Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Hkcee Biology - 4.5 Gas Exchange in Humans - P.1
Încărcat de
irisyyy27Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Hkcee Biology - 4.5 Gas Exchange in Humans - P.1
Încărcat de
irisyyy27Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
80
1. 1990/I/1b
The graph below shows the changes in air pressure in the lungs of a man measured during a single breath at
rest. The atmospheric pressure was at 760 mm Hg.
(i) Sate the period of time during which the man was breathing out air ? Explain how you arrive at your
answer. (2 marks)
(ii) Describe how the actions of the respiratory muscles brought about the changes in air pressure in the
lungs when the man was breathing out. (4 marks)
(iii) Describe the rate of breathing of the man at rest. (1 mark)
(iv) Copy the axes of the graph above and sketch a curve showing the likely changes in the air pressure
in his lungs when the man is exercising. (2 marks)
2. 1991/I/3c
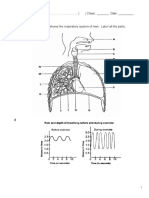
The diagram below shows part of the human respiratory system :
(i) Name the ring-like structure A. State its function. (2 marks)
(ii) (1) Name the structures labelled B. (1 mark)
(2) Explain why the lung will collapse if structure B is punctured in an accident. (2 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.5 Gas exchange in humans | P.1
81
(iii) What would happen to muscle C when a person tries to breathe out as much air as possible ?
(1 mark)
(iv) Explain how each of the following features of the alveoli facilitate gaseous exchange in the lungs :
(1) one-cell thick
(2) greatly folded
(3) moist (3 marks)
(v) Cigarette smoke may inhibit the beating of the cilia in the respiratory tract. Explain how this could
reduce the efficiency of the lungs in gaseous exchange. (2 marks)
3. 1992/I/3c
A student was asked to perform a physical exercise. Before and after the exercise, he rested on a chair. His
breathing rate was measured at intervals. The results are shown in the graph below :
(i) What is the increase in the breathing rate as a result of the exercise ? (1 mark)
(ii) Explain the significance of such an increase in the breathing rate. (3 marks)
(iii) Describe and explain the mechanism of inspiration (breathing in). (5 marks)
(iv) Besides becoming faster, what other change in the breathing movement would occur during exercise ?
(1 mark)
4. 1992/I/4civ
Describe how the body can prevent the entry of respirable suspended particles. (5 marks)
5. 1995/I/2a
The table below shows the breathing rate and the volume of air inhaled per breath of a healthy woman at
rest and during exercise :
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.5 Gas exchange in humans | P.2
82
At rest During exercise
Breathing rate
(times per minute)
18 36
Volume of air inhaled per breath
(cm
3
)
500 1000
Ventilation rate
(cm
3
per minute)
9000 ?
(i) Calculate the ventilation rate of the woman during exercise. (2 marks)
(ii) Explain the significance of the increase in ventilation rate during exercise. (4 marks)
(iii) The air inhaled by the woman contains lots of dust particles but very few of them reach her lungs.
Explain why. (3 marks)
(iv) Draw and label a set-up to estimate the volume of air exhaled in a breath. (3 marks)
6. 1997/I/2a
The photograph below show the sections of the lung tissues of a cigarette smoker and a non-smoker
observed under the microscope with the same magnification :
(i) What is structure A ? (1 mark)
(ii) Describe and explain the mechanism by which air from the atmosphere is drawn into structure A.
(4 marks)
(iii) With reference to the photographs, explain how the function of structure A is affected by cigarette
smoking. (2 marks)
(iv) (1) State a disease which may be caused by tar in cigarette smoke. (1 mark)
(2) Draw a labelled diagram of a set-up used to show the presence of tar in cigarette smoke.
(3 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.5 Gas exchange in humans | P.3
83
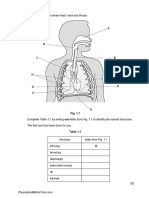
7. 2000/I/1c
The diagram below shows the structure of an air sac of the human lung. The tidal air refers to the air that can
be breathed in and out of the body in each breath. The residual air refers to the air that cannot be exchanged
with the atmosphere during breathing.
(i) Describe how oxygen in the tidal air reaches the blood. (3 marks)
(ii) (1) If a person breathes deeply, how will the volume of tidal air inhaled be affected ? (1 mark)
(2) Based on your answer to (1), explain the effect of deep breathing on the rate of oxygen uptake
in the blood. (2 marks)
(iii) Explain one effect of smoking on the process described in (i). (2 marks)
8. 2001/I/4b
The graph below shows the changes in lung volume of a boy at rest over a period of 30 seconds :
(i) Determine the rate and depth of breathing of the boy at rest. (2 marks)
(ii) State the period of time in the first 5 seconds during which air was flowing out of the lungs.
(1 mark)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.5 Gas exchange in humans | P.4
84
(iii) Explain how the outflow of air from the lungs was brought about by the breathing mechanism.
(4 marks)
(iv) If the pleural membrane on the left side of the boys thorax is punctured, his left lung will collapse
while his right lung will not. What would be the change in
(1) his breathing movement, (1 mark)
(2) the air flow of his left and right lungs ? (2 marks)
9. 2003/I/1ai-iv
To study the effect of concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide on the breathing rate, a healthy person
was asked to inhale different gas mixtures. The results are shown in the table below :
Concentration of gas (%) Gas mixture
Oxygen Carbon dioxide
Breathing rate
(breaths per min)
P 21 0.03 17
Q 21 4.00 34
R 16 0.03 17
S 16 4.00 34
(i) With reference to the above information, state the factor that affects the breathing rate of the person.
Explain how you arrive at your answer. (3 marks)
(ii) Which of the four gas mixtures has similar concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide as exhaled
air ? (1 mark)
(iii) Mouth-to-mouth ventilation is a method for rescuing a person who fails to breathe but still has
heartbeat. It involves blowing exhaled air into the patient's body through the mouth as shown below :
Based on the composition of exhaled air, explain why this method can help the patient stay alive
before he can breathe again. (2 marks)
(iv) Suggest why it is necessary to do the following when carrying out mouth-to-mouth ventilaton :
(1) Tilt the patient's head as shown in the diagram, instead of letting it lie flat. (1 mark)
(2) Observe whether the patient's chest rises when blowing air into the patient. (1 mark)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.5 Gas exchange in humans | P.5
85
10. 2004/I/1ci,ii
The diagram below shows an air sac of the lung and its blood supply :
(i) Explain the importance of the water film in gaseous exchange. (2 marks)
(ii) SARS patients may have fluid accumulated in the air sac. Explain how the accumulation of fluid
may affect the oxygen content of the blood of the patients. (3 marks)
11. 2005/I/4
The photomicrograph below shows a section of a mammalian lung:
(a) With reference to two features observable in the photomicrograph, explain how the lung tissue is
adapted to gas exchange. (4 marks)
(b) Oxygen moves continuously from the air in A into the capillaries. However, the oxygen content in A
remains relatively high. Explain how this is achieved. (2 marks)
(c) Eric wanted to compare the oxygen content of atmospheric air and exhaled air, so he prepared two jars
of gas as shown below:
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.5 Gas exchange in humans | P.6
86
(i) Draw a labelled diagram to show a set-up that can be used to collect the air exhaled from his
lungs. (4 marks)
(ii) Describe what Eric should do in order to compare the oxygen content of the two air samples.
(2 marks)
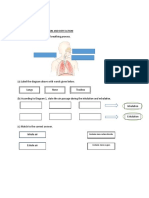
12. 2008/I/3
The following diagram shows part of the human respiratory system.
(a) Name structure X and describe its function. (3 marks)
(b) Construct a flowchart to show the path of air passing from the atmosphere to the air sacs of the lungs.
(2 marks)
(c) Asthma is a respiratory disease. When it attacks, structure Y constricts and the patient will have
breathing difficulty. Explain the effect of asthma on the rate of removal of carbon dioxide from the
blood of the lungs. (4 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 4.5 Gas exchange in humans | P.7
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument9 paginiGas Exchange in HumanscherylrachelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Revision WorksheetDocument2 paginiBiology Revision WorksheetskeltenboiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFDocument7 paginiChapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFben martin100% (1)
- F3 Topic 11 & 12 PracticeDocument10 paginiF3 Topic 11 & 12 PracticePianna IeongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Revision Exercise - Answer KeyDocument11 paginiBio Revision Exercise - Answer Keynmhk89100% (1)
- Hkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1Document13 paginiHkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- Solved Ig-Ii Vle Assignment RespirationDocument5 paginiSolved Ig-Ii Vle Assignment RespirationhelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Previous Year Problems: Topic Name: RespirationDocument5 paginiPrevious Year Problems: Topic Name: RespirationAtharv AggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument2 paginiBreathing and Exchange of Gasessherilmary7Încă nu există evaluări
- Respiration Worksheet 1 With AnswersDocument4 paginiRespiration Worksheet 1 With AnswersshannonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul4Document15 pagini07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul4Komalesh TheeranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class11 Biology Chapter 17. BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESDocument5 paginiClass11 Biology Chapter 17. BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESrn0828027Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio4 5Document11 paginiBio4 5HarmonyChuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daily Lesson Plan of Science Form 3: (SPS Activity 1.1)Document2 paginiDaily Lesson Plan of Science Form 3: (SPS Activity 1.1)T Ibrahim T SohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument38 paginiGas Exchange in HumansGift Blessed NgoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 11 WS2 IGCSE Bio 11.01Document6 paginiChap 11 WS2 IGCSE Bio 11.01ipradhiputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam March 2010 Aviation Human Factors Question BankDocument7 paginiFinal Exam March 2010 Aviation Human Factors Question Banknikhil0% (1)
- Breathing QuestionsDocument1 paginăBreathing QuestionsAgagwa AgagwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Past PaperDocument6 paginiBio Past Paperzwindows123456789Încă nu există evaluări
- Respiration WorksheetDocument4 paginiRespiration WorksheetAshley BedassieÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2324 2nd S4理 WS 3Document5 pagini2324 2nd S4理 WS 3kitkitsousouÎncă nu există evaluări
- FCA (SA) Part I Past PapersDocument72 paginiFCA (SA) Part I Past PapersmatentenÎncă nu există evaluări
- B8 U1 Revision TestDocument3 paginiB8 U1 Revision TestLithium KwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q Gaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDocument6 paginiQ Gaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsAngie machariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.DAY-8 ZOO - Breathing and Exchange of Gases - 25-05-2020Document11 pagini8.DAY-8 ZOO - Breathing and Exchange of Gases - 25-05-2020Ramakrishna ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 (WEEK 3) : Respiration During ExerciseDocument56 paginiLecture 3 (WEEK 3) : Respiration During ExerciseHidayah HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet - RespirationDocument8 paginiWorksheet - RespirationTanmay Karur100% (1)
- Science RespirationDocument2 paginiScience Respirationmihirgokhale31Încă nu există evaluări
- Modul 1Document28 paginiModul 1Irrinna Shakinah100% (1)
- Respiration and BreathingDocument6 paginiRespiration and BreathingBonny Ya SakeusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument4 paginiGaseous ExchangeArvin DiNozzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Biology Paper A FINAL - txt000000000Document16 paginiIGCSE Biology Paper A FINAL - txt000000000fahdtheemperorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Life On Earth 11Th Edition Audesirk Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiBiology Life On Earth 11Th Edition Audesirk Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFbridget.price734100% (14)
- JOSH RANDOLPH - The Respiratory System IIDocument1 paginăJOSH RANDOLPH - The Respiratory System IIjosh.randolphÎncă nu există evaluări
- X910 - ALBiology - Assignment - 03 V2Document14 paginiX910 - ALBiology - Assignment - 03 V2Mikila GittensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Test Science Year 10Document2 paginiSimple Test Science Year 10Dara MooreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test - Biology - AS1 - Respiration 1Document8 paginiTest - Biology - AS1 - Respiration 1Herry CenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contains More Carbon DioxideDocument4 paginiContains More Carbon DioxidePUVANES RAMACHANDRANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ujian 1Document10 paginiUjian 1Tajul Azhar BaharudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Worksheeet 2Document4 paginiRevision Worksheeet 2SpablaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER Respiration and CirculationDocument5 paginiCHAPTER Respiration and CirculationlatasabarikÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQs On Respiratory System - BiologyDocument12 paginiMCQs On Respiratory System - Biologysonia keniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 11 Gas Exchange in HumanDocument23 paginiTopic 11 Gas Exchange in HumanPianna IeongÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExerciseDocument16 paginiExercisePriyanshu PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 9 WW1 Q1Document5 paginiGrade 9 WW1 Q1JOEL MONTERDEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 paginiRespiratory Systemameershahat22Încă nu există evaluări
- Gas Exhange Grade 11 Life SciencesDocument22 paginiGas Exhange Grade 11 Life Sciencesgg5834256Încă nu există evaluări
- GR 10 Science - Biology - CH-5 - Respiration & Transportation Revision WSDocument2 paginiGR 10 Science - Biology - CH-5 - Respiration & Transportation Revision WSsohailmohammed077Încă nu există evaluări
- P.E FORM 3 Half - Term Feb 2024Document1 paginăP.E FORM 3 Half - Term Feb 2024changdilz64Încă nu există evaluări
- Online CT-1 (Respiration in Humans)Document5 paginiOnline CT-1 (Respiration in Humans)Sayma AkterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breathing Exchange and Gases 3Document3 paginiBreathing Exchange and Gases 3Dr. D. kumar Harshit -apexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 08 Gas Excgange - SDocument14 paginiChapter 08 Gas Excgange - SFelix CheungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio 10th - Respiration - Extensive TestDocument2 paginiBio 10th - Respiration - Extensive TestDharmendra SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home Test (Jan-21)Document10 paginiHome Test (Jan-21)Damon SalvatoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- FCA (SA) - Part - I - Past - Papers 4Document58 paginiFCA (SA) - Part - I - Past - Papers 4matentenÎncă nu există evaluări
- QB 1B Ch07e FDocument40 paginiQB 1B Ch07e FRyan KwokÎncă nu există evaluări
- SNS 1 (Breathing)Document7 paginiSNS 1 (Breathing)Dheeraj KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology TheoryDocument13 paginiBiology TheoryZaw Linn PhyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exposure Assessment and Safety Considerations for Working with Engineered NanoparticlesDe la EverandExposure Assessment and Safety Considerations for Working with Engineered NanoparticlesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10lecture Sivin-Shen 20160401aDocument38 pagini10lecture Sivin-Shen 20160401airisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- HKDSE Free MockDocument23 paginiHKDSE Free Mockirisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- Lee Wai Sze SarahDocument1 paginăLee Wai Sze Sarahirisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- Org ChemDocument20 paginiOrg Chemirisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- HKCEE BIOLOGY - 7.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - P.1Document6 paginiHKCEE BIOLOGY - 7.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - P.1irisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- Hkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1Document10 paginiHkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- Hkcee Biology - 7.1 Types of Cell Division - P.1Document1 paginăHkcee Biology - 7.1 Types of Cell Division - P.1irisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- Hkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1Document13 paginiHkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- Hkcee Biology - 4.1 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants - P.1Document5 paginiHkcee Biology - 4.1 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants - P.1irisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology Notes Section 3a Topic: Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantsDocument3 paginiBiology Notes Section 3a Topic: Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plantsirisyyy27Încă nu există evaluări
- 1) CORRECT - Assess For Patency of The NG Tube Muscle Spasms Associated With VomitingDocument39 pagini1) CORRECT - Assess For Patency of The NG Tube Muscle Spasms Associated With VomitingJujuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessing An Apical-Radial PulseDocument2 paginiAssessing An Apical-Radial PulsecrrfrncÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluoroquinolone-Associated Tendon-Rupture: A Summary of Reports in The Food and Drug Administration's Adverse Event Reporting SystemDocument9 paginiFluoroquinolone-Associated Tendon-Rupture: A Summary of Reports in The Food and Drug Administration's Adverse Event Reporting SystemMadalinaMadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MotherFirst - Maternity Mental Health Strategy: Building Capacity in SaskatchewanDocument64 paginiMotherFirst - Maternity Mental Health Strategy: Building Capacity in SaskatchewankidSKAN Director100% (1)
- Bronchial Asthma SeminarDocument64 paginiBronchial Asthma SeminarShidevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pain Management Teaching PlanDocument9 paginiPain Management Teaching PlanMarion Liana DayritÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrisi EnteralDocument51 paginiNutrisi EnteralIsma Awalia Habibah14Încă nu există evaluări
- TEST 1 Nursing FundamentalsDocument11 paginiTEST 1 Nursing FundamentalsLisa Keefer100% (1)
- Physiological Changes in Elderly RespiDocument23 paginiPhysiological Changes in Elderly RespiIrwan M. IskoberÎncă nu există evaluări
- On-Call Plus Product Insert 3146file1Document0 paginiOn-Call Plus Product Insert 3146file1Abdul Shakur FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Career Track 1 MedicDocument9 paginiCareer Track 1 MedicSolomaniRuler100% (1)
- Health Care Provider Involved in ICUDocument1 paginăHealth Care Provider Involved in ICUKathleen BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entreprenurse BrochureDocument2 paginiEntreprenurse Brochurederic100% (2)
- Updates in The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Kathryn Evans Kreider, DNP, FNP-BCDocument7 paginiUpdates in The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Kathryn Evans Kreider, DNP, FNP-BCLenin Zavaleta RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Presenting With Priapism 2329 6917 1000171Document5 paginiChronic Myeloid Leukemia Presenting With Priapism 2329 6917 1000171SalwiyadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal and Ethical Issues-ModifiedDocument29 paginiLegal and Ethical Issues-Modifiedmonir61100% (1)
- RS 071812finalDocument28 paginiRS 071812finalrspublishing100% (1)
- Sensation MethodDocument5 paginiSensation MethodDr. Nancy MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Not GlaucomaDocument5 paginiNot GlaucomaFabio LuccheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Professional Development PlanDocument3 paginiProfessional Development Planapi-385831843Încă nu există evaluări
- PCL ProtocolDocument5 paginiPCL ProtocolZ TariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- WNSSP Estimulacion SensorialDocument3 paginiWNSSP Estimulacion Sensoriallgomezb11100% (1)
- Vericose Veins: Seth Duncan-WesleyDocument44 paginiVericose Veins: Seth Duncan-WesleyKojo Duncan100% (1)
- Diagnostic TestsDocument5 paginiDiagnostic TestsAastha jainÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEMF To Support Heavy Metal Detoxification (Truly Heal)Document50 paginiPEMF To Support Heavy Metal Detoxification (Truly Heal)Vas Ra100% (5)
- Pediatric DosaPediatric Dosages Based On Body Weightges Based On Body WeightDocument7 paginiPediatric DosaPediatric Dosages Based On Body Weightges Based On Body WeightdjbhetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume 2021Document4 paginiResume 2021api-555218722Încă nu există evaluări
- Genetic Engineering Has Applications in MedicineDocument6 paginiGenetic Engineering Has Applications in Medicineshiv kapilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is ThalassemiaDocument2 paginiWhat Is ThalassemiaFatima Azzahra Khairul AnuarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genu ValgumDocument2 paginiGenu ValgumPurohit_R0% (1)