Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Dok Flipchart
Încărcat de
api-2503452020 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
113 vizualizări25 paginiTitlu original
dok flipchart
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
113 vizualizări25 paginiDok Flipchart
Încărcat de
api-250345202Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 25
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
A Guide for Using
Webbs Depth of Knowledge
by Karin Hess, Ed. D.
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
2
This guide was developed by Karin K. Hess for C2 Collaborative, Inc. It consolidates numerous
tools educators use to implement Webbs Depth of Knowledge for curriculum and assessment. The
examples herein are drawn from several classroom-tested DOK tools: Hess Cognitive Rigor Matrices
for ELA-Social Studies, Writing, and Math-Science developed by Karin Hess, at the Center for
Assessment; Norman Webbs Alignment Tool from Wisconsin Center of Educational Research; and
the Florida Department of Educations guide for Depth of Knowledge Questions.
ISBN: 978-0-9857219-4-7
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
3
Table of Contents
Overview ................................................................................... Page 4
Level 1 ......................................................................................... Page 6
Level 2 .................................................................................... Page 10
Level 3 ...................................................................................... Page 14
Level 4 ...................................................................................... Page 18
Content/Curriculum Analysis Form .............................. Page 22
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
4
An Educators Guide for Applying Webbs Depth-of-Knowledge
Levels to the College and Career Readiness Standards
Overview
At the heart of College and Career Readiness is the need to increase the level of rigor in our classrooms for all students. The College and Career
Readiness are a step in the right direction. However, the standards alone will not bring rigor to our classrooms. The implementation of these
standards requires practical tools to develop local curricula and assessments and to promote classroom discourse aligned to higher levels of
cognitive demand.
Norman Webbs Depth-of-Knowledge (DOK) schema has become one of the key tools educators can employ to analyze the cognitive demand
(complexity) intended by the standards, curricular activities, and assessment tasks. Webb (1997) developed a process and criteria for systematically
analyzing the alignment between standards and test items in standardized assessments. Since then the process and criteria have demonstrated
application to reviewing curricular alignment as well. The model categorizes assessment tasks by diferent levels of cognitive expectation, or depth
of knowledge, required to successfully complete the task. Hess (2004-2012) further articulated the model with content-specifc descriptions for
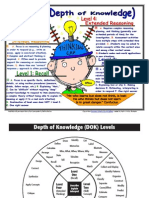
use by classroom teachers and organizations conducting alignment studies. The table below outlines the Webb DOK levels:
DOK Level Description of Level
1 Recall & Reproduction
2 Skills & Concepts
3 Strategic Thinking & Reasoning
4 Extended Thinking
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
5
The DOK level assigned should refect the level of work students are most commonly required to perform
in order for the response to be deemed profcient, such as in rubric descriptions describing profcient
performance.
The DOK level should refect the complexity of cognitive processes demanded by the learning or assessment
objective and task, rather than its difculty. Ultimately, the DOK level describes the depth of understanding
required by a task, not whether or not the task is considered difcult.
If there is a question regarding which of two levels a standard addresses, such as Level 1 - Level 2, or Level
2 - Level 3, it is appropriate to assign the highest level as the DOK ceiling for the task, but also provide
opportunities at the lower DOK levels as an instructional progression (e.g., summarizing a text/DOK 2 before
analyzing a text/DOK 3; making observations/DOK 2 before conducting investigation/DOK 3) (Hess, 2004-
2006).
The DOK level should be assigned based upon the cognitive demand (mental processing) required by the
central performance described in the objective or task.
The tasks objectives central verb(s) alone is/are not sufcient to assign a DOK level. Developers must consider
what comes after the verb - the complexity of the task and content/concepts -- in addition to the mental
processing required by the requirements set forth in the objective (Webbs Depth of Knowledge Guide).
The intended DOK level can be assigned to anything from an instructional
question, to broader course objectives and assessment items/tasks using
the following general guidelines:
6
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
Curricular elements that fall into this category involve basic tasks that require students to recall or reproduce knowledge and/or skills. The subject
matter content at this level usually involves working with facts, terms, details, calculations, principles, and/or properties. It may also involve use of
simple procedures or formulas. There is little or no transformation of the target knowledge or skill required by the tasks that fall into this category. A
student answering a Level 1 item either knows the answer or does not; that is, the answer does not need to be fgured out or solved.
Fill-in-the-blank tasks
Recite-math facts, poems, etc.
Plot/locate points on a graph
Edit sentences
Identify/write sentence types
Highlight key words
Bookmark websites
Use key word search
Use dictionary, thesaurus
Follow steps/directions (e.g., recipe, long
division, make model)
Explain, demonstrate
Show & Tell
Locate or recall quotes
Document /cite sources
Brainstorm related ideas
Represent math relationships in words,
pictures, or symbols
Write complete sentences
Identify parts of speech
Label or locate parts in diagram
List related parts or kinds (e.g., triangles)
Vocabulary defnitions-look up, recall, use
in sentences
Calculate, compute
Measure, record data
Reproduce map or diagram
Use map key to locate information
Oral reading fuency
Decoding words
Use formulas
Evaluate expressions
Possible Products
Verbs Teacher Role Student Role
Locate, calculate, defne, identify, list,
label, match, measure, copy, memorize,
repeat, report, recall, recite, recognize,
state, tell, tabulate, use rules, answer who,
what, when, where, why, how
Questions to direct or focus attention,
shows, tells, demonstrates, provides
examples, examines, leads, breaks down,
defnes
Recognizes, responds, remembers,
memorizes, restates, absorbs, describes,
demonstrates, follows directions, applies
routine processes, defnitions, and
procedures
Level 1: Recall & Reproduction
7
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
Use step-by-step directions to make a model, plant seeds, bake a
cake, etc.
Describe an event, character, setting, etc. in a story
Write a list of key words you know about...
Recite/recall a fact or date related to ...
Write/retell in your own words ...
Cut out, draw, or match a picture that illustrates an event, process,
or story
Report or present fndings to the class
Memorize lines for a play
Skim for facts/details/dates about an event
Retell in your own words/paraphrase
Locate information found in a map, chart, tables, graph, diagram,
caption
Use a dictionary, glossary, or thesaurus to fnd word meanings
Make conversions between metric and customary units
Recall, restate, remember, or recognize facts, terms, properties heard,
viewed, or read
Complete basic /routine calculation tasks (e.g., addition, subtraction,
division, etc.)
Locate or retrieve information in verbatim form to answer a question
Recognize or identify features, objects, or steps that dont vary
greatly in form (e.g., recognizing features of basic tools or shapes,
properties of materials or objects)
Edit applying a standard set of conventions and/or criteria
that should eventually be automated (e.g., applying rules for
punctuation, grammar, spelling)
Complete measurement tasks (e.g., use a ruler to measure length;
thermometer or temperature probe to measure temperature)
Memorize and recognize formulas and algorithms
Use a formula where at least one of the unknowns are provided
(e. g., area formula, y=mx + b)
Potential Activities
8
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
ELA, History & Social Studies Alignment to Blooms Taxonomy (source: Hess ELA-SS CRM)
Revised Blooms Taxonomy Webbs DOK Level 1 | Recall & Reproduction
REMEMBER
Retrieve knowledge from long-term memory,
recognize, recall, locate, identify
Recall, recognize, or locate basic facts, details, events, or ideas explicit in texts
Read words orally in connected text with fuency & accuracy
UNDERSTAND
Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent,
translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize,
summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion,
predict, compare/contrast, match like ideas, explain,
construct models
Identify or describe literary elements (e.g., characters, setting, problem-solution,
confict, etc.)
Select appropriate words when intended meaning/defnition is clearly evident
Describe/explain who, what, where, when, or how
Defne/describe facts, details, terms, principles
Write simple sentences
APPLY
Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation,
carry out (apply) to a familiar task, or use (apply) to an
unfamiliar task
Use language structure (pre/sufx) or word relationships (synonym/antonym) to
determine meaning of words
Apply rules or resources to edit spelling, grammar, punctuation, conventions, word use
Apply basic formats for documenting sources
ANALYZE
Break into constituent parts, determine how parts
relate, diferentiate between relevant-irrelevant,
distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, fnd
coherence, deconstruct (e.g. for bias or point of view)
Identify whether specifc information is contained in graphic representations
(e.g. map, chart, table, graph, T-chart, diagram) or text features (e.g., headings,
subheadings, captions)
Decide which text structure is appropriate to audience and purpose
EVALUATE
Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect
inconsistencies, or fallacies, judge, critique
Not Applicable
CREATE
Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures,
generate, hypothesize, design, plan, produce
Brainstorm ideas, concepts, problems, or perspectives related to a topic or concept
9
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
Math & Science Alignment to Blooms Taxonomy (source: Hess Math-Science CRM)
Revised Blooms Taxonomy Webbs DOK Level 1 | Recall & Reproduction
REMEMBER
Retrieve knowledge from long-term memory,
recognize, recall, locate, identify
Recall, observe & recognize facts, principles, properties
Recall/identify conversions among representations or numbers (e.g., customary and
metric measures)
UNDERSTAND
Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent,
translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize,
summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion (such
as from examples given), predict, compare/contrast,
match like ideas, explain, construct models
Evaluate an expression
Locate points on a grid or number on a number line
Solve a one-step problem
Represent math relationships in words, pictures, or symbols
Read, write, compare decimals in scientifc notation
APPLY
Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation,
carry out (apply to a familiar task), or use (apply) to an
unfamiliar task
Follow simple procedures (e.g., recipe-type directions)
Calculate, measure, apply a rule (e.g., rounding)
Apply algorithm or formula (e.g., area, perimeter)
Solve linear equations
Make conversions among representations or numbers, or within and between
customary and metric measures
ANALYZE
Break into constituent parts, determine how parts
relate, diferentiate between relevant-irrelevant,
distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, fnd
coherence, deconstruct
Retrieve information from a table or graph to answer a question
Identify whether specifc information is contained in graphic representations (e.g.
table graph, T-chart, diagram)
Identify a pattern/trend
EVALUATE
Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect
inconsistencies or fallacies, judge, critique
Not Applicable
CREATE
Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures,
generate, hypothesize, design, plan, construct, produce
Brainstorm ideas, concepts, or terms related to a topic
10
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
Level 2 includes the engagement of mental processing beyond recalling, reproducing, or locating an answer. This level generally requires students
to compare or diferentiate among people, places, events, objects, text types, etc.; apply multiple concepts when responding; classify or sort items
into meaningful categories; describe or explain relationships such as cause and efect or character relationships; and provide and explain examples
and non-examples. A Level 2 describe or explain task requires students to go beyond a basic description or defnition to predict a possible result
or explain why something might happen. The learner makes use of information provided in context to determine intended word meanings,
which tools or approach is appropriate to fnd a solution (e.g., in a math word problem), or which characteristics to pay attention to when making
observations.
At this level, students are asked to transform/process target knowledge before responding. Example mental processes that often denote this
particular level include: summarize, estimate, organize, classify, extend, and make basic inferences.
Level 2: Skill/Concept
Verbs Teacher Role Student Role
Infer, categorize, organize and display,
compare-contrast, modify, predict,
interpret, distinguish, estimate, extend
patterns, interpret, use context clues,
make observations, summarize, translate
from table to graph, classify, show cause/
efect, relate, edit for clarity
Questions to diferentiate, infer, or check
conceptual understanding, models,
organizes/reorganizes, explores possible
options or connections, provides
examples and non-examples
Solves routine problems/tasks involving
multiple decision points and concepts,
constructs models to show relationships,
demonstrates use of conceptual
knowledge, compiles and organizes,
illustrates/explains with examples or
models, examines
11
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
Captioned
Photos Summary
Time-line
Demonstration
Presentation Interview
Diary entry
Graphic organizer
Reverse-Engineering
Cracking Codes Outline
Relationship Mind Maps
Blog Commenting
Survey development
Spreadsheet
Science logs
Sequence a key chain of events and supporting details using a time-
line, cartoon strip, outline or fow chart
Write a summary /informational report or develop an outline of
central ideas and supporting details
Develop a concept map or diagram showing a process or describing
relationships about a topic of study
Explain a series of steps used to fnd a solution
Construct a model to demonstrate how it looks or works
Make a diorama to illustrate/explain an event
Write a diary/blog entry for a character or historical fgure
Make a captioned scrapbook or photo essay about the area of study
Make a topographic map using data provided/data collected
Make a puzzle or game about the topic
Explain the meaning of a concept using words, objects, and/or
visuals
Demonstrate how to perform a particular task
Complete complex recognition tasks that involve recognizing
concepts and processes that may vary in how they appear
Complex calculation tasks involving decision point s (e.g., standard
deviation)
Identify appropriate strategies or sources for conducting research
projects that involve locating, collecting, organizing and displaying,
and summarizing information
Create a questionnaire or survey to answer a question
Conduct measurement or observational tasks that involve organizing
the data collected into basic presentation forms such as a table,
graph, Venn diagram, etc.
Participate in a simulation in order to understand and describe
difering perspectives
How or why would you use...?
What examples/non-examples can you fnd to...?
How would you organize_ to show...?
How could you show your understanding of... ?
What approach/tools would you use to...?
How would you apply what you learned to develop... ?
What other way could you solve/fnd out...?
What is your predictionand why?
How would you organize these facts/observations?
If you changed these elements what would/might happen?
What facts are relevant to show...?
What questions would you ask in an interview /survey about ...?
What question is being asked in this problem?
Potential Questions
Potential Activities
Possible Products
12
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
ELA, History & Social Studies Alignment to Blooms Taxonomy (source: Hess ELA-SS CRM)
Revised Blooms Taxonomy Webbs DOK Level 2 | Skills & Concepts
REMEMBER
Retrieve knowledge from long-term memory,
recognize, recall, locate, identify
Not Applicable
UNDERSTAND
Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent,
translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize,
summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion,
predict, compare/contrast, match like ideas, explain,
construct models
Specify, explain, show relationships, explain why, cause-efect
Give non-examples/examples
Summarize results, concepts, ideas in one text or one data set
Make basic inferences or logical predictions from data or texts
Identify main ideas or accurate generalizations of texts or issues
Locate information to support explicit-implicit central ideas
APPLY
Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation,
carry out (apply) to a familiar task, or use (apply) to an
unfamiliar task
Use context to identify the meaning of words/phrases
Obtain and interpret information using text features
Develop a text that may be limited to one paragraph
Apply simple organizational structures (paragraph, sentence types) in writing
ANALYZE
Break into constituent parts, determine how parts
relate, diferentiate between relevant-irrelevant,
distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, fnd
coherence, deconstruct (e.g. for bias or point of view)
Categorize/compare library elements, terms, facts/details, events
Identify use of literary devices
Analyze format, organization & internal text structure (e.g., signal words, transitions,
semantic cues) of diferent texts
Distinguish relevant-irrelevant information, fact/opinion
Identify characteristic text features; distinguish between texts, genres
EVALUATE
Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect
inconsistencies, or fallacies, judge, critique
Not Applicable
CREATE
Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures,
generate, hypothesize, design, plan, produce
Generate conjectures or hypotheses based on observations or prior knowledge and
experience
13
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
Math & Science Alignment to Blooms Taxonomy (source: Hess Math-Science CRM)
Revised Blooms Taxonomy Webbs DOK Level 2 | Skills & Concepts
REMEMBER
Retrieve knowledge from long-term memory,
recognize, recall, locate, identify
Not Applicable
UNDERSTAND
Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent,
translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize,
summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion (such
as from examples given), predict, compare/contrast,
match like ideas, explain, construct models
Specify and explain relationships (e.g., non-examples/examples, cause-efect)
Make and record observations
Explain steps followed
Summarize results or concepts
Make basic inferences or logical predictions from data/observations
Use models (e.g., diagrams to represent or explain mathematical concepts)
Make and explain estimates
APPLY
Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation,
carry out (apply to a familiar task), or use (apply) to an
unfamiliar task
Select a procedure according to criteria and perform it
Solve routine problem applying multiple concepts or decision points
Retrieve information from a table, graph, or fgure and use it to solve a problem
requiring multiple steps
Translate between tables, graphs, words, and symbolic notations (e.g., graph data from
a table)
Construct models given criteria
ANALYZE
Break into constituent parts, determine how parts
relate, diferentiate between relevant-irrelevant,
distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, fnd
coherence, deconstruct
Categorize, classify materials, data, fgures based on characteristics
Organize or order data
Compare/contrast fgures or data
Select appropriate graph and organize & display data
Interpret data from a simple graph
Extend a pattern
EVALUATE
Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect
inconsistencies or fallacies, judge, critique
Not Applicable
CREATE
Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures,
generate, hypothesize, design, plan, construct, produce
Generate conjectures or hypotheses based on observations or prior knowledge and
experience
14
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
Tasks and classroom discourse falling into this category demand the use of planning, reasoning, and higher order thinking processes, such
as analysis and evaluation, to solve real-world problems or explore questions with multiple possible outcomes. Stating ones reasoning and
providing relevant supporting evidence are key markers of DOK 3 tasks. The expectation established for tasks at this level require an in-depth
integration of conceptual knowledge and multiple skills to reach a solution or produce a fnal product. DOK 3 tasks and classroom discourse focus
on in-depth understanding of one text, one data set, one investigation, or one key source, whereas DOK 4 tasks expand the breadth of the task
using multiple texts or sources, or multiple concepts/disciplines to reach a solution or create a fnal product.
Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Reasoning
Verbs Teacher Role Student Role
Critique, appraise, revise for meaning,
assess, investigate, cite evidence, test
hypothesis, develop a logical argument,
use concepts to solve non-routine
problems, explain phenomena in terms
of concepts, draw conclusions based on
data
Questions to probe reasoning and
underlying thinking, asks open-ended
questions, acts as a resource and coach,
provides criteria and examples for
making judgments and supporting
claims, encourages multiple approaches
and solutions; determines when/where
(text, concept) depth and exploration is
most appropriate
Uncovers and selects relevant and
credible supporting evidence for
analyses, critiques, debates, claims and
judgments; plans, initiates questions,
disputes, argues, tests ideas/solutions,
sustains inquiry into topics or deeper
problems, applies to the real world
Complex Graph
Set up a database
Conduct or critique a
designed investigation
Video cast or podcast
Analyze survey results
Debate from a given
perspective
Develop storyboard for
flm or cartoon animation
Multi-paragraph essay or
short story
Literary critique
Play, book, music, or
movie review
Informational report with
several subtopics
Fact-based argument (Is
this criticism supported by
the historical facts?)
Create a Wiki or website
Possible Products
15
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
Analyze results of a questionnaire or survey (e.g., survey classmates/
industry members to fnd out what they think about a current issue)
Prepare an informational report about an area of study
Write a letter to the editor after evaluating a product
Prepare for and participate in a debate
Use evidence to generate criteria for making judgments
Make a booklet or brochure about a topic, organization, or issue
Participate on a panel to discuss difering viewpoints on
Prepare a speech to support your perspective about
Explain and apply abstract terms and concepts to real-world
situations
Solve complex, non-routine problems that draw upon multiple skills,
concepts, and processes
Write an essay, short story, poem, or play
Create complex graphs or databases where reasoning and approach
to data organization is not obvious
Design, conduct, or critique an investigation to answer a research
question
Propose an alternate solution to a problem studied
What are the possible design faws in?
What is the theme/the lesson learned?
How would the theme change if?
What underlying bias is there?
What inferences will these facts support?
How does the author create tension/suspense?
What is the authors chain of reasoning or point of view for?
What is the impact on the reader /viewer for use of this (rhetorical de-
vice, analogy, fgurative language use, visual image, etc.)?
What conclusions can you draw?
How can you prove that your solution or estimate is reasonable?
What evidence can you fnd to support?
What ideas justify this position?
Potential Questions
Potential Activities
16
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
ELA, History & Social Studies Alignment to Blooms Taxonomy (sources: Hess ELA-SS and Writing CRMs)
Revised Blooms Taxonomy Webbs DOK Level 3 | Strategic Thinking & Reasoning
REMEMBER
Retrieve knowledge from long-term memory,
recognize, recall, locate, identify
Not Applicable
UNDERSTAND
Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent,
translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize,
summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion,
predict, compare/contrast, match like ideas, explain,
construct models
Explain, generalize, or connect ideas using supporting evidence (e.g., quote, example,
text reference)
Identify/make inferences about explicit or implicit themes
Describe how word choice, point of view, or bias may afect the readers interpretation
of a text
Write multi-paragraph composition for specifc purpose, focus, voice, tone & audience
APPLY
Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation,
carry out (apply) to a familiar task, or use (apply) to an
unfamiliar task
Apply a concept in a new context
Revise fnal draft for meaning or progression of ideas
Apply internal consistency of text organization and structure to composing a full
composition
Apply word choice, point of view, style to impact readers/viewers interpretation of a
text
ANALYZE
Break into constituent parts, determine how parts
relate, diferentiate between relevant-irrelevant,
distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, fnd
coherence, deconstruct (e.g. for bias or point of view)
Analyze information within a text or source
Analyze interrelationships among concepts, issues, problems
Analyze or interpret authors craft (literary devices, viewpoint, or potential bias) to
create or critique a text or to support text interpretations
Use reasoning and evidence to generate criteria for making and supporting an
argument of judgment (e.g., Was FDR a great president? Who was the greatest ball
player?)
EVALUATE
Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect
inconsistencies, or fallacies, judge, critique
Cite evidence and develop a logical argument for conjectures
Describe, compare, and contrast solution methods
Verify reasonableness of results
Justify or critique conclusions drawn
CREATE
Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures,
generate, hypothesize, design, plan, produce
Synthesize information within one source or text
Develop a complex model for a given situation
Develop an alternative solution
17
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
Math & Science Alignment to Blooms Taxonomy (source: Hess Math-Science CRM)
Revised Blooms Taxonomy Webbs DOK Level 3 | Strategic Thinking & Reasoning
REMEMBER
Retrieve knowledge from long-term memory,
recognize, recall, locate, identify
Not Applicable
UNDERSTAND
Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent,
translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize,
summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion,
predict, compare/contrast, match like ideas, explain,
construct models
Use concepts to solve non-routine problems
Explain, generalize, or connect ideas using supporting evidence
Make and justify conjectures
Explain thinking when more than one response/solution is possible
Explain phenomena in terms of concepts
APPLY
Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation,
carry out (apply to a familiar task), or use (apply) to an
unfamiliar task
Design investigation for a specifc purpose or research question
Conduct a designed investigation
Use concepts to solve non-routine problems
Use and show reasoning, planning, and evidence
Translate between problem & symbol notation when not a direct translation
ANALYZE
Break into constituent parts, determine how parts
relate, diferentiate between relevant-irrelevant,
distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, fnd
coherence, deconstruct
Compare information within data sets or texts or across related data sets
Analyze and draw conclusions from data, citing evidence
Generalize a pattern
Interpret data from complex graph
Analyze similarities/diferences between research procedures or solutions
EVALUATE
Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect
inconsistencies or fallacies, judge, critique
Cite evidence and develop a logical argument for concepts or solutions
Describe, compare, and contrast solution methods
Verify reasonableness of results
CREATE
Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures,
generate, hypothesize, design, plan, construct,
produce
Synthesize information within one data set, source or text
Formulate an original problem given a situation
Develop a scientifc/mathematical model for a complex situation
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
18
Curricular elements assigned to this level demand extended and integrated use of higher order thinking processes such as critical and creative-
productive thinking, refection, and adjustment of plans over time. Students are engaged in conducting multi-faceted investigations to solve
real-world problems with unpredictable solutions. Employing and sustaining strategic thinking processes over a longer period of time to solve the
problem or produce an authentic product is a key feature of curricular objectives assigned to DOK 4. Key aspects that denote this particular level
typically include authentic problems and audiences, and collaboration within a project-based setting.
Level 4: Extended Thinking
Verbs Teacher Role Student Role
Initiate, design and conduct, collaborate,
research, synthesize, self-monitor,
critique, produce/present
Questions to extend thinking and
broaden perspectives; facilitates teaming,
collaboration, self-evaluation
Designs, takes risks, researches
synthesizing multiple resources,
collaborates, plans, organizes, and
modifes, creates concrete tangible
products
Short flm
Agency presentation
Research report
Play
Video Game
Documentary
Newspaper or series of articles
Multi-Media product
Anthology of original writing, art, music, etc.
Possible Products
Applying information from more than one discipline to solve ill-
defned problems in novel or real-world situations
Research tasks that involve generating questions, and formulating
and testing hypotheses
Tasks that require making multiple strategic and procedural
decisions as new information is processed
Tasks that require multiple roles and collaboration and coordination
with others (e.g., script writing, camera work, editing, and acting/
talent)
Tasks that involve drawing evidence from multiple sources to
support solutions/conclusions
Conducting an internship in industry where students are faced with
real-world, unpredictable problems
Organizing/conducting a community service project or school-
based event
Potential Activities
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
19
What changes would you make to solve or address this major prob-
lem/ or issue?
How would you improve upon this invention or innovation?
Can you propose an alternative solution to?
What could be done to minimize (maximize)?
In what way would you design or redesign...and why ?
What evidence would you cite to defend the actions of?
How would you evaluate?
How would you prioritize criteria for making this (local zoning)
decision and why?
How would you evaluate the works by this author over time?
Can you formulate and test a conjecture for?
Can you predict the potential benefts and drawbacks if this law
does/does not pass?
Can you construct a model that would change?
Can you think of an original way to apply?
Do you agree with the actions? with the outcomes? with the
decision to?
How would you prove? disprove?
Can you assess the value or importance of?
What information would you use to support a difering
perspective?
What can be learned about this time in history from reading and
analyzing various cultural, political, and social perspectives?
Potential Questions
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
20
ELA, History & Social Studies Alignment to Blooms Taxonomy (sources: Hess ELA-SS and Writing CRMs)
Revised Blooms Taxonomy Webbs DOK Level 4 | Extended Thinking
REMEMBER
Retrieve knowledge from long-term memory,
recognize, recall, locate, identify
Not Applicable
UNDERSTAND
Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent,
translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize,
summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion,
predict, compare/contrast, match like ideas, explain,
construct models
Use multiple sources to elaborate on how concepts or ideas specifcally draw from
other content domains or difering concepts (e.g., research paper, arguments of policy:
should this law be passed? What will be the impact of this change?)
Develop generalizations about the results obtained or strategies used and apply them
to a new problem or contextual scenario
APPLY
Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation,
carry out (apply to a familiar task), or use (apply) to an
unfamiliar task
Select or devise an approach among many alternatives to research and present a
novel problem or issue
Illustrate how multiple themes (e.g., historical, geographic, social) may be interrelated
within a text or topic
ANALYZE
Break into constituent parts, determine how parts
relate, diferentiate between relevant-irrelevant,
distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, fnd
coherence, deconstruct
Analyze multiple sources of evidence, or multiple works by the same author, or across
genres, or time periods
Analyze complex/abstract themes, perspectives, concepts
Gather, analyze, and organize multiple information sources
Compare and contrast conficting judgments or policies (e.g., Supreme Court
decisions)
EVALUATE
Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect
inconsistencies or fallacies, judge, critique
Evaluate relevancy, accuracy, and completeness of information across multiple sources
Apply understanding in a novel way, provide argument or justifcation for the
application
Critique the historical impact (e.g., policy, writings, discoveries, etc.)
CREATE
Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures,
generate, hypothesize, design, plan, construct, produce
Synthesize information across multiple sources or texts in order to articulate a new
voice, alternate theme, new knowledge or nuanced perspective
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
21
Math & Science Alignment to Blooms Taxonomy (source: Hess Math-Science CRM)
Revised Blooms Taxonomy Webbs DOK Level 4 | Extended Thinking
REMEMBER
Retrieve knowledge from long-term memory,
recognize, recall, locate, identify
Not Applicable
UNDERSTAND
Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent,
translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize,
summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion (such
as from examples given), predict, compare/contrast,
match like ideas, explain, construct models
Relate mathematical or scientifc concepts to other content areas, other domains, or
other concepts
Develop generalizations of the results obtained and the strategies used (from
investigation or readings) and apply them to new problem situations
APPLY
Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation,
carry out (apply to a familiar task), or use (apply) to an
unfamiliar task
Select or devise an approach among many alternatives to solve a problem
Conduct a project that specifes a problem, identities solution paths, solves the
problem, and reports results
ANALYZE
Break into constituent parts, determine how parts
relate, diferentiate between relevant-irrelevant,
distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, fnd
coherence, deconstruct
Analyze multiple sources of evidence
Analyze complex/abstract themes
Gather, analyze, and evaluate information
EVALUATE
Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect
inconsistencies or fallacies, judge, critique
Gather, analyze, & evaluate information in order to draw conclusions
Apply understanding in a novel way, provide argument or justifcation for the
application
CREATE
Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures,
generate, hypothesize, design, plan, construct, produce
Synthesize information across multiple sources or texts
Design a mathematical model to inform and solve a practical or abstract situation
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
22
DOK Level(s) Objective
TARGET
DOK Level (s)
Location/
Performance or
Assessment
LEVEL 1
Recall/
Reproduction
of Information
& Procedures
LEVEL 2
Working with
Skills and
Concepts
LEVEL 3
Strategic
Thinking &
Reasoning
LEVEL 4
Extended
Strategic
Thinking
Content/Curriculum Analysis
Course or Unit Name:
List course or unit learning objectives under the correct DOK Level.
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
25
Resources:
Anderson, L., Krathwohl, D., Airasian, P., Cruikshank, K., Mayer, R., Pintrich, P., Raths, J., & Wittrock, M. (Eds)
(2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Blooms taxonomy of educational
objectives. New York: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.
Florida Department of Education, Depth of Knowledge Questions
Hess, K. K. (2004-2012). Center for Assessment, National Center for the Improvement of Educational
Assessment, Inc. [papers posted and available ] www.nciea.org
Webb, N. (March 28, 2002) Depth-of-Knowledge Levels for four content areas, unpublished paper.
Webb, N. (August 1999). Research Monograph No. 18: Alignment of science and mathematics standards and
assessments in four states. Washington, D.C.: CCSSO.
Webb, N. (1997). Research Monograph Number 6: Criteria for alignment of expectations and assessments on
mathematics and science education. Washington, D.C.: CCSSO.
2014 C2 Collaborative, Inc.
2014 Center for Assessment
ISBN: 978-0-9857219-4-7
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Webbs DOK GuideDocument13 paginiWebbs DOK GuideNightwing10Încă nu există evaluări
- Dps Grade 4 Ela Unit Map 4 1Document7 paginiDps Grade 4 Ela Unit Map 4 1api-264363149Încă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Item 2: Units of Work and Assessment Value: Due Date: Return Date: Submission Method OptionsDocument6 paginiAssessment Item 2: Units of Work and Assessment Value: Due Date: Return Date: Submission Method Optionsapi-402868357Încă nu există evaluări
- Establishing Learning TargetsDocument8 paginiEstablishing Learning TargetsJayCesarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 Planning For Effective AssessmentDocument31 paginiModule 3 Planning For Effective AssessmentazimaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clo TemplateDocument5 paginiClo Templatesaira tahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 10 Unit ExampleDocument2 paginiEnglish 10 Unit ExampleJordanPridemore100% (1)
- Tool1 Assessment Validation ChecklistDocument4 paginiTool1 Assessment Validation Checklistjkclements100% (1)
- Depth of Knowledge GuideDocument13 paginiDepth of Knowledge GuideErikson LázaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Field Experience III School Buildings. Goals Will Be Assessed As Part of The Lesson Plan CommentaryDocument10 paginiField Experience III School Buildings. Goals Will Be Assessed As Part of The Lesson Plan Commentaryapi-463534174Încă nu există evaluări
- Math Lesson 10 31 23 of 3Document5 paginiMath Lesson 10 31 23 of 3api-699093963Încă nu există evaluări
- Rosales National High School: Mapeh DepartmentDocument59 paginiRosales National High School: Mapeh Departmentharold carbonelÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAT-150 Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 paginiMAT-150 Lesson Plan Templatennpw9rjgsvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPG 1Document4 paginiEdtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPG 1api-638180600Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit Plan TemplateDocument3 paginiUnit Plan TemplateMs Deanna Ponnuthurai100% (1)
- SS301 - Learning OutcomeDocument31 paginiSS301 - Learning OutcomeEVELYN GRACE TADEOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan ProformaDocument4 paginiLesson Plan ProformaHassan M KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec-490 Step Template-RasconDocument26 paginiSec-490 Step Template-Rasconapi-434753918Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 4 Mini Unit Plan-2Document20 paginiAssignment 4 Mini Unit Plan-2api-287129687Încă nu există evaluări
- Align AssessmentsDocument25 paginiAlign AssessmentsRosemarie R. ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Lesson PlanDocument17 paginiReading Lesson Planapi-483982390Încă nu există evaluări
- Literacy Lesson Plan and Commentary Assignment Description 02Document20 paginiLiteracy Lesson Plan and Commentary Assignment Description 02api-712289610Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan: Curriculum ConnectionsDocument3 paginiLesson Plan: Curriculum Connectionsapi-397840564Încă nu există evaluări
- Subtraction W RegroupingDocument5 paginiSubtraction W Regroupingapi-255377985Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 paginiLesson Plan Templatedham4schoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2018 Ela Edtpa Lesson Plan 1Document5 paginiFall 2018 Ela Edtpa Lesson Plan 1api-327064630Încă nu există evaluări
- Sondra Polan Edit 614 Keystone ProjectDocument16 paginiSondra Polan Edit 614 Keystone Projectapi-399832630Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan: Step 1: Curriculum ConnectionsDocument6 paginiLesson Plan: Step 1: Curriculum Connectionsapi-395233182Încă nu există evaluări
- Edu 412 Strategy Based Comprehension Lesson PlanDocument9 paginiEdu 412 Strategy Based Comprehension Lesson Planapi-667056132Încă nu există evaluări
- Backward Design/Downward Design Cross-Curricular Planning ModelDocument3 paginiBackward Design/Downward Design Cross-Curricular Planning ModelDaniela AlloccaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Empty Your Cup: An Old Buddhist TaleDocument99 paginiEmpty Your Cup: An Old Buddhist TaleJulz QuilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literacy Lesson Plan and Commentary Assignment DescriptionDocument10 paginiLiteracy Lesson Plan and Commentary Assignment Descriptionapi-731796072Încă nu există evaluări
- Math Smart Word ProblemsDocument5 paginiMath Smart Word Problemsapi-255377985Încă nu există evaluări
- Portfolios, Rubrics, Learning Outcomes ..Oh My!: Session Five The Cordon Bleu Barbara Packer-Muti, EddDocument30 paginiPortfolios, Rubrics, Learning Outcomes ..Oh My!: Session Five The Cordon Bleu Barbara Packer-Muti, EddRommelie Perez PelicanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Episode 10 Fs 2Document12 paginiEpisode 10 Fs 2Verna Bem Valle100% (2)
- BGSU CTE Lesson Plan Communication and InstructionsDocument4 paginiBGSU CTE Lesson Plan Communication and InstructionsShannonMaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidance On Command Words Used in Learning Outcomes and Question Papers DIPLOMA v2 Sept15 (010915 Rew) 179201551521 - NoRestrictionDocument6 paginiGuidance On Command Words Used in Learning Outcomes and Question Papers DIPLOMA v2 Sept15 (010915 Rew) 179201551521 - NoRestrictionAli MohdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment and EvaluationDocument8 paginiAssessment and EvaluationhuwainaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lewis Ed508-5e-Lesson-Plan 1Document4 paginiLewis Ed508-5e-Lesson-Plan 1api-702871490Încă nu există evaluări
- TEAM Lesson Plan Template: StandardsDocument10 paginiTEAM Lesson Plan Template: Standardslbrinson1Încă nu există evaluări
- Bllom Taxaonomy For Lesson Plan PreparationDocument28 paginiBllom Taxaonomy For Lesson Plan PreparationChandramala AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deirdres rg10Document2 paginiDeirdres rg10api-350688071Încă nu există evaluări
- 04 Module Assessement-and-Evaluation 04Document13 pagini04 Module Assessement-and-Evaluation 04Christine LopenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ST Mary Mackillop Unit Plan User GuideDocument2 paginiST Mary Mackillop Unit Plan User Guideapi-320230014Încă nu există evaluări
- KPUPDocument8 paginiKPUPjessicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cognitive Functioning and Psychological ProcessingDocument37 paginiCognitive Functioning and Psychological ProcessingAnonymous wu6RXu100% (1)
- Grammar Subject Verb AgreementDocument7 paginiGrammar Subject Verb AgreementwindowsÎncă nu există evaluări
- To Use T&L Instructional Plan Template: Cat A Cupcake and Showing How The Author Uses Extra Details in The StoryDocument10 paginiTo Use T&L Instructional Plan Template: Cat A Cupcake and Showing How The Author Uses Extra Details in The Storyapi-430958670Încă nu există evaluări
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument22 paginiBloom's TaxonomyElvin CornelioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2018 Edtpa Lesson Plan 4Document5 paginiFall 2018 Edtpa Lesson Plan 4api-327064630Încă nu există evaluări
- Learning OutcomesDocument6 paginiLearning OutcomesjovinerlactÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goal Objective Reference ToolDocument6 paginiGoal Objective Reference Toolapi-290951950Încă nu există evaluări
- Bloom's Original Taxonomy of The Cognitive DomainDocument4 paginiBloom's Original Taxonomy of The Cognitive DomainSarah AnneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument32 paginiBlooms Taxonomyapi-2660718240% (1)
- Lesson Plan 2Document4 paginiLesson Plan 2api-288764826Încă nu există evaluări
- Using Assessment To Change Student Learning 1: Problems With Traditional Summative Assessment (Testing)Document11 paginiUsing Assessment To Change Student Learning 1: Problems With Traditional Summative Assessment (Testing)Eko Setyo BudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scoring RubricsDocument14 paginiScoring RubricsRay Chris Ranilop OngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doke Ose Learning Project Management GuideDocument12 paginiDoke Ose Learning Project Management Guideshaiful akhmar mohd noorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6-8 2017-18 Ssyra PosterDocument1 pagină6-8 2017-18 Ssyra Posterapi-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- Wms Fsa What Parents Should Know Literacy Night Powerpoint FinalDocument17 paginiWms Fsa What Parents Should Know Literacy Night Powerpoint Finalapi-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- Superintendent Letter 10-31-2017 FinalDocument4 paginiSuperintendent Letter 10-31-2017 Finalapi-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- Library ResourcesDocument4 paginiLibrary Resourcesapi-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- Internet Safety 2015Document41 paginiInternet Safety 2015api-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- RequireDocument5 paginiRequireapi-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- Ssms Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 paginiSsms Lesson Plan Templateapi-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- Dok Question StemsDocument1 paginăDok Question Stemsapi-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- Modified With Permission From A Pam Lowe Poster by Debbie Perkins Clip Art From - Created by Mark A. Hicks, IllustratorDocument2 paginiModified With Permission From A Pam Lowe Poster by Debbie Perkins Clip Art From - Created by Mark A. Hicks, Illustratorapi-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- Unpacking WorksheetDocument1 paginăUnpacking Worksheetapi-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- Bianchi Formative Assessment Times Vol 1Document1 paginăBianchi Formative Assessment Times Vol 1api-250345202Încă nu există evaluări
- KWIC Case StudyDocument7 paginiKWIC Case StudyTharakesh ChowdharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Responsory From GroveDocument14 paginiResponsory From GroveAlessandra RossiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 2 EspDocument105 paginiGrade 2 EsplyncheoquendoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yct 1Document3 paginiYct 1teryÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Rothschild House - The Owners of The WorldDocument54 paginiThe Rothschild House - The Owners of The WorldAlexandre FonsecaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bibliography Edu2141005Document5 paginiBibliography Edu2141005api-564736435Încă nu există evaluări
- Debate 3rd SpeakerDocument5 paginiDebate 3rd SpeakerJohn RivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP SRM TCodes PDFDocument6 paginiSAP SRM TCodes PDFtoabhishekpalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide Engineering Optimization L TEX Style Guide For Authors (Style 2 + Chicago Author-Date Reference Style)Document17 paginiGuide Engineering Optimization L TEX Style Guide For Authors (Style 2 + Chicago Author-Date Reference Style)skyline1122Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Fundamental Theorem of Integral CalculusDocument11 paginiChapter 1 - Fundamental Theorem of Integral CalculusCGD ReviewÎncă nu există evaluări
- The American Novel in The 21st Century: Changing Contexts, Literary Developments, New Modes of ReadingDocument49 paginiThe American Novel in The 21st Century: Changing Contexts, Literary Developments, New Modes of ReadingАлександра ГеркероваÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenaga D. Silat ArticleDocument185 paginiTenaga D. Silat Articlebrendan lanza100% (1)
- MiddlewareDocument13 paginiMiddlewareNarsing Rao PampariÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Use secureCRT Startup Log FileDocument17 paginiHow To Use secureCRT Startup Log FileMecael DesuyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEXGEN-4000 PLC: 4 Channel, 16 Bit Analog Output Module (Ordering Code - 4334)Document2 paginiNEXGEN-4000 PLC: 4 Channel, 16 Bit Analog Output Module (Ordering Code - 4334)arunkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adv 1 Unit 3 Borrow Vs Lend (Modal Requests)Document1 paginăAdv 1 Unit 3 Borrow Vs Lend (Modal Requests)Arley YanezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation SCADA GroupDocument59 paginiPresentation SCADA GroupUdit Upreti100% (1)
- BIT 2109 Integrative Programming and TechnologiesDocument4 paginiBIT 2109 Integrative Programming and TechnologiesHerwin CapiñanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Spark ShellDocument12 paginiOpen Spark ShellRamyaKrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frendx: Radio AustraliaDocument60 paginiFrendx: Radio AustraliaKasi XswlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Data Structures and Programming Techniques (CPSC 223, Spring 2021)Document659 paginiNotes On Data Structures and Programming Techniques (CPSC 223, Spring 2021)KALKA DUBEYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Braille 2520fluency3 Standard 7Document2 paginiLesson Plan Braille 2520fluency3 Standard 7api-315690330Încă nu există evaluări
- Church History (By Watchman Nee)Document76 paginiChurch History (By Watchman Nee)Yohannes BushoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MMW - Lesson03 - Intro To Set TheoryDocument7 paginiMMW - Lesson03 - Intro To Set TheoryDexter CaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Series 0i-D (E) - V05aDocument16 paginiSeries 0i-D (E) - V05aPaulus PramudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Year Project DocumentationDocument90 paginiFinal Year Project DocumentationMilion NugusieÎncă nu există evaluări
- L7 Duality IDocument11 paginiL7 Duality ILauraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piccolo Sample ItemsDocument1 paginăPiccolo Sample Itemsapi-432499175Încă nu există evaluări
- Arabic Chatbots A SurveyDocument8 paginiArabic Chatbots A SurveyAmera SabriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer NetworkDocument14 paginiComputer NetworkRoger FreeÎncă nu există evaluări