Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
EYE
Încărcat de
Kory Christina0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
52 vizualizări7 paginiNursing Study Guide
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentNursing Study Guide
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
52 vizualizări7 paginiEYE
Încărcat de
Kory ChristinaNursing Study Guide
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 7
CH 44 EYE Disorders
Title Pathophysiology Treatment & Care
Cataracts
(Disorder that causes lens or its capsule
to lose its transparency and/or become
opaque)
As clouding develops, visual impairment
occurs. Usually affects both eyes, but
visually impairment is different in each
eye. Typically associated with aging,
however it can be congenital, caused by
eye injury, or secondary to a systemic
disease (diabetes).
Only treatment is surgical removal of
the lens, and ONLY when significant
vision loss has occurred. An intraocular
lens is generally implanted (glasses or
special contacts are also used). Eye
surgery is done outpatient under local
anesthesia. Valium can be given for
anxiety. Pre Op patients can relieve
medications to prepare eye for surgery:
mydriactic (dilates) & cycloplegic
(paralyzes cillary muscle). *Must have
someone else drive you home, & driving
is restricted for a few days. *After
surgery avoid coughing & sneezing. Dark
glasses to relieve glare.
Glaucoma
(Tunnel Vision)
(Abnormally high pressure of fluid
inside eyeball)
Fluid accumulates in anterior chamber.
If pressure continues it could bring on
blindness. Two forms: Primary (acute) &
Closed (chronic).
PRIMARY: angle where the iris & cornea
join is open but the canal is blocked and
aqueous humor cannot drain from the
eye. Causes rise in IOP, slow loss of
peripheral vision, and ultimate
blindness. *Most preventable form,
usually bilateral.
CLOSED: attacks of suddenly increased
IOP (bulging iris).
SECONDARY: results from ocular or
Drug therapy to reduce IOP.
Betagan, Betopic decrease IOP. These
drugs have systematic effects that
include: bradycardia, hypotension,
BRONCHOSPASM, respiratory failure
(esp. with clients with asthma).
Administering eye drops for glaucoma:
Press lightly for 1 min on lacrimal sac
after instilling the drops to decrease
systemic effect of medication. If more
than one eye drop is used, wait 5
minutes between each instillation of
each type.
CH 44 EYE Disorders
systemic disorder that elevates IOP, this
can happen quickly without warning & it
is a medical EMERGENCY. African
Americans over 40 years old are 5x
more likely to have glaucoma than
Caucasians.
Retinal Detachment
(Retina separates from choroid)
Partial separation becomes complete if
not treated. Painless because there are
no pain receptors in retina.
Surgical procedure: Scleral Buckling
(sometimes used). Reduces the scleral
surface & allows contact between
choroid & retina. Pneumatic
Retinopexy used for uncomplicated
detachment. Draws small amount of
fluid from anterior chamber and gas is
injected into posterior chamber. Gas
pushes the retinal tear and seals it off. **
Fluid under the retinal tear is absorbed
& gas is released from eye over several
weeks. Prone position. Treat nausea,
vomiting, and pain. Bilateral eye
patches.
Infections KERATITIS: inflammation of cornea due
to infection, irritation, injury, or
allergies. Symptoms: eye pain, Red
watery eyes, photophobia (sensitive to
light).
STYE (Hordeolum): pustule
inflammation on eyelash follicle or
sebaceous gland on the lid margin,
commonly by staphylococcal.
KERATITIS: optical anesthetics for pain,
mydriactics to dilate pupils, dark
sunglasses, antibiotics.
STYE: warm compresses & antibiotics.
Severe cases require drainage, once pus
is drained the pain is relieved and
healing begins.
CHALAZION: surgical incision if cyst is
CH 44 EYE Disorders
Symptoms: pain, redness, swelling of
specific area of eyelid.
CHALAZION: cyst of meibomian gland.
Hard cyst is filled with fatty material.
Pain & swelling for weeks.
CONJUNCTIVITIS (PINK EYE):
inflammation of conjunctiva. Caused by
bacteria, viral, or rickettsial, allergens,
or irritants. Symptoms: burning itching
eyes, discharge, swelling pain, and
redness.
large or infected, interferes with vision,
or closure of eyelids. Cyst remains when
inflammation subsides.
PINK EYE: warm compresses (saline or
boric acid), instilling antibiotic or
antiviral drops. If allergen
antihistamines Rx. ** Proper hand
hygiene or nurse and client. NO
STERIODS they can mess up the cornea.
Refractive Errors Myopia: Nearsightedness (cant see
distance)
Hyperopia: Farsightedness (cant see
up close) vision beyond 20 feet is
normal.
Astigmatism: football shape. Visual
distortion.
Strabismus: inability of eyes to focus in
same direction) eye constantly deviated
to one side.
Presbyopia: inability of lens to change
curvature and focus on near objects.
Eyes cant focus on near objects but
remains accommodated for far objects
Rx glasses or contacts. Radial
keratotomy is surgical procedure that
corrects myopia and astigmatism. LASIK
& PRK use lasers to correct near & far
sightedness.
Eye Injuries Injuries to eye require IMMEDIATE
attention from an ophthalmologist.
Flush sterile saline from sclera and let
flow across to cornea. If particle is not
CH 44 EYE Disorders
If there is foreign object in the eye cover
and go to ER, do not try to remove.
removed or located Sterile fluorescein
drops or strips are instilled to find
particle. Welder, swimmers need to
wear protective goggles.
Impaired Vision Blindness evokes an image of total
darkness & used for legal purposes
when vision is 20/200 or less with
corrective lenses in better eye. Those
with 20/70 & 20/200 in better eye with
use of glasses are referred to as partial
blindness.
Magnifying glasses, telescopes, large
print books, braille books, timers,
ticking clocks & seeing eye dog.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
(Atrophy or deterioration of macula)
Loses central vision, but has peripheral
vision. Risk Factors: Caucasian, smoking,
family Hx, female, Obese. Two Forms:
DRY: vessels not ruptured (most start
with this form). Blurred vision that goes
away with brighter light. Drusen, small
yellow deposits on retina and macula,
indicates breakdown. WET: vessels
rupture & leak blood and fluid. Found in
10% of people with AMD. Straight lines
appear crooked.
AVASTIN treats both, monthly
injections, slows progression. Vitamin C,
Vitamin E, Beta-carotene, Zinc, Copper,
Ocubite med OTC. WET can be treated
with laser surgery. Provide safe
environment & announce your presence.
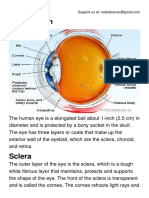
Sclera: white of the eye
Cornea: window of the eye
6 OCCULAR MUSCLES
**** Tears contain lysozyme, muramidase, that destroys pathogens.
CH 44 EYE Disorders
Eye changes in adults: tear production decreases, Grey ring around eyes (if younger than 40 indicates high cholesterol build
up), pytosos, fat decreases (sunken eyes), wrinkling, bags.
EYE SURGERY:
-Elevate head of bed to decrease pressure
-No bending forward
-No lifting (gallon of milk)
-No straining vagus nerve (stool softener will be Rx to prevent straining)
-No lying on affected side
-Treat nausea
-Wear dark glasses
NORMAL INTRAOCCULAR PRESSURE: 10-20 or 12-22
Mydriatic: Pupils Dilate
Miotic: Pupils Contract
Pytosis: droopy eyelids
EYES CHECKED:
Q Year Contacts
Q 2 Years Glasses
Blown Pupil indicates stroke.
PERRLA (pupils equal, round, reactive to light, and accommodation)
*Fluorescein angiography- Visualizes structures in the retina and choroid (particle lost in eye)
*Snellen Test- normal value 20/20 for visual acuity
*Tonometry- monitors treatment of glaucoma, measures IOP.
CH 44 EYE Disorders
CH 44 EYE Disorders
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Causes, Signs, Diagnosis and Treatment of Different Types of ShockDocument4 paginiCauses, Signs, Diagnosis and Treatment of Different Types of ShockKory Christina100% (2)
- Occlusive Disorders and HFDocument4 paginiOcclusive Disorders and HFKory ChristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inflammatory Cardiac DisordersDocument3 paginiInflammatory Cardiac DisordersKory ChristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BurnsDocument4 paginiBurnsKory ChristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio TerrismDocument4 paginiBio TerrismKory ChristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EARDocument6 paginiEARKory ChristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensory DisordersDocument2 paginiSensory DisordersKory ChristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Risks and Complications of LASIKDocument7 paginiRisks and Complications of LASIKdonkalonkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurosesnsory EYESDocument92 paginiNeurosesnsory EYESMae MarcojosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnosis and Blepharoplastic Repair of Conformational Eyelid DefectsDocument11 paginiDiagnosis and Blepharoplastic Repair of Conformational Eyelid Defectstaner_soysurenÎncă nu există evaluări
- SENSORY ORGANS: ANIMAL PERCEPTIONDocument19 paginiSENSORY ORGANS: ANIMAL PERCEPTIONWE ARE CRaZyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sonomed 300 Series ManualDocument52 paginiSonomed 300 Series ManualJorge Alfonso Fernandez50% (2)
- Anatomy of The Eye PDFDocument3 paginiAnatomy of The Eye PDFPerry SinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retinitis Pigmentosa and Diabetic Retinopathy QuestionsDocument10 paginiRetinitis Pigmentosa and Diabetic Retinopathy QuestionsYUAN LIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ronan Canty - Research Paper 2020Document4 paginiRonan Canty - Research Paper 2020api-497492580Încă nu există evaluări
- DR Stefan Sacu CVDocument10 paginiDR Stefan Sacu CVpeiras2011Încă nu există evaluări
- CER60 Glaucoma-Treatment 20120524Document443 paginiCER60 Glaucoma-Treatment 20120524Jessica StephanieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 21 EyeDocument7 paginiLecture 21 EyeDesak LaksmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bullous Keratopathy PRDocument12 paginiBullous Keratopathy PRshevinesaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retinopathy of PrematurityDocument49 paginiRetinopathy of PrematuritybhartiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Anterior Chamber Angle and Physiology ofDocument24 paginiAnatomy of Anterior Chamber Angle and Physiology ofAnumeha Jindal100% (1)
- Anterior Segment Diseases: Instant Clinical Diagnosis in OphthalmologyDocument440 paginiAnterior Segment Diseases: Instant Clinical Diagnosis in OphthalmologyPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hospital and Dispensary Management.: (MavhDocument1 paginăHospital and Dispensary Management.: (MavhAnonymous plTPAIjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Refractive Error On VEP in Myopic Boys and GirlsDocument3 paginiEffect of Refractive Error On VEP in Myopic Boys and GirlsNational Journal of Medical Research &Yoga ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- To No Me TryDocument79 paginiTo No Me TryAbhijit HandiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogo Lentes VolkDocument48 paginiCatalogo Lentes VolkDepartamento ComercialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures For Primary Care - Chalazion N HordeolumDocument6 paginiPfenninger and Fowler's Procedures For Primary Care - Chalazion N HordeolumCarimaGhalieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refractive Errors in State Junior High School Students in BandungDocument4 paginiRefractive Errors in State Junior High School Students in BandungRosaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 Samuel EtalDocument4 pagini9 Samuel EtaleditorijmrhsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Encyclopedia of OphthalmologyDocument1.998 paginiEncyclopedia of OphthalmologySmara100% (3)
- Assessing The Eye Structures and Visual AcuityDocument5 paginiAssessing The Eye Structures and Visual Acuitymalyn1218Încă nu există evaluări
- SightMD Referral Form PDFDocument2 paginiSightMD Referral Form PDFHENRYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Referat Cystoid Macular Edema Periode 17 Juni - 20 Juli 2019Document25 paginiReferat Cystoid Macular Edema Periode 17 Juni - 20 Juli 2019CharlotteGraceNusiferaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Eye and The Colorful World - Class Notes - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024Document41 paginiHuman Eye and The Colorful World - Class Notes - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024jyotikushwahasmart0222Încă nu există evaluări
- AlbinismDocument3 paginiAlbinismTanvi ManjrekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arvind Eye Hospital - Rural MarketingDocument38 paginiArvind Eye Hospital - Rural Marketingsumeetdas09Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Kasus Mata BedaDocument7 pagini2 Kasus Mata BedaREGINE YEO ZHI SHUENÎncă nu există evaluări