Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Respiratory System Anatomy Guide
Încărcat de
Jenn GosiengfiaoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Respiratory System Anatomy Guide
Încărcat de
Jenn GosiengfiaoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
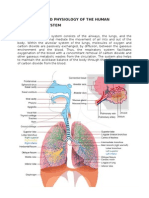
Anatomy and Physiology
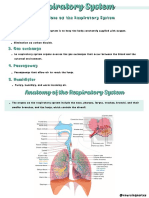
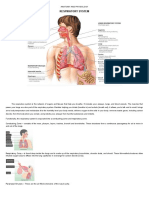
Respiratory System
Upper Respiratory Tract
- Refers to the:
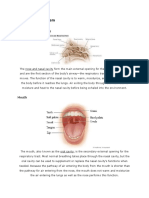
Nose
- Consists of the external nose and nasal cavity.
External nose - is the visible structure that forms a prominent feature of the face.
Nasal cavity - extends from the nares to the choanes, it is where air can flow when the
mouth is closed or when the oral cavity is full of food.
Pharynx
- Is the common passageway of both respiratory tract and digestive system. The pharynx leads to
the rest of the respiratory system through the esophagus. It can be divided in to three regions:
the nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx.
Nasopharynx it is the superior part of the pharynx
Oropharynx- extends from the uvula to the epiglottis, and the oral cavity open into the
oropharynx. Thus food, drink, and all air pass through the oropharynx.
Laryngopharynx food and drink pass through the laryngopharynx to the esophagus. A
small amount of air is usually swallowed with food and drink.
Lower Respiratory Tract
Larynx
- organ of voice production between the pharynx and the tracheal; it consists of a framework of
cartilages and elastic membranes housing the vocal folds and the muscles that control the
position and tension of these elements.
Trachea
- trachea or windpipe, is a membranous tube that consists of connective tissue with c-shaped
cartilages. It is lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium, which contains numerous cilia
and goblet cells.
Bronchi
- the trachea divides into the left and right main bronchi, each of which connects to a lung. The
left main bronchus is more horizontal than the right main bronchus because it is displaced by
the heart.
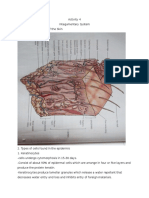
Lungs
- are the principal organs of respiration. Each lung is cone-shaped, with its base resting on the
diaphragm and its apex extending superiorly to appoint about 2.5 cm above the clavicle.
- The right lung has three lobes: the superior, middle, and inferior lobes. While the left lung has
two lobes called the superior and inferior lobes.
- Each lobe is divided into bronchopulmonary segments separated from one another by
connective tissue septa, but these separations are not visible as surface fissures.
- Each main bronchus divides into lobar bronchi as they enter their respective lungs. The lobar
(secondary) bronchi two in the left lung and three in the right lung, conduct air to each lobes.
- The lobar bronchi in turn give rise to segmental (tertiary) bronchi, which extend to the
bronchopulmonary segments of the lung. The bronchi continue to branch many times, finally
giving rise to bronchioles.
Bronchioles
- A small airway of the respiratory system extending from the bronchi into the lobes of the lung. The
bronchioles are made up of smooth muscle cells and are smaller than 1 millimeter in diameter. The
bronchioles do not have glands or cartilage. The epithelial cells of the bronchioles are cuboidal in shape.
Two divisions of Brocnhioles:
1. Terminal bronchioles- passively conduct inspired air from the bronchi to the respiratory bronchioles
and expired air from the respiratory bronchioles to the bronchi.
2. Respiratory bronchioles- these are short tubes regarded as areas of transition between the
conducting and respiratory portion of the respiratory system. The diameter of the respiratory
bronchioles is about 0.5 mm
Respiratory portion of the lungs:
The functional unit of the lungs includes the:
Alveolar ducts- The alveolar duct is the connection between the alveoli and the smaller bronchi.
It is a passage way for air.
Alveolar sacs- these are chambers connected to two or more alveoli
Alveoli- Alveoli are the tiny pockets in your lungs that store air for brief periods to allow time for
oxygen to absorb into the blood-stream.
-These form sponge-like, elastic, thin-walled air filled structure with extensive capillary beds, where
respiratory gas exchange occurs.
The Pores of Kohn are pores between adjacent alveoli, or interalveolar connections. They functions as a
means of collateral ventilation; that is, if the lung is partially deflated, ventilation can occur to some
extent through these pores. The pores also allow the passage of other materials such as fluid and
bacteria.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksDe la EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System Explained in 40 CharactersDocument9 paginiRespiratory System Explained in 40 CharactersShivani Sriram100% (1)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionDe la EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2A)Document4 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2A)Raiden VizcondeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Respiratory System Consists of 2 PartsDocument3 paginiThe Respiratory System Consists of 2 PartsAquardoleo ValentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- OxygenationDocument20 paginiOxygenationKhie-An OcampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument15 paginiThe Human Respiratory SystemNandita Halder100% (1)
- Respiratory System PDFDocument16 paginiRespiratory System PDFMary Ann SacramentoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System PreDocument11 paginiRespiratory System PrecontehamosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory SystemDocument18 paginiParts and Functions of Respiratory Systemjosephabram051590Încă nu există evaluări
- Iv. Anatomy and Physiology of The Human Respiratory SystemDocument5 paginiIv. Anatomy and Physiology of The Human Respiratory SystemJenny Vi CodenieraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument11 paginiAnatomy and Physiologyjawn09euclidÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Respiratory SystemDocument16 paginiThe Respiratory SystemAirene Mae Lamputi SupilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System GuideDocument8 paginiRespiratory System GuideKhushi JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument5 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemLek Bassig ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiration, Types of Respiration and Anatomy of Human Respiratory SystemDocument8 paginiRespiration, Types of Respiration and Anatomy of Human Respiratory Systemegfr3yfgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tracheobroncheal Tree:-: The Right BronchusDocument5 paginiTracheobroncheal Tree:-: The Right BronchusPriyanjali SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory SystemDocument2 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory SystemRam Pgdt50% (4)
- Anatomi Sistem PernapasanDocument64 paginiAnatomi Sistem PernapasanLili ManaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Respiratory SystemDocument3 paginiThe Respiratory Systempaulo_camuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organs of the Respiratory System FunctionsDocument3 paginiOrgans of the Respiratory System FunctionsEmmeth ArdienteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology Assignment 3Document6 paginiAnatomy and Physiology Assignment 3api-238869728Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of The Respiratory System 1Document8 paginiAnatomy of The Respiratory System 1Grace Noviyanthi SinambelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory AssessmentDocument12 paginiRespiratory AssessmentAmanda ScarletÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iv. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 paginiIv. Anatomy and PhysiologyMonica Gagarin CortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument5 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemNesra de PeraltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dulutalias - Chapter23-THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument15 paginiDulutalias - Chapter23-THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMKie MusstisqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Anatomy GuideDocument9 paginiRespiratory Anatomy GuideLiza Marie Cayetano AdarneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology: The Respiratory SystemDocument82 paginiAnatomy and Physiology: The Respiratory SystemMaria Angelique Ofciar100% (2)
- Functions of The Respiratory System: BloodDocument12 paginiFunctions of The Respiratory System: BloodSesrine BuendiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument12 paginiRespiratory System Anatomy & PhysiologyDgjj CompuiterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewDocument8 paginiAnatomic and Physiologic OverviewJoseph King MacaranasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReproductiveDocument5 paginiReproductiveJason Vinluan CarinanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology: PHYSIOLOGY-the Branch of Biology That Deals With The Internal Workings ofDocument4 paginiAnatomy and Physiology: PHYSIOLOGY-the Branch of Biology That Deals With The Internal Workings ofshonievin100% (2)
- Introduction To Acute Respiratory FailureDocument6 paginiIntroduction To Acute Respiratory FailureErieca Barsabal PamittanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 paginiAnatomy and PhysiologyKelly Camero ÜÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Anatomy and Functions of the Respiratory SystemDocument15 paginiThe Anatomy and Functions of the Respiratory SystemNahid ParveenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 paginiRespiratory SystemTricia CabiliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Respiratory SystemDocument6 paginiIntroduction To Respiratory SystemRM100% (1)
- Unit - 1 Second Sem Human Anatomy Notes PDFDocument34 paginiUnit - 1 Second Sem Human Anatomy Notes PDFeduardo vieiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEC - Week 9 (Respiratory)Document42 paginiLEC - Week 9 (Respiratory)Al SerenosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 paginiAnatomy and PhysiologyBlessyl Mae EstenzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACFrOgCYzyAtlOdYv5jafLv-AubsWO2slT5n-CLAKbsxs37xlcq301vUs KfW9yPahBUJ3tJd68DH3Rf-H3JFeaJn BOx82c QRBoNJMxjZCNQIg-sy KVTI5Rx7OB93lfvgdTKZs1 3ImlTKcEhDocument37 paginiACFrOgCYzyAtlOdYv5jafLv-AubsWO2slT5n-CLAKbsxs37xlcq301vUs KfW9yPahBUJ3tJd68DH3Rf-H3JFeaJn BOx82c QRBoNJMxjZCNQIg-sy KVTI5Rx7OB93lfvgdTKZs1 3ImlTKcEhEmmanuel David PereaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 paginăAnatomy and PhysiologyDian Rose Sebanes MamintaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group1 Review of Respiratory SystemDocument41 paginiGroup1 Review of Respiratory Systemjohn obinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Respiratory System: Dr. Dwi Rita Anggraini, MkesDocument64 paginiAnatomy of Respiratory System: Dr. Dwi Rita Anggraini, MkesFira TasyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of The Respiratory System 2Document5 paginiStructure of The Respiratory System 2domhughes1093Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomi Sistem ParuDocument64 paginiAnatomi Sistem ParuMochammad Fariz AmsalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System Anatomy and Functions EX36Document57 paginiRespiratory System Anatomy and Functions EX36royanirudh99Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology PneumoniaDocument4 paginiAnatomy and Physiology PneumoniaJohnson MallibagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 paginiRespiratory System - Anatomy and PhysiologyJay Crishnan Morales CajandingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology GuideDocument20 paginiRespiratory Anatomy and Physiology GuideBon BonselÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organs of the Respiratory System ExplainedDocument12 paginiOrgans of the Respiratory System ExplainedSeptian PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument37 paginiAnatomy of The Respiratory SystemPal SedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System: Group 5Document16 paginiRespiratory System: Group 5Rashid DayaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANAPHYDocument10 paginiANAPHYcharles babasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System: Nose and Nasal CavityDocument8 paginiRespiratory System: Nose and Nasal CavityJasper AlbuferaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System Chapter SummaryDocument7 paginiRespiratory System Chapter Summaryqueen nurseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 paginiRespiratory SystemКрістіна БаландаÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For ManuscriptDocument7 paginiNCP For ManuscriptJenn GosiengfiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maley Ch8csDocument4 paginiMaley Ch8csJenn GosiengfiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Context: Amado ValdezDocument2 paginiTime Context: Amado ValdezJenn GosiengfiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 10 BiochemDocument3 paginiExp 10 BiochemJenn Gosiengfiao80% (5)
- Maley Ch8csDocument4 paginiMaley Ch8csJenn GosiengfiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marrying The CasanovaDocument2.200 paginiMarrying The CasanovaJenn Gosiengfiao100% (4)
- Activity 4Document5 paginiActivity 4Jenn GosiengfiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Just Consequentialism and Computing: James H. MoorDocument6 paginiJust Consequentialism and Computing: James H. MoorJenn GosiengfiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument7 paginiDrug StudyJenn GosiengfiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICD 10 (3) edit-TERAKHIRDocument14 paginiICD 10 (3) edit-TERAKHIRStefanus Ferry SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breathing and RespirationDocument5 paginiBreathing and RespirationPriyansh PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prework QuestionsDocument6 paginiPrework Questionsapi-648757084Încă nu există evaluări
- 4 Stages of Speech ProductionDocument3 pagini4 Stages of Speech ProductionEve RulonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OtalgiaDocument57 paginiOtalgiaKamal-Eldin Ahmed Abou-ElhamdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch15 Lecture PPT ADocument17 paginiCh15 Lecture PPT AEulanda DelenÎncă nu există evaluări
- VitalStim Electrode Placement GuideDocument1 paginăVitalStim Electrode Placement GuideMd Sherajul HaqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System Anatomy GuideDocument3 paginiDigestive System Anatomy GuideAngelica JavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Lymphatic Drainage of the Head and NeckDocument35 paginiThe Lymphatic Drainage of the Head and Neckboomb162006100% (1)
- Case Study - Congestive Heart FailureDocument71 paginiCase Study - Congestive Heart FailureFrancis Adrian100% (3)
- 3.14 Course Notes PDFDocument27 pagini3.14 Course Notes PDFDarkOne96Încă nu există evaluări
- Roses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.Document249 paginiRoses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.MabesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 - Chapter 5 PDFDocument234 pagini13 - Chapter 5 PDFDinda PangalilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Connor J D Phonetics PDFDocument329 paginiO Connor J D Phonetics PDFksenya71% (7)
- Respiratory System GuideDocument54 paginiRespiratory System GuideHannah YsaBelle LeguroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immaculate Conception Parochial School Science ExamDocument4 paginiImmaculate Conception Parochial School Science ExamJullina DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 150 CPC Exam 2008 QuestionsDocument25 pagini150 CPC Exam 2008 QuestionsMagical 25100% (1)
- Otolaryngology Guide to Head & Neck ExamsDocument52 paginiOtolaryngology Guide to Head & Neck ExamsNemer Al-Khtoum100% (3)
- Congenital SyphilisDocument3 paginiCongenital SyphilisLakshya J BasumataryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Tonsil Lo PharyngitisDocument27 paginiAcute Tonsil Lo PharyngitisCheysser Alagao50% (2)
- Respiratory SystemDocument36 paginiRespiratory SystemLovejoy TiñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Pathology of DiphtheriaDocument5 paginiThe Pathology of DiphtheriaKang KikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tonsillar Crypts and Bacterial Invasion of Tonsils: A Pilot StudyDocument4 paginiTonsillar Crypts and Bacterial Invasion of Tonsils: A Pilot Study'ranu HerjunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Download ebook Netters Advanced Head And Neck Flash Cards Pdf full chapter pdfDocument67 paginiDownload ebook Netters Advanced Head And Neck Flash Cards Pdf full chapter pdfkatie.watson104100% (25)
- Development of Palate and Its AnamoliesDocument19 paginiDevelopment of Palate and Its AnamoliesAkshayaa BalajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-Pharynx. Diseases of NasopharynxDocument54 pagini3-Pharynx. Diseases of NasopharynxislamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions of The Respiratory SystemDocument10 paginiFunctions of The Respiratory SystemKrisha AvorqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Pharynx: Keerthi Ns 2010 BATCHDocument21 paginiAnatomy of Pharynx: Keerthi Ns 2010 BATCHAdam NoheÎncă nu există evaluări
- E0294Document158 paginiE0294Mayuresh DeoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Practice Test: Home Chapter 22: The Respiratory SystemDocument4 paginiChapter Practice Test: Home Chapter 22: The Respiratory SystemHUAWEI HUAWEIÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDe la EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (402)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (78)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDe la EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (13)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDe la EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDe la EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementDe la EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (40)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDe la EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDe la EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (169)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDe la EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesDe la EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDe la EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDe la EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDe la EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (8)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDe la EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (33)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.De la EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingDe la EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDe la EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (253)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsDe la EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossDe la EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (4)