Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Financial Intermediaries
Încărcat de
Rishikaysh KaakandikarDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Financial Intermediaries
Încărcat de
Rishikaysh KaakandikarDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
www.dcoermba.blogspot.
com
Financial Intermediaries
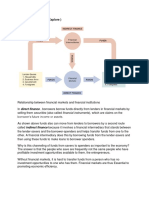
Financial intermediation consists of channeling funds between surplus and deficit agents. A financial
intermediary is a financial institution that connects surplus and deficit agents. The classic example of a
financial intermediary is a bank that transforms bank deposits into bank loans.
Through the process of financial intermediation, certain assets or liabilities are transformed into different
assets or liabilities. As such, financial intermediaries channel funds from people who have extra money
(savers) to those who do not have enough money to carry out a desired activity (borrowers).
Functions performed by financial intermediaries
Financial intermediaries provide 3 major functions:
1. Maturity transformation
Converting short-term liabilities to long term assets (banks deal with large number of lenders and
borrowers, and reconcile their conflicting needs)
2. Risk transformation
Converting risky investments into relatively risk-free ones. (lending to multiple borrowers to
spread the risk)
3. Convenience denomination
Matching small deposits with large loans and large deposits with small loans
Advantages of financial intermediaries
There are 2 essential advantages from using financial intermediaries:
1. Cost advantage over direct lending/borrowing
.
2. Market failure protection the conflicting needs of lenders and borrowers are reconciled,
preventing
market failure
The cost advantages of using financial intermediaries include:
1. Reconciling conflicting preferences of lenders and borrowers
2. Risk aversion intermediaries help spread out and decrease the risks
3. Economies of scale using financial intermediaries reduces the costs of lending and borrowing
4. Economies of scope intermediaries concentrate on the demands of the lenders and borrowers
and are able to enhance their products and services (use same inputs to produce different
outputs)
www.dcoermba.blogspot.com
Types of financial intermediaries
Financial intermediaries include:
Banks
Building societies
Credit unions
Financial advisers or brokers
Insurance companies
Collective investment schemes
Pension funds
1) A bank is a financial institution and a financial intermediary that accepts deposits and channels
those deposits into lending activities, either directly or through capital markets. A bank connects
customers that have capital deficits to customers with capital surpluses.
Due to their critical status within the financial system and the economy
generally, banks are highly
regulated in most countries. Most banks operate under a system known asfractional reserve
banking where they hold only a small reserve of the funds deposited and lend out the rest for
profit. They are generally subject to minimum capital requirements which are based on an
international set of capital standards, known as the Basel Accords.
2) A building society is a financial institution owned by its members as a mutual organization.
Building societies offer banking and related financial services, especially mortgage lending.
These institutions are found in the United Kingdom (UK) and several other countries.
The term "building society" first arose in the 18th century in Great Britain from cooperative
savings groups. In the UK today, building societies actively compete with banks for most
consumer banking services, especially mortgage lending and deposits.
3) A credit union is a member-owned financial cooperative, democratically controlled by its
members, and operated for the purpose of promoting thrift, providing credit at competitive rates,
and providing other financial services to its members.
Many credit unions also provide services intended to support community development
or
sustainable international development on a local level, and could be consideredcommunity
development financial institutions.
Worldwide, credit union systems vary significantly in terms of total system assets and average
institution asset size,ranging from volunteer operations with a handful of members to institutions
with several billion dollars in assets and hundreds of thousands of members.
www.dcoermba.blogspot.com
4) A financial adviser is a professional who helps clients to maintain the desired balance of investment
income, capital gains, and acceptable level of risk by using proper asset allocation. Financial advisers
use stock, bonds, mutual funds, real estate investment trusts (REITs), options, futures, notes,
andinsurance products to meet the needs of their clients. Many financial advisers receive
a commissionpayment for the various financial products that they broker, although "fee-based" planning is
becoming increasingly popular in the financial services industry.
A further distinction should be made between "fee-based" and "fee-only" advisers. Fee-based advisers
often charge asset based fees but may also collect commissions. Fee-only advisers do not collect
commissions or referral fees paid by other product or service providers.
Some investment advisers only charge a fee based on the assets managed for the client. Typically they
charge about 1.0 to 1.5% per year to make the investment decisions for the client. They do not collect
commissions.
5) A broker is an individual or party (brokerage firm) that arranges transactions between a buyer and
a seller, and gets a commissionwhen the deal is executed. A broker who also acts as a seller or as a
buyer becomes a principal party to the deal. Distinguish agent: one who acts on behalf of a principal.
In general a broker is an independent agent used extensively in some industries. The prime responsibility
of a broker is to bring sellers and buyers together. Therefore, a broker is the third -person facilitator
between a buyer and a seller. An example would be a real estate broker who facilitates the sale of a
property.
6) Insurance is a form of risk management primarily used to hedge against the risk of a
contingent, uncertain loss. Insurance is defined as the equitable transfer of the risk of a loss, from one
entity to another, in exchange for payment. An insurer is a company selling the insurance; the insured, or
policyholder, is the person or entity buying the insurance policy. The amount to be charged for a certain
amount of insurance coverage is called the premium. Risk management, the practice of appraising and
controlling risk, has evolved as a discrete field of study and practice.
The transaction involves the insured assuming a guaranteed and known relatively small loss in the form
of payment to the insurer in exchange for the insurer's promise to compensate (indemnify) the insured in
the case of a financial (personal) loss. The insured receives a contract, called the insurance policy, which
details the conditions and circumstances under which the insured will be financially compensated.
7) A pension fund is any plan, fund, or scheme which provides retirement income.
Pension funds are important shareholders of listed and private companies. They are especially important
to the stock market where large institutional investors dominate. The largest 300 pension funds
collectively hold about $6 trillion in assets. In January 2008, The Economist reported that Morgan
Stanley estimates that pension funds worldwide hold over US$20 trillion in assets, the largest for any
category of investor ahead of mutual funds,insurance companies, currency reserves, sovereign wealth
funds, hedge funds, or private equity. Although the (Japan) Government Pension Investment Fund (GPIF)
lost 0.25 percent, in the year ended March 31, 2011 GPIF was still the world's largest public pension fund
which oversees 114 trillion Yen ($1.5 trillion).
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Financial Intermediaries' Evolving RolesDocument5 paginiFinancial Intermediaries' Evolving RolesSmriti KhannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1Document16 paginiUnit 1Shivam YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus PGDM FMDocument73 paginiSyllabus PGDM FMyash_meetuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus PGDM FMDocument73 paginiSyllabus PGDM FMyash_meetuÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic DevelopmentDocument4 paginiFINANCIAL SYSTEM Role in Economic Developmentrevathi alekhya80% (10)
- Financial Institutions (Coleen) : Term Funds For The Economy. These Institutions Provide A Variety of FinancialDocument4 paginiFinancial Institutions (Coleen) : Term Funds For The Economy. These Institutions Provide A Variety of Financialsheinamae quelnatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mutual Funds for Beginners Learning Mutual Funds BasicsDe la EverandMutual Funds for Beginners Learning Mutual Funds BasicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial IntermediariesDocument5 paginiFinancial Intermediariespintu_brownyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial IntermediaryDocument10 paginiFinancial Intermediaryalajar opticalÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Financial Intermediary (Final)Document6 paginiWhat Is A Financial Intermediary (Final)Mark PlancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Financial IntermediationDocument10 paginiIntroduction To Financial IntermediationbugmenomoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Function of Financial Intermediaries PDFDocument29 paginiFunction of Financial Intermediaries PDFOliwaOrdanezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM Assignment AnswersDocument4 paginiFM Assignment Answerskarteekay negiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finmar - Chapter 12 - 14Document24 paginiFinmar - Chapter 12 - 14AlexanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Money Banking Chapter 5Document12 paginiMoney Banking Chapter 5ebsa ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finalcil Market - Bba Unit One &twoDocument79 paginiFinalcil Market - Bba Unit One &twoBhagawat PaudelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit ThreeDocument22 paginiUnit ThreeEYOB AHMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sumber KeuanganDocument43 paginiSumber KeuanganMarshella WijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finmar NotesDocument5 paginiFinmar NotesariannejonesmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engaging Activity Unit 4 Financial InstitutionDocument2 paginiEngaging Activity Unit 4 Financial InstitutionMary Justine ManaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document11 paginiChapter 2desktopmarsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 1 FIIMDocument28 paginiCH 1 FIIMKume MezgebuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial InstitutionsDocument4 paginiFinancial InstitutionsTrifan_DumitruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Institution Chapter TwoDocument14 paginiFinancial Institution Chapter TwoKalkayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial IntermediationDocument20 paginiFinancial IntermediationFrances Bea Waguis100% (1)
- CH 1 FIIMDocument28 paginiCH 1 FIIMMulata KahsayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions of Financial IntermediariesDocument3 paginiFunctions of Financial IntermediariesErin SuryandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document11 paginiChapter 2Lencho MusaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial SystemDocument3 paginiFinancial SystemAbdul Wahid BataloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial IntermediaryDocument4 paginiFinancial IntermediaryValerie Mae AbuyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Management Principles and Applications 8th Edition Titman Solutions ManualDocument8 paginiFinancial Management Principles and Applications 8th Edition Titman Solutions ManualRichardSmithosjpc100% (13)
- CHAPTER 2powerpointDocument33 paginiCHAPTER 2powerpointMintayto TebekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH2@Financial InstitutionsDocument10 paginiCH2@Financial Institutionstamiratg24Încă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Financial Institutions and IntermediariesDocument28 paginiUnderstanding Financial Institutions and IntermediariesChristine Kaye DamoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled 1Document3 paginiUntitled 1cesar_mayonte_montaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Markets and Institutions Explained (Explore RelationshipDocument6 paginiFinancial Markets and Institutions Explained (Explore RelationshipKhen CaballesÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntroductionDocument10 paginiIntroductionHala EdwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of The Financial System PDFDocument33 paginiOverview of The Financial System PDFFlorence Joy AbkilanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Two Financial Institutions in The Financial System: Saving and Loan Associations (S&LS)Document13 paginiChapter Two Financial Institutions in The Financial System: Saving and Loan Associations (S&LS)Nahum DaichaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial IntermediaryDocument3 paginiFinancial IntermediaryAnil KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Christiene P. Schwandner: Financial Sector DefinedDocument4 paginiChristiene P. Schwandner: Financial Sector DefinedGladys Gaccion OpitzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Ins & MKTDocument7 paginiFinancial Ins & MKTdkaluale16Încă nu există evaluări
- Financial InstitutionDocument3 paginiFinancial InstitutionroilesatheaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dolly Jain 2GI2BA035Document41 paginiDolly Jain 2GI2BA035RahulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod 1 EconomicsDocument7 paginiMod 1 Economics062 Mehta UrmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter2. Financial Inst&capital ArketsDocument12 paginiChapter2. Financial Inst&capital Arketsnewaybeyene5Încă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 3 - Financial Institutions, Intermediaries and Asset ManagementDocument14 paginiCHAPTER 3 - Financial Institutions, Intermediaries and Asset ManagementReggie AlisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regulations and Types of FIDocument5 paginiRegulations and Types of FIAbdul AleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Financial Institutions: Commercial Banks, Investment Banks, Insurance Companies & MoreDocument11 paginiTypes of Financial Institutions: Commercial Banks, Investment Banks, Insurance Companies & MoreJenina Rose SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial MarketDocument8 paginiFinancial Marketshahid3454Încă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Financial Services IndustryDocument4 paginiClassification of Financial Services IndustryRiteshHPatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Institutions in The Financial SystemDocument15 paginiFinancial Institutions in The Financial SystemNigussie Berhanu100% (1)
- Answer:: 1. What Is Financial Intermediary?Document2 paginiAnswer:: 1. What Is Financial Intermediary?aprilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Debre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceDocument14 paginiDebre Markos Universty College of Post-Graduate Studies Department of Accounting and FinanceMikias DegwaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capital Markets Lesson 4Document4 paginiCapital Markets Lesson 4Jane AtendidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Money MarketDocument8 paginiIndian Money MarketRey ArÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3 - Function of Financial IntermediariesDocument3 paginiAssignment 3 - Function of Financial IntermediariesJea Ann CariñozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insurance: Insurance Is A Means of Protection From Financial Loss. It Is A Form ofDocument7 paginiInsurance: Insurance Is A Means of Protection From Financial Loss. It Is A Form ofPREM NAGARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Overview of the Financial SystemDocument7 paginiChapter 5 Overview of the Financial Systemshai santiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Two-The Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions and Investment BanksDocument4 paginiChapter Two-The Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions and Investment Banksmaquesurat ferdousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document10 paginiChapter 1tamirat tadeseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bonds Decoded: Unraveling the Mystery Behind Bond MarketsDe la EverandBonds Decoded: Unraveling the Mystery Behind Bond MarketsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panchayat Executive RolesDocument32 paginiPanchayat Executive RolesKranthi PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panchayat Executive RolesDocument32 paginiPanchayat Executive RolesKranthi PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 Profits and Gains of Business or ProfessionDocument119 paginiUnit 4 Profits and Gains of Business or ProfessionRishikaysh KaakandikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntermediariesDocument4 paginiIntermediariesRishikaysh KaakandikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Intermediaries: Financial Institution Bank Bank Deposits Loans Assets LiabilitiesDocument3 paginiFinancial Intermediaries: Financial Institution Bank Bank Deposits Loans Assets LiabilitiesRishikaysh KaakandikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Intermediaries: Financial Institution Bank Bank Deposits Loans Assets LiabilitiesDocument3 paginiFinancial Intermediaries: Financial Institution Bank Bank Deposits Loans Assets LiabilitiesRishikaysh KaakandikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntermediariesDocument4 paginiIntermediariesRishikaysh KaakandikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Intermediaries: Financial Institution Bank Bank Deposits Loans Assets LiabilitiesDocument3 paginiFinancial Intermediaries: Financial Institution Bank Bank Deposits Loans Assets LiabilitiesRishikaysh KaakandikarÎncă nu există evaluări