Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
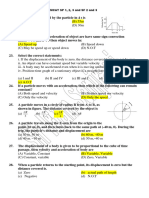
Physics: Section - I Straight Objective Type
Încărcat de
Sayan Kumar KhanTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Physics: Section - I Straight Objective Type
Încărcat de
Sayan Kumar KhanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PHYSICS
SECTION I
Straight Objective Type
This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D),
out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
24. Velocity of a particle moving along a straight line is related with position as
2 2
a
v
(b x )
here, a and b are positive constants.
Draw the approximate graph of acceleration versus position.
(A)
a
x
(B)
a
x
(C)
a
x
(D) none of these.
25. Assuming all the surfaces to be frictionless find the
magnitude of net acceleration of smaller block m with
respect to ground
(A)
2 5mg
(5m M)
(B)
2mg
(5m M)
M
m
(C)
7 5mg
(5m M)
(D) none of these.
26. Resultant of two vectors having same magnitude forms an angle with any of the vectors. If
the magnitude of second vector is reduced to half of initial magnitude wit hout changing the
angle between the direction of new resultant vector and first vector is also reduced to half,
then the angle between the two vectors is
(A) 120 (B) 60
(C) 90 (D) 45.
27. A particle of mass m moving due east with a speed v collides with another particle of same
mass and same speed moving due north. The two particles coalesce on collision. Find the
velocity of the new particle ?
(A) v (B) 2v
(C)
v
2
(D) none of these.
28. To a man moving due north with a speed 5 ms
1
, the rain appears to fall vertically. When the
man doubles his speed, the rain appears to fall at 60. Find the actual speed of the rain and its
direction.
(A) 10 m/s, 120 (B) 10 m/s, 180
(C) 10 m/s, 90 (D) 10 m/s, 60.
29. A car is travelling at a velocity 10 kmh
1
on a straight road. The driver of the car throws a
parcel with a velocity
1
10
kmh
2
when car is passing by a man standing on the side of a road.
If parcel just reaches the man, find the angle which the direction of throw makes an angle
with the direction of car ?
(A) 135 (B) 45
(C)
1
tan 2 (D)
1
1
tan
2
.
SECTION II
Multiple Correct Answer Type
This section contains 4 multiple correct answer(s) type questions. Each question has 4 choices
(A),(B), (C) and (D), out of which ONE OR MORE is/are correct.
30. In the figure, the pulley P moves to the right with a constant
speed u. The downward speed of A is
A
, and the speed of B to
the right is
B
(A)
A B
(B)
B A
u
A
B
P
u
(C)
B A
u
(D) the two blocks have accelerations of the same magnitude
31. Two particles A and B start simultaneously from the same point and move in a horizontal
plane. A has an initial velocity u
1
due east and acceleration a
1
due north. B has an initial
velocity u
2
due north and acceleration a
2
due east
(A) their paths must intersect at some point
(B) they must collide at some point
(C) they will collide only if a
1
u
1
= a
2
u
2
(D) if u
1
> u
2
and a
1
< a
2
, the particles will have the same speed at some point of time
32. A large rectangular box ABCD falls vertically with an acceleration
a. A toy gun fixed at A and aimed towards C fires a particle P.
(A) P will hit C if a = g
(B) P will hit the roof BC if a > g
A
B C
D
P
u
(C) P will hit the wall CD or the floor AD if a < g
(D) may be either (A), (B) or (C), depending on the speed of projection of P
33. A man who can swim at a speed relative to the water wants to cross a river of width d,
flowing with a speed u. the point opposite him across the river is P.
(A) the minimum time in which has can cross the river is
d
(B) he can reach the point P in time
d
(C) he can reach the point P in time
2 2
d
u
(D) he cannot reach P if u >
SECTION III
Reasoning Type
This section contains 4 reasoning type questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D),
out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Code
(A) STATEMENT1 is True, STATEMENT2 is True; STATEMENT2 is a correct explanation for
STATEMENT1
(B) STATEMENT1 is True, STATEMENT2 is True; STATEMENT2 is NOT a correct explanation for
STATEMENT1
(C) STATEMENT1 is True, STATEMENT2 is False
(D) STATEMENT1 is False, STATEMENT2 is True
34. STATEMENT 1
The maximum range along the inclined plane, when through downward is greater than that
when thrown upward along the same inclined plane with constant velocity.
because
STATEMENT 2
The maximum range along inclined plane is independent of angle of inclination.
35. STATEMENT 1
A particle is projected at an angle ( < 90) to horizontal, with a velocity u. When particle
strikes the ground its speed is again u.
because
STATEMENT 2
Velocity along horizontal direction remains same but velocity along vertical direction is
changed. When particle strikes the ground then magnitude of final vertical velocity is equal to
magnitude of initial vertical velocity.
36. STATEMENT 1
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined plane of inclination with the horizontal.
The force exerted by the plane on the block has a magnitude mg cos .
because
STATEMENT 2
Normal reaction always acts perpendicular to the contact surface.
37. STATEMENT 1
In high jump, it hurts less when an athlete lands on a heap of sand.
because
STATEMENT 2
Because of greater distance and hence greater time over which the motion of an athlete is
stopped, the athlete experience less force when lands on heap of sand.
SECTION IV
Linked Comprehension Type
This section contains 3 paragraphs. Based upon each paragraph, 3 multiple choice questions have
to be answered. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of which ONLY ONE is
correct.
Paragraph for Questions Nos. 38 to 40
When a particle is projected at some angle with the horizontal, the path of the particle is parabolic in
nature. In the process the horizontal velocity remains constant but the magnitude of vertical velocity
changes. At any instant during flight the acceleration of particle remains g in vertically downward
direction. During flight at any point the path of particle can be considered as a part of circle and
radius of that circle is called the radius of curvature of the path of particle.
Consider that a particle is projected with velocity u = 10 m/s at an angle = 60 with the horizontal
then :
Answer the following questions
38. The radius of curvature of path of particle at the instant when the velocity vector of the
particle becomes perpendicular to initial velocity vector is
(A)
20
m
3 3
(B)
10
m
3 3
(C)
40
m
3 3
(D)
80
m
3 3
39. The magnitude of acceleration of particle at that instant is
(A) 10 m/s
2
(B)
2
5 3m/ s
(C) 5 m/s
2
(D)
2
10 3m/ s
40. Tangential acceleration of particle at that instant will be
(A) 10 m/s
2
(B) 20 m/s
2
(C) 5 m/s
2
(D)
2
5 3m/ s
Paragraph for Questions Nos. 41to 43
II. A particle is projected with velocity u at an angle with an
inclined plane of inclination < 45 with the horizontal.
u
41. The time taken when velocity of projectile becomes parallel to the plane
(A)
usin
g
(B)
ucot
g
(C)
2u tan
g
(D)
u tan
g
42. The net velocity at the time when velocity is parallel to the plane is
(A)
ucos
g
(B)
usin 2
g
(C)
u cos 2
cos
(D) u tan
43. Radius of curvature of the path of projectile when velocity is parallel to the plane
(A)
2 2
u cos
g
(B)
2 2
3
u cos 2
gcos
(C)
2
u cos
g
(D)
2
3
u
gcos
Paragraph for Questions Nos. 44 to 46
An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion will continue its motion with a constant
velocity unless it experiences a net external force. But the magnitude of force given by Newtons 2
nd
law and 3
rd
law represents or gives the information about the nature of force. The second law gave a
specific way of determining how the velocity changes under different influences called forces. There
are so many forces calculated by Newtons law such as Normal force, Tension, Viscous, Weight but
Newtons laws are not applicable, when velocity of an object comparable to the velocity of light and
microscopic particle. If the system contains large number of particles, then if we apply the Newtons
laws, concept of centre of mass is included.
44. Pulley and strings are massless. The force acting on the
block of mass m :
(A) 2F (B) F
(C)
F
2
(D) 4F.
m
F
T T
TT
45. A particle of mass m moves along a circle of radius R. The modulus of average value of force
acting on particle over the distance equal to a quarter of circle, if the particle moves
uniformly with velocity v is :
(A)
2
2mv
r
(B)
2
2
2 2mv
r
(C)
2
2 2mv
r
(D)
2
mv
r
.
46. If force of movable pulley is V and velocities of block of
masses m
1
and m
2
are V
1
and V
2
then the correct relation
between them :
(A) V = V
1
+ V
2
(B)
1 2
V V
V
2
(C) V = 2 (V
1
+ V
2
) (D) V = V
1
V
2
.
M
1
M
0
M
2
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Complete Course in Physics ( Graphs ) - First EditionDe la EverandA Complete Course in Physics ( Graphs ) - First EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy 01Document212 paginiPhy 01Varsha Dange100% (1)
- 112學年A卷題庫Document10 pagini112學年A卷題庫larry940106Încă nu există evaluări
- JEE Main 2020-22 PYQ KinematicsDocument158 paginiJEE Main 2020-22 PYQ Kinematicspankaj baidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsDe la EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Physics Section - IDocument6 paginiPhysics Section - ISayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Kinematics Anil SirDocument9 pagini01 Kinematics Anil SirOasisEducation Oes100% (1)
- Kinematics QuestionDocument10 paginiKinematics QuestionNITESH BHARGAVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iit PaceDocument19 paginiIit PaceabhishekjanjalkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Book-I (First Test)Document4 paginiFull Book-I (First Test)Syed Shahzad AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jee Main Part Test 1Document13 paginiJee Main Part Test 1Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion in Plane-SubjectiveDocument4 paginiMotion in Plane-Subjective21- VARNIKA DALALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion in Plane AssignmentDocument3 paginiMotion in Plane Assignmentdishugirdhar08Încă nu există evaluări
- Test02 SolDocument11 paginiTest02 Solnareshsuja123Încă nu există evaluări
- XI Mock TestDocument15 paginiXI Mock TestDont KnowÎncă nu există evaluări
- KinematicsDocument9 paginiKinematicsChunu Physics loverÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 - Phy - Sample Paper - Half Yearly-Set ADocument5 pagini11 - Phy - Sample Paper - Half Yearly-Set Ajaiswalswayam05Încă nu există evaluări
- Motion in One and Two Dimensions PDFDocument4 paginiMotion in One and Two Dimensions PDFTarun GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Final TestDocument9 paginiOpen Final Testneerajnitin0110% (1)
- Objective Booklet - 2/physics: Motion in Two Dimension Chapter - 3Document8 paginiObjective Booklet - 2/physics: Motion in Two Dimension Chapter - 3abhishekagarwala21Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Document7 paginiSample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Sukhwinder KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projectile Motion and Kinematics QuestionsDocument12 paginiProjectile Motion and Kinematics QuestionsManish GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Praveen-Fl (22-23) MPT - 1Document14 paginiPraveen-Fl (22-23) MPT - 1Duckiest :DÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Paper: Class: XI General InstructionsDocument8 paginiSample Paper: Class: XI General InstructionsShivam KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- P - 3Y - Test Paper - Motion in 2 Dimension.Document5 paginiP - 3Y - Test Paper - Motion in 2 Dimension.sudhir_kumar_33Încă nu există evaluări
- QPDocument5 paginiQPSamuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- P0IITU05 - Rotational Motion QnsDocument7 paginiP0IITU05 - Rotational Motion QnsxTERMINATOR007Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics ProjectDocument16 paginiPhysics ProjectVivek SreerajÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Physics A1A2 Annual Exam 2023 24 MSDocument14 pagini11 Physics A1A2 Annual Exam 2023 24 MSharshitsharmasportsÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Motion in a PlaneDocument31 paginiMCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Motion in a Planekirki pÎncă nu există evaluări
- PT 1Document8 paginiPT 1LOVELESH KHATTERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 11Document21 paginiTest 11Babbi SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jee KinematicsDocument8 paginiJee KinematicsSankar KumarasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Test 2-2Document16 paginiPractice Test 2-2ชวิศา อาภาวรรัฐÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Test Contains A Total of 10 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDocument19 paginiThis Test Contains A Total of 10 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE Markingvarunkohliin100% (1)
- DPP - Force and MotionDocument3 paginiDPP - Force and MotionaasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jee 2014 Booklet2 HWT Motion in 2dDocument16 paginiJee 2014 Booklet2 HWT Motion in 2dvarunkohliinÎncă nu există evaluări
- G-11 Physics FinalDocument6 paginiG-11 Physics FinalAlok DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- General PhysicsmidDocument4 paginiGeneral Physicsmidkoket engidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics QPDocument13 paginiPhysics QPAniket DebnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABC XI TEST SERIES TEST-02 CHAPTER 2 and 3 2023-24Document2 paginiABC XI TEST SERIES TEST-02 CHAPTER 2 and 3 2023-24Ashish GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinematics + Particle of Dynamics (QB) For - FDocument16 paginiKinematics + Particle of Dynamics (QB) For - FRaju SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xi - DPP # Mechanics (22.3.2016)Document12 paginiXi - DPP # Mechanics (22.3.2016)Sankar Kumarasamy0% (2)
- QP G11 Phy Ae 2023Document9 paginiQP G11 Phy Ae 2023snikitha.padalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIT JEE Physics Question Bank RBC Kinematics Circular Motion Friction NLM WPEDocument33 paginiIIT JEE Physics Question Bank RBC Kinematics Circular Motion Friction NLM WPEMUSIC WORLDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion in A Plane: © Ncert Not To Be RepublishedDocument10 paginiMotion in A Plane: © Ncert Not To Be RepublishedAnchitBansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11th Physics PT-2Document2 pagini11th Physics PT-2raghavendra jÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.7-8, TEST - ROTATION AND GRAVITATION COMBINED MCQs 21-22Document6 pagini11.7-8, TEST - ROTATION AND GRAVITATION COMBINED MCQs 21-22AJAY SINGH RAGHAVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iit (M+a) & Jee Mains Only-Diwali Assignment-XiDocument60 paginiIit (M+a) & Jee Mains Only-Diwali Assignment-XiSara WolfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Motion (MCQ)Document17 paginiCircular Motion (MCQ)Laxman Selvam100% (5)
- Circular MotionDocument37 paginiCircular MotionSaurav Biyani100% (1)
- Class 11 Physics PRE TERM 1 Revision WorksheetDocument4 paginiClass 11 Physics PRE TERM 1 Revision WorksheetSuman KunduÎncă nu există evaluări
- XI MCQ UP To ROTATION-converted-compressedDocument22 paginiXI MCQ UP To ROTATION-converted-compressedEkamjot SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objective Question Bank: KinematicsDocument11 paginiObjective Question Bank: KinematicsAtulÎncă nu există evaluări
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN DEHRADUN REGION SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER (2022-23) CLASS XI PHYSICSDocument13 paginiKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN DEHRADUN REGION SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER (2022-23) CLASS XI PHYSICSAmythÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Irfan MCATDocument6 paginiPhysics Irfan MCATjaipal singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monday Test 1 Xi 21-22Document5 paginiMonday Test 1 Xi 21-22Yash MorjhawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 KinematicsDocument7 paginiUnit 2 KinematicsSabia IdrisiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gate Mathematics: MAI) 4SDocument258 paginiGate Mathematics: MAI) 4SManivannan VadiveluÎncă nu există evaluări
- NetMarks C 19122017Document132 paginiNetMarks C 19122017Manish SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DurgaSoft SCJP Notes Part 1 - JavabynataraJ PDFDocument255 paginiDurgaSoft SCJP Notes Part 1 - JavabynataraJ PDFSiva Sai Charan KondapiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compiler Hand Written Notes Made EasyDocument127 paginiCompiler Hand Written Notes Made EasyArpkeet IJÎncă nu există evaluări
- View - Print Submitted Form PDFDocument2 paginiView - Print Submitted Form PDFRAHUL KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicrocontrollerDocument414 paginiMicrocontrollerSayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating System GATE NotesDocument176 paginiOperating System GATE NotesVicky TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSC JE Result Notice 2016Document2 paginiSSC JE Result Notice 2016Kabya Srivastava100% (1)
- SSC JE Result Notice 2016Document2 paginiSSC JE Result Notice 2016Kabya Srivastava100% (1)
- Ju Ug Placement Records 2019-20Document2 paginiJu Ug Placement Records 2019-20Sayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Novak DjokovicDocument12 paginiNovak DjokovicSayan Kumar Khan100% (1)
- Hibernate - Natraj - SatyaDocument262 paginiHibernate - Natraj - SatyaMichael J GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicroProcessor & Computer OrganisationDocument74 paginiMicroProcessor & Computer OrganisationAnubhab BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Java Applet BasicsDocument10 paginiJava Applet BasicsrednriÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP QBDocument19 paginiMP QBRaji SharmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8085 Microprocessor Opcode TableDocument6 pagini8085 Microprocessor Opcode TableSagnik Gangopadhyay67% (3)
- Micro NotesDocument24 paginiMicro NotesSayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8051 ExplainedDocument16 pagini8051 ExplainedApurva DesaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Notes 2-1Document11 paginiMicro Notes 2-1Sayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 16Document28 paginiPaper 16Sayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 29 QusDocument16 pagini29 QusAsafAhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 15Document26 paginiPaper 15Sayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 9Document20 paginiPaper 9Sayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 33 QusDocument15 pagini33 QusAsafAhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 6Document20 paginiPaper 6Sayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 13Document22 paginiPaper 13Sayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiitjee: JEE (Advanced), 2015Document24 paginiFiitjee: JEE (Advanced), 2015Sayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 8Document23 paginiPaper 8Sayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 7Document22 paginiPaper 7Sayan Kumar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eca Lab Record PDFDocument71 paginiEca Lab Record PDFAlokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eng Grammar Book 8Document77 paginiEng Grammar Book 8ЖАНСАЯ Сейдахмет50% (2)
- Accelerate your career with online coursesDocument22 paginiAccelerate your career with online coursesAYEDITAN AYOMIDEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux OS LabDocument2 paginiLinux OS LabSubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 2Document16 paginiTest 2edwardÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-Lecture 03 Translational Mechanical System3-SDocument23 pagini3-Lecture 03 Translational Mechanical System3-SHamza KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Molecules and Compounds: Practice TestDocument2 pagini3 - Molecules and Compounds: Practice Testfamily_jvcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document11 paginiChapter 1bekemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catchment YieldDocument7 paginiCatchment YieldBernard PalmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazardous Area Hazardous Area ClassificaDocument106 paginiHazardous Area Hazardous Area ClassificaHedi Ben MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart Card/Proximity Based Vehicle Identification & Access Control SystemDocument4 paginiSmart Card/Proximity Based Vehicle Identification & Access Control SystemkarunamoorthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matrix Inversion Note in Mathematics MagazineDocument2 paginiMatrix Inversion Note in Mathematics Magazinejuan carlos molano toroÎncă nu există evaluări
- TP 03: Technique D'optimisation PSODocument3 paginiTP 03: Technique D'optimisation PSOCEM Yelle N centreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability DPP (1 To 7) 13th WADocument16 paginiProbability DPP (1 To 7) 13th WARaju SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- ETABS Building Structure Analysis and Design ReportDocument84 paginiETABS Building Structure Analysis and Design ReportMd Awesshadab0% (1)
- Alkali Boil Out ProcedureDocument7 paginiAlkali Boil Out Procedureismail karmanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and Bases NotesDocument17 paginiAcids and Bases NotesNap DoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eps Manual NissanDocument8 paginiEps Manual Nissanjoiler pajueloÎncă nu există evaluări
- LsApi PDFDocument347 paginiLsApi PDFEduardo Martin Vega100% (2)
- It Tigear2Document2 paginiIt Tigear2rrobles011Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit - L: List and Explain The Functions of Various Parts of Computer Hardware and SoftwareDocument50 paginiUnit - L: List and Explain The Functions of Various Parts of Computer Hardware and SoftwareMallapuram Sneha RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Live load and wind pressure on sloping roofsDocument11 paginiLive load and wind pressure on sloping roofsAbel BerhanemeskelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modular Forms Exam - Homework RewriteDocument2 paginiModular Forms Exam - Homework RewritejhqwhgadsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Angles and Inscribed Angles GuideDocument22 paginiCentral Angles and Inscribed Angles GuideEric de Guzman100% (1)
- Kidney AnatomyDocument55 paginiKidney AnatomyMohammad zreadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fix Disk & Partition ErrorsDocument2 paginiFix Disk & Partition Errorsdownload181Încă nu există evaluări
- The Pauli Exclusion PrincipleDocument33 paginiThe Pauli Exclusion Principle3449336893Încă nu există evaluări
- Programming structures if, for and while loopsDocument16 paginiProgramming structures if, for and while loopsFrancisco AristizabalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eee f111 Electrical Sciences1Document3 paginiEee f111 Electrical Sciences1aryan mittalÎncă nu există evaluări
- IJETR032052Document6 paginiIJETR032052erpublicationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDe la EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (69)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDe la EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDe la EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (48)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDe la EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDe la EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDe la EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (500)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceDe la EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDe la EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1395)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDe la EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (125)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDe la EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2193)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishDe la EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (18)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsDe la EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (94)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDe la EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (409)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDe la EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)De la EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (155)
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityDe la EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (380)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDe la EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (8)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsDe la EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (57)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDe la EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDe la EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (76)
- The 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishDe la EverandThe 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (4)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationDe la EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (158)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseDe la EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (13)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsDe la EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)