Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Design of Foundations in France With The
Încărcat de
76027074Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Design of Foundations in France With The
Încărcat de
76027074Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1
Design of foundations in France with the
use of Mnard pressuremeter tests (MPM)
Roger FRANK
Ecole nationale des ponts et chausses
UR Navier, CERMES (ENPC-LCPC), Paris
Gersevanovskie Chteniya
Gersevanovskie Chteniya
Laboratory and in
Laboratory and in
-
-
situ soil investigation
situ soil investigation
Moscow, 15 April 2009
Moscow, 15 April 2009
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
2
I. The Mnard pressuremeter :
general
II. Bearing capacity and settlement
of shallow foundations
III. Bearing capacity of piles
IV. Settlement of piles & laterally
loaded piles
V. Annexes in Eurocode 7 Part 2
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
3
CPV SPAD
Tubulure
I. The Mnard pressuremeter : general
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
4
Lola
Inflated probe
Compressed
nitrogen bottle
Pressure-Volume
controller
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
5
(from ENV 1997-3,
1999)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
6
Pressuremeter probe placement techniques
(AFNOR Standard, 1991)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
7
Allowed boring techniques (prEN ISO 22476-4)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
8
Allowed boring techniques (cntd)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
9
Caption
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
10
Drilling stage length (prEN ISO 22476-4)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
11
(from ENV 1997-3,
1999)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
12
DOCUMENT APAGEO - XPRESSIO
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
0 0,2 0,4 0,6 0,8 1 1,2 1,4 1,6 1,8
p
1
p
2
p
f
EM = 23 MPa
P
l
=
1
,
7
M
P
a
V
S
+ 2V
1
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
13
Influence of placement
Influence of placement
method
method
St St- -Malo de Phily sand Malo de Phily sand
(after Jzquel, Lemasson (after Jzquel, Lemasson
& Touz, 1968) & Touz, 1968)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
14
Standards
NF P 94-110-1
Standard in use in France presently.
Data recording is mandatory
EN ISO 22476-4
Project for European standard under
publication. Data recording is optional
(procedure B)
ASTM D-4719
American standard (1987)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
15
Pressuremeter soil profile
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
16
Use of in situ test results
The direct method (semi-empirical) should be preferred
i.e direct rules for determining the bearing capacity of
foundations from the test results :
(and possibly the displacements)
Specific advantages of the Pressuremeter
with the limit pressure p
LM
:
bearing capacity of shallow foundations (q
p
)
axial bearing capacity of deep foundations (q
p
and q
s
)
With the pressuremeter modulus E
M
:
settlement of shallow foundations (s)
analysis of the behaviour of deep foundations under
transverse loading
q
d
,N,q
c
, etc.
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
17
Bearing capacity : the pressuremeter faith
q
u
= q
o
+ k
p
(p
le
- p
o
)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
18
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
19
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
20
44
48
0
4
4 8
Pic de Aneto
3404m
150 km
Mt-Blanc
4807 m
CHANNEL
ATLANTIC
OCEAN
MEDITERRANEAN
SEA
PARIS
BASIN
Armorican Massif
Ardennes
Alps
Central
Massif
Jura
Vosges
Pyrenees
BASIN
AQUITAINE
Volcanic rocks
Tectonic faulting
Hercynian massifs
Sedimentary basins
Littoral plains
Alluvial valleys
Alpine chains
Subsidence valleys
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
21
Table 2 Field and laboratory tests feasability after Bustamante & Gianeselli (2006)
Test carried out to full
design length (1)
incomplete test
(2)
not carried out
(3)
not applicable
(4)
PMT
pressuremeter
(p
l
)
155 3 46 0
CPT
(q
c
)
60 79 23 42
laboratory
tests
(c
u
, c', ')
21 67 69 47
SPT
(N)
26 54 72 52
(1) including the full length of pile + additional metres below the pile point
(2) due to premature refusal for CPT; sampling not possible for laboratory tests; soil
strength too high for SPT
(3) feasible but not planned when the investigation campaign was decided
(4) considered from the beginning as inadequate with respect to soil nature or strength
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
22
settlement s,
differential settlement
s, rotation and
angular strain
relative deflection
and deflection ratio /L
and relative rotation
(angular distortion)
(after Burland and Wroth,
1975)
smax
s
m
a
x
Allowable settlements of structures
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
23
Foundations of buildings (Eurocode 7, 1994)
* Serviceability limit states (SLS) :
max
1/500
* Ultimate limit states (ULS) :
max
1/150
s
max
50 mm
smax
20 mm
Foundations of bridges
Moulton (1986) for 314 bridges in the US and Canada :
*
max
1/250 (continuous deck bridges)
and
max
1/200 (simply supported spans)
* s
Hmax
40 mm
In France, in practice :
ULS :
max
1/250
SLS :
max
1/1000 1/500
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
24
The pressuremeter test can be performed
in all types of soils and soft rocks
It provides the soil engineer with both a
failure parameter and a deformation
parameter measured in situ
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
25
Soil type
p
l
(MPa)
q
c
(MPa)
Clay A soft < 0.7 < 3
Silt B stiff 1.2 - 2 3 - 6
C hard(clay) > 2.5 > 6
Sand A loose < 0.5 < 5
Gravel B medium 1- 2 8 - 15
C dense > 2.5 > 20
A soft < 0.7 < 5
Chalk B weathered 1 - 2.5 > 5
C dense > 3 -
Marl A soft 1.5 - 4 -
Calcareous marl B dense > 4.5 -
Rock A weathered (1) 2.5 - 4 -
B fragmented > 4.5 -
(1) use the value of the most similar soil.
Conventional categories in F 62-V
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
26
II. Bearing capacity and settlement
of shallow foundations
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
27
Bearing factors for square or circular footings
(LCPC, 1988)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
28
Bearing factors for strip footings
(LCPC, 1988)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
29
Design bearing capacity
Reference stress q
rf
:
i
reduction factor depends on , , d/B
e
, D
e
/B
e
And
q
= 2 for ULS
q
= 3 for SLS
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
30
Pressuremeter method for settlement
prediction
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
31
Mnards formula for settlement
years)
is the volumetric settlement
is the deviatoric settlement
Rheological coefficient
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
32
Selection of moduli E
c
and E
d
E
c
= E
1
and
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
33
Experimental assessment
(Amar et al.,1987)
Comparions of estimated 10 year settlements under q
u
/2
from measurements, Mnard formula and elasticity theory
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
34
III. Bearing capacity of piles
(Bustamante & Gianeselli, 1982, under revision,
see Bustamante & Gianeselli, 2006, 2008)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
35
Pressuremeter method : point resistance
q
u
= q
o
+ k
p
(p
le
- p
o
)
Table of bearing factors k
p
SOIL NON DISPLACEMENT PILE DISPLACEMENT PILE
A 1.1 1.4
Clay & Silt B 1.2 1.5
C 1.3 1.6
A 1.0 4.2
Sand & Gravel B 1.1 3.7
C 1.2 3.2
A 1.1 1.6
Chalk B 1.4 2.2
C 1.8 2.6
A Marl & Calcareous Marl
B
1.8 2.6
A
Weak Rock
B
1.1 to 1.8 1.8 to 3.2
(after Bustamante and Gianeselli, 1982)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
36
Pressuremeter method : unit shaft friction
q
s
= f (soil, p
l
*; pile + specific conditions)
(after Bustamante and Gianeselli, 1982)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
37
Q
7
(7) Q
6
Q
6
Q
5
- Q
6
Q
5
Q
5
Q
4
- High pressure
injected (6)
- Q
5
Q
4
Q
3
Q
2
Q
3
Q
2
Q
1
Low pressure
injected
- Q
4
Q
3
(4) Q
4
Q
3
Q
2
Q
1
Driven coated
- Q
4
Q
3
Q
3
Q
2
Q
1
Q
3
Q
2
Q
2
Q
1
Driven moulded
Q
4
Q
4
Q
3
(4) Q
3
Q
2
Q
1
Driven concrete
Q
4
Q
4
Q
3
(4) Q
3
Q
2
Q
2
Q
1
Steel driven
closed-ended
Q
6
Q
5
Q
4
Q
3
Q
2
Q
1
- Q
2
Q
1
Piers (5)
- Q
3
Q
2
(4) Q
2
Q
1
Q
1
Drilled,
permanent casing
- Q
4
Q
3
Q
3
Q
4
(3)
Q
3
Q
1
Q
3
Q
2
(2)
Q
2
Q
1
(2)
Q
1
Q
1
Q
1
Drilled, removed
casing
Q
6
Q
4
Q
5
(1)
Q
3
Q
4
Q
5
(1)
Q
3
Q
1
Q
3
Q
2
(2)
Q
2
Q
1
(2)
Q
1
Q
1
Q
2
(1)
Q
1
Drilled with mud
Q
6
Q
4
Q
5
(1)
Q
3
Q
4
Q
5
(1)
Q
3
Q
1
- Q
2
Q
3
(1)
Q
1
Q
2
(1)
Q
1
Drilled no mud
C B A C B A C B A C B A
ROCK MARL CHALK SAND & GRAVEL CLAY & SILT Type of pile
(1)trimmed and grooved at the end of drilling (2)for long piles (longer than 30 m) (3)dry excavation, no rotation of
casing (4)in chalk, qs can be very low for some types of piles ; a specific study is needed (5)without permanent
casing (rough pile walls) (6)low rate injection and repeated grouting at selected depths (7)(6)plus preliminary treatment
of fissured or fractured masses and filling of cavities.
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
38
Ultimate limit states :
- fundamental combinations :
- Q
tu
/ 1.4 Q
d
Q
u
/ 1.4
- accidental combinations :
- Q
tu
/ 1.3* Q
d
Q
u
/ 1.2
(* for micropiles the minimum is : : -Q
tu
/ 1.2)
Serviceability limit states :
- rare combinations :
- Q
tc
/ 1.4* Q
d
Q
c
/ 1.1
- quasi-permanent combinations:
-0** Q
d
Q
c
/ 1.4
(for micropiles: * the minimum is - Q
tc
/1.1 ; ** the minimum is - Q
tc
/1.4)
Creep load
ND piles : Q
c
= Q
p
/ 2 + Q
s
/ 1,5
D piles : Q
c
= Q
p
/ 1,5 + Q
s
/ 1,5
Design bearing capacity
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
39
IV. Settlement of piles
& laterally loaded piles
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
40
k
q
s
q
s
2
z
k
5
k
q
q
b
q
b
2
q
z
b
5
k
q
Settlement of piles
T-z curves from Mnard pressuremeter modulus E
M
for fine grained soils :
k
= 2.0 E
M
/B and k
q
= 11.0 E
M
/B
for granular soils
kt = 0.8 E
M
/B and k
q
= 4.8 E
M
/B
(after Frank et Zhao, 1982)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
41
Example : driven pile in marl (Le Vair)
(after Bustamante, Frank & Gianeselli, 1989)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
42
s
e
t
t
l
e
m
e
n
t
S
o
(
m
m
)
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
0 500 1000 1500
Load Q
o
(kN)
calculated
measured
Example : screw pile in Ypresian clay (Belgium)
(Bustamante & Gianeselli, 1993)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
43
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
0 10 20 30 40
E
M
(MPa)
z
(
m
)
EM moyen
EM-Forage100
EM-Forage-10
EM-Forage20
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
0,0 0,5 1,0 1,5 2,0
p
LM
(MPa)
z
(
m
)
pLM moyen
pLM-Forage100
pLM-Forage10
pLM-Forage20
Example : CFA pile in silt and clay (Northern France)
B = 0.5 m ; D = 12 m (ISP5 exercise, 2005)
(Reiffsteck, 2005)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
44
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400
Charge en tte / vertical load (kN)
d
p
l
a
c
e
m
e
n
t
/
s
e
t
t
l
e
m
e
n
t
(
m
m
)
Pieu test/pile tested
(Bustamante M. et Gianeselli L.)
Antoinet et al.
Bahar et al.
Robas et Kuder
Said et al.
Mecsi
Monnet
Results of the exercise (ISP5)
* *
* *
* * using Frank & Zhao using Frank & Zhao
(1982) (1982)
(Reiffsteck, 2005)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
45
Laterally loaded piles : the Mnard
subgrade reaction modulus method
P(y)
P(y)
Reaction curve P-Y
for long duration loads
18
E
s
= E
M
--------------------------------
4(2,65 B/Bo)
Bo/B + 3
E
s
= Mnard reaction modulus
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
46
d
4
y
EI ---- + P(y - g) = 0
dz
4
Extension to lateral thrusts
(LCPC, 1981)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
47
Example : the Provins pile
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
48
(Bigot, Bourges and Frank, 1982)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
49
V. Annexes in Eurocode 7 Part 2
In informative annexes : examples of
calculation models :
Spread foundations :
Bearing resistance (Annex E.1)
Settlement (Annex E.2)
Pile bearing resistance (Annex E.3)
(Annexes E.1, E.2 and E.3 are the models of Fascicule 62 (Annexes E.1, E.2 and E.3 are the models of Fascicule 62 (Annexes E.1, E.2 and E.3 are the models of Fascicule 62 (Annexes E.1, E.2 and E.3 are the models of Fascicule 62- -- -
V presented above) V presented above) V presented above) V presented above)
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
50
Conclusions for MPM
Mnard pressuremeter tests can be performed in
all soils and soft rocks
It provides for a deformation as well as for a
failure parameters
These parameters, used with simple rules, charts
or softwares (for t-z or p-y approaches) can
solve most of the current problems of shallow
and deep foundations
This vision is fully compatible with Eurocode 7...
The rest is a matter of engineering judgement !
R Frank, Design of foundations in France with the use MPM tests, RSSMGFE Seminar, Moscow, 15 April 2009
51
Thank you for your attention !
!
Acknowledgments :
and
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Technical CharacteristicsDocument36 paginiTechnical Characteristics76027074Încă nu există evaluări
- Pressuremeter Method For Foundation in HongkongDocument13 paginiPressuremeter Method For Foundation in Hongkong76027074Încă nu există evaluări
- T.C. Williams High SchoolDocument31 paginiT.C. Williams High School76027074Încă nu există evaluări
- En 1998: Eurocode 8 Design of Structures For Earthquake ResistanceDocument214 paginiEn 1998: Eurocode 8 Design of Structures For Earthquake Resistance76027074100% (2)
- IBC1997-UBC2000 Structural Comparison and Cross ReferenceDocument240 paginiIBC1997-UBC2000 Structural Comparison and Cross Referencerobersasmita100% (1)
- UK National Annex To Eurocode 9: Design of Aluminium StructuresDocument14 paginiUK National Annex To Eurocode 9: Design of Aluminium Structures76027074Încă nu există evaluări
- SAP ManualDocument159 paginiSAP Manual76027074Încă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- 11 Design of FootingDocument127 pagini11 Design of FootingWesam Salah Aloolo100% (1)
- AASHTO GeoTechnical Design of PileDocument5 paginiAASHTO GeoTechnical Design of PiletrannguyenvietÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Foundation Engineering: (7th Edition)Document3 paginiPrinciples of Foundation Engineering: (7th Edition)cristhian zamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
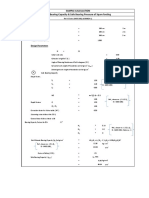
- Swimming Pool Structural CalcsDocument7 paginiSwimming Pool Structural CalcsFrederick QuintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Shallow Foundation 1 43Document11 paginiChapter 1 Shallow Foundation 1 43చిమ్ముల సందీప్ రెడ్డిÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis and Design of Secant PilesDocument57 paginiAnalysis and Design of Secant PilesRohan BhagatÎncă nu există evaluări
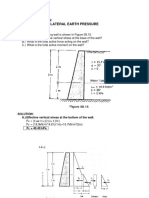
- Lateral Earth Pressure Sample ProblemsDocument10 paginiLateral Earth Pressure Sample ProblemsMugiwara Sparrow100% (1)
- Analysis of Bearing Capacity Shallow FoundationDocument12 paginiAnalysis of Bearing Capacity Shallow FoundationgreenwalletÎncă nu există evaluări
- UG 4-1 R19 Civil SyllabusDocument42 paginiUG 4-1 R19 Civil SyllabusMasimukkala SunithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Field TestsDocument45 paginiField TestsVivek DhutÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMPUTATION OF BEARING CAPACITY FACTOR NQDocument10 paginiCOMPUTATION OF BEARING CAPACITY FACTOR NQRené Acco RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buoyancy Control For Pipelines Buoyancy Control For PipelinesDocument12 paginiBuoyancy Control For Pipelines Buoyancy Control For PipelinesMukiara LuffyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Show All The Necessary Steps To Solve The Following ProblemsDocument2 paginiShow All The Necessary Steps To Solve The Following ProblemsMistireselassieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effective Bearing Length of Crane Mats - DuerrDocument8 paginiEffective Bearing Length of Crane Mats - DuerrbuthainasalehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Calculation Safe Bearing Capacity & Safe Bearing Pressure of Squre FootingDocument2 paginiSample Calculation Safe Bearing Capacity & Safe Bearing Pressure of Squre Footingdharmpal yadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Calculation & AnalysisDocument13 paginiDesign Calculation & AnalysisAbel Meketa100% (1)
- Yeo 1993Document14 paginiYeo 1993RooyagroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCHRP24-17 AppendixDDocument70 paginiNCHRP24-17 AppendixDHassan HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typical Soil ReportDocument19 paginiTypical Soil Reportk.chethuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 32 Pile Desing Clay Soils PDFDocument23 pagini32 Pile Desing Clay Soils PDFSebastian TrescureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maritime Geotechnics I Homework # 2 Topics: Shallow FoundationsDocument5 paginiMaritime Geotechnics I Homework # 2 Topics: Shallow FoundationsWilliams AnthonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Failure Analysis of Reinforced Foundation Using Transparent SoilsDocument9 paginiFailure Analysis of Reinforced Foundation Using Transparent SoilsJianfeng XueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample GT 1Document1 paginăSample GT 1vivekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Móng Nông - Thầy Sỹ HùngDocument51 paginiMóng Nông - Thầy Sỹ HùngThành TríÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanically Stabilized Earth WallDocument8 paginiMechanically Stabilized Earth WallDadi YashwantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wells & Caissons CHAPTER 1 IntroductionDocument3 paginiWells & Caissons CHAPTER 1 IntroductionSunil Sekhar RathÎncă nu există evaluări
- S3 BMC - Mod2Document52 paginiS3 BMC - Mod2DHEESHNA DILEEP 200545Încă nu există evaluări
- Well FoundationDocument143 paginiWell FoundationJagat Kumar Shrestha100% (2)
- Bearing Capacity of Soils - Lec 1Document18 paginiBearing Capacity of Soils - Lec 1JavidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WONG & GOH Basal Heave Stability For Wide ExcavationsDocument7 paginiWONG & GOH Basal Heave Stability For Wide ExcavationsdnavarroÎncă nu există evaluări