Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
VSD 50 HZ 201.21-NM2 167-1
Încărcat de
Asanka Rodrigo0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
59 vizualizări1 paginăThe document discusses the operation and controls of a variable speed drive (VSD). It describes that the modulating frequency can range from 0-200 Hz and utilizes a sinusoidal waveform with 16.66% of the third harmonic component. The maximum VSD frequency varies depending on jumper settings from 178-200 Hz. The VSD output is a pulse width modulation signal that simulates an AC waveform to control motor speed and maintain a constant voltage-to-frequency ratio. The modulation percentage increases above 100% at frequencies above 189.6 Hz to achieve the line voltage at maximum output frequency.
Descriere originală:
VSD
Titlu original
VSD 50 Hz 201.21-NM2 167-1
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe document discusses the operation and controls of a variable speed drive (VSD). It describes that the modulating frequency can range from 0-200 Hz and utilizes a sinusoidal waveform with 16.66% of the third harmonic component. The maximum VSD frequency varies depending on jumper settings from 178-200 Hz. The VSD output is a pulse width modulation signal that simulates an AC waveform to control motor speed and maintain a constant voltage-to-frequency ratio. The modulation percentage increases above 100% at frequencies above 189.6 Hz to achieve the line voltage at maximum output frequency.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
59 vizualizări1 paginăVSD 50 HZ 201.21-NM2 167-1
Încărcat de
Asanka RodrigoThe document discusses the operation and controls of a variable speed drive (VSD). It describes that the modulating frequency can range from 0-200 Hz and utilizes a sinusoidal waveform with 16.66% of the third harmonic component. The maximum VSD frequency varies depending on jumper settings from 178-200 Hz. The VSD output is a pulse width modulation signal that simulates an AC waveform to control motor speed and maintain a constant voltage-to-frequency ratio. The modulation percentage increases above 100% at frequencies above 189.6 Hz to achieve the line voltage at maximum output frequency.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
167 YORK INTERNATIONAL
FORM 201.21-NM2 (405)
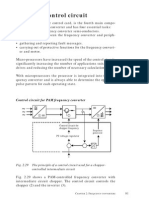
VSD OPERATION AND CONTROLS (CON'T)
Modulating Frequency
The modulating frequency range will range from 0 to
200 Hz. The modulating frequency waveform con-
sists of a sinusoidal waveform summed together with
16.66% of the third harmonic component of the sinu-
soidal waveform. Utilization of this waveform as the
modulating waveform will permit the drive to generate
a fundamental line to line voltage equal to the DC bus
voltage divided by 1.414.
Maximum VSD Frequency
The maximum VSD frequency will vary for each
chiller model. The microprocessor board determines
the frequency according to jumpers factory installed in
the wiring on the J7 plug of the microprocessor board.
The location of these jumpers is interpreted as a binary
value, which presently allows 7 speed selections plus a
default. The maximum frequency may vary from 178
to 200 Hz. If the J7 plug is not installed, the speed will
default to 178 Hz. Details on the location of the jump-
ers and the associated maximum speed are provided
on PAGE 137 in the CHILLER CONFIGURATION
JUMPERS section.
VSD % Modulation
The voltage and frequency commands issued by the VSD
Logic Board microprocessor are determined by the fre-
quency command from the Chiller Control Board. The
VSD output is a PWM signal (FIG. 2), which has effects
on the motor comparable to an AC voltage sinusoidal
waveform. To change the speed of an AC motor, the
frequency of the AC voltage must be changed. When-
ever frequency is changed, the voltage is changed in a
linear ratio. Maintaining a relatively constant V/F ratio
as speed changes assures motor losses and overheating
do not occur.
The output voltage of the VSD is not a sinusoidal wave-
form. Instead, the PWM generator provides an output
that simulates a true AC waveform by repetitively turn-
ing on and off the voltage to the motor to create an aver-
age voltage that is equal to a lower AC voltage at lower
frequencies and a higher voltage at higher frequencies.
The PWM generator also changes the % modulation
of the waveform to simulate the frequency change to
maintain the V/F ratio with motor speed changes.
The PMW generator is programmed to essentially oper-
ate a linear volts/Hz ratio over the 0 200 Hz frequency
range. The complex control algorithm modies the
voltage command to boost the voltage of the V/F ratio
at lower speeds to provide additional torque.
The 100% modulation operating point occurs at a
fundamental frequency of 189.6 Hz. As the output
frequency increases above 189.6 Hz, the drive operates
in an over-modulated mode. For example, at 200 Hz
fundamental modulating frequency the PWM waveform
is over-modulated by approximately 18%. This will yield
a fundamental output line to line voltage applied to the
motor terminals at maximum output frequency that is
equal to the input line to line voltage applied to the drive
(provided the DC bus current remains continuous).
8
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Inverters For Ac Motor DriveDocument17 paginiInverters For Ac Motor DriveAslam SdÎncă nu există evaluări
- I2c ProtocolDocument28 paginiI2c Protocolishapatil86Încă nu există evaluări
- Component and Types of VFDDocument11 paginiComponent and Types of VFDArsalan Danish100% (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Evaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (3)
- 8086 - 8088 - 80286 Assembly LanguageDocument408 pagini8086 - 8088 - 80286 Assembly LanguagelordpinoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC Drive Theory and Application: Benefits of Using AC DrivesDocument8 paginiAC Drive Theory and Application: Benefits of Using AC DrivesRaghu KodiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VFD Theory and CommissioningDocument44 paginiVFD Theory and Commissioningengkos koswaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10-1 - Engine Numbering & IdentificationDocument13 pagini10-1 - Engine Numbering & IdentificationRiddhi DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- VFD BasicsDocument9 paginiVFD BasicsDinesh KumaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-2006Document8 pagini1-2006Asanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuji LP5500R/LP5700R INSTALLATION MANUALDocument64 paginiFuji LP5500R/LP5700R INSTALLATION MANUALAndrás Geisz100% (1)
- List of Space Flight Simulator GamesDocument55 paginiList of Space Flight Simulator GamesAshay Verma100% (1)
- Variable Frequency Drives: Presented By: Rajarshi Ghose Dastidar. ROLL: 149. REGD. NO: 070906360Document54 paginiVariable Frequency Drives: Presented By: Rajarshi Ghose Dastidar. ROLL: 149. REGD. NO: 070906360Rajarshi Ghose Dastidar100% (1)
- Variable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersDe la EverandVariable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPWM V/HZ InverterDocument51 paginiSPWM V/HZ InverterLabi BajracharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drive Sizing KVADocument4 paginiDrive Sizing KVAerickelsafan0% (1)
- AC Drives and Soft Starter Application Guide - AllenBradleyCoDocument5 paginiAC Drives and Soft Starter Application Guide - AllenBradleyCojoyama100% (1)
- Writing Tips: Thesis: Which SectionsDocument4 paginiWriting Tips: Thesis: Which SectionsAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)Document8 paginiVariable Frequency Drive (VFD)vishnurajpattambiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variable Frequency DrivesDocument52 paginiVariable Frequency DrivesveguruprasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Benefits of Applying 61000-5-2 To Cable Shield Bonding and Earthing, 21 May 04Document6 paginiThe Benefits of Applying 61000-5-2 To Cable Shield Bonding and Earthing, 21 May 04Asanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument48 paginiSpeed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorChancy Dash100% (3)
- Governor: BY Er. Tanuj Sharma Student of PGDC Hydro POWER PLANT (2010-11), NPTI NangalDocument24 paginiGovernor: BY Er. Tanuj Sharma Student of PGDC Hydro POWER PLANT (2010-11), NPTI NangalTanuj SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VD SeriesDocument4 paginiVD SeriesintrudentalertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Induction Motor Speed ControlDocument35 paginiSingle Phase Induction Motor Speed ControlHarshit Sengar100% (2)
- Unit-6 Distributed Shared MemoryDocument71 paginiUnit-6 Distributed Shared Memorydeepak2083Încă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous Motor Drives: Open Loop V/F Control of Synchronous MotorDocument11 paginiSynchronous Motor Drives: Open Loop V/F Control of Synchronous MotorSaish Dalvi100% (1)
- Weller WCB 2 Mjerac Tempearture PDFDocument1 paginăWeller WCB 2 Mjerac Tempearture PDFslvidovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSSE InstallDocument26 paginiPSSE InstallshyamdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VFD Types: Igbts ThyristorsDocument8 paginiVFD Types: Igbts ThyristorsAshok MoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Motor ControlDocument91 paginiDC Motor ControlElvins AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variable Frequency Drive Navigation Search: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 paginiVariable Frequency Drive Navigation Search: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMadhar ShaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VVVF - Working Principle & Its OperationDocument18 paginiVVVF - Working Principle & Its Operationdownload4sumitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pulse Width ModulationDocument5 paginiPulse Width ModulationMunira ZulkefliÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC MotorDocument91 paginiDC MotorSatadal DashÎncă nu există evaluări
- VVC ControlDocument14 paginiVVC ControlRyte EchanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignemnt 2Document3 paginiAssignemnt 2Joshua Jayaraaj JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drives BasicDocument32 paginiDrives BasicCubix AutomationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Loop Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Using SVMDocument5 paginiOpen Loop Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Using SVMVipin_am100% (1)
- Module-4 Notes - Induction MachinesDocument25 paginiModule-4 Notes - Induction Machineschandu 77Încă nu există evaluări
- Active Energy Control - Optimum Solution For Maximum Savings: Industry Application IA04008001EDocument4 paginiActive Energy Control - Optimum Solution For Maximum Savings: Industry Application IA04008001ESaju V KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Energy Control Application NoteDocument4 paginiActive Energy Control Application NotemoxlindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regarding Selection - WORD 97 FORMATDocument22 paginiRegarding Selection - WORD 97 FORMATSurya Prakash SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drives and SoftstarterDocument7 paginiDrives and SoftstarterElectrification100% (1)
- Camille Ri 99Document5 paginiCamille Ri 99tip31Încă nu există evaluări
- Presented By: Bheemanna Angadi (1OX13EE020) The Oxford College of Engg-BangaloreDocument17 paginiPresented By: Bheemanna Angadi (1OX13EE020) The Oxford College of Engg-BangaloreRashed AlbarakehÎncă nu există evaluări
- L T D I V F D: Atest Echnological Evelopments N Ariable Requency RivesDocument18 paginiL T D I V F D: Atest Echnological Evelopments N Ariable Requency RivesBijay AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- F I U Sterowania SilnikiemDocument4 paginiF I U Sterowania SilnikiemTomasz Artur JachymekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benefits of VSD SystemsDocument7 paginiBenefits of VSD Systemsalx 100Încă nu există evaluări
- Space Vector PWM VSI Induction Motor DriveDocument11 paginiSpace Vector PWM VSI Induction Motor DrivesjillelamoodiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Guideline For Flyback Charger Using FAN302HL/ULDocument20 paginiDesign Guideline For Flyback Charger Using FAN302HL/ULteomondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WECS CSI HV Synch GenDocument23 paginiWECS CSI HV Synch GenPrasann KatiyarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A CD Rive CharacteristicsDocument6 paginiA CD Rive CharacteristicsbedreddiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of PWM Techniques and Inverter Performance: Raja Ram Kumar, Sunil Kumar, Alok YadavDocument5 paginiComparison of PWM Techniques and Inverter Performance: Raja Ram Kumar, Sunil Kumar, Alok YadavchaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Help - Brushless DC Motor Drive - Blocks (SimPowerSystems™)Document15 paginiHelp - Brushless DC Motor Drive - Blocks (SimPowerSystems™)lojain centerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Lva1 App6891Document13 pagini2 Lva1 App6891gouravÎncă nu există evaluări
- Efficiency Comparison of PWM Controlled and PAM Controlled Sensor Less BLDMDocument6 paginiEfficiency Comparison of PWM Controlled and PAM Controlled Sensor Less BLDMRoger LiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Variable Frequency Drive?Document4 paginiWhat Is A Variable Frequency Drive?Vinod GnanasekaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of AC Induction Motors With VFDsDocument10 paginiApplication of AC Induction Motors With VFDsDeepjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of DSP-Based Control For AC Machines: by Finbarr Moynihan, Embedded Control Systems GroupDocument4 paginiFundamentals of DSP-Based Control For AC Machines: by Finbarr Moynihan, Embedded Control Systems Groupveer110Încă nu există evaluări
- Research To Study Variable Frequency Drive and ItsDocument4 paginiResearch To Study Variable Frequency Drive and ItsPramono MuktiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation of Ac Induction Motor Control Using Constant V/HZ Principle and Sine Wave PWM Technique WITH TMS320F28027Document7 paginiImplementation of Ac Induction Motor Control Using Constant V/HZ Principle and Sine Wave PWM Technique WITH TMS320F28027edi ediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research To Study Variable Frequency Drive and Its Energy SavingsDocument4 paginiResearch To Study Variable Frequency Drive and Its Energy SavingsIjsrnet EditorialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensorless Control of Induction Motors Using Multi-Level ConvertersDocument11 paginiSensorless Control of Induction Motors Using Multi-Level ConvertersmssmsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vsi Fed 3ph ImDocument13 paginiVsi Fed 3ph ImWisemin LinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of Modulation Index of PWM Wave Form Feed To Inverter Feed Induction MotorDocument18 paginiCalculation of Modulation Index of PWM Wave Form Feed To Inverter Feed Induction MotorSathishkumar MalipeddiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Converting Generator FrequenciesDocument2 paginiConverting Generator FrequenciesGopalakrishnan KuppuswamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q02201300137Document8 paginiQ02201300137Vikas PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vsi Csi With Various LoadsDocument56 paginiVsi Csi With Various LoadsDeependra RastogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ED Write UpdocumentDocument12 paginiED Write UpdocumentMeenakshi ChaudhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Output Current Harmonics of Voltage Source Inverter Used Different PWM Control TechniquesDocument10 paginiComparison of Output Current Harmonics of Voltage Source Inverter Used Different PWM Control TechniquesFitri AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesDe la EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Examples of Circuit-Breaker Selections For An LV InstallationDocument9 pagini4 Examples of Circuit-Breaker Selections For An LV InstallationAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Discrimination With Power Circuit-BreakersDocument9 pagini3 Discrimination With Power Circuit-BreakersAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation Research Procedia 25 (2017) 4529-4543Document1 paginăTransportation Research Procedia 25 (2017) 4529-4543Asanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Techno-Economic Analysis of Intermittent Renewable Energy Penetration With The Proposed India-Sri Lanka HVDC InterconnectionDocument13 paginiTechno-Economic Analysis of Intermittent Renewable Energy Penetration With The Proposed India-Sri Lanka HVDC InterconnectionAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radiant Energy: Capable of Exciting The Retina and Producing A Visual SensationDocument1 paginăRadiant Energy: Capable of Exciting The Retina and Producing A Visual SensationAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cahier Technique: Discrimination With LV Power Circuit BreakersDocument10 paginiCahier Technique: Discrimination With LV Power Circuit BreakersAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SL Energy Policy 2019Document3 paginiSL Energy Policy 2019Asanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colorimetry & StandardsDocument4 paginiColorimetry & StandardsAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lightning: 1% of Strokes Exceed 200 KaDocument1 paginăLightning: 1% of Strokes Exceed 200 KaAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Linear Model For Bi-Color LED: Two LED Sets From Two Different Colors Warm White and Cool WhiteDocument4 paginiNon Linear Model For Bi-Color LED: Two LED Sets From Two Different Colors Warm White and Cool WhiteAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Measurements: RGB Value Tristimulus Value Chromaticity Coordinate CCTDocument3 paginiColor Measurements: RGB Value Tristimulus Value Chromaticity Coordinate CCTAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- RH TechPaperIESL Oct06Document9 paginiRH TechPaperIESL Oct06Asanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transient Over VoltagesDocument5 paginiTransient Over VoltagesAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overcurr Ent Protection: Location 2 Phase A Instantaneous Cur Rent I 1aDocument1 paginăOvercurr Ent Protection: Location 2 Phase A Instantaneous Cur Rent I 1aAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semester 1: Curriculum - B.Sc. Engineering Honours in Electrical EngineeringDocument3 paginiSemester 1: Curriculum - B.Sc. Engineering Honours in Electrical EngineeringAsanka RodrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Play Multimedia Files Using MCIDocument4 paginiPlay Multimedia Files Using MCIEKAUMAGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dell EMC Konesalituoteperhe 1Document24 paginiDell EMC Konesalituoteperhe 1amit_post2000Încă nu există evaluări
- Electric Actuator EPI2Document6 paginiElectric Actuator EPI2ilkinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Samsung Hlr4264wx Xac Chassis l62bDocument81 paginiSamsung Hlr4264wx Xac Chassis l62bDaniboy1994Încă nu există evaluări
- COM 325 Human Computer InterfaceDocument8 paginiCOM 325 Human Computer InterfaceRay ZamaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data AcquisitionDocument4 paginiData Acquisitionmattew657Încă nu există evaluări
- Diploma in Aircraft Maintenance TechnologyDocument3 paginiDiploma in Aircraft Maintenance Technologyjohn christian de leonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ks0071 Keyestudio Mini Tank (21 12cmDocument89 paginiKs0071 Keyestudio Mini Tank (21 12cmOctavio Castillo GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Computers Based On Principles of OperationDocument6 paginiTypes of Computers Based On Principles of OperationMayank Jain NeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semiconductor Main MemoryDocument15 paginiSemiconductor Main MemoryBereket TarikuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructiuni Pix SpionDocument2 paginiInstructiuni Pix SpionIonut AnghelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2008-Flex Air Cookbook Feb2008Document77 pagini2008-Flex Air Cookbook Feb2008AnkitJainÎncă nu există evaluări
- BI Interview Questions Ver1.0Document71 paginiBI Interview Questions Ver1.0Siddhu GottipatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembly Language ProgrammingDocument20 paginiAssembly Language ProgrammingSolomon SBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brosur Urine PU-4010Document1 paginăBrosur Urine PU-4010Dewi WyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scd2100 Rtu Manual B0780ad CDocument52 paginiScd2100 Rtu Manual B0780ad CShie Othong100% (1)
- 2015 ACM Syrian Collegiate Programming ContestDocument13 pagini2015 ACM Syrian Collegiate Programming ContestZeyad EtmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADEL Lock System Interface Function (SDK) ManualDocument6 paginiADEL Lock System Interface Function (SDK) ManualAnonymous 3UwGpOmFATÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radium InfoDocument8 paginiRadium InfolistentomerijnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ict NotesDocument3 paginiIct NoteshelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For Managing Data FilesDocument15 paginiGuidelines For Managing Data Fileslamxung123Încă nu există evaluări