Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Introduction To Foundry Processes
Încărcat de
Atul Gaur100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
708 vizualizări22 paginimanufacturing
Titlu original
Introduction to Foundry Processes
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentmanufacturing
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
708 vizualizări22 paginiIntroduction To Foundry Processes
Încărcat de
Atul Gaurmanufacturing
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 22
Introduction to Foundry Processes
1.2 Types of Foundries
1.3 Advantages of Metal Casting
1.4 Applications of Metal Casting
1.5 Comparison of Casting with metal Joining, Metal Removing Processes
1.6 Different Sections of a Foundry
Exp.2 To Study about Pattern, Pattern Making, Pattern Allowances & Types of Patterns
2.1 Types of Material used for making Pattern with description
2.2 Difference between Pattern and Casting
2.3 Types of Pattern
2.4 Design consideration of the Pattern
2.5 Types of Allowances for the Pattern with description
2.6 Colour Code of the Pattern
Exp. 3 To Study about Molding sand, its properties & Sand Testing
3.1 Types of Molding Sand with Properties of each sand.
3.2 Testing of Molding Sand
3.3 Testing of Core Sand
Exp. 4 To Study about Mold & Mold Making
4.1 Molding Tools & Equipments with Figure
4.2 Molding Machines
4.3 Hand Molding Tools
4.4 Types of Molding
4.4.1 Bench Molding
4.4.2 Floor Molding
4.4.3 Pit Molding
4.4.4 Green Sand Molding
4.4.5 Dry Sand Molding
4.4.6 Loam Sand Molding
4.4.7 Machine Molding
Exp. 5 To Study about Core & Core Making
5.1 Introduction & Defination
5.2 Types of Core
5.3 Core making Machines
5.4 Core Prints
5.5 Core Venting & Baking
5.6 Core Shifting & Chaplets
5.7 Finishing of Core
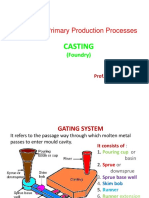
Exp. 6 To Study about Getting Systems Processes
6.1 Introduction
6.2 Types of Gates & Risers
6.3 Gating Ratio
6.4 Design of Risers
6.5 Directional Solidification in Casting
6.6 Physical Behaviours of Metal during Solidification
Exp.7 To study about Melting Practices
7.1 Types of Foundry Furnace
7.1.1 Crucible Furnace
7.1.2 Cupola Furnace
7.1.3 Electric Arc Furnace
7.1.4 Induction Furnace
Exp. 8 To study about Advance Casting Processes
8.1 Investment Casting
8.2 Continues Casting
8.3 Centrifugal Casting
8.4 Shell Molding
8.5 Gravity/ Permanent Die Casting
8.6 Pressure Die Casting
8.7 Vacuum Casting
8.8 Full Mold Casting
8.9 Slush Casting
Exp.9 To inspect & perform Testing of Casting
9.1 Casting Defects their Causes & Remedies
9.2 Non- Destructive testing of the Casting
Exp. 10 To study about Modernizing & Mechanization of Foundry
10.1 Typical Layout
10.2 Sand Reclamation Tech.
10.3 Material Handling
10.4 Application of Computer in Casting Processes
PRODUCTION ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
CASTING TECHNOLOGY
OBJECTIVE TYPE PRESENTATION
================================================================
NOTE:-
Give short presentation for answer and for all other wrong answer with detail description
Each student having only one unique question
Roll No. as per the Sequence i.e. 1) For roll No. 5001 and so
on. Some questions
having Bold Font gives right answer.
1) Cope in Foundry Practice refers to
a. Bottom half of moulding box
b. Top half of moulding box
c. Middle Portion of half of moulding box
d. Coating of the Mould face
2) In Sand Mouling, The middle Part of Flask is called
a. Cope
b. Cheek
c. Drag
d. Flask- Middle
3) Riddle is
a. A round sleve
b. A long, flat metal Plate fitted with an offset handle
c. Used to make or repair corners in a mould
d. Used to scoop sand deep in the mould
4) In order to ram the sand softer on the pattern face and harder at the back of the mould,
following type of moulding machine is used
a. Jolt
b. Sand slingers
c. Squeezing
d. Stripper plate
5) Uniform sand hardness is obtain through the mould by following machine
a. Jolt
b. Sand slingers
c. Squeezing
d. Stripper Plate
e. Diaphragm Moulding
Page2
6) The Purpose of Chaplets is
a. Just like chills to ensure directional solidification
b. To provide efficient venting
c. To support the core
d. To join lower & upper parts of the moulding box
e. Compress moulding sand
7) Which of the following is not a casting defect
a. Hot tear
b. Blow Hole
c. Scab
d. Decarburization
e. Shift
8) Chills are metal insert of steel that are placed at appropriate locations in the mould walls to
a. Decrease the freezing rate
b. Increase the freezing rate
c. Help directional solidification
d. Prevent directional solidification
e. Help progressive solidification
9) Fluidity is greatly influenced by
a. Carbon Content of molten metal
b. Melting temperature of molten metal
c. Inoculants addition
d. Pouring temperature of molten metal
e. Finishing of the mould
10) The chief advantage of Die casting is
a. Possibility of incorporating thick sections in small castings
b. Casting of inserts is possible
c. Wide tolerances are possible
d. High production rates are possible
e. Any material can be die cast easily
11) The main Advantage of shell moulding is that
a. A metallic pattern is used
b. The moulds are stronger
c. Thin sections can be easily obtained
d. Highly complex section can be easily obtained
e. High production rate is possible
12) For mounting several pattern at a time following type of pattern is used
a. Combined pattern
b. Loose piece pattern
c. Sweep pattern
d. Match Plate Pattern
e. Metallic Pattern
Page3
13) Draft on pattern for casting is
a. Shrinkage allowances
b. Identification number marked on it
c. Taper to facilitate its removal from mould
d. Increase in size of cavity due to shaking pattern
e. For machining allowances
14) Strength and permeability of served sand are related to
a. Grain size
b. Clay content
c. Hardness
d. Moisture content
e. Type of sand
15) Casting Process is preferred for parts having
a. A few detail
b. Many detail
c. No details
d. Non symmetrical shape
e. None of the above
16) In order to facilitate the withdrawal of pattern
a. Pattern is made smooth
b. Water is applied on pattern surface
c. Allowances are made on the pattern
d. Draft is provided on Pattern
e. Withdrawing facilities are provided
17) Least shrinkage allowance is provided in the case of following
a. Brass
b. Aluminium
c. Cast Iron
d. Steel
e. White cast iron
18) The draft allowance on the patterns is provided in order to
a. Provide good draft of air in the sand moulding
b. Provide for distortion that might take place
c. Remove the pattern easily from the moulding
d. Increase the strength of the mould wall
e. Push the pattern easily into the moulding
19) The taper provided on pattern for its easy and clan withdrawal from the mould is called
a. Taper allowance
b. Draft allowance
c. Distortion allowance
d. Pattern allowances
e. Casting allowance
Page4
20) The draft allowance on the metallic pattern in comparison to wooden ones is
a. Same
b. More
c. Less
d. More/less depending on size
e. None of the above
21) A big advantage of using synthetic sand in foundry shop is that
a. It is less costly
b. Its properties can be controlled easily
c. It possesses high moisture
d. It possesses high % of Clay
e. It is highly refractory
22) Which of the following materials has more shrinkage allowance
a. Cast Iron
b. Brass
c. Lead
d. Aluminium alloys
e. Steel
23) Which of the following provides an added projection on a pattern and forms a seat to
support and locate the core in the mould
a. Mould print
b. Core print
c. Drag
d. Cope
e. Chaplet
24) The mould is housed in a
a. Flask
b. Cope
c. Drag
d. Cheek
e. Moulding box
25) Loose piece patterns are
a. A sort of split pattern
b. Used when the pattern cant be drawn from the mould
c. Similar to core prints
d. Never used in foundry work
e. None of the above
26) Cores are used to
a. Make desired recess in the casting
b. Strengthen moulding sand
c. Support loose pieces
d. Remove pattern easily
e. None of the above
27) Trovel is
Page5
a. A round sleve
b. A long, flat metal plate fitted with an offset handle
c. Used to make or repair corners in a mould
d. Used to scoop sand deep in the mould
e. None of the above
28) Shrinkage allowance is made by
a. Adding to external and internal dimensions
b. Subtracting from external and internal dimensions
c. Subtracting from external dimensions and adding to internal dimensions
d. Adding to external dimensions and subtracting from internal dimensions
e. None of the above
29) Which of the following is not a casting process
a. Extrusion Process
b. Semi Centrifugal Method
c. Slush Process
d. None of the above
30) Shell Moulding Wood for pattern is considered dry when moisture content is
a. zero %
b. 5%
c. Less than 15%
d. Less than 25%
e. None of the above
31) The purpose of the gate is to
a. Feed the casting at a rate consistent with the rate of solidification
b. Act as reservoir for molten metal
c. Help feed the casting until all solidification takes place
d. Feed molten metal from pouring basin to gate
e. None of the above
32) Pick up correct statement
a. Loose piece patterns are used when the pattern can be drawn from the mould
b. Sweep pattern eliminate the need for 3D pattern
c. Match Plate patterns are made by fastening each half of a split pattern on the same
side of one plate
d. Cope and drag patterns are solid one piece patterns
33) Lifter is
a. A round sleve
b. A long, flat metal plate fitted with an offset handle
c. Used to make or repair corners in a mould
d. Used to scoop sand deep in the mould
e. None of the above
34) The impurities in true centrifugal casting
a. Get collected at outer surface
b. Mix up thoroughly throughout
c. Get collected at the inner surface
Page6
d. Ger collected at the middle portion in between inner & outer surface
e. Are thrown out
35) Which of the following type of sand is used ot keep the green sand from sticking to the
pattern
a. Burnt sand
b. Synthetic sand
c. Core sand
d. Parting sand
e. Loam sand
36) Facing sand used in foundry work comprises of
a. Alumina, silica and clay
b. Silica & clay
c. Clay and alumina
d. Silica and alumina
37) Loam sand comprises of
a. 50% sand and 10% of moisture
b. 40% clay and 10% moisture
c. 50% clay and 18% moisture
d. 80% clay and 20% moisture
e. None of the above
38) Dilatometer is used to find out following property of moulding sand
a. Permeability
b. Moisture content
c. Hot strength
d. Compactness
e. Fineness
39) The purpose of sprue is to
a. Feed the casting at a rate consistent with the rate of solidification
b. Act as a reservoir for molten metal
c. Help feed the casting until all solidification takes place
d. Feed molten metal from pouring basin to gate
e. None of the above
40) Accuracy of shell moulding is of the order of
a. 0.001 mm/mm
b. 0.003 to 0.005 mm/mm
c. 0.01 mm/mm
d. 0.1 mm
e. None of the above
41) The mould for casting ferrous materials in continuous casting process is made of
a. Low carbon steel
b. Medium carbon steel
c. High carbon steel
d. Copper
e. None of the above
Page7
42) Sand slingers gives
a. Better packing of sand near pattern
b. Better packing of sand near the flask
c. Uniform sand density in the mould
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
43) The trowel in a foundry shop is used to
a. Ram the moulding sand
b. Swab the edges and the mould cavity
c. Blow excess sand
d. Repair corners in a mould
e. Flatten and smoothen the sand during moulding operation
44) When using disposable pattern the metal should be poured
a. Very slowly
b. Rather rapidly
c. At same rate as for other casting processes
d. Any rate
e. None of the above
45) The purpose of pouring basin is to
a. Feed the casting at a rate consistent with the rate of solidification
b. Act as a reservoir for molten metal
c. Help feed the casting until all solidification takes place
d. None of the above
46) Match plate pattern is used in
a. Green sand moulding
b. Bench moulding
c. Pit moulding
d. Machine moulding
e. None of the above
47) For steel casting, the following types of sand is batter
a. Fine grain
b. Coarser grain
c. Medium grain
d. All are eqaually good
e. None of the above
48) All the size of casting increases, it is often better to use increasingly
a. Fine grain
b. Medium grain
c. Coarse grain
d. Any one of the above
e. None of the above
Page8
49) The purpose of riser to
a. Feed the casting at a rate consistent with the rate of solidification
b. Act as a reservoir for molten metal
c. Help feed the casting until all solidification takes places
d. Feed molten metal from pouring basin to gate
50) Slick is
a. A round sleve
b. A long, flat metal Plate fitted with an offset handle
c. Used to make or repair corners in a mould
d. Used to scoop sand deep in the mould
51) Hot Tears refers to
a. Casting defects
b. Processes of fabrication
c. Process of heat treatment
d. Weathering of non ferrous materials
e. Strengthening of alloys
52) Slick in a foundry shop is used to
a. Make and repair corners in a mould
b. Thoroughly mix up moulding sand
c. Make venting holes in the mould
d. Prepate gates
e. Swab the edges of the mould cavity
53) True centrifugal casting
a. Is used to ensure purity and density at extremities of a casting
b. Is used to cast symmetrical objects
c. Is used to obtain high density and pure casting
d. Uses a heavy cast iron mould to act as chill
e. None of the above
54) Investment casting is used for
a. Shapes which are made by difficulty using complex pattern in sand casting
b. Mass production
c. Shapes which are very complex and intricate and cant be cast by any other
method
d. There is nothing like investment casting
e. Stainless steel parts
55) The material of pattern in the case of investment casting
a. Thermosetting resin
b. Special plastic
c. Synthetic sand
d. Wax
e. Mercury
56) Pipes subjected to very heavy pressure of the order of 100 kg/cm2 are made by
Page9
a. Electric resistant welding
b. Centrifugal casting
c. Die casting
d. Extrusion process, as seamless pipes
e. Gravity continues casting
57) Water pipes of large length and diameter are made by
a. Semi-centrifugal casting
b. Continuous casting
c. Sand casting
d. Forging
58) Which of the following processes would produce strongest components
a. Die casting
b. Hot rolling
c. Extrusion
d. Cold rolling
e. Forging
59) The runners and ingates, respectively are located as follows in casting of ferrous metals
a. In cope and in drag
b. In drag and in cope
c. Both in cope
d. Both in drag
e. In any of the above arrangements
60) In centrifugal casting cores are made of
a. Steel
b. Cast iron
c. Hard sand
d. Plastic
e. None of the above
61) Semi- centrifugal casting
a. Is used to ensure purity and density at extremities of a casting
b. Is used to cast symmetrical objects
c. Is used to obtain high density and pure casting
d. Uses heavy cast iron mould to act as chill
e. Is not used for any purpose
62) For gravity Cast iron the pattern shrinkage allowance is of the order of
a. 2 to 5 mm/m
b. 5 to 7 mm/m
c. 7 to 10.5 mm/m
d. 10.5 to 13.5 mm/m
e. 13.5 to 18 mm/m
63) Surface to be machined are marked on the pattern by the following colour
a. Black
Page10
b. Yellow
c. Red
d. Blue
e. Green
64) Colour scheme is employed on the pattern in order to identify the
a. Pattern allowances
b. Cope and drag
c. Location of core print
d. Material of pattern
e. None of the above
65) Blue colour on the pattern is marked for
a. Machineed surface
b. Unfinished surface
c. Loose piece pattern
d. Surfaces to be chilled
e. Never used in pattern making operation
66) For gray cast iron, the volumetric shrinkage is of the order of
a. 6-5 %
b. 5-3.5%
c. 3.5-2.5%
d. 1.9 to negative value
67) The pouring Temperature for grey cast iron
a. 1000C
b. 1250C
c. 1400C
d. 1550C
e. 1650C
68) Chilled surfaces are mark on the pattern by
a. Oblique red strips
b. Yellow cross strips
c. Black cross strips on yellow
d. Oblique red strips on yellow
e. None of the above
69) A large intricate heavy casting weighing in tons is to be cast. The most appropriate moulding
process would be
a. Machine moulding
b. Pit moulding
c. Cement moulding
d. Green sand moulding
e. Ceramic moulding
70) The patterns in the case of machine moulding are mounted on
a. Match plats
Page11
b. Moulding boards
c. Follow boards
d. Steel table
e. Plastic boards
71) In the die casting process
a. Molten metal is fed into the cavity in metallic mould by gravity
b. Metal is poured into die cavity and after a predetermined time the mould is inverted
to permit a part of metal still in molten state to flow out of cavity
c. Cavity is filled with a pre calculated quality of metal and core or plunger is inserted
to force the metal into cavity
d. Metal is forces into mould under high pressure
e. None of the above
72) The hot chamber die casting method is used in cast
a. Brass
b. Magnesium
c. Aluminium
d. Alloys of lead, tin and zinc
e. All of the above
73) In hot chamber method of die casting
a. Only low melting point metals can be cast
b. High melting point metal can be cast
c. Die is kept hot by electrical heating
d. Die is kept cold by circulating water
e. None of the above
74) In general the draft on the casting is of the order of
a. 1-5 mm/m
b. 5-10 mm/m
c. 10-15mm/m
d. 15-20 mm/m
e. 20-30 mm/m
75) Blind risers
a. Assist in feeding the metal into casting proper
b. Help to trap slag or other lighter partials
c. Supply the hottest metal when pouring is completed
d. Do not exist
e. None of the above
76) The allowances to be provided in disposable pattern are
a. Shrinkage and finish
b. Distortion
c. Draft
d. Shake
e. (a) and (b) above
Page12
77) Honey combing/ Sponginess refers to
a. Presence of impurities in molten metal
b. Molten metal at low temperature
c. Formation of a no. Of cavities in close proximity in a casting
d. Defects due to poor heat treatment
e. Surface defects produced during hot working
78) The sand is packed on pit mould with
a. Manually
b. Sqaueezers
c. Jolt machine
d. Sand slingers
e. Portable blowers
79) Sprue in casting refers to
a. Gate
b. Runner
c. Riser
d. Horizontal passage
e. Vertical passage
80) Which of the following casting process utilises wax pattern
a. Shell moulding
b. Plaster moulding
c. Slush moulding
d. Investment casting
e. Semi- centrifugal casting
81) In slush casting processes
a. Molten metal is fed in to the cavity in metallic mould by gravity
b. Metal is poured in to die cavity and after a predetermined time the mould is
inverted to permit a part of metal still in molten state to flow out of cavity
c. Cavity is filled with a precalulated quantity of metal and a core or plunger in inserted
to force the metal in to cavity
d. Metal is forces into mould under high pressure
e. None of the above
82) In slush casting
a. Consumable pattern are used
b. Plunger is used to force molten metal to fill up cavities
c. Vacuum is applied to facilitate complete filling of casting
d. When a solid shell of sufficient thickness has formed remaining liquid is poured out
e. Mercury is used for filling the master mould at normal temperature
83) Ornaments are cast by
a. Die casting
b. Continuous casting
c. Pressed casting
d. Centrifugal casting
Page13
e. Gravity casting
84) Statues, toys, etc are cast by
a. Die casting
b. Pressed casting
c. Centrifugal casting
d. Slush casting
e. None of the above
85) Steel and cast iron pipes are cast by
a. Die casting
b. Continous casting
c. True centrifugal casting
d. Centrifuging
e. Investment casting
86) In centrifugal casting, the impurities are
a. Uniformly distributed
b. Collected in the centre of casting
c. Forced outside the surface
d. Present in the middle section of casting
e. None of the above
87) The core in the centrifugal casting is made of
a. Carbon steel
b. Properly treated sand
c. Plastic
d. Abrasive material
e. No core is used
88) Large and heavy casting are made by
a. Green sand moulding
b. Pit moulding
c. Dry sand moulding
d. Pressure moulding
e. Machine moulding
89) The tolerance produced by the investment casting process are of the order of
a. A few microns
b. +/- 0.05 mm
c. +/- 1 mm
d. +/- 5 mm
e. None of the above
90) Sweep pattern is used for moulding parts having
a. Rectangular section
b. Elliptical shape
c. Uniform symmetrical shape
d. Complicated shape having intricate details
Page14
e. None of the above
91) Flogging in foundry practices refers to
a. A type of moulding method
b. Removal of sprues and risers
c. A non destructive testing method
d. Removal of slag during pouring
e. A casting defects
92) The internal cracks in casting can be easily found out by the following method of testing
a. Magnetic particle inspection
b. Fluorescent penetranent
c. Ultrasonic Testing
d. Dye penetrant
e. None of the above
93) The surface and subsurface cracks in non magnetic alloys can be easily located and detected
by the following inspection method
a. X- ray testing
b. Ultrasonic testing
c. Magnetic particle inspection testing
d. Dye penetrant testing
e. Any one of the above
94) Internal hot tear defects in casting can be inspected by the following method
a. Radiography
b. Visual inspection
c. Damping test
d. Fluorescent penetrant test
e. Hardness test
95) Fettling is an operation performed
a. Before casting
b. During casting
c. After casting
d. After heat treatment
e. Before heat treatment
96) Shell moulding process requires
a. Wooden pattern
b. Sand pattern
c. Plastic pattern
d. Metal pattern
e. None of the above
97) Slag inclusion in casting is a
a. Surface defect
b. Internal defect
c. Crack
Page15
d. Notch
e. No defect
98) Core Prints are used to
a. Strengthen core
b. Form seat to support and hold the core in place
c. Fabrication core
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
99) Jolt machine produce
a. Uniform ramming about the pattern
b. Uniform ramming about the flask
c. Uniform distribution throughout
d. Pack sand loosely all around
e. None of the above
100) Blow holes are casting defects
a. Which occur due to some sand shearing from the cope surface
b. Which take the form of internal voids or surface depression due to excessive
gaseous material not able to escape
c. Which occur due to discontinuity in metal casting resulting from hindered
contraction
d. Caused by two streams of metals that are too cold to fuse properly
e. None of the above
101) Which is the most widely used metal for casting
a. Aluminium
b. Brass
c. Magnesium alloys
d. Cast iron
102) For small and intricate casting the sand grains should be
a.Fine
b.Medium
c. Coarse
d.Rounded
103) Permeability is poor for
a.Fine grains
b.Medium grains
c. Coarse grains
d.Rounded grains
104) Match the appropriate combination between foundry tools
Foundry tool The purpose served by them
Swab Repairing and finishing the mould
Slick Reinforcement of sand in the top part of the
moulding box
Page16
Lifter Moistening the sand around the edges before
removing the pattern
Riddle Smoothing and cleaning out depressions in the
mould
105) Which of the following in not foundry tool?
a. Trowel
b. Arbour
c. Riddle
d. Slick
106) Chaplets in the foundry practice are used to
a. Provide efficient venting
b. Ensure directional solidification
c. Support the core
d. Reinforce the sand in the top part of the moulding box
107) The wood pattern used for the production of a metal is called
a. Master
b. Skelton
c. Duplicate
d. Investment
108) Metal patterns are used for
a. Small casting
b. Large casting
c. Precise and intricate casting
d. Large scale production casting
109) The surface to be left un-machined is marked on the pattern by
a. Green colour
b. Black colour
c. Yellow colour
d. Blue colour
110) Wax pattern is used in
a. Shell moulding
b. Die casting
c. Investment casting
d. Centrifugal casting
111) Carburettors are manufactured by
a. Fine sand casting
b. Die casting
c. Slush casting
d. Shell moulding
112) Hollow casting of desired thickness are producted by a permanent mould without
used of cores in
Page17
a. Machine moulding
b. Slush casting
c. Pressed casting
d. Investment casting
113) The most preferred process for casting gas turbine blades is (IES- 97)
a. Die moulding
b. Shell moulding
c. Investment casting
d. Sand casting
114) The plastic articles are usually produced by
a. Shell moulding
b. Green sand moulding
c. Plaster moulding
d. Injection casting
115) Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
Aluminium Pressure die casting
Jewellery Lost wax process
Large Pipes Centrifugal Casting
Large Bells Loam Moulding
116) Two streams of metal that are not hot enough to fuse properly result into a casting
defect known as
a. Cold shots
b. Swell
c. Shrinkage
d. Sand wash
117) Match 4 correct pairs between list-1 and 2
Processes Products
Investment Casting Turbine Rotor
Die Casting Turbine Blades
Centrifugal Casting Connecting Rods
Drop Forging Cast Iron Pipes
Caruretter Body
Find the answer...
118) Wax Pattern is used
a. Shell moulding
b. Die casting
c. Investment casting
d. Centrifugal casting
119) The vertical surfaces of a pattern are provided a taper known as ________
allowance
a. Distortion
b. Machining
c. Draft
d. Shrinkage
Page18
120) Which is the negative allowance in the pattern making of sand casting
a. Distortion
b. Machining
c. Draft
d. Shrinkage
e. Rapping
121) They Binder in case of synthetic sand is
a. Clay
b. Water
c. Molasses
d. Bentonite and water
122) In the sand moulding top flask is known as
a. Cope
b. Drag
c. Fillet
d. Cheek
123) In the sand moulding the bottom flask is known as
a. Cope
b. Drag
c. Fillet
d. Cheek
124) Match plate pattern is used in
a. Green sand moulding
b. Bench moulding
c. Pit moulding
d. Machine moulding
e. None of the above
125) In order to facilitate the withdrawal of pattern
a. Pattern is made smooth
b. Water is applied on pattern surface
c. Allowances are made on the pattern
d. Draft is provided on Pattern
e. Withdrawing facilities are provided
126) Slick in a foundry shop is used to
a. Make and repair corners in a mould
b. Thoroughly mix up moulding sand
c. Make venting holes in the mould
d. Prepare gates
e. Swab the edges of the mould cavity
==================================================================================
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Continuous casting The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideDe la EverandContinuous casting The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 PDFDocument199 pagini3 PDFsanku surya sai charanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Pump ReportDocument15 paginiWater Pump ReportMohammed BashierÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelDe la EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sand Casting: Pouring Cup Cope Down Sprue RiserDocument71 paginiSand Casting: Pouring Cup Cope Down Sprue Riservenkat4Încă nu există evaluări
- Discrete Element Method to Model 3D Continuous MaterialsDe la EverandDiscrete Element Method to Model 3D Continuous MaterialsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Casting Project 1Document18 paginiCasting Project 1tamertunali100% (1)
- Casting Fundamentals DesignDocument35 paginiCasting Fundamentals DesignRia Sharma0% (1)
- Gating Ratio: Choke EffectDocument9 paginiGating Ratio: Choke EffectSiddhant SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 2202 - PPP Casting-03Document63 paginiME 2202 - PPP Casting-03Satyajeet SahooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 FurnacesDocument36 paginiChapter 4 FurnacesMohamed AlkharashyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piston ManufacturingDocument41 paginiPiston ManufacturingDima AlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Core CastingDocument27 paginiCore Castingchetan100% (1)
- Training ModuleDocument44 paginiTraining ModulegereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tolerances For Aluminium Die CastingsDocument3 paginiTolerances For Aluminium Die CastingsShankar V IyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME2121 - ME2121E Slides Chapter 1 (2014)Document13 paginiME2121 - ME2121E Slides Chapter 1 (2014)FlancÎncă nu există evaluări
- Casting Slides 103-130Document28 paginiCasting Slides 103-130Swaraj PrakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manufacturing Process-I (Casting)Document25 paginiManufacturing Process-I (Casting)Rahul Deb PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dry Sand MouldingDocument3 paginiDry Sand Mouldingরিপন মন্ডলÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: Qualitative ProblemsDocument14 paginiFundamentals of Metal Casting: Qualitative ProblemsEspen KolåsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metal Casting Process - 3Document11 paginiMetal Casting Process - 3kiran_wakchaureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elementary Statics and DynamicsDocument15 paginiElementary Statics and DynamicsPooja Bk0% (1)
- Metal CastingDocument8 paginiMetal CastingYash DesaaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction Injection MoldingDocument8 paginiReaction Injection MoldingAmeer_Takashim_9385Încă nu există evaluări
- Design of Components With Casting ConsiderationsDocument49 paginiDesign of Components With Casting ConsiderationsOrville SutariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cleaness Steel CastingDocument61 paginiCleaness Steel CastingSUNDRAMNAGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProjectDocument14 paginiProjectoladipo GraceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vinodhini B. - Mercury PorosimetryDocument35 paginiVinodhini B. - Mercury PorosimetryHarry JakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11-Metal Casting ProcessesDocument80 paginiChapter 11-Metal Casting ProcessesMuhammad Qasim QureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Integrated Taguchi and TOPSIS Method For Optimization of Process Parameters For Dimensional Accuracy in Turning of EN25 SteelDocument9 paginiApplication of Integrated Taguchi and TOPSIS Method For Optimization of Process Parameters For Dimensional Accuracy in Turning of EN25 SteelKenan MuhamedagicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advan Machining SLDNDocument4 paginiAdvan Machining SLDNmhuzaimi77Încă nu există evaluări
- Ch-21 Sand CastingDocument156 paginiCh-21 Sand CastingMANJEET KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risers Design Unit-IDocument24 paginiRisers Design Unit-IQUAZI ADYAN AHMAD 160419736049Încă nu există evaluări
- IE 337 W10 Lecture 7.casting 1Document48 paginiIE 337 W10 Lecture 7.casting 1linkinunÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Runner-Gate Design System For Die CastingDocument4 paginiA Runner-Gate Design System For Die CastingDiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- M - I U - 1 C P: Anufacturing Processes NIT Asting RocessesDocument246 paginiM - I U - 1 C P: Anufacturing Processes NIT Asting RocessesMahesh SalotagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundry Technology QuestionsDocument2 paginiFoundry Technology Questionsshady_hrn100% (1)
- Core Sand MaterialDocument20 paginiCore Sand MaterialsudhirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metal Casting Design: Mold and Gating System Design, Directional Solidification, and TroubleshootingDocument7 paginiMetal Casting Design: Mold and Gating System Design, Directional Solidification, and TroubleshootingzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compensation To Opening BC BhattacharyaDocument18 paginiCompensation To Opening BC BhattacharyaRADHE GRAPHICSÎncă nu există evaluări
- PM 2 LibroDocument18 paginiPM 2 LibrolupitagonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringDocument19 paginiSudipta Nath: Materials EngineeringSudipta NathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of Resin Coated Sand: Ravi AutosDocument5 paginiDevelopment of Resin Coated Sand: Ravi AutosInsan KamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- MOULDINGDocument35 paginiMOULDINGsumitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Riser Casting ReportDocument47 paginiRiser Casting Reportganesh0% (1)
- Product Design For Sand CastingDocument10 paginiProduct Design For Sand CastingChinmay Das100% (7)
- Working With The Cold Box ProcessDocument21 paginiWorking With The Cold Box ProcessAnonymous iztPUhIiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingot StructureDocument5 paginiIngot StructureklawsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production of Automotive Components: Jerome GDocument24 paginiProduction of Automotive Components: Jerome GMr. Jerome Nithin Gladson100% (1)
- Copper TubesDocument9 paginiCopper TubesVarun AbrolÎncă nu există evaluări
- MT-2 Core MaterialsDocument3 paginiMT-2 Core MaterialsRavasaheb BholeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Calculation of Worm and Worm Gear Tangential LoadDocument5 paginiDesign Calculation of Worm and Worm Gear Tangential LoadVenkateswaran venkateswaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example For Milling CalculationDocument3 paginiExample For Milling CalculationAbd Muhaimin AmmsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Metal Casting ProcessDocument8 paginiIntroduction To Metal Casting ProcessRiya PanwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crane Ball ValveDocument20 paginiCrane Ball ValveRicardo de Jesus Rondon GamboaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial CastingDocument4 paginiTutorial CastingFaIz FauziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aor 41-82Document122 paginiAor 41-82Engr SwapanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forgingforging ProcessDocument13 paginiForgingforging Processpatel ketanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15ume302 - MT - I BankDocument17 pagini15ume302 - MT - I BankKARTHICK MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advances in Mechanical Engineering ME 702Document2 paginiAdvances in Mechanical Engineering ME 702Atul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimization of Process Parameters of Al2024-Sic Composite On Quality Characteristics in End MillingDocument2 paginiOptimization of Process Parameters of Al2024-Sic Composite On Quality Characteristics in End MillingAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mody University of Science and TechnologyDocument1 paginăMody University of Science and TechnologyAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- End Term-Back Paper-Engineering Mechanics - Spring 2013Document3 paginiEnd Term-Back Paper-Engineering Mechanics - Spring 2013Atul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mos Lab ManualDocument71 paginiMos Lab ManualAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- TeachingDocument2 paginiTeachingAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mody Institute of Technology and Science, Lakshmangarh Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument2 paginiMody Institute of Technology and Science, Lakshmangarh Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuously Variable Transmission CVT 1Document8 paginiContinuously Variable Transmission CVT 1Atul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mody Institute of Technology and Science, Lakshmangarh Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument3 paginiMody Institute of Technology and Science, Lakshmangarh Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Mechanics NotesDocument111 paginiEngineering Mechanics NotesAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbon Steel: StressDocument3 paginiCarbon Steel: StressAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- QP Material Science and MetallurgyDocument2 paginiQP Material Science and MetallurgyAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Chapter8Document51 paginiRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Chapter8Richard Weimer100% (2)
- Non Circular GearsDocument1 paginăNon Circular GearsAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mody Institute of Technology and Science, Lakshmangarh Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument1 paginăMody Institute of Technology and Science, Lakshmangarh Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Library RulesDocument2 paginiLibrary RulesAtul GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam NozzleDocument1 paginăSteam NozzleAtul Gaur100% (1)
- ArrowrootDocument8 paginiArrowrootSevi CameroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auto Turn-Off For Water Pump With Four Different Time SlotsDocument3 paginiAuto Turn-Off For Water Pump With Four Different Time SlotsKethavath Sakrunaik K100% (1)
- Uh 60 ManualDocument241 paginiUh 60 ManualAnonymous ddjwf1dqpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yarn HairinessDocument9 paginiYarn HairinessGhandi AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mother Tongue K To 12 Curriculum GuideDocument18 paginiMother Tongue K To 12 Curriculum GuideBlogWatch100% (5)
- Course DescriptionDocument54 paginiCourse DescriptionMesafint lisanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Contemporary Fibers in Apparel - LyocellDocument5 paginiApplication of Contemporary Fibers in Apparel - LyocellVasant Kothari100% (1)
- Reference by John BatchelorDocument1 paginăReference by John Batchelorapi-276994844Încă nu există evaluări
- Essay Final ProjectDocument7 paginiEssay Final Projectapi-740591437Încă nu există evaluări
- Rs2-Seamanship (Inc Anchoring, Mooring, Berthing, Pilot Ladder)Document19 paginiRs2-Seamanship (Inc Anchoring, Mooring, Berthing, Pilot Ladder)Mdpn. Salvador67% (3)
- Participatory EvaluationDocument4 paginiParticipatory EvaluationEvaluación Participativa100% (1)
- Mangement of Shipping CompaniesDocument20 paginiMangement of Shipping CompaniesSatyam MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Description of Function For Every Unit OperationDocument3 paginiProcess Description of Function For Every Unit OperationMauliduni M. AuniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Empanelled Hospitals List Updated - 06-12-2022 - 1670482933145Document19 paginiEmpanelled Hospitals List Updated - 06-12-2022 - 1670482933145mechmaster4uÎncă nu există evaluări
- University Fees Structure (Himalayan Garhwal University) - UttarakhandDocument1 paginăUniversity Fees Structure (Himalayan Garhwal University) - UttarakhandabhaybaranwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zigbee Technology:19-3-2010: Seminor Title DateDocument21 paginiZigbee Technology:19-3-2010: Seminor Title Dateitdep_gpcet7225Încă nu există evaluări
- XU-CSG Cabinet Minutes of Meeting - April 4Document5 paginiXU-CSG Cabinet Minutes of Meeting - April 4Harold John LaborteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Designing An Active Directory InfrastructureDocument18 paginiIntroduction To Designing An Active Directory InfrastructurepablodoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- English For General SciencesDocument47 paginiEnglish For General Sciencesfauzan ramadhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AAR Shell ProgrammingDocument13 paginiAAR Shell ProgrammingMarimuthu MuthaiyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- UBMM1011 Unit Plan 201501Document12 paginiUBMM1011 Unit Plan 201501摩羯座Încă nu există evaluări
- D. Das and S. Doniach - Existence of A Bose Metal at T 0Document15 paginiD. Das and S. Doniach - Existence of A Bose Metal at T 0ImaxSWÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Modern Equipment and Farm ToolsDocument15 paginiList of Modern Equipment and Farm ToolsCarl Johnrich Quitain100% (2)
- Current Surgical Therapy 13th EditionDocument61 paginiCurrent Surgical Therapy 13th Editiongreg.vasquez490100% (41)
- Asu 2019-12Document49 paginiAsu 2019-12janineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ged 102 Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument84 paginiGed 102 Mathematics in The Modern WorldKier FormelozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are Some of The Best Books On Computer ScienceDocument9 paginiWhat Are Some of The Best Books On Computer ScienceSarthak ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- A2 UNIT 5 Culture Teacher's NotesDocument1 paginăA2 UNIT 5 Culture Teacher's NotesCarolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LSL Education Center Final Exam 30 Minutes Full Name - Phone NumberDocument2 paginiLSL Education Center Final Exam 30 Minutes Full Name - Phone NumberDilzoda Boytumanova.Încă nu există evaluări
- VerificationManual en PDFDocument621 paginiVerificationManual en PDFurdanetanpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simplified Organization: Learn to Love What Must Be DoneDe la EverandSimplified Organization: Learn to Love What Must Be DoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- House Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetDe la EverandHouse Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eat That Frog!: 21 Great Ways to Stop Procrastinating and Get More Done in Less TimeDe la EverandEat That Frog!: 21 Great Ways to Stop Procrastinating and Get More Done in Less TimeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3226)
- Root to Leaf: A Southern Chef Cooks Through the SeasonsDe la EverandRoot to Leaf: A Southern Chef Cooks Through the SeasonsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Edward's Menagerie New Edition: Over 50 easy-to-make soft toy animal crochet patternsDe la EverandEdward's Menagerie New Edition: Over 50 easy-to-make soft toy animal crochet patternsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldDe la EverandThe Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (5)
- Summary of Goodbye, Things: The New Japanese Minimalism by Fumio SasakiDe la EverandSummary of Goodbye, Things: The New Japanese Minimalism by Fumio SasakiEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (5)
- Clean Mama's Guide to a Healthy Home: The Simple, Room-by-Room Plan for a Natural HomeDe la EverandClean Mama's Guide to a Healthy Home: The Simple, Room-by-Room Plan for a Natural HomeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- How To Win Friends And Influence PeopleDe la EverandHow To Win Friends And Influence PeopleEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6520)
- Lightly: How to Live a Simple, Serene & Stress-free LifeDe la EverandLightly: How to Live a Simple, Serene & Stress-free LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (12)
- The Gentle Art of Swedish Death Cleaning: How to Free Yourself and Your Family from a Lifetime of ClutterDe la EverandThe Gentle Art of Swedish Death Cleaning: How to Free Yourself and Your Family from a Lifetime of ClutterEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (467)
- 100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiDe la Everand100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Crochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!De la EverandCrochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (10)
- The Fitness Mindset: Eat for energy, Train for tension, Manage your mindset, Reap the resultsDe la EverandThe Fitness Mindset: Eat for energy, Train for tension, Manage your mindset, Reap the resultsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (31)
- Permaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreDe la EverandPermaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (33)
- How to Keep House While Drowning: A Gentle Approach to Cleaning and OrganizingDe la EverandHow to Keep House While Drowning: A Gentle Approach to Cleaning and OrganizingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (847)
- Crochet Zodiac Dolls: Stitch the horoscope with astrological amigurumiDe la EverandCrochet Zodiac Dolls: Stitch the horoscope with astrological amigurumiEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Aristotle and Dante Discover the Secrets of the UniverseDe la EverandAristotle and Dante Discover the Secrets of the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2341)
- Crochet Southwest Spirit: Over 20 Bohemian Crochet Patterns Inspired by the American SouthwestDe la EverandCrochet Southwest Spirit: Over 20 Bohemian Crochet Patterns Inspired by the American SouthwestEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- The Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingDe la EverandThe Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (11)
- Minimalism: Minimalism for Beginners. How to Live Happy While Needing Less in This Modern Material WorldDe la EverandMinimalism: Minimalism for Beginners. How to Live Happy While Needing Less in This Modern Material WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (39)
- The Life-Changing Magic of Tidying Up: The Japanese Art of Decluttering and OrganizingDe la EverandThe Life-Changing Magic of Tidying Up: The Japanese Art of Decluttering and OrganizingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2997)
- It's All Too Much: An Easy Plan for Living a Richer Life with Less StuffDe la EverandIt's All Too Much: An Easy Plan for Living a Richer Life with Less StuffEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (232)
- Success at Home with ADHD.: Practical Organization Strategies to Make Your Life Easier.De la EverandSuccess at Home with ADHD.: Practical Organization Strategies to Make Your Life Easier.Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (17)
- Crochet Creatures of Myth and Legend: 19 Designs Easy Cute Critters to Legendary BeastsDe la EverandCrochet Creatures of Myth and Legend: 19 Designs Easy Cute Critters to Legendary BeastsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (10)
- The 21 Irrefutable Laws of Leadership 25th Anniversary: Follow Them and People Will Follow YouDe la EverandThe 21 Irrefutable Laws of Leadership 25th Anniversary: Follow Them and People Will Follow YouEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (417)
- Swatch This, 3000+ Color Palettes for Success: Perfect for Artists, Designers, MakersDe la EverandSwatch This, 3000+ Color Palettes for Success: Perfect for Artists, Designers, MakersEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)