Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
f5 c4 Vectors New
Încărcat de
Arthas Rhee HermanDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
f5 c4 Vectors New
Încărcat de
Arthas Rhee HermanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
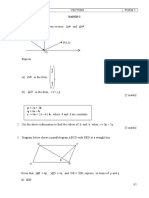
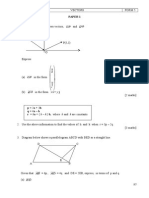
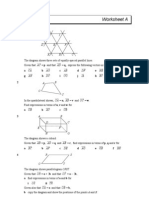
CHAPTER 4 VECTORS FORM 5
97
PAPER 1
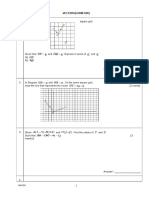
1. Diagram below shows two vectors, OP and QO
Q(-8,4)
P(5,3)
Express
(a) OP in the form ,
|
|
.
|
\
|
y
x
(b) QO in the form x i + y j
[2 marks]
2. Use the above information to find the values of h and k when r = 3p 2q.
[3 marks]
3. Diagram below shows a parallelogram ABCD with BED as a straight line.
D C
E
A B
Given that AB = 6p , AD = 4q and DE = 2EB, express, in terms of p and q
(a) BD
(b) EC
[4 marks]
O
p = 2a + 3b
q = 4a b
r = ha + ( h k ) b, where h and k are constants
CHAPTER 4 VECTORS FORM 5
98
4. Given that O(0,0), A(-3,4) and B(2, 16), find in terms of the unit vectors, i and j,
(a) AB
(b) the unit vector in the direction of AB
[4 marks]
5. Given that A(-2, 6), B(4, 2) and C(m, p), find the value of m and of p such that
AB + 2 BC = 10i 12j.
[4 marks]
6. Diagram below shows vector OA drawn on a Cartesian plane.
y
A
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 x
(a) Express OA in the form
|
|
.
|
\
|
y
x
(b) Find the unit vector in the direction of OA
[3 marks]
7. Diagram below shows a parallelogram, OPQR, drawn on a Cartesian plane.
y
Q
R P
O x
It is given that OP = 6i + 4j and PQ = - 4i + 5j. Find PR .
[3 marks]
6
4
2
CHAPTER 4 VECTORS FORM 5
99
8. Diagram below shows two vectors, OA and AB .
y
A(4,3)
O x
-5
Express
(a) OA in the form
|
|
.
|
\
|
y
x
(b) AB in the form xi + yj
[2 marks]
9. The points P, Q and R are collinear. It is given that PQ= 4a 2b and
b k a QR ) 1 ( 3 + + = , where k is a constant. Find
(a) the value of k
(b) the unit vector in the direction of PQ
[4 marks]
10. Given that j i a 7 6 + = and , 2 j pi b + = find the possible value (or values) of p for following
cases:-
a) b a and are parallel
b) b a =
[5 marks]
B
CHAPTER 4 VECTORS FORM 5
100
PAPER 2
1. Give that
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
3
2
,
7
5
OB AB and
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
5
k
CD , find
(a) the coordinates of A, [2 marks]
(b) the unit vector in the direction of OA, [2 marks]
(c) the value of k, if CD is parallel to AB [2 marks]
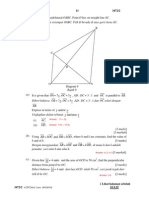
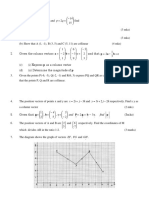
2. Diagram below shows triangle OAB. The straight line AP intersects the straight line OQ at R. It
is given that OP = 1/3 OB, AQ = AB, x OP 6 = and . 2y OA=
A
R
O P B
(a) Express in terms of x and/or y:
(i) AP
(ii) OQ [4 marks]
(b) (i) Given that , AP h AR = state AR in terms of h, x and y.
(ii) Given that , OQ k RQ = state RQ in terms of k, x and y.
[2 marks]
(c) Using AR and RQ from (b), find the value of h and of k.
[4 marks]
Q
CHAPTER 4 VECTORS FORM 5
101
3. In diagram below, ABCD is a quadrilateral. AED and EFC are straight lines.
D
E F C
A B
It is given that = AB 20x, = AE 8y, DC = 25x 24y, AE = AD
and EF =
5
3
EC.
(a) Express in terms of x and/or y:
(i) BD
(ii) EC [3 marks]
(b) Show that the points B, F and D are collinear. [3 marks]
(c) If | x | = 2 and | y | = 3, find | BD |. [2 marks]
4. Diagram below shows a trapezium ABCD.
B C
F
A E D
It is given that AB =2y, AD= 6x, AE =
3
2
AD and BC =
6
5
AD
(a) Express AC in terms of x and y [2 marks]
(b) Point F lies inside the trapezium ABCD such that 2 EF = m AB , and m is a
constant.
(i) Express AF in terms of m , x and y
(j) Hence, if the points A, F and C are collinear, find the value of m.
[5 marks]
CHAPTER 4 VECTORS FORM 5
102
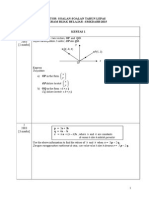
ANSWERS (PAPER 1)
1. a)
|
|
.
|
\
|
3
5
1
b) 8i 4j 1
2. r = - 2a + 11b
r = ha + (h k)b
1
h = -2 1
(h k) = 11
k = 13
1
3 a)
BD = 6p + 4q
1
b)
DB= BD
= 6p 4q
1
EB =
3
DB
4
2
3
p q =
1
BC EB EC + =
8
2
3
p q = +
1
4. a)
j i AB ) 4 16 ( )) 3 ( 2 ( + =
1
= 5i + 12j 1
b)
u ) 12 5 (
12 5
1
2 2
j i +
+
=
1
) 12 5 (
13
1
j i + =
1
5.
) ) 2 ( 2 ) 4 (( 2 ) 4 6 ( 2 j p i m j i BC AB + + = +
1
= (-2+2m)i + (-8+2p)j 1
m = 6 1
p = -2 1
6. a)
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
5
12
OA
1
b)
) 5 12 (
5 12
1
2 2
j i u +
+
=
1
) 5 12 (
13
1
j i + = 1
CHAPTER 4 VECTORS FORM 5
103
7.
OP PO =
j i 4 6 =
1
PQ OR =
j i 5 4 + =
1
PR PO OR = +
j i + = 10
1
8. a)
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
3
4
OA
1
b)
j i AB 8 4 =
1
9. a)
PQ m QR =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ 2
4
1
3
m
k
1
3 = m(4)
4
3
= m
1
1+ k = m(-2)
2
5
= k
1
b)
2 2
4 ( 2)
PQ
u =
+
1
(4 2 )
20
a b =
1
10 a)
b k a =
) 2 ( 7 6 j pi k j i + = +
1
2
7
= k 1
7
12
= p 1
b)
b a =
2 2 2 2
6 7 2 p + = +
1
9 = p
1
CHAPTER 4 VECTORS FORM 5
104
ANSWERS (PAPER 2)
1 (a)
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
4
3
AO
1
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
4
3
OA
A = (-3,-4)
1
(b)
OA
OA
u =
OA
2 2
4 3
1
+
=
1
( ) j i u 4 3
5
1
=
1
(c)
AB m CD =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
7
5
5
m
k
1
7
5
= m
7
25
= k
1
2 (a) (i)
6 2 AP x y =
1
(ii)
18 2 AB x y =
1
9 1
2 2
AQ x y =
1
9 3
2 2
OQ x y = +
1
(b) (i)
hy hx AR 2 6 =
1
9 3
2 2
RQ kx ky = +
1
(c)
AQ RQ AR = +
y x y k h x k h
2
1
2
9
2
3
2
2
9
6 =
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
|
.
|
\
|
+
1
3
1
= k
1
2
1
= h
1
CHAPTER 4 VECTORS FORM 5
105
3 (a) (i)
y x BD 32 20 + =
1
(ii)
AD ED
4
3
=
= 24y
1
x EC 25 =
1
(b)
x FC 10 =
DC BD BC + =
y x 8 5 + =
1
CF BC BF + =
y x 8 5 + =
1
y x BD 32 20 + =
) 8 5 ( 4 y x + =
) ( 4 BF =
1
(c) 2 2
32 20 y x BD + =
( )
2 2
3 32 ) 2 20 ( + =
1
= 104 1
4 (a)
AD BC
6
5
=
= 5x
1
BC AB AC + =
= 5x + 2y
1
(b) (i)
AB m EF = 2
my EF =
1
AD AE
3
2
=
= 4x
1
EF AE AF + =
= 4x + my
1
(ii)
y x AC 2 5 + =
( ) y x AC 2 5
5
4
5
4
+ =
y x AC
5
8
4
5
4
+ =
1
Assume A, F, C collinear,
AF AC =
5
4
= 4x + my
5
8
= m
1
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Tables of Racah Coefficients: Mathematical Tables SeriesDe la EverandTables of Racah Coefficients: Mathematical Tables SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Extension of Casson's Invariant. (AM-126), Volume 126De la EverandAn Extension of Casson's Invariant. (AM-126), Volume 126Încă nu există evaluări
- f5 c4 VectorsnewDocument9 paginif5 c4 VectorsnewmmmmmmmmrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vector SPM 2003 - 2007Document4 paginiVector SPM 2003 - 2007Rosmizar AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.vektor 2015 (2003 - 2010)Document14 pagini4.vektor 2015 (2003 - 2010)Zuraidah BasriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vector Paper 2Document3 paginiVector Paper 2Aileen Beh Chik HeangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vector Past YearDocument2 paginiVector Past YearteeplÎncă nu există evaluări
- f5 c4 Vectors NewDocument9 paginif5 c4 Vectors NewksganÎncă nu există evaluări
- C4 Vectors A - QuestionsDocument2 paginiC4 Vectors A - QuestionsKevin DanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vectors MathsDocument2 paginiVectors Mathszainab MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Add Maths Vectors Pat YearsDocument10 paginiAdd Maths Vectors Pat YearsHo Yen SzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vectors Exercises - PrintDocument6 paginiVectors Exercises - PrintMuhammad FikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- BY Moses Ssali at GHS 2020 0775620833/0704221195: Prov 1:7Document5 paginiBY Moses Ssali at GHS 2020 0775620833/0704221195: Prov 1:7Athiyo MartinÎncă nu există evaluări
- F5 C4 VectorsDocument9 paginiF5 C4 VectorsWong Wai LunÎncă nu există evaluări
- (B) Given That: RevisionDocument2 pagini(B) Given That: RevisionAzizah Haji KamarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.2: Addition & Subtraction of Vectors: OD X yDocument3 pagini4.2: Addition & Subtraction of Vectors: OD X ymohamad_bidariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Year SPM QuestionsDocument6 paginiPast Year SPM QuestionsLee ElaineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6: Coordinate GeometryDocument11 paginiChapter 6: Coordinate GeometryHayati Aini AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- O4Qvec - c4 SoomenxDocument11 paginiO4Qvec - c4 SoomenxKapilanNavaratnamÎncă nu există evaluări
- AHL 3.13 Scalar ProductDocument53 paginiAHL 3.13 Scalar Productpelin petekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vector Past YearDocument8 paginiVector Past YearWan AfiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- AHL 3.12 Vector DefinitionsDocument52 paginiAHL 3.12 Vector Definitionspelin petekÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM F5 Ch4 PDF - UnlockedDocument11 paginiSPM F5 Ch4 PDF - UnlockedkokleongÎncă nu există evaluări
- f5 Additional Mathematics Revision Exercise Past Paper 20091125 Locus VectorsDocument2 paginif5 Additional Mathematics Revision Exercise Past Paper 20091125 Locus VectorsWallStreet HKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formative Question (Vector)Document4 paginiFormative Question (Vector)Jamaliah DaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics: Date: Name: Time: FormDocument51 paginiMathematics: Date: Name: Time: Formnsiu1234Încă nu există evaluări
- FX X X: Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument2 paginiFX X X: Answer All Questions in This SectionGeethanjali SivakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- F.5 Revision Exercise For MT 1Document18 paginiF.5 Revision Exercise For MT 1AndromedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Given That Points 5. in The Diagram Below,: A 3i+7 J 5kDocument2 paginiGiven That Points 5. in The Diagram Below,: A 3i+7 J 5kDavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument56 paginiUntitledNicole WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 0Document2 paginiProblem Set 0Toby ChengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Year SPM Vectors QuestionsDocument6 paginiPast Year SPM Vectors QuestionsAnonymous wksd8qcaZ50% (2)
- IB2 AA HL Test Makeup Vectors 2022Document10 paginiIB2 AA HL Test Makeup Vectors 2022football.hd.371Încă nu există evaluări
- Vector Paper 2 PDFDocument12 paginiVector Paper 2 PDFՙՙՙՙÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vectors QDocument7 paginiVectors Qideal writersÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines: C, Correct To 3 Significant FiguresDocument2 pagini11 Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines: C, Correct To 3 Significant Figures(4C27) Wong Ching Tung, Zoey 20181D043spss.hkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vectors (F5) Kertas 1Document7 paginiVectors (F5) Kertas 1Bariza BaharomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solomon C4 VectorsDocument11 paginiSolomon C4 Vectorssim887Încă nu există evaluări
- Vectors (Add Math) Unsolved PDFDocument14 paginiVectors (Add Math) Unsolved PDFSuhaan HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21 Vectors 1+++Document22 pagini21 Vectors 1+++Sugar Saleh100% (1)
- Problem Sets ALL PDFDocument34 paginiProblem Sets ALL PDFLeroy ChengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vectors QDocument6 paginiVectors QJOSHUA TAWANANYASHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Juj 2009 PDFDocument36 paginiJuj 2009 PDFMohd Khir ZainunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Chapter 4 (Rectangular Coordinates)Document6 paginiUnit 1 Chapter 4 (Rectangular Coordinates)Foysal ZaynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vectors Maths T Tingkiatan 6Document6 paginiVectors Maths T Tingkiatan 6limsiewthiangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ix - Class Sample Paper Mathematics: General InstructionDocument6 paginiIx - Class Sample Paper Mathematics: General InstructionRia Zita GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Challenging 3B08 eDocument6 paginiChallenging 3B08 e盧鈺恩Încă nu există evaluări
- Triangle of Area Triangle of Area Triangle of Area: OAB BCD ODEDocument17 paginiTriangle of Area Triangle of Area Triangle of Area: OAB BCD ODEjonathanyewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 1 SPM 2003Document3 paginiPaper 1 SPM 2003Marsilah Anum MarhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salomon VectorsDocument2 paginiSalomon Vectorsjsy7w7z8q7Încă nu există evaluări
- STPM (Q) TOPIC 6 VectorsDocument3 paginiSTPM (Q) TOPIC 6 VectorsMelody Ong0% (1)
- VectorsDocument14 paginiVectorsEdgardo Leysa100% (2)
- OC - C and OV V.: (A) (I) P Is The Point (-2, 3) - Work Out The Co-Ordinates of Q. (Ii) Work OutDocument5 paginiOC - C and OV V.: (A) (I) P Is The Point (-2, 3) - Work Out The Co-Ordinates of Q. (Ii) Work OutAyesha AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vectors 1Document5 paginiVectors 1Japhet MubaiwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scalar Product of VectorsDocument5 paginiScalar Product of VectorsSudibyo GunawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vectors in Two Dimensions: PracticeDocument4 paginiVectors in Two Dimensions: PracticeJohn GohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Set 16B (3-D) : Lines and Planes in Space (Chapter 16)Document4 paginiReview Set 16B (3-D) : Lines and Planes in Space (Chapter 16)Nhocticaro NhocÎncă nu există evaluări
- E4Qvec XDocument11 paginiE4Qvec XFarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- F3 Ch11 HWADocument4 paginiF3 Ch11 HWAJustin ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperbolic Functions: with Configuration Theorems and Equivalent and Equidecomposable FiguresDe la EverandHyperbolic Functions: with Configuration Theorems and Equivalent and Equidecomposable FiguresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 10Document13 paginiGroup 10Arthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Climate ThreatDocument3 paginiClimate ThreatArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Climate ThreatDocument3 paginiClimate ThreatArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Worn Path: Type of Work and Publication YearDocument5 paginiA Worn Path: Type of Work and Publication YearArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identify Poetic Device From An Unknown Poem and Explain How It Contributes To The Meaning of The PoemDocument10 paginiIdentify Poetic Device From An Unknown Poem and Explain How It Contributes To The Meaning of The PoemArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Everythinhis ArrangedDocument5 paginiEverythinhis ArrangedArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 8 Presentation: Aina Fatini Lim Jing YeeDocument7 paginiGroup 8 Presentation: Aina Fatini Lim Jing YeeArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Motivation in Second Language Learning (Role-Play)Document5 paginiRole of Motivation in Second Language Learning (Role-Play)Arthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Printed Mtrls S WDocument6 paginiPrinted Mtrls S WArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bil. Nama Kelas T. Tangan 1. Amanda Chee Pau Zhen T1SN2 2. Goh Ding Bang T2SN3 3. Hoh Chen Shan T1SN2 4. Ooi Min Huan T3Tesl 5. Wong Boon Hao T3SejDocument2 paginiBil. Nama Kelas T. Tangan 1. Amanda Chee Pau Zhen T1SN2 2. Goh Ding Bang T2SN3 3. Hoh Chen Shan T1SN2 4. Ooi Min Huan T3Tesl 5. Wong Boon Hao T3SejArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnl 1Document1 paginăJurnl 1Arthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Date Time Class Number of Pupils Level of Proficiency Subject Theme Topic Focused Skills Integrated Skills Content StandardDocument6 paginiDate Time Class Number of Pupils Level of Proficiency Subject Theme Topic Focused Skills Integrated Skills Content StandardArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Everythinhis ArrangedDocument5 paginiEverythinhis ArrangedArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reasons For Committing Suicide in MalaysDocument16 paginiReasons For Committing Suicide in MalaysArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Krashen TheoryDocument21 paginiKrashen TheoryKarla LintuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 15Document5 pagini8 15Arthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Another Day of DawnDocument2 paginiAnother Day of DawnArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Counter Culture - Hippies: By: Meg, Rose, MollyDocument12 paginiCounter Culture - Hippies: By: Meg, Rose, MollyArthas Rhee Herman100% (1)
- Year 4 RPHDocument6 paginiYear 4 RPHArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 1 DramaDocument5 paginiTask 1 DramaArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Sentences That Can Be Used As Games Material To Help Poor English Level Students.Document6 paginiSimple Sentences That Can Be Used As Games Material To Help Poor English Level Students.Arthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RPT Bi Year 4 2018Document13 paginiRPT Bi Year 4 2018Sarath Kumar100% (1)
- PRKA 3012 (Tutorial)Document17 paginiPRKA 3012 (Tutorial)Arthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2017 Excel Calendar Planner 12Document12 pagini2017 Excel Calendar Planner 12JDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Borang Skema TLO EDUP3043 EngDocument12 paginiBorang Skema TLO EDUP3043 EngArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- G1Q1Document8 paginiG1Q1Arthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Draft 5111a OOI MIN HUAN'S WORKDocument7 paginiGrammar Draft 5111a OOI MIN HUAN'S WORKArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Teach Weather PDFDocument5 paginiHow To Teach Weather PDFArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian CustomsDocument6 paginiIndian CustomsArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Components in The Daily Teaching Plan Using The KSSR Standard Documents: Learning Objectives & Standard Based AssessmentDocument12 paginiComponents in The Daily Teaching Plan Using The KSSR Standard Documents: Learning Objectives & Standard Based AssessmentArthas Rhee HermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Relativity Solutions To Exercises by Sergei WinitzkiDocument39 paginiGeneral Relativity Solutions To Exercises by Sergei WinitzkiMichael Anthony Mendoza83% (6)
- OrthotropyDocument17 paginiOrthotropyAndrés MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MA/MSCMT-01 M.A./M.Sc. (Previous) Mathematics Examination Advanced Algebra Paper - MA/MSCMT-01Document3 paginiMA/MSCMT-01 M.A./M.Sc. (Previous) Mathematics Examination Advanced Algebra Paper - MA/MSCMT-01pradyum choudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BE Mech 2008-1Document87 paginiBE Mech 2008-1erfergaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Source of Entropy For Black Holes Bombelli 1986Document11 paginiQuantum Source of Entropy For Black Holes Bombelli 1986pline11691Încă nu există evaluări
- S.Y.B.Sc - Mathematics PDFDocument16 paginiS.Y.B.Sc - Mathematics PDFhrishi kathaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carrell J - Groups, Matrices, and Vector SpacesDocument414 paginiCarrell J - Groups, Matrices, and Vector SpacesWichi100% (3)
- Linear Algebra and Analytical Geometry: A B C Ab CDDocument3 paginiLinear Algebra and Analytical Geometry: A B C Ab CDTooba AkhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- MA111 Test 1 S1 2019Document8 paginiMA111 Test 1 S1 2019Nitesh ChandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vector CalculusDocument144 paginiVector CalculusramiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Mathematics For Computational Design 4th Edition - Page 17 To 26Document10 paginiEssential Mathematics For Computational Design 4th Edition - Page 17 To 26dramachinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vision Dummy PDFDocument51 paginiVision Dummy PDFDango Daikazoku100% (1)
- Excel Solve EigenvalueDocument2 paginiExcel Solve EigenvalueMadana RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Array Functions (2D Array) : Each Questions CarryDocument5 paginiArray Functions (2D Array) : Each Questions CarryAbdullah JuttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vector Integration Vector Line IntegralsDocument6 paginiVector Integration Vector Line IntegralsDdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solving Differential Riccati Equations A NonlinearDocument20 paginiSolving Differential Riccati Equations A NonlinearCarlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- AL3451 - Unit 1Document12 paginiAL3451 - Unit 1jeffrinsb7Încă nu există evaluări
- Matrices Notes by TrockersDocument48 paginiMatrices Notes by TrockersMichael MyamboÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Journal of Engineering Science: Wenbin Yu, Dewey H. Hodges, Jimmy C. HoDocument25 paginiInternational Journal of Engineering Science: Wenbin Yu, Dewey H. Hodges, Jimmy C. HosquijanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mma PDFDocument377 paginiMma PDFtrue_hindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 110: Linear Algebra Practice Final SolutionsDocument7 paginiMath 110: Linear Algebra Practice Final SolutionsCody SageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Algebra With Applications 2nd Edition Holt Solutions ManualDocument61 paginiLinear Algebra With Applications 2nd Edition Holt Solutions Manualmouldywolves086ez100% (27)
- Linear Algebra - DPP 05Document2 paginiLinear Algebra - DPP 05Gaurav SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joseph Muscat - Elementary Linear Algebra (Expository Notes) (2009)Document40 paginiJoseph Muscat - Elementary Linear Algebra (Expository Notes) (2009)tiberius innocentiusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formula List Matrices and DeterminantDocument11 paginiFormula List Matrices and DeterminantSujal KapoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1a MaterialDocument22 pagini1a MaterialKshavzhxnÎncă nu există evaluări
- TO Origin D1 D2 D3 D4: DemandDocument8 paginiTO Origin D1 D2 D3 D4: DemandSab NamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color: Representation of Color in MATLABDocument4 paginiColor: Representation of Color in MATLABsharmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Algebra - Challenging Problems For Students - Fuzhen ZhangDocument266 paginiLinear Algebra - Challenging Problems For Students - Fuzhen Zhanggeeorgi23100% (9)
- List of Star Pattern and Arrays Programming ExercisesDocument26 paginiList of Star Pattern and Arrays Programming ExercisesHarsh KashyapÎncă nu există evaluări