Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Paper
Încărcat de
Vinicius SouzaDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Paper
Încărcat de
Vinicius SouzaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Adv. Eng. Tec. Appl. 7, No. ?, 1-??
(2013) 1
Advanced Engineering Technology and Application
An International Journal
http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/aeta/paper
COMPUTER SIMULATION OF OIL DISPERSION IN
RIVERS IN BRAZIL FOLLOWING A SPILL: A case study
involving the Berigui and Iguau Rivers
Vincius Alexandre Sikora de Souza
1
and Assed Naked Haddad
2
1
Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil
2
Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil
Received: 7 Jun. 2012, Revised: 21 Sep. 2012, Accepted: 23 Sep. 2012
Published online: 1 Jan. 2013
Abstract: This study analyzed the dispersion of oil leaked from the Presidente Getlio Vargas Renery in 2000 into the Iguau and
Berigui Rivers, both in the State of Paran, Brazil. We studied three (3) ow scenarios: the rst with the values observed on the day of
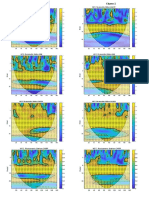
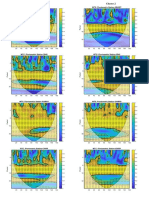
the accident, the second utilizing peak values and the third, using low ow. We used Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) to simulate
propagation of the plume. The plume showed a greater spread during the maximum ow of water, while for less ow, less dispersion
of oil occurred. These results show that in situations of low ow, adoption of measures aimed at mitigating environmental damage
(containment and recovery of spilled oil) are easier than recovery of spilled oil dispersed in the plume at high ow.
Keywords: oil spill, dispersion, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
1 Introduction
Surface water sources have multiple uses, especially
supply for human consumption [?,?]. Beyond this, other
uses also deserve mention because of their importance in
agricultural and industrial use, primarily watering
livestock and recreation. Water for each of these sectors
should be available in quantity, but it is also essential that
quality characteristics are appropriate for the use
[?].Environmental degradation of water resources has
limited the use of potential water sources.
The current commitment of resources, having utilized
watercourses that drain urban centers has eliminated
sources with great potential to supply metropolitan areas
[?]. Degradation of the quality aspects of these water
bodies occurs mainly by discharges of wastewater from
industrial and diffuse sources [?].
Environmental accidents are also responsible for the
deterioration of water resources. The oil spill in the
stream in Sardenha, discussed here, occurred in 2000 in
the metropolitan region of Curitiba. The spill of oil and its
derivatives into water bodies, in addition to causing
pollution of these water resources, is responsible for
environmental damage. As [?] discuss, oil has
characteristics harmful to exposed organisms and may
cause chronic effects even in low concentration. These
authors also emphasize that the impact of oil spills is not
necessarily related to volume, as small leakages can result
in considerable damage to the contaminated areas and
bodies of water exposed.
The recent problems of quantity and quality, mainly
observed in surface waters, showed that availability is not
innite and degradation capacity is limited [?]. Because
of this problem, researchers recently have used models to
predict degradation of water quality of rivers and lakes
from point sources, and highlight problems involving
domestic efuents. Although water quality models are
common, simulation of the impacts of accidental
discharges, such as oil spills, is undergoing development.
Study of these models is highly relevant to predict
damage to aquatic fauna and water quality, and generate
information simulating scenarios of environmental
pollution and the effect of mitigation measures on the
quality of water resources.
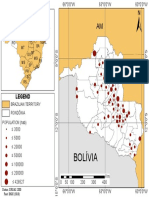
This study evaluates the dispersion in the Berigui and
Iguau Rivers of 4000 m of crude oil (Cusiana - 41,
American Petroleum Institute) for 2 hours in July 2000 in
Corresponding author e-mail: vinicius@coc.ufrj.br
c 2013 NSP
Natural Sciences Publishing Cor.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Eia ReportDocument185 paginiEia ReportClement Song Hua Ong100% (3)
- The Upward Flow of Human Development: Title: DateDocument36 paginiThe Upward Flow of Human Development: Title: DateBlessolutions100% (1)
- Analise de Tendencia para Dados Pluviometricos NoDocument10 paginiAnalise de Tendencia para Dados Pluviometricos NoVinicius SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LOCpoproDocument1 paginăLOCpoproVinicius SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WTC: Pluviometric Station-3B42RT WTC: Pluviometric Station-3B42RTDocument5 paginiWTC: Pluviometric Station-3B42RT WTC: Pluviometric Station-3B42RTVinicius SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WTC PDFDocument5 paginiWTC PDFVinicius SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determinação de Processos Hidrossedimentológicos em Uma Bacia Hidrográfica Pouco Monitorada Da Amazônia Ocidental - Rio MachadinhoDocument2 paginiDeterminação de Processos Hidrossedimentológicos em Uma Bacia Hidrográfica Pouco Monitorada Da Amazônia Ocidental - Rio MachadinhoVinicius SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SuaContaClaro Ago 16Document1 paginăSuaContaClaro Ago 16Vinicius SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spatio-Temporal Rainfall Variability in The Amazon Basin Countries (Brazil, Peru, Bolivia, Colombia, and Ecuador)Document21 paginiSpatio-Temporal Rainfall Variability in The Amazon Basin Countries (Brazil, Peru, Bolivia, Colombia, and Ecuador)Vinicius SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling of Water QualityDocument146 paginiModeling of Water QualityMartin Daniel Palacios QuevedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3Document8 paginiModule 3LA Marie100% (5)
- Aeronautical Engineering PDFDocument137 paginiAeronautical Engineering PDFsabbithiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Small Water Impounding Project SWIPDocument2 paginiSmall Water Impounding Project SWIPAnonymous dtceNuyIFI100% (1)
- Analytical Calculation Methods of Riverbank FiltrationDocument6 paginiAnalytical Calculation Methods of Riverbank FiltrationLuiz Alves0% (1)
- The Five Grim LakesDocument26 paginiThe Five Grim LakesChristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Ways To Conserve Water at HomeDocument2 paginiBest Ways To Conserve Water at HomePerly PeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aklilu MegeboDocument108 paginiAklilu Megeboteme beyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factsheet STADocument2 paginiFactsheet STAhuyarchitect89Încă nu există evaluări
- Swmi Scotland MainDocument158 paginiSwmi Scotland MainghjdsjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kumarakom Specific PDFDocument15 paginiKumarakom Specific PDFJacob K PhilipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidrologi - Struktur Dan PeralatanDocument277 paginiHidrologi - Struktur Dan PeralatanAlanMahmoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presidential Decree No. 1067 Water Code of The Philippines BackgroundDocument23 paginiPresidential Decree No. 1067 Water Code of The Philippines BackgroundJoanne besoy100% (1)
- B.SC - GeographyDocument20 paginiB.SC - GeographyArjun ParmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrology D 19 00079 PDFDocument25 paginiHydrology D 19 00079 PDFBikas C. BhattaraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ran2b PDFDocument152 paginiRan2b PDFCesar YamutaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sociology PPT FinalDocument26 paginiSociology PPT Finalarsalkhan_superÎncă nu există evaluări
- IFC's Commitment To Water & Wastewater in Emerging MarketsDocument14 paginiIFC's Commitment To Water & Wastewater in Emerging MarketsADBI EventsÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Far Are We Along The Path To A Green Economy?Document10 paginiHow Far Are We Along The Path To A Green Economy?ABC News OnlineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Repsol's Clearwater River Water Licence ApplicationDocument32 paginiRepsol's Clearwater River Water Licence ApplicationThe NarwhalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 3Document9 paginiTest 3Anonymous KewVAoFYeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DhuleDocument19 paginiDhuleBobby MathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete ES1 2023 Vol1Document334 paginiComplete ES1 2023 Vol1Chandu SeekalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S004896971732973X MainDocument14 pagini1 s2.0 S004896971732973X MainBrhane YgzawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two Minute Thesis and Poster Abstracts2Document160 paginiTwo Minute Thesis and Poster Abstracts2Zeyu YaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitigating Climate Change Related Floods in Urban Poor Areas. Green Infrastructure ApproachDocument15 paginiMitigating Climate Change Related Floods in Urban Poor Areas. Green Infrastructure ApproachFahmy AtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albert Zambrano Rising Core House Espasyo2009xDocument102 paginiAlbert Zambrano Rising Core House Espasyo2009xalbertsantoszambrano100% (2)
- English Notes 10th ClassDocument12 paginiEnglish Notes 10th ClassAqeel Ahmad100% (1)