectrc
spark produced by the spark pug. Combuston of ar fue mxture pushes the pston
n the downward drecton, on the power stroke producng usefu work. The
movement of the power acton s over, the exhaust port s uncovered. The exhaust
gases escape to the atmosphere. Further movement of the pston covers the net
port and the fresh charge s compressed n the crankcase. Smutaneousy the
transfer port s aso uncovered. The compressed mxture of ar fue enters the
combuston chamber. The defected shape of the pston avods nter-mxng of the
fresh charge and exhaust gases .e. the fresh charge rses to the top of the cynder
and pushes out most of the exhaust gases. Thus the three actons, power, exhaust
and nducton are competed from TDC to BDC poston competng one cyce .e.
two stroke of the pston and one revouton of the crankshaft as shown n Fg. (c)
and (d).
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL
ENGINEERING LABORATOR+
PRACTICAL MAN1AL
FOR
T* ,-%dy -e >ap*%r !*0pre,,'*& Re.r')era-'*& $y,-e0
a&d de-er0'&a-'*& *. '-, C#O#P#
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 3 TECHNOLOG+
BAHAL-157056
BHI4ANI(HAR+ANA)
E/per'0e&- N*: 9
AIM:- To study the vapour compresson Refrgeraton System and
determnaton of ts C.O.P.
Appara-%,: - Refrgeraton Traner.
Te*ry:-
In vapour compresson refrgeraton system workng fud s refrgerant whch
undergoes phase change at east durng one process ..e. t evaporator and
condenses or changes aternatey between vapour and qud phases wthout
eavng the refrgeraton system. In evaporaton, refrgerant absorbs atent
heat from the cod body. Ths atent heat s used for convertng the qud to
vapour, whe condensng; t re|ects atent heat to externa body to create
coong effects n the workng fud.
$'0p(e :ap*%r- !*0pre,,'*& Re.r')era-'*& Cy!(e-
In a smpe vapour- compresson Refrgeraton cyce, there are four
fundamenta processes are requred to compete one cyce. These are
foows.
1) C*0pre,,'*&- The functon of compressor s to mantan the fow of the
refrgerant n the system. It sucks the ow pressure and ow temperature
refrgerant from the evaporator, compresses t by rasng ts pressure and
temperature unt the vapour temperature s greater than the condenser
temperature. The coong meda of compressor s ar or water.
2) C*&de&,a-'*&- In the condenser, atent heat of vaporzaton s removed
from the hgh pressure and hgh temperature vapours. The vapours are
condensed nto hgh pressure qud. The hgh pressure and ow temperature
vapours are coected n the recever tank unt needed to fow ahead.
3) E/pa&,'*&- From the recever tank, the qud refrgerants are passes
through the expanson vave. The expanson vave contros the fow of qud
refrgerant to the evaporator. It s the dvdng pont between the hgh
pressure and ow pressure sde of the system. When the hgh pressure qud
refrgerant passes through the expanson vave, some of t fashes nto
vapour and coos the remanng qud to a ow temperature of about -10C.
4) :ap*%r',a-'*&- The ow temperature and ow pressure quds enters the
evaporator. It absorbs heat from the surroundngs and changes nto vapour
form, after absorbng atent heat of vapoursaton. The ow temperature and
ow pressure vapours formed n the evaporator are sucked back by the
compressor, competng the functon of one cyce of compresson
refrgeraton system.
Pr'&!'pa( par-, *. a ,'0p(e >ap*%r !*0pre,,'*& re.r')era-'*&
,y,-e0-
The prncpa parts of a smpe vapour compresson refrgeraton system
shown n the fow dagram of fgure. These parts are foow:
1) Evaporator 2) Sucton ne
3) Compressor 4) Dscharge ne
5) Condenser 6) Drer
7) Lqud ne 8) Expanson Vave
Ob,er>a-'*&,-
1) Expanson devce used-capary tube
2) Tme for 10 revoutons of compressor energy meter (t
c
)-____ sec.
3) Evaporator water fows- _______ Lt. /sec.
4) Water Temperature-
a) Evaporator net, t
w
- _____C
b) Evaporator outet, t
wo
- _____C
Ca(!%(a-'*&,-
1) Refrgeraton effect s baanced by water crcuaton;
So heat gven by water=Refergeraton effect
R.E. = mc
p
AT kw
Where, m = mass fow rate of water, Lt. per second.
C
p
= 4.2 K|/Kg k
AT = t
w
- t
wo
2 ) Compressor Work (CW) = (n X 3600) /( t
c
EMC)
Where t
c
= tme for compressor energy meter dsc
EMC = Compressor energy meter constant
3) Actua C.O.P. = R.E. / CW
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL
ENGINEERING LABORATOR+
PRACTICAL MAN1AL
FOR
T* ,-%dy -e .%&!-'*&'&) *. 4'&d*2 R**0 A'r C*&d'-'*&er#
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 3 TECHNOLOG+
BAHAL-157056
BHI4ANI(HAR+ANA)
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL
ENGINEERING LABORATOR+
PRACTICAL MAN1AL
FOR
T* ,-%dy -e C*&,-r%!-'*&a( .ea-%re, a&d 2*r"'&) *.
Pe(-*& 4ee( T%rb'&eA Fra&,', T%rb'&e a&d <ap(a&
T%rb'&e#
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 3 TECHNOLOG+
BAHAL-157056
BHI4ANI(HAR+ANA)
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL
ENGINEERING LABORATOR+
PRACTICAL MAN1AL
FOR
T* ,-%dy -e !*&,-r%!-'*& 3 2*r"'&) *. !e&-r'.%)a( p%0p
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 3 TECHNOLOG+
BAHAL-157056
BHI4ANI(HAR+ANA)
E/per'0e&- N*: 6
AIM: - T* ,-%dy -e !*&,-r%!-'*& 3 2*r"'&) *. !e&-r'.%)a( p%0p#
Appara-%, %,ed: - Mode of centrfuga pump.
THEOR+:- A Centrfuga pump s rotodynamc or dynamc pressure pump
where the workng fud or qud or quds s sub|ected to whng moton by
means of backward curved bades mounted on a whee caed mpeer. A
centrfuga pump s named so, because the energy added by the mpeer to
the fud s argey due to centrfuga effects. The qud enters the mpeer at
ts centre caed the eye of the pump and the mpeer dscharge the qud
nto the casng surroundng the mpeer. The deveoped pressure head s
purey due to the whrng moton of the qud mparted by the rotatng
mpeer and s not due to any dspacement or mpart.
A ayout of a centrfuga pump s shown n Fgure.
Te 0a'& !*0p*&e&-, *. a !e&-r'.%)a( p%0p are:
1. Straner and foot vave
2. Sucton ppe
3. Pump (A) Impeer (B) Casng
4. Devery vave
5. Devery ppe
1. $-ra'&er a&d .**- >a(>e: It s ftted at one end of the sucton ppe and s
submerged n water n such a way that t s aways a few meters above the
surface of water from the sump enters the sucton ppe through the straner
and foot vave.
Foot vave s a non return vave .e. t does not aow the water to go back to the
sump.
2. $%!-'*& p'pe: A ppe whose one end s connected to the net of the pump
and the other end dps nto the water n a sump s known as sucton ppe.
Ppe fttng shoud be ar tght because a pump cannot run f t contans ar
pockets.
3. P%0p: The pump many conssts of an mpeer and casng. The water enters
the mpeer at ts center, caed eye of the pump and mpeer dscharges
water nto the casng.
(A) I0pe((er: The rotatng whee of a centrfuga pump s caed mpeer. It has a
number forward curved or backward curved bades, dependng upon whether
t s a sow speed or a hgh speed mpeer. When the mpeer rotates, a
negatve pressure (ower than the atmospherc pressure) s created near the
eyes of the pump and water enters the mpeer. The pressure head created
by the centrfuga acton s entrey due to the veocty mparted to water by
the rotatng mpeer, and not due to any dspacement or mpart.
(B) Ca,'&): The casng of a centrfuga pump s smar to the casng of a casng
of a reacton turbne. It s an ar tght passage surroundng the mpeer and s
desgned n such a way that the K.E. of the water dscharged at the outet of
the mpeer s converted nto pressure energy before the water eaves the
casng and enters the devery ppe.
Voute casng s used for snge stage pump and dffuser casng for mutstage
pumps.
4. De('>ery >a(>e: The devery vave connects the pump outet and the
devery ppe. It remans cosed before the pump s swtched on. When the
pump buds up ts pressure, t s opened and can be used to contro or vary
the dscharge.
The devery vave s cosed agan before the pump s swtched off so that the
devery pressure s not transmtted to the sucton ppe.
5. De('>ery p'pe: A ppe whose one end s connected to the outet of the pump
and devery the water at a requred heght s known as devery ppe.
4OR<ING OF A CENTRIF1GAL P1MP:-
To start the pump prmng s the frst step for the workng of pump. The prmng
s the operaton of fng the sucton ppe, casng of the pump, and the porton of
the devery ppe up to the devery vave, so that no ar pocket s eft. The
presence of a sma ar pocket may hamper the workng of pump as the densty
of ar s usuay very ow compared to qud beng pumped.
The centrfuga acton deveoped s drecty proportona to the densty of fud n
contact wth mpeer, the presence of ar resut n neggbe pressure rse, so no
qud w be fted up by the pump. Ths makes the prmng an essenta step
before startng pump.
The second step s the revouton of the pump mpeer nsde a casng fu of
water to produce a forced vortex whch s responsbe for mpartng a centrfuga
head to water. For ths purpose the devery vave s st kept cosed to reduce
startng torque and the eectrc motor s started to rotate the mpeer. The
devery vave s opened when the pressure of the qud surroundng the mpeer
s consderaby ncreased. The rotaton of the mpeer aso cause a reducton of
pressure at the center, due to whch the water n sucton ppe rushes nto the
eye to repace the qud whch s beng dscharged from the entre crcumference
of the mpeer.
F')%re: C%--a2ay >'e2 *. a !e&-r'.%)a( p%0p#
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL
ENGINEERING LABORATOR+
PRACTICAL MAN1AL
FOR
T* ,-%dy -e 2*r"'&) *. ,'&)(e p(a-e !(%-!
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 3 TECHNOLOG+
BAHAL-157056
BHI4ANI(HAR+ANA)
E/per'0e&- N*: B
AIM: - T* ,-%dy -e 2*r"'&) *. ,'&)(e p(a-e !(%-!#
Appara-%,: - Mode of snge pate cutch.
THEOR+:-
C(%-!:-
It s a devce whch dsconnects the engne from the rest of the transmsson
and enabes the engne to run wthout movng the vehce.
Type, *. !(%-!:-
Cutch can be cassfed beows:
$INGLE PLATE CL1TCH:-
It s the most common type of cutch used n motor
vehces. Bascay, t conssts of ony one cutch pate, mounted on the
spnes of the cutch shaft, as shown n Fgure. The fywhee s mounted on
the engne crankshaft and rotates wth t. The pressure pate s boted to the
fywhee through cutch sprngs, and s free to sde on the cutch shaft when
the cutch peda s operated. When the cutch s engaged, the cutch pate s
grpped between the fywhee and the pressure pate. The frcton nngs are
on both the sdes of the cutch pate. Due to the frcton between the
fywhee, cutch pate and pressure pate, the cutch pate revoves wth the
fywhee. As the cutch pate revoves, the cutch shaft aso revoves. Cutch
shaft s connected to the transmsson (.e. Gear box). Thus the engne power
s transmtted to the crankshaft to the cutch shaft.
When the cutch peda s pressed, the pressure pate moves back aganst the
force of the sprngs, and the cutch pate becomes free between the fywhee
and the pressure pate. Thus, the fywhee remans rotatng as ong as the
engne s runnng and the cutch shaft speed reduces sowy and fnay t
stops rotatng. As soon as the cutch peda s pressed, the cutch s sad to be
dsengaged, otherwse t remans engaged due to the sprng forces.
BA$IC$ OF MECHANICAL
ENGINEERING LABORATOR+
PRACTICAL MAN1AL
FOR
T* ,-%dy d'..ere&- -ype, *. )ear, %,ed .*r p*2er
-ra&,0',,'*&
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 3 TECHNOLOG+
BAHAL-157056
BHI4ANI (HAR+ANA)
E/per'0e&- N*: 10
AIM: - T* ,-%dy d'..ere&- -ype *. )ear, %,ed .*r p*2er -ra&,0',,'*&#
Appara-%,: - Mode of dfferent types of gears.
THEOR+:-
GEAR: - The gear s defned as a toothed eement whch s used for
transmttng rotary moton from one shaft to another. When teethes are
provded on ts nterna surface, known as nterna gear or annuar whee.
When teethes are provded on ts externa surface, known as externa gear.
T+PE$ OF GEAR AND THEIR APPLICATION$:
The gear can be cassfed n the foowng ways:
1# A!!*rd'&) -* -e p*,'-'*& *. a/e, *. -e ,a.-,:
a) Parae shafts
b) Intersectng shafts
c) Nether parae nor ntersectng shafts
a) Gear .*r !*&&e!-'&) para((e( ,a.-,: The gear used to connect the
shaft n whch ther axes of rotaton are parae to each other are-
I. $p%r )ear,: The gear used to connect two parae shafts and havng
straght teeth whch are parae to the axs of the whee are known as spur
gears. They mpose ony rada oads. These are sow speed gears. If nose s
not a probem, these can be used for any speed. The most usua
arrangement s an externa gear and pnon combnaton. If centre dstance s
to be reduced, the nterna gear wth externa pnon combnaton s aso
used. Gears rotate n opposte drecton n case of externa gearng and n
same drecton n case of nterna gearng. Fgure show the spur gears. These
are generay used n athes for speed change mechansm.
II. $p%r Ra!" a&d p'&'*&: Spur Rack s a speca case of a spur gear. It has
nfntey arge ptch dameter. The spur rack and pnon combnaton converts
rotary moton nto transator moton or vce-versa. Fgure shows the rack and
pnon.
III. He('!a( )ear,: Fgure shows the heca gear. In heca gears, teeth are
ncned to the axs of the shaft and are n form of hex. Two meshng gears
have the same hex ange but have teeth of opposte hands .e. a rght hand
pnon meshes wth a eft hand gear and a eft hand pnon meshes wth a
rght hand gear. These gears are consdered for hgh speed and can take
hgher oads as compared to equa sze spur gear.
Snge heca gears mpose both rada and thrust oads on ther bearngs.
IV. D*%b(e e('!a( )ear,: These gears have two sets of opposte heca teeth
.e. one has rght handed hex and other a eft handed hex. The teeth of two
rows are separated by a groove used for too run-out. These can be run at
hgher speeds wthout nose and vbratons. There s no axa thrust on the
bearng. Doube heca gear s shown n fgure.
Fgure- Doube Heca Gear
V. Herr'&) b*&e )ear,: These gears are shown n fgure. These are essentay
the same as the doube heca gears but n these gears, there s no space
separatng the two opposed sets of heca teeth. These are used n turbnes.
b) Gear, .*r !*&&e!-'&) '&-er,e!-'&) ,a.-,: The gears used to connect
two ntersectng shafts are known as beve gears.
If the teeth on the gears are straght rada to the pont of ntersecton of
shaft axes then gears are known as straght beve. But f teeth are ncned
then gears are known as heca beve (or spra beve).
I. $-ra')- be>e( )ear,: Fgure shows the straght beve gears. In straght
beve gears, teeth are straght, rada to the pont of ntersecton of the shaft
axs. There s varaton n cross-secton throughout ther ength. Athough
they are made for a shaft ange of 90, can be produced for amost any
ange. Straght beve gears make the ne contact smar to spur gears. These
can be nterna beve gears aso smar to nterna spur gears. Two such gears
of the same sze wth shaft ange of 90 are known as mtre gears.
II. $p'ra( be>e( )ear,: In these beve gears, the teeth are ncned. These are
most sutabe for hgh speeds. These can run more quety and can take up
more oad than straght beve gears, but the thrust oads are greater. These
are used for the drve to the dfferenta of an automobe. Spra beve gear s
shown n fgure.
F')%re- $-ra')- Be>e( Gear F')%re-
$p'ra( Be>e( Gear
!) Ne'-er para((e( &*r '&-er,e!-'&) ,a.-,: The axs of such shafts
crosses n space. The shaft whch es n parae may skewed at any ange
between 0 and 90. The foowng man types of gears are used between
such shafts:
I. $p'ra( )ear,: These are aso caed crossed heca gears. There s no
dfference between these gears and heca gears unt they are mounted n
mesh wth each other. A par of meshed crossed heca gears usuay has the
same hand. The teeth of these gears have pont contact wth each other and
are used for ow oads.
II. Hyp*'d )ear,: these are smar to spra beve gears wth the dfference that
the axes of the shafts do not ntersect. The term offset s the dstance
between a hypod pnon axs and the axs of the hypod gear. Hypod gears
become spra beve gears, f the offset s zero. The shafts ange s usuay 90
but other anges are not possbe. The tooth acton between such gears s a
combnaton of rong a sdng aong a straght ne. Hypod gear s shown n
fgure.
Fgure- Hypod Gear
III. 4*r0 )ear,: n such gears one gear has screw threads. Due to ths factor,
they are quet, vbraton free and gve a smooth run. These gears are used
wth shaft anges of 90, but other anges are not possbe.
F')%re- 4*r0 a&d 4*r0 2ee(
5# A!!*rd'&) -* -e per'pera( >e(*!'-y *. -e )ear,: The gears may be
cassfed on the bass of perphera veocty as;
a) L*2 >e(*!'-y: The gears havng veocty ess than 3m/s are known as ow
veocty gears.
b) Med'%0 >e(*!'-y: The gears havng veocty between 3m/s to 15 m/s are
known as Medum veocty gears.
c) H') >e(*!'-y: The gears havng veocty more than 15 m/s are known as
Hgh veocty gears.
7# A!!*rd'&) -* -e -ype, *. )ear'&): The gears, accordng to the type of
gearng may be cassfed as:
a) E/-er&a( )ear'&): In ths case the teeth are provded on the externa
surface. When the gears of the two shafts mesh externay wth each other, t
s known as externa gearng. In ths case the moton of the two gears s
aways opposte. The gear s known as spur whee and smaer s known as
pnon. Externa gearng shown n fgure.
b) I&-er&a( )ear'&): In ths case, the teeth are provded on ts nterna
surface. Fgure shows the nterna gearng, n whch the gears of two shafts
mesh nternay wth each other. The arger whee s known as annuar whee
whe the smaer whee pnon. The moton of the two gears s aways same.
c) Ra!" a&d p'&'*&: Spur Rack s a speca case of a spur gear. It has nfntey
arge ptch dameter. The spur rack and pnon combnaton converts rotary
moton nto transatory moton or vce-versa.
8# A!!*rd'&) -* -e ,ape *. -ee- *. -e )ear,: The gears may be
cassfed as:
a) $-ra')- -ee- )ear,: Spur gears have straght teeth.
b) I&!('&ed -ee- )ear,: Heca gears have ncned teeth (whch are ncned
to the whee rm surface).
c) C%r>ed )ear,: Spra gears have the curved teeth over the rm surface.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ME LAB MANUAL RevisedDocument64 paginiME LAB MANUAL RevisedClint Baring ArranchadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Civil and Mechanical-Unit-4-Boilers-Support Notes-Studyhaunters PDFDocument11 paginiBasic Civil and Mechanical-Unit-4-Boilers-Support Notes-Studyhaunters PDFSriram J100% (1)
- Soot and Scale ProblemDocument12 paginiSoot and Scale ProblemgksamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bme - Lab Manual - SitDocument39 paginiBme - Lab Manual - Sitdevlalit2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Basics OF Mechanical Engineering Laboratory: Practical ManualDocument7 paginiBasics OF Mechanical Engineering Laboratory: Practical ManualRyan TogononÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module p3 BiologyDocument16 paginiModule p3 BiologyRaj GobalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diploma 4 THERMAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL (Copy)Document19 paginiDiploma 4 THERMAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL (Copy)AjitKumarPandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics OF Mechanical Engineering Laboratory: Practical ManualDocument7 paginiBasics OF Mechanical Engineering Laboratory: Practical ManualRyan TogononÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No. 9: To Study Construction Features and Working of A Cross Tube Vertical Cradely Boiler and Babcock and Wilcox BoilerDocument4 paginiExperiment No. 9: To Study Construction Features and Working of A Cross Tube Vertical Cradely Boiler and Babcock and Wilcox BoilerhloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Experiment No 1 - SGTC LABDocument13 pagini1 - Experiment No 1 - SGTC LABRushi vedeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maintenance and Operation of BoilersDocument40 paginiMaintenance and Operation of BoilersMico CampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATD LabDocument32 paginiATD Labneeraj sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FME Lab WorkDocument14 paginiFME Lab WorkVranda MaheshwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Generators-Fire Tube BoilersDocument11 paginiSteam Generators-Fire Tube BoilersGokulAgÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Marine EngineeringDocument67 paginiGeneral Marine EngineeringSailorprof100% (3)
- Bme Lab Me-107-F Iisem PDFDocument33 paginiBme Lab Me-107-F Iisem PDFshyam sundar dutta100% (1)
- Study of Water and Fire Tube BoilersDocument13 paginiStudy of Water and Fire Tube BoilersPriyanshu NandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Boiler Lab ManualDocument64 paginiSteam Boiler Lab Manualvikramnikhilanshi0% (2)
- Case Studies in Boiler Vibration and BFP Cavitation by K.K.parthibanDocument15 paginiCase Studies in Boiler Vibration and BFP Cavitation by K.K.parthibanparthi20065768Încă nu există evaluări
- Steam Generators or Boilers: Chapter-2 Steam Generator (25 Marks) 5 Sem Mechanical EnggDocument12 paginiSteam Generators or Boilers: Chapter-2 Steam Generator (25 Marks) 5 Sem Mechanical EnggDarklightÎncă nu există evaluări
- BVF3184 Topic 4 Part 1 - Boiler ComponentsDocument44 paginiBVF3184 Topic 4 Part 1 - Boiler ComponentswidadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Murshidabad Institute of Technology: Cossimbazar, BerhamporeDocument9 paginiMurshidabad Institute of Technology: Cossimbazar, BerhamporeDipak MondalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report by KKParthiban On Boiler Explosion of A Shell Type High PR BoilerDocument97 paginiReport by KKParthiban On Boiler Explosion of A Shell Type High PR Boilerparthi20065768100% (1)
- Cochran and Babcock & Wilcox BoilersDocument3 paginiCochran and Babcock & Wilcox BoilersAshish VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BoilersDocument8 paginiBoilersKarthiKeyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Efficiency of Steam SeparatorDocument96 paginiEfficiency of Steam SeparatorFajar Azhari SalehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Engine TwoDocument34 paginiThermodynamics Engine TwoUsamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Fittings and AccessoriesDocument30 paginiBoiler Fittings and Accessorieskowsar0221Încă nu există evaluări
- Super Heater Trouble Shooting Report at A Hi Plant by KKPDocument68 paginiSuper Heater Trouble Shooting Report at A Hi Plant by KKPparthi20065768100% (2)
- Introduction To Boilers: BoilerDocument31 paginiIntroduction To Boilers: BoilerNeeraj SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lancashire BoilerDocument6 paginiLancashire BoilerNikhilesh BhargavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vortex TubeDocument10 paginiVortex TubeMohamed MosaedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boe Notes by RameshDocument22 paginiBoe Notes by RameshVelpuri RameshBabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Foster WheelerDocument48 paginiBoiler Foster WheelersprotkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Questions BtechDocument5 paginiBoiler Questions BtechRishav Raj100% (1)
- Types - Of.boilers Draught Thermal - PlantDocument11 paginiTypes - Of.boilers Draught Thermal - PlantPraveen PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boilers InspectionDocument62 paginiBoilers Inspectionrty288% (16)
- COE Phase 2 Partial Requirement: Operation and Maintenance of BoilersDocument11 paginiCOE Phase 2 Partial Requirement: Operation and Maintenance of BoilersMico CampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPG LAbDocument32 paginiSPG LAbDinesh ScientificÎncă nu există evaluări
- BME ManualDocument32 paginiBME ManualSudhanshuAtkareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studyof60horsepo00evan PDFDocument86 paginiStudyof60horsepo00evan PDFDaniel InostrozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me-143 BcmeDocument73 paginiMe-143 BcmekhushbooÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02.understanding Process Equipment For Operators & Engineers-54Document5 pagini02.understanding Process Equipment For Operators & Engineers-54Aatish ChandrawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Generators Lecture No.-1Document18 paginiSteam Generators Lecture No.-1rathoraryan2003Încă nu există evaluări
- Experiment One-To Study The Cochran and Babcock and Wilcox BoilersDocument8 paginiExperiment One-To Study The Cochran and Babcock and Wilcox BoilersHasib IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- BoilerDocument14 paginiBoilerSK MD WALI ULLAH BULONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler 1Document44 paginiBoiler 1Emmanuel AyisiÎncă nu există evaluări
- GE2152 BCM Power Plant Engineering Notes 2Document13 paginiGE2152 BCM Power Plant Engineering Notes 2Alagar SamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Boiler Certification QuestionsDocument4 paginiSample Boiler Certification Questionssirsa11Încă nu există evaluări
- Boiler OverhaulDocument9 paginiBoiler OverhaulHemant PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 365, December 30, 1882De la EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 365, December 30, 1882Încă nu există evaluări
- Maxims and Instructions for the Boiler Room: Useful to Engineers, Firemen & Mechanics; Relating to Steam Generators, Pumps, Appliances, Steam Heating, Practical Plumbing, etcDe la EverandMaxims and Instructions for the Boiler Room: Useful to Engineers, Firemen & Mechanics; Relating to Steam Generators, Pumps, Appliances, Steam Heating, Practical Plumbing, etcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersDe la EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesDe la EverandOil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Engineering Bulletin No 1: Boiler and Furnace TestingDe la EverandEngineering Bulletin No 1: Boiler and Furnace TestingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 633, February 18, 1888De la EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 633, February 18, 1888Încă nu există evaluări
- CastingDocument26 paginiCastingInayat KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument64 paginiBasic Mechanical EngineeringSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 - Fundamentals of Metalworking PDFDocument50 pagini01 - Fundamentals of Metalworking PDFSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elements of Mechanical EngineeringDocument33 paginiElements of Mechanical EngineeringSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lathe AccessoriesDocument63 paginiLathe AccessoriesMohammed Rehan0% (1)
- FE EEE ManualDocument31 paginiFE EEE ManualSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop ManualDocument60 paginiWorkshop ManualSadasiva Rao T83% (6)
- CarpentryDocument35 paginiCarpentrySadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review On Optimization of Machining OperationDocument10 paginiReview On Optimization of Machining OperationSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 ExtrusionDocument57 pagini04 Extrusion9811923100% (1)
- L5 Metal CastingDocument27 paginiL5 Metal Castingpradeep_i19Încă nu există evaluări
- Analitical Modelling of Residual StressDocument11 paginiAnalitical Modelling of Residual StressSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 DrillingDocument26 pagini4 DrillingSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Shaper and PlanerDocument33 pagini5 Shaper and PlanerSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Power Plant Layout: Steam TurbineDocument1 paginăThermal Power Plant Layout: Steam TurbineSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orthographic ProjectionDocument29 paginiOrthographic ProjectionSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICE1Document8 paginiICE1Sadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 MillingDocument34 pagini6 MillingSadasiva Rao TÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISOMETRICDocument39 paginiISOMETRICKaustubh MallikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machining TurningDocument10 paginiMachining Turningasa_aha789Încă nu există evaluări
- FEM For StressDocument9 paginiFEM For Stresstasha_oksariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Behaviors of End Milling Inconel 718 Superalloy by Cemented Carbide ToolsDocument6 paginiBehaviors of End Milling Inconel 718 Superalloy by Cemented Carbide ToolsMathieu_94Încă nu există evaluări
- PCTDS 027 Fendolite MII Cold Wet Weather ApplicationDocument2 paginiPCTDS 027 Fendolite MII Cold Wet Weather ApplicationMohammed AhteshamÎncă nu există evaluări
- YesDocument80 paginiYesRonnie TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigerator: Service ManualDocument44 paginiRefrigerator: Service ManualBetileno QuadAlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigating The Effect of Liquid Viscosity On Two Phase Gas Liquid FlowDocument252 paginiInvestigating The Effect of Liquid Viscosity On Two Phase Gas Liquid FlowAnonymous DMh6pdl0aÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Related Topics Automatic IrrigationDocument13 pagini2 Related Topics Automatic IrrigationSftvsn Giovanni TandogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalog: Ningbo Liftstar Material Handling Equipment Co., LTDDocument27 paginiCatalog: Ningbo Liftstar Material Handling Equipment Co., LTDKiều Văn TrungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standards of MeasurementDocument12 paginiStandards of MeasurementShubham KheraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab3 BJT Current MirrorsDocument5 paginiLab3 BJT Current MirrorsaublysodonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cryptographic Systems Tend To Involve Both Algorithm and ADocument6 paginiCryptographic Systems Tend To Involve Both Algorithm and APawan Kumar ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of IEC IP and UL/NEMA TYPE Ratings: ControlsDocument1 paginăComparison of IEC IP and UL/NEMA TYPE Ratings: ControlsEdwin LinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fema 154 FormsDocument3 paginiFema 154 FormslesgiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- GAPS Guidelines: Deep Fat FryersDocument4 paginiGAPS Guidelines: Deep Fat FryersAsad KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- California Bearing Ratio, Evaluation and Estimation: A Study On ComparisonsDocument4 paginiCalifornia Bearing Ratio, Evaluation and Estimation: A Study On ComparisonsAmyra MiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Propeller Stockpile Measurement and Reports With Drone Surveying EbookDocument17 paginiPropeller Stockpile Measurement and Reports With Drone Surveying EbookmuazeemK100% (1)
- Chemistry, Intermediate II Year Model Question PapersDocument3 paginiChemistry, Intermediate II Year Model Question PapersAkshay PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi Spindl Drilling MachineDocument38 paginiMulti Spindl Drilling MachineBoopathi KalaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Misumi s5m Pulley p1117Document1 paginăMisumi s5m Pulley p1117tigor carakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liebert PDX PCW Thermal Management System User ManualDocument184 paginiLiebert PDX PCW Thermal Management System User ManualJeffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gear Trains ProblemsDocument9 paginiGear Trains Problemsa c s Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter5 Memory ManagementDocument78 paginiChapter5 Memory ManagementJackYuan JinFengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gestrast 6Document3 paginiGestrast 6iran1362Încă nu există evaluări
- Continuous Thread Stud Double End Stud ADocument11 paginiContinuous Thread Stud Double End Stud AMarius Mihai Buzduga0% (1)
- ManualDocument90 paginiManualBhárbara Idk100% (1)
- LOLERDocument68 paginiLOLERpraba8105100% (3)
- Annex12 Technical Cards For Accessible ConstructionDocument44 paginiAnnex12 Technical Cards For Accessible Constructionarchitectfemil6663Încă nu există evaluări
- 3 Esrtos IntroDocument8 pagini3 Esrtos IntroVijayaraghavan VÎncă nu există evaluări
- AA Holtz & Kovacs - An Introduction To Geotechnical Engineering PDFDocument746 paginiAA Holtz & Kovacs - An Introduction To Geotechnical Engineering PDFPeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spirent TestCenter Automation Obj RefDocument3.210 paginiSpirent TestCenter Automation Obj Refokie11Încă nu există evaluări
- NEOCLASSICAL CITY PlanningDocument10 paginiNEOCLASSICAL CITY PlanningAfrahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Processors and RAM'sDocument26 paginiTypes of Processors and RAM'sSneha NairÎncă nu există evaluări