Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Sagar Cement Points
Încărcat de
Sakhamuri Ram'sDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sagar Cement Points
Încărcat de
Sakhamuri Ram'sDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRY PROFILE:
The Indian Cement industry is the second largest cement producer in the
world, with an installed capacity of 144 million tones. The industry has undergone
rapid technological up gradation and vibrant growth during the last two decades,
and some of the plants can be compared in every respect with the best operating
plants in the world. The industry is highly energy intensive and the energy bill in
some of the plants is as high as 60% of cement manufacturing cost. Although the
newer plants are equipped with the latest state-of-the-art equipment, there
exists substantial scope for reduction in energy consumption in many of the older
plants adopting various energy conservation measures.
The Indian cement industry is a mixture of mini and large capacity cement
plants, ranging in unit capacity per kiln as low as 10 tpd to as high as 7500 tpd.
Majority of the production of cement in the country (94%) is by large plants,
which are defined as plants having capacity of more than 600 tpd. At present
there are 124 large rotary kiln plants in the country. The Ordinary Portland
Cement (OPC) enjoys the major share (56%) of the total cement production in
India followed by Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) and Portland Slag Cement
(PSC).
History of Indian Cement Industry
By stating production in 1914 the story of story of Indian cement is a stage
of continuous growth. Cement is derived from the Latin word cementam.
Egyptians and Romans found the process of manufacturing cement. In England
during the first century the hydraulic cement has become more versatile building
material. Later on, Portland cement was invented and the invention was usually
attributed to Joseph Aspdin of Enland.
India is the worlds 4
th
largest cement produced after China, Japan and
U.S.A. The South Industries have produced cement for the first time in 1904. The
company was setup in Chennai with the installed capacity of 30 tonnes per day.
Since then the cement industry has progressing leaps and bounds and evolved into
the most basic and progressive industry. Till 1950-1951, the capacity of
production was only 3.3 million tonnes. So far annual production and demand have
been growing a pace at roughly 78 million tonnes with an installed capacity of 87
million tonnes.
Problems:
The rising cost of energy transportation and persistent raw material pressures have been
playing a heavy strain on the cement and construction industry. As a result, Indian Companies
have to not only explore alternate sources of energy and materials but also strive to enhance
operational efficiency. But Indias potential for growth remains intact. The need of the hour is
to spend invest adequately in developing human resources capable of addressing the
professional needs of construction industry like application of advanced technologies and
construction practices, project management construction, litigation, insurance and finance, etc.
Indian Cement Industry is in search of competitive advantage, therefore, it is continuously
improving on the innovation and optimization front. While embracing its commitment to grow
and compete globally, it is however not neglecting the ecological and environmental needs.
Cement sector is adopting sustainable development practices and conservation measures while
harnessing energy for its use. The industry if fully committed and partner global efforts to
reduce Green House Gases impact and mitigating the evil of climate change.
Government policies:
Objective
The objectives of the engagement were
To analyze the competitiveness of Indian Cement industry vis--vis international competitors
and to devise strategies to ensure long-term sustainability of growth in the cement industry in a
globalized environment
To assess the Global competitiveness of the Indian Cement Industry focusing on
- Progress and prospects of the industry
- Constraints faced by the industry
- Steps to contain them
To recommend strategies for enhancement of global competitiveness of the Indian cement industry
Action Points
The action points identified at the conclusion of the study conducted by KPMG Consulting are as
classified under three heads:
Government: Action points for the Ministry of Commerce, Central and State government
oragnisations
Industry: Action points for the Cement manufacturers and other players in the cement indfyustry
Research / Industry bodies (NCB): Action points for industry research bodies such as NCB
competitors
Name of the
company
Andhra Cements
Chettinad Cement
Dalmia Cement
India Cements
Madras Cement
Rain Commodities
zuari Cements
Suggestions:
Cement industry in India is currently going through a technological change as a lot of
upgradation and assimilation is taking place. Currently, almost 93% of the total capacity is
based entirely on the modern dry process, which is considered as more environment-friendly.
Only the rest 7% uses old wet and semi-dry process technology. There is also a huge scope of
waste heat recovery in the cement plants, which lead to reduction in the emission level and
hence improves the environment.
INTRODUCTION TO SAGAR GROUP
Sagar Group, a reputed industrial house in Andhra Pradesh, is a 25
year old enterprise, which has its interests in Cement and Power generation and a
group turnover of Rs.1300 millions.
Shri. S. Veera Reddy, a well known industrialist hailing from Nalgonda
District in A.P., along with his friends and associates, promoted the Sagar Cements
Limited (SCL), the flagship company of the Group, in 1981. This Company
established a mini cement plant at Mattampally in Nalgonda district as an assisted
unit under the auspices of A.P. Industrial Development Corporation. SCL has
chequiered history of growth and, but for a brief interval of a few years, has paid
dividend consistently at reasonable levels.
In the year 1994, Sagar Power Ltd., (SPL) was promoted by SCL along
with Shri S. Veera Reddy and has relatives as co-promoters. SPL having
successfully implemented two hydel projects in A.P. part of this plan; it is
presently implementing two hydel projects in the Karnataka State.
For fully appreciating the other aspects of this Group, company wise
profile of the group is given below
Sagar Cements Limited:
A.VISION
STRATEGIC THEMES OF THE COMPANY.
To develop its Brand Sagar Priya as a major supply brand in a
Market through its Quality products and to become a Major
Cement Company in India .Acquire leadership in national and
international market.
MISSION:
Sagar cements is a main unit of Progressive growth oriented SAGAR
Group of companies, specialist in producing variety of cements which is essential
commodity.
AIM:
The aim of the Sagar Marketing department is to penetrate the product Sagar
Brand to nook and corner to all nearby markets in Andhra Pradesh to take the
product near to customer.to stimulate continue and accelerate efforts to
develop and maximize the contribution of infrastructure sector to the economy
of the country.
Sophisticated, very efficient operating systems with Advanced Technologies. With
Action planning firmly launched for diversification of its business into Power
generation projects and Pharmaceutical & Real Estate.
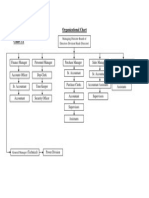
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
CHAIRMAN
MANAGING DIRECTOR
EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR BOARD OF DIRECTORS
DIRECTOR TECHNICAL COMPANY SECRETARY
S.G.M(Proj). V.P(Markg) G.M(Finance) SR.V.P(W) Mgr(Adm
Engineers Mkg.Mgr. Mgr(Accounts) Site. Adm .staff ..
Executive
Mgr
PROMOTERS
Chairman - Sri. O. Swaminatha Reddy
Managing Director - Sri S. Veera Reddy
Director - Sri K. Thnu Pillai
Executive Director - Dr. S. Anand Reddy
Director (Technical) - Sri S. Srikanth Reddy
Secretary - Sri R. Soundararajan
General Manger (works) - Sri N. Bhasker Reddy
ACHIEVEMENTS:
SHORT TERM OBJECTIVES
Achieve major reductions in wage expense.
Reduces transportation charges through Putting Our sincere follow up with
Railway Authority for developing Railway Line route from Jaggaya to Dammar
cherla via our Plant .
The Central Govt proposed the same in Annual Budget.
Acquire full pledged Mineing Lease for meeting Our Plant Raw Material
Requirment. Procurement of Quality Coal & other raw material at lower cost. If
possible may plan for importing the coal; with cheeper rate
Products
Sagar Cement is a leading producer of different types of Cements in the
State of Andhra Pradesh.
The different types of cement produced include:
53 Grade OPC 43 Grade OPC
53 Grade OPC is a higher strength
cement to meet the needs of the
consumer for higher strength
concrete...
The 43 grade OPC is the most
popular general-purpose cement in
the country today. The production of
43 grade OPC is nearly...
read more read more
33 Grade OPC Portland Pozzolana Cement
This cement is used for general civil
construction work under normal
environmental conditions. The
compressive strength...
Portland Pozzolana Cement is a kind
of Blended Cement which is
produced by either intergrinding of
OPC clinker...
POLICIES:
Sagar Cements was built on a strong foundation of fundamental values of
responsibility, respect & trust.
We are committed to encouraging our employees to do their best while
respecting other employees, agents , customers & others, ensuing highest
safety standards , and adhering to local and international standards of
manufacturing.
VALUES:
Sagar Cements actively supports skill development programs to train workers to
professional level. It will improve their talents, upgrade their skills and add values
to Indian masons. This commitment reflects Sagar Cements' concern for the
preservation of traditional community values the strong foundation of our
society.
Sagar Cements is committed to providing safe and healthy working environments
for its employees and also contributing to the enhancement of quality of life of the
people residing in and around the plant and other parts of the state by conducting
several community programs and contributing to welfare measures.
COMPETITORS
KCP Cement
Bharathi cements
Ambuja Cement
Birla Corporation
Kesoram Cements
JK Lakshmi Cement
Shree chakra Cement
UltraTech Cement
Strengths
A firm's strengths are its resources and capabilities that can be used as a basis for
developing a competitive advantage. Examples of such strengths include:
Patents
Strong brand names
Good reputation among customers
Cost advantages from proprietary know-how
Exclusive access to high grade natural resources
Favorable access to distribution networks
Weaknesses
The absence of certain strengths may be viewed as a weakness. For example, each
of the following may be considered weaknesses:
Lack of patent protection
A weak brand name
Poor reputation among customers
High cost structure
Lack of access to the best natural resources
Lack of access to key distribution channels
In some cases, a weakness may be the flip side of strength. Take the case in which
a firm has a large amount of manufacturing capacity. While this capacity may be
considered a strength that competitors do not share, it also may be a considered a
weakness if the large investment in manufacturing capacity prevents the firm from
reacting quickly to changes in the strategic environment.
Opportunities
The external environmental analysis may reveal certain new opportunities for
profit and growth. Some examples of such opportunities include:
An unfulfilled customer need
Arrival of new technologies
Loosening of regulations
Removal of international trade barriers
Threats
Changes in the external environmental also may present threats to the firm. Some
examples of such threats include:
Shifts in consumer tastes away from the firm's products
Emergence of substitute products
New regulations
Increased trade barriers
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- "Funds Flow Statement": Eswar College of EngineeringDocument8 pagini"Funds Flow Statement": Eswar College of EngineeringSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ratio Analysis 1012Document74 paginiRatio Analysis 1012Sakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Funds Flow StatementDocument101 paginiFunds Flow StatementSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ancient Greek: Agriculture Agriculture, Also Called Farming or Husbandry, Is The Cultivation ofDocument4 paginiAncient Greek: Agriculture Agriculture, Also Called Farming or Husbandry, Is The Cultivation ofSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Funds Flow Statement Tirumala MilkDocument101 paginiFunds Flow Statement Tirumala MilkSakhamuri Ram's100% (3)
- List of The Tables: SL NO NO Title of The Table Page NoDocument9 paginiList of The Tables: SL NO NO Title of The Table Page NoSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance AppraisalDocument85 paginiPerformance AppraisalSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eswar College of Engineering: "Financial Statement Analysis"Document6 paginiEswar College of Engineering: "Financial Statement Analysis"Sakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Reports of Devi Sea LTD: Profit & Loss Account For The Year Ended 31St March, 2009Document11 paginiFinancial Reports of Devi Sea LTD: Profit & Loss Account For The Year Ended 31St March, 2009Sakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industry Indan Cotton Textile ProfileDocument30 paginiIndustry Indan Cotton Textile ProfileSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amaravathi 16 PointsdDocument16 paginiAmaravathi 16 PointsdSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training & Development TirumalaDocument103 paginiTraining & Development TirumalaSakhamuri Ram's0% (1)
- CottonDocument17 paginiCottonSakhamuri Ram's100% (1)
- Industry Indan Cotton Textile ProfileDocument30 paginiIndustry Indan Cotton Textile ProfileSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emp Name Shaik Khadeer Emp Code 11366 Joining Date 16-03-2013 Working Branch Bapatla Gannavaram Warangal Month JAN FEB MAR TotalDocument2 paginiEmp Name Shaik Khadeer Emp Code 11366 Joining Date 16-03-2013 Working Branch Bapatla Gannavaram Warangal Month JAN FEB MAR TotalSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master of Business Administration: A Study On Ratio Analysis With Reference To Jocil LimitedDocument97 paginiMaster of Business Administration: A Study On Ratio Analysis With Reference To Jocil LimitedSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cotton IndustryDocument18 paginiCotton IndustrySakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- KCP Final Project - 2.1Document110 paginiKCP Final Project - 2.1Sakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organizational Chart Chart 3.1: Managing Director-Board of Directors Division Head (Director)Document1 paginăOrganizational Chart Chart 3.1: Managing Director-Board of Directors Division Head (Director)Sakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Satisfaction Nagarjuna FertilizersDocument97 paginiCustomer Satisfaction Nagarjuna FertilizersSakhamuri Ram's100% (2)
- A Study On Consumer PerceptionDocument4 paginiA Study On Consumer PerceptionSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Statement Sivaswathi TEXTILESDocument103 paginiFinancial Statement Sivaswathi TEXTILESSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Satisfaction AmaravathiDocument84 paginiCustomer Satisfaction AmaravathiSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory Management SWATHIDocument96 paginiInventory Management SWATHISakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Satisfaction AmaravathiDocument84 paginiCustomer Satisfaction AmaravathiSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory Management PROJECTDocument47 paginiInventory Management PROJECTSakhamuri Ram'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Neil Armstrong Interview (1969)Document8 paginiNeil Armstrong Interview (1969)Aviation/Space History LibraryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article - LNF Q230 Particle CountDocument2 paginiArticle - LNF Q230 Particle CountSyaiful FuadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 011 - CAR Corrective Action ReportDocument4 pagini011 - CAR Corrective Action ReportRocky BisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Computing: Discovery, Communication, and CollaborationDocument25 paginiNetwork Computing: Discovery, Communication, and Collaborationangelhope64Încă nu există evaluări
- HVAC Installation ManualDocument215 paginiHVAC Installation Manualmeeng2014100% (5)
- Sizing Duct Work SheetDocument4 paginiSizing Duct Work SheetMaulana MaftuhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Change ManagementDocument20 paginiChange ManagementDrRameesha KalraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essays On InfrastructureDocument4 paginiEssays On InfrastructureKogree Kyaw Win OoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation and Owner's Manual: EnglishDocument19 paginiInstallation and Owner's Manual: Englishn8rld4879Încă nu există evaluări
- Pmi-Acp: Agile Continuous ImprovementDocument49 paginiPmi-Acp: Agile Continuous Improvementswati jainÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Choose An EPC Contractor For PV ProjectsDocument14 paginiHow To Choose An EPC Contractor For PV Projectsavnish_parashar9292Încă nu există evaluări
- JIG Bulletin 74 Fuelling Vehicle Soak Testing Procedure During Commissioning Feb 2015Document2 paginiJIG Bulletin 74 Fuelling Vehicle Soak Testing Procedure During Commissioning Feb 2015Tirumal raoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Operations Manager in Melbourne FL Resume Leslie DahringDocument2 paginiSupply Chain Operations Manager in Melbourne FL Resume Leslie DahringLeslieDahringÎncă nu există evaluări
- VP Senior Director IT in Emerson NJ Resume Mark BrackenburyDocument3 paginiVP Senior Director IT in Emerson NJ Resume Mark BrackenburyMarkBrackenburyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid 09Document190 paginiFluid 09Edgar HuancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tronox LP Eng GesichertDocument3 paginiTronox LP Eng GesichertForeverÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRYSMIAN M&M PowerLink Brochure SingDocument6 paginiPRYSMIAN M&M PowerLink Brochure SingFaisal OzairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finish TG Eim Final 12-27-14Document78 paginiFinish TG Eim Final 12-27-14Kit Galingan100% (3)
- 28385-1 Quotation 333kW Containerized Soluttion Genesis ElectricityDocument10 pagini28385-1 Quotation 333kW Containerized Soluttion Genesis ElectricityNelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- A2 Planche Tanja+Tim Print UKDocument1 paginăA2 Planche Tanja+Tim Print UKTim Nøhr ElkærÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementing Avaya Aura CM6Document194 paginiImplementing Avaya Aura CM6Clive BurkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5) BL Corrector y Manifiesto de CargaDocument3 pagini5) BL Corrector y Manifiesto de CargaKevin Yair FerrerÎncă nu există evaluări
- PMI-ANSI Standards Development and The Scheduling StandardDocument28 paginiPMI-ANSI Standards Development and The Scheduling Standard1meander23Încă nu există evaluări
- Albion TradingDocument1.074 paginiAlbion TradingalcatéiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Residential Slabs and Footings Workshop 1 DayDocument1 paginăResidential Slabs and Footings Workshop 1 DayredpuffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribution Channel of CSR Forging Pvt. Ltd.Document33 paginiDistribution Channel of CSR Forging Pvt. Ltd.Dheeraj SinghalÎncă nu există evaluări
- WindturbinebladedesignDocument27 paginiWindturbinebladedesignDaizLee AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 MacroDocument52 paginiChapter 9 MacroRusselle AdrianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Index of WorkshopDocument4 paginiIndex of Workshopapi-3709247Încă nu există evaluări
- MSA safetySCOPE - European Product Portfolio. Available From Coyle & Associates (WWW - Canda.ie)Document144 paginiMSA safetySCOPE - European Product Portfolio. Available From Coyle & Associates (WWW - Canda.ie)Coyle & Associates100% (1)