Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Introduction To Expert Systems
Încărcat de
Andres GuevaraDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Introduction To Expert Systems
Încărcat de
Andres GuevaraDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Introduction to Expert
Introduction to Expert
Systems
Systems
Dr. Khaled Shaalan
Prof. Dr. Ahmed Rafea
Central Lab. For Agricultural Expert Central Lab. For Agricultural Expert
Systems Systems
Topics
What is AI ?
What is KBS?
What is expert system?
The structure of an expert system
Characteristics of an expert system
When are expert systems useful?
The players in the expert system game
Evolution of expert systems
What is AI?
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)
IS A BRANCH OF COMPUTER
SCIENCE THAT IS STUDYING
HOW TO LET COMPUTERS
PERFORM FUNCTIONS
CONSIDERED TO BE HIGH
LEVEL HUMAN ACTIVITIES
What is KBS?
A KNOWLEDGE - BASED SYSTEM
(KBS) IS A COMPUTER PROGRAM
THAT USES KNOWLEDGE AND
PROBLEM SOLVING TECHNIQUES
What is expert system?
AN EXPERT SYSTEM (ES) IS A
COMPUTER PROGRAM DESIGNED
TO SIMULATE THE PROBLEM-
SOLVING BEHAVIOR OF AN
EXPERT IN A NARROW DOMAIN
OR DISCIPLINE.
What is expert system?(cont.)
ARTIFICIAL
INTELLIGENCE
PROGRAMS
Exhibit intelligent
behavior by skillful
application of heuristics
make domain knowledge
explicit and separate from
the rest of the system
KNOWLEDGE-BASED
SYSTEMS
Apply expert knowledge
to difficult, real world
problems
EXPERT
SYSTEMS
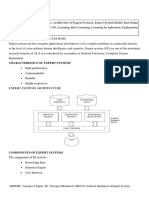
The structure of an expert system
KNOWLEDGE BASE
Domain Knowledge
FACTS
RULES
INTERPRETER
SCHEDULER
Organizing Knowledge
EXPERT SYSTEM
INFERENCE ENGINE
General
problem-solving
knowledge
Representing knowledge
l Rule-based methods
l Frame-based methods
Rules
l A rule is a formal way of specifying a
recommendation, directive, or advice
l A rule is expressed as
IF IF premise premise THEN THEN conclusion conclusion
or
IF IF condition condition THEN THEN action action
A diagnostic rule
IF IF there are spots on leaves, and
the color of spots is pale
yellow, gray, or purple, and
the shape of spots is bounded
making acute angle with veins,
and the season is spring
Then Then the disease is downy mildew -
probability = 0.9
A treatment rule
IF IF the disease is downy mildew
THEN THEN the treatment method is chemical
spraying, and the material used is
redomil+copper
Drawing inferences from rules
l Forward chaining
l Backward chaining
Frames
l A frame is a description of an object that
contains slots for all of the information
associated with the object
l Slots may contain (default) values, or
procedures by which values may be
obtained
Soil Frame
Slots Facets
Ph value type: real
single/multiple: single
possible value: > 0.0 & 14.0
EC value type: real
single/multiple: single
possible value: > 0.0
Texture value type: nominal
single/multiple: single
possible value: sand, loam, clay, heavy clay,
gravely, coarse sand, silty clay, silty clay
loam, salt loam, fine sand, sand clay loam,
silt loam, sandy loam, loamy fine sand
Frames connected by IS-A relation
Leaf mold
Downy mildew
Fungal
Mosaic
Green Mosaic
Viral
Disease
Spiders
Broad mite
Mites
Low temperature
Heavy irrigation
Environmental
aphids
Insect
Nitrogen
Iron
Nutrition Deficiency
Bromide
Bazamide
Toxicity
Root knot
Root lesion
Nematode
Disorder
Disorder hierarchy
generic
specialized
Drawing inferences from
frames
l Inheritance
l Procedure attachment
Characteristics of an expert system
Expert System
Expertise
Symbolic reasoning
Depth
Self-knowledge
Exhibit expert performance
Have high level of skill
Have adequate robustness
Represent knowledge symbolically
Reformulate symbolic knowledge
Handle difficult problem domains
Use complex rules
Examine its own reasoning
Explain its operation
When are expert systems useful?
l Nature of the task
Experts can do better than nonexperts
The task involves reasoning and
knowledge, not intuitions or reflexes
The task can be done by a person in
minutes or hours
The task is concrete enough to codify
The task is commonly taught to novices
in the area
When are expert systems useful?
(Cont.)
l Availability of knowledge
Recognized experts exist
There is general agreement among experts
Experts are able and willing to articulate the
way they approach problems
The players in the expert system game
Tool builder
EXPERT
SYSTEM
BUILDING
TOOL
Domain
expert
Knowledge
engineer
EXPERT
SYSTEM
Clerical
Staff
End-user
Interviews
Builds
refines
and tests
Extends
and test
Builds
Uses
Uses
l Programming language
l Shell
Expert system building
tool
Shells VS Programming
languages
Features Shells Prog. Lang.
Ease & speed of
development
Higher Less
KB Structure
&reasoning
Restricted by
the tool
May be developed
As needed
KB maintenance Easier Difficult
Shells VS Programming languages
(Cont.)
Features Shells Prog. Lang.
I nterfaces Not always
friendly or
available
Have to be
developed
Efficiency/
Performance
Slower Faster
Explanation Restricted by
the tool
May be developed
as needed
Evolution of expert systems
Development Stage Description
Demonstration
Prototype
The system solves a portion of the problem
undertaken, suggesting that the approach is viable
and system development is achievable. (test ideas)
Research
prototype
The system displays credible performance on the
entire problem but may be fragile due to incomplete
testing and revision. (test cases)
Field prototype The system displays good performance with adequate
reliability and has been revised based on extensive
testing in the user environment. (test real problems)
Production model The system exhibits high quality, reliable, fast, and
efficient performance in the user environment.
(extensive field tests)
Commercial
system
The system is a production model being used on a
regular commercial basis.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chs 1,2Document24 paginiChs 1,2RajatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Lecture csc462Document47 pagini14 Lecture csc462Hàssáñ YàsèéñÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert Systems - Class2 PDFDocument41 paginiExpert Systems - Class2 PDFJ Andrés SalasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AI Unit 5Document18 paginiAI Unit 5Thumbiko MkandawireÎncă nu există evaluări
- AI-Unit 5Document6 paginiAI-Unit 5MeeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03a04chapter2v4 2Document50 pagini03a04chapter2v4 2api-3738694Încă nu există evaluări
- 18-Knowledge Bases PDFDocument57 pagini18-Knowledge Bases PDFAdwaithAdwaithDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert SystemsDocument29 paginiExpert SystemsKeith Tanaka MagakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert SystemsDocument14 paginiExpert SystemskeyurÎncă nu există evaluări
- AI Chapter 4Document3 paginiAI Chapter 4Beki TubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Lectures 5 6 AI ApplicationsDocument34 pagini2 - Lectures 5 6 AI ApplicationsfaizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge Base & Knowledge Engineering Process: Knowledge Representation & Reasoning WID2001Document29 paginiKnowledge Base & Knowledge Engineering Process: Knowledge Representation & Reasoning WID2001Marina MELÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert Systems AIDocument16 paginiExpert Systems AIANAKHA R MScAI23-25Încă nu există evaluări
- Expert System PDFDocument8 paginiExpert System PDFViscous GuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert SystemDocument65 paginiExpert SystemBharathi ArikerieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert SystemsDocument35 paginiExpert SystemsRammah YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert System in AIDocument11 paginiExpert System in AIAlvi HotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCDE In-Depth - Orhan ErgunDocument556 paginiCCDE In-Depth - Orhan ErgunKhánh LêÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 7 Expert SystemDocument8 paginiCH 7 Expert SystemgaurabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial Intelligence - Expert SystemsDocument6 paginiArtificial Intelligence - Expert SystemsFahad AslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge Representation and Expert SystemDocument36 paginiKnowledge Representation and Expert SystemJiawei TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Language Processing System NotesDocument55 paginiLanguage Processing System NotesAnamika MondalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuliah 2 - Akusisi PengetahuanDocument44 paginiKuliah 2 - Akusisi Pengetahuantutur ramdaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- AWS Solutation Architech Job Roles and ResponsiblityDocument9 paginiAWS Solutation Architech Job Roles and Responsiblitypra_narviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scribd Artificial IntelligenceDocument31 paginiScribd Artificial Intelligencehossam2100% (1)
- Expert Systems: Dr.P.Mohan DcmsDocument23 paginiExpert Systems: Dr.P.Mohan DcmsHonour TesemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert Systems: RABI DEYASHI (30000216016) MD SAMEEM ALI (30000216018)Document25 paginiExpert Systems: RABI DEYASHI (30000216016) MD SAMEEM ALI (30000216018)Sameem AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 6 Expert Systems 1Document46 pagini4 6 Expert Systems 1ghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1introDocument4 paginiChapter 1introriandakotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert-Systems AI PresDocument21 paginiExpert-Systems AI PresuzaifaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge Based Expert System: Abhay Kumar Associate Professor, DFT, NIFT, PatnaDocument25 paginiKnowledge Based Expert System: Abhay Kumar Associate Professor, DFT, NIFT, PatnaMard GeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customizable Embedded Processors PDFDocument527 paginiCustomizable Embedded Processors PDFEfraín HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument31 paginiArtificial IntelligenceKushal Kumawat100% (2)
- AI Expert SystemsDocument38 paginiAI Expert SystemsInvincible AmadisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expertsystems 131123032428 Phpapp01Document23 paginiExpertsystems 131123032428 Phpapp01swati shuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial Intelligence: Advantages DisadvantagesDocument6 paginiArtificial Intelligence: Advantages DisadvantagesvihangimaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Expert Systems (1 of 2)Document27 paginiIntroduction To Expert Systems (1 of 2)Muhammad Tahir KhaleeqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5 Expert SystemsDocument50 paginiLecture 5 Expert SystemsHarris ChikunyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert Systems: AbstractDocument15 paginiExpert Systems: Abstractapi-26830587Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 6Document27 paginiUnit 6khatuaryan16Încă nu există evaluări
- Accenture Imp MaterialDocument75 paginiAccenture Imp Materialabhilash gowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norvig Lisp StyleDocument116 paginiNorvig Lisp StyleDragan100% (1)
- Unit IvDocument4 paginiUnit IvSuramsetti LingaiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aswini Expert SystemsDocument37 paginiAswini Expert SystemsKarishma Satheesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Knowledge-Based SystemsDocument36 paginiIntroduction To Knowledge-Based SystemsVigneshwaran SrinivasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus For The Trade of Computer Operator and Programming AssistantDocument17 paginiSyllabus For The Trade of Computer Operator and Programming AssistantDrAjay SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert Systems: Dr.P.Mohan DcmsDocument23 paginiExpert Systems: Dr.P.Mohan DcmsKaushik GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- RuleBased IA TIPDocument68 paginiRuleBased IA TIPmarlon_tayagÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are Compilers?Document52 paginiWhat Are Compilers?Bhavya NagÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOEN4302 Formal Methods and Models in Software EngineeringDocument19 paginiSOEN4302 Formal Methods and Models in Software EngineeringSanusi SuleimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 2Document44 paginiLec 2Lyu PhilipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled PresentationDocument165 paginiUntitled PresentationDalia MahmoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accenture 2021 Zone 1 and Zone 2 Slot AnalysisDocument75 paginiAccenture 2021 Zone 1 and Zone 2 Slot AnalysisIshita100% (2)
- An Expert System Is A Computer Program That Is Designed To Hold The Accumulated Knowledge of One or More Domain ExpertsDocument19 paginiAn Expert System Is A Computer Program That Is Designed To Hold The Accumulated Knowledge of One or More Domain ExpertsNikhil Jaiswal100% (1)
- Introduction To Expert SystemsDocument54 paginiIntroduction To Expert SystemsBroor BeboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - 4 AIDocument75 paginiUnit - 4 AIManikantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asus Test ReportDocument3 paginiAsus Test ReportAndres GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Heritage of ThalesDocument305 paginiThe Heritage of ThalesAndres Guevara100% (2)
- Fritzing EGR270Document8 paginiFritzing EGR270Andres Guevara100% (1)
- Comparatives ExplanationDocument4 paginiComparatives ExplanationAndres GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radar Signal Processing Using MATLAB: Ir. Dr. KOO Voon-ChetDocument67 paginiRadar Signal Processing Using MATLAB: Ir. Dr. KOO Voon-Chetfox_a_foxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Como Escribir ArticuloDocument3 paginiComo Escribir ArticuloAndres GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Received 12 December 2005Document7 paginiReceived 12 December 2005Andres GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- AstronomiaDummies 1ercapDocument55 paginiAstronomiaDummies 1ercapAndres Guevara75% (4)
- Faculty of Science: Supporting The Mutual Prosperity of Mankind and NatureDocument2 paginiFaculty of Science: Supporting The Mutual Prosperity of Mankind and NatureAndres GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6825 Sp13WuDocument7 pagini6825 Sp13WuAndres GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hilbert Vibration DecompositionDocument31 paginiHilbert Vibration DecompositionAndres Guevara0% (1)
- 72552Document8 pagini72552Andres GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noncommunicable Diseases Prevention and Control in The South-Eastern Europe Health NetworkDocument44 paginiNoncommunicable Diseases Prevention and Control in The South-Eastern Europe Health NetworkAndres GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Publicaciones Relacionadas IADocument40 paginiPublicaciones Relacionadas IAAndres GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Operation: SiemensDocument3 paginiMath Operation: SiemensAndres GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Innovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschDocument28 paginiInnovativ and Liabl :: Professional Electronic Control Unit Diagnosis From BoschacairalexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internship ReportDocument36 paginiInternship ReportM.IMRAN0% (1)
- Elastomeric Impression MaterialsDocument6 paginiElastomeric Impression MaterialsMarlene CasayuranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Tanker Check ListDocument8 paginiWater Tanker Check ListHariyanto oknesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual: Functional SafetyDocument24 paginiManual: Functional SafetymhaioocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vernacular ArchitectureDocument4 paginiVernacular ArchitectureSakthiPriya NacchinarkiniyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neelima A Kulkarni ResumeDocument3 paginiNeelima A Kulkarni ResumeAcademics LecturenotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revit 2023 Architecture FudamentalDocument52 paginiRevit 2023 Architecture FudamentalTrung Kiên TrầnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Will Smith BiographyDocument11 paginiWill Smith Biographyjhonatan100% (1)
- Principles of Business Grade 10 June 2021 Time: 1 1/2 Hrs. Paper 2 Answer ONLY 1 Question in Section I. Section IDocument3 paginiPrinciples of Business Grade 10 June 2021 Time: 1 1/2 Hrs. Paper 2 Answer ONLY 1 Question in Section I. Section Iapi-556426590Încă nu există evaluări
- 21st CENTURY TECHNOLOGIES - PROMISES AND PERILS OF A DYNAMIC FUTUREDocument170 pagini21st CENTURY TECHNOLOGIES - PROMISES AND PERILS OF A DYNAMIC FUTUREpragya89Încă nu există evaluări
- Aquaculture - Set BDocument13 paginiAquaculture - Set BJenny VillamorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency Response For Control System Analysis - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument7 paginiFrequency Response For Control System Analysis - GATE Study Material in PDFNarendra AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contoh Assignment PDFDocument18 paginiContoh Assignment PDFSiti Fatimah A Salam67% (3)
- Rare Malignant Glomus Tumor of The Esophagus With PulmonaryDocument6 paginiRare Malignant Glomus Tumor of The Esophagus With PulmonaryRobrigo RexÎncă nu există evaluări
- IG Deck Seal PumpDocument3 paginiIG Deck Seal PumpSergei KurpishÎncă nu există evaluări
- TrellisDocument1 paginăTrellisCayenne LightenÎncă nu există evaluări
- LM2TB8 2018 (Online)Document252 paginiLM2TB8 2018 (Online)SandhirÎncă nu există evaluări
- ULANGAN HARIAN Mapel Bahasa InggrisDocument14 paginiULANGAN HARIAN Mapel Bahasa Inggrisfatima zahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4Document15 paginiUnit 4David Lopez LaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- HemoptysisDocument30 paginiHemoptysisMarshall ThompsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 200150, 200155 & 200157 Accelerometers: DescriptionDocument16 pagini200150, 200155 & 200157 Accelerometers: DescriptionJOSE MARIA DANIEL CANALESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 1Document8 paginiHomework 1Yooncheul JeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- En 50124 1 2001Document62 paginiEn 50124 1 2001Vivek Kumar BhandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audi R8 Advert Analysis by Masum Ahmed 10PDocument2 paginiAudi R8 Advert Analysis by Masum Ahmed 10PMasum95Încă nu există evaluări
- Understanding The Marshall AttackDocument6 paginiUnderstanding The Marshall Attacks.for.saad8176Încă nu există evaluări
- De DusterDocument6 paginiDe DusterArstÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 and 2Document4 paginiUnit 1 and 2Aim Rubia100% (1)
- Vocations The New Midheaven Extension ProcessDocument266 paginiVocations The New Midheaven Extension ProcessMiss M.100% (24)
- TRICARE Behavioral Health Care ServicesDocument4 paginiTRICARE Behavioral Health Care ServicesMatthew X. HauserÎncă nu există evaluări