Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cirrhosis Patient Education 2014
Încărcat de
Robert G. Gish, MD0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
225 vizualizări3 paginiCirrhosis is a scarring process where liver cells are destroyed and unable to function properly. It has many causes including viruses like hepatitis B and C. Patients with cirrhosis may experience warning signs such as swollen feet and abdomen, confusion, vomiting blood, and abnormal liver function tests. Those with cirrhosis have an increased risk of liver cancer and should undergo screening with ultrasound and blood tests. Treatment focuses on vaccinations, a low sodium diet, avoiding medications like NSAIDs, and potentially liver transplantation.
Descriere originală:
Cirrhosis Patient Education 2014
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentCirrhosis is a scarring process where liver cells are destroyed and unable to function properly. It has many causes including viruses like hepatitis B and C. Patients with cirrhosis may experience warning signs such as swollen feet and abdomen, confusion, vomiting blood, and abnormal liver function tests. Those with cirrhosis have an increased risk of liver cancer and should undergo screening with ultrasound and blood tests. Treatment focuses on vaccinations, a low sodium diet, avoiding medications like NSAIDs, and potentially liver transplantation.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
225 vizualizări3 paginiCirrhosis Patient Education 2014
Încărcat de
Robert G. Gish, MDCirrhosis is a scarring process where liver cells are destroyed and unable to function properly. It has many causes including viruses like hepatitis B and C. Patients with cirrhosis may experience warning signs such as swollen feet and abdomen, confusion, vomiting blood, and abnormal liver function tests. Those with cirrhosis have an increased risk of liver cancer and should undergo screening with ultrasound and blood tests. Treatment focuses on vaccinations, a low sodium diet, avoiding medications like NSAIDs, and potentially liver transplantation.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
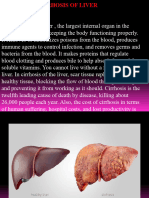
Cirrhosis of the Liver
Know the Warning Signs of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is defined as a scarring process where liver cells are replaced or destroyed
and are unable to function. Cirrhosis can be caused by many different factors.
Alcohol is only one of many causes of cirrhosis. The most common causes of
cirrhosis in the world are viruses such as hepatitis B and C.
When the liver does not function properly, patients may experience one or
more of the following warning signs:
Swollen feet
Swollen abdomen (ascites)
Confusion (encephalopathy)
Progressive memory loss
Difficulty sleeping during the night and increased sleeping during the day
Vomiting blood
Passing blood, purple or black bowel movements
Yellow eyes and/or skin
Abnormal liver function:
thin blood (an increased or prolonged prothrombin timealso called a
P.T.this test is now also defined as an INR. The INR number increases
as the liver fails)
high bilirubingreater than 2.0 mg/dL is a concern
low albuminless than 3.5 mg/dL is a concern
low cholesterolless than 100 mg/dL is a concern
low plateletsless than 150,000 is a concern and 100,000 a major concern
for cirrhosis. (Platelets are cells involved in blood clotting)
Flapping of the extended hands (asterixis) for liver encephalopathy
Muscle loss
What Can You Expect for your care?
You will consult with a specialized doctor (Hepatologist) or a
Gastroenterologist who has an interest in liver disease.
You will discuss liver transplantation with a Hepatologist; if
needed. Transplantation is one of many options.
Learn treatment options for cirrhosis.
Learn the probable or definite cause of your cirrhosis.
Participate in a review of the possible complications from cirrhosis.
Information Sheet:: Cirrhosis of the Liver
Screening and Surveillance Tests Evaluating for Increased Risk of
Liver Cancer
If you have cirrhosis, there is a markedly increased risk of liver cancer. It is important
to discuss with your doctor the need for screening tests for liver cancer. These
screening tests may include:
Ultrasound of the liver (a liver scan)
Alpha-fetoprotein blood test
Other advanced testing as indicated by your doctor (for example: liver cancer
marker)
Treatment Recommendations for Patients Diagnosed with Cirrhosis
Hepatitis A & B Vaccinations: You should be vaccinated for Hepatitis B
(HBV) (unless you have hepatitis B infection) and Hepatitis A (HAV) if you are
not immune.
Alcohol-Free Diet: Patients with cirrhosis should not drink any alcohol. Your
diet should be alcohol free.
Diet Recommendations: Your diet should be low in sodium (salt), high
carbohydrate. Do not eat raw shellfish. Five small meals per day with starchs
and protein (100 gm per day) are important, avoid red meat, avoid fat.
Avoiding Certain Medications: Patients with cirrhosis should not take
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAID) such as Ibuprofen (Advil,
Motrin) or aspirin-type drugs. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is safe if you take less
than six 325 mg tablets each day (2,000 mg per day). Because cirrhosis patients
are at increased risk of ulcer disease, you should discuss with your doctor about
taking an anti-ulcer drug.
Information Sheet:: Cirrhosis of the Liver
More Ways to Learn
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What is cirrhosis of the liver?
Answer: Cirrhosis is defined as a scarring process where liver cells are replaced or
destroyed and are unable to function.
Question: What are the warning signs that show the liver is not functioning properly?
Answer: Warning signs: swollen feet & abdomen, confusion, memory loss, difficulty
sleeping at night, increased sleeping during the day, vomiting blood, passing blood,
purple or black bowel movements, yellow eyes and/or skin, abnormal liver function,
flapping of the hands & muscle loss.
Question: What screening tests are available to diagnose cirrhosis?
Answer: An ultrasound or MR or CT of the liver
The Alpha-fetoprotein blood test is a test for risk for liver cancer not diagnosis.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cirrhosis of The Liver: Handout and Information SheetDocument3 paginiCirrhosis of The Liver: Handout and Information SheetRobert G. Gish, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver CirhosisDocument8 paginiLiver CirhosisMUHAMMAD YASINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 8-Liver Cirrhosis-DonghitDocument8 paginiActivity 8-Liver Cirrhosis-DonghitAllona Jane Beatrice DonghitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis in ChildrenDocument4 paginiCirrhosis in ChildrenFakhri DesktopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesDe la EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cirrhosis TreatmentDocument5 paginiLiver Cirrhosis TreatmentPrajith NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Guide to Gallbladder Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDe la EverandA Simple Guide to Gallbladder Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatty Liver AssignmentDocument9 paginiFatty Liver AssignmentMaryam ShahzadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primary Billiary CirrhosisDocument6 paginiPrimary Billiary CirrhosisElvantia MarilynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pangungusap Bahagi NG PangungusapDocument20 paginiPangungusap Bahagi NG PangungusapJoshua BoncodinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver CirrhosisDocument7 paginiLiver CirrhosisJohn Yves B. SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatty Liver: Recipes and Guide to Prevent, Cure and Reverse Fatty Liver Disease, Lose Weight and Promote Good HealthDe la EverandFatty Liver: Recipes and Guide to Prevent, Cure and Reverse Fatty Liver Disease, Lose Weight and Promote Good HealthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Livng With CirrhosisDocument16 paginiLivng With CirrhosisN. Hansraj100% (1)
- Cirrhosis of The Liver - Facts & TreatmentDocument6 paginiCirrhosis of The Liver - Facts & TreatmentpakdejackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatty Liver and Cirrhosis - DR GurbilasDocument7 paginiFatty Liver and Cirrhosis - DR GurbilasDr. Gurbilas P. SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- CalculationDocument16 paginiCalculationjananeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis of The LiverDocument4 paginiCirrhosis of The LiverDaphineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver CirrhosisDocument5 paginiLiver CirrhosisRLLTÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Guide to Hepatic Cancer, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDe la EverandA Simple Guide to Hepatic Cancer, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cancer Treatment in Pakistan - NewDocument3 paginiLiver Cancer Treatment in Pakistan - NewMuhammad Shahrukh KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis: On This PageDocument23 paginiCirrhosis: On This PageHasna FauziyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dealing With Fatty Liver: Healthy Lifestyle Healthy LiverDe la EverandDealing With Fatty Liver: Healthy Lifestyle Healthy LiverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Paper On Liver CirrhosisDocument5 paginiResearch Paper On Liver Cirrhosisipkpzjbkf100% (1)
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ColDocument40 paginiCol12F 24 Renu SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatic Fibrosis, (Liver Cirrhosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandHepatic Fibrosis, (Liver Cirrhosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report For Liver CancerDocument10 paginiReport For Liver CancerMary Rose VitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arcipe Iccu Case 5Document98 paginiArcipe Iccu Case 5Maria Charis Anne Indanan100% (1)
- Neethus Part A 40 TestDocument244 paginiNeethus Part A 40 TestNadeeka GamageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Diet Cookbook: 100 Simple & Delicious Kidney-Friendly Recipes To Manage Kidney Disease (CKD) And Avoid Dialysis (The Kidney Disease Cookbook)De la EverandRenal Diet Cookbook: 100 Simple & Delicious Kidney-Friendly Recipes To Manage Kidney Disease (CKD) And Avoid Dialysis (The Kidney Disease Cookbook)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Fatty Liver Cookbook: Ultimate Guide With Over 100 Recipes To Reverse Fatty Liver DiseaseDe la EverandFatty Liver Cookbook: Ultimate Guide With Over 100 Recipes To Reverse Fatty Liver DiseaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis Is A Late Stage of Scarring (Fibrosis) of The Liver Caused byDocument7 paginiCirrhosis Is A Late Stage of Scarring (Fibrosis) of The Liver Caused byAnne MaputiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Diet Cookbook: 100 Easy And Effective Low Potassium, Low Sodium Kidney-Friendly Recipes To Manage Kidney Disease (CKD) (The Kidney Disease Cookbook)De la EverandRenal Diet Cookbook: 100 Easy And Effective Low Potassium, Low Sodium Kidney-Friendly Recipes To Manage Kidney Disease (CKD) (The Kidney Disease Cookbook)Încă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis of The Liver: CausesDocument6 paginiCirrhosis of The Liver: CausespakdejackÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionDe la EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Your Liver-It Is Amazing and EssentialDocument5 paginiYour Liver-It Is Amazing and Essentialsudha_karÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cirrhosis: Nikko G. MelencionDocument38 paginiLiver Cirrhosis: Nikko G. MelencionNikko MelencionÎncă nu există evaluări
- AST Normal Results: CirrhosisDocument7 paginiAST Normal Results: CirrhosisVijay RajaindranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis of The LiverDocument12 paginiCirrhosis of The LiverherlindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatty Liver Diet Cookbook: Triumph Over FLD and Hepatic Steatosis with Scrumptious Low-Fat Recipes, Harness Your Metabolism, and Embrace a Swell-Free Life Naturally [II EDITION]De la EverandFatty Liver Diet Cookbook: Triumph Over FLD and Hepatic Steatosis with Scrumptious Low-Fat Recipes, Harness Your Metabolism, and Embrace a Swell-Free Life Naturally [II EDITION]Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (7)
- .Uk Home The Liver Liver Disease Tests Explained Liver Function TestsDocument3 pagini.Uk Home The Liver Liver Disease Tests Explained Liver Function TestsmmtariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver CirrhosisDocument4 paginiLiver CirrhosisromyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis of Liver, Liver Cancer, HepatitisDocument72 paginiCirrhosis of Liver, Liver Cancer, HepatitisBabita DhruwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver CirrhosisDocument69 paginiLiver CirrhosisAhmed Alboun75% (4)
- No Gallbladder Diet Cookbook: Discover Flavorful and Nourishing Recipes to Revitalize Your Metabolism After Gallbladder Surgery [III EDITION]De la EverandNo Gallbladder Diet Cookbook: Discover Flavorful and Nourishing Recipes to Revitalize Your Metabolism After Gallbladder Surgery [III EDITION]Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (24)
- Jaundice: (Yellowing of Skin)Document4 paginiJaundice: (Yellowing of Skin)mrmr92Încă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosisoftheliver 2016Document4 paginiCirrhosisoftheliver 2016Nazimr RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chirosis HepaticDocument8 paginiChirosis HepaticCikalHrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Easy Renal Diet Cookbook: Ultimate Guide To Manage Kidney DiseaseDe la EverandEasy Renal Diet Cookbook: Ultimate Guide To Manage Kidney DiseaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH Le BotomyDocument15 paginiPH Le BotomyPatty MenéndezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exocrine Pancreatic and Biliary Disorders and ManagementDocument77 paginiExocrine Pancreatic and Biliary Disorders and ManagementAnthon Kyle TropezadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Diet Best Cookbook: Eat right and Become HealthierDe la EverandRenal Diet Best Cookbook: Eat right and Become HealthierEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Renal Diet Best Cookbook: Eat Right And Become HealthierDe la EverandRenal Diet Best Cookbook: Eat Right And Become HealthierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sirrhosis HatiDocument6 paginiSirrhosis HatikimokberusungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Kidney FailureDocument4 paginiAcute Kidney FailureBonaventure NzeyimanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cancer:: It'S Causes, Preventions, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument25 paginiLiver Cancer:: It'S Causes, Preventions, Symptoms and TreatmentchetankumarbhumireddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fast Facts for Patients and Supporters: Cholangiocarcinoma: A cancer of the bile duct and liver Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeDe la EverandFast Facts for Patients and Supporters: Cholangiocarcinoma: A cancer of the bile duct and liver Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fulminant Hepatic FailureDocument10 paginiFulminant Hepatic FailureAira Anne Tonee VillaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Letter To MHPA Jeff MyersDocument4 paginiLetter To MHPA Jeff MyersRobert G. Gish, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatitis C Rallies in San FranciscoDocument1 paginăHepatitis C Rallies in San FranciscoRobert G. Gish, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- CME Conference: Hepatitis C From A To ZDocument2 paginiCME Conference: Hepatitis C From A To ZRobert G. Gish, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conference: Focus On The Hepatitis B VirusDocument52 paginiConference: Focus On The Hepatitis B VirusRobert G. Gish, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Press ReleaseDocument3 paginiPress ReleaseRobert G. Gish, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Center For Liver Disease and Transplantation: Message From The DirectorDocument5 paginiCenter For Liver Disease and Transplantation: Message From The DirectorRobert G. Gish, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimates On HCV Disease Burden Worldwide - Filling The GapsDocument5 paginiEstimates On HCV Disease Burden Worldwide - Filling The GapsRobert G. Gish, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physicians Update June-July 2015Document2 paginiPhysicians Update June-July 2015Robert G. Gish, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hosa Happenings 2021 1Document8 paginiHosa Happenings 2021 1api-524471148Încă nu există evaluări
- Refers To Leisure Pursuits Engaged in The Outdoors, Often in Natural or Semi-Natural Settings Out of TownDocument21 paginiRefers To Leisure Pursuits Engaged in The Outdoors, Often in Natural or Semi-Natural Settings Out of TownSam CajesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control of Pandemic Infectious Disease Procedure - Landkap - Gitt 00Document25 paginiControl of Pandemic Infectious Disease Procedure - Landkap - Gitt 00ahar85Încă nu există evaluări
- Scenihr o 046Document116 paginiScenihr o 046Ana NicoletaÎncă nu există evaluări
- You Get To Know "Why" in Everything You Do, You'll Know More Than You Knew. 2Document16 paginiYou Get To Know "Why" in Everything You Do, You'll Know More Than You Knew. 2ChaoticMikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Coaching NP4 Set 1Document13 paginiFinal Coaching NP4 Set 1STEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essie Hoiball and T.C. Fry - I Live On Fruit (1981)Document40 paginiEssie Hoiball and T.C. Fry - I Live On Fruit (1981)Charles100% (11)
- Seatone InfoDocument7 paginiSeatone InfoJugal ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effectiveness of Psychoeducation For Relapse, Symptoms, Knowledge, Adherence and Functioning in Psychotic Disorders: A Meta-AnalysisDocument14 paginiEffectiveness of Psychoeducation For Relapse, Symptoms, Knowledge, Adherence and Functioning in Psychotic Disorders: A Meta-AnalysisPatty IzquierdoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutical Market Europe - June 2020Document50 paginiPharmaceutical Market Europe - June 2020Areg GhazaryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHD Research ProposalDocument8 paginiPHD Research ProposalMalik Ijaz Khan100% (1)
- Antibiotic Resistance Lesson Plan Final ProjectDocument10 paginiAntibiotic Resistance Lesson Plan Final Projectapi-436796283Încă nu există evaluări
- Colic in Horse: A Presentation OnDocument32 paginiColic in Horse: A Presentation OnMuhammad Saif KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burning Mouth Syndrome 1Document16 paginiBurning Mouth Syndrome 1Mihika BalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non - Food Meher Final Report (2023)Document87 paginiNon - Food Meher Final Report (2023)atakltigebertsadikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subcutaneous Mycoses: Presenter: DR Pranay Reddy Moderator: DR Tonita MNDocument81 paginiSubcutaneous Mycoses: Presenter: DR Pranay Reddy Moderator: DR Tonita MNSandipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tof Care PlanDocument4 paginiTof Care Plankayal67% (12)
- Introduction of The Topic: Nano-BiotechnologyDocument7 paginiIntroduction of The Topic: Nano-BiotechnologyAbhishek YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuliah PF Jantung Prof IIDocument32 paginiKuliah PF Jantung Prof IIannis100% (1)
- Hallie Berger Resume 11-2Document2 paginiHallie Berger Resume 11-2api-281008760Încă nu există evaluări
- AyyDocument187 paginiAyyZoé WolfesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument64 paginiGrowth and DevelopmentRahul Dhaker100% (1)
- Ozone Unsung Hero by Navy Captain - Ajit VadakayilDocument153 paginiOzone Unsung Hero by Navy Captain - Ajit Vadakayilsudhir shahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wvgrd5c40vivpeavmmpsf3cvDocument4 paginiWvgrd5c40vivpeavmmpsf3cvVishav Jindal100% (1)
- FNCP-Presence of Breeding or Resting Sites of Vectors of DiseasesDocument5 paginiFNCP-Presence of Breeding or Resting Sites of Vectors of DiseasesAlessa Marie BadonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presc Audit ReportDocument85 paginiPresc Audit ReportAnuj KaushalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Splice PDFDocument5 paginiSplice PDFpedroÎncă nu există evaluări
- At Merienda - Individual ActivityDocument6 paginiAt Merienda - Individual ActivityMoreno, John Gil F.Încă nu există evaluări
- US - Inggris 2017Document5 paginiUS - Inggris 2017SmabaitulhikmahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ghidul de Prevenire A Miopiei - de Dr. Kaisu VIIKARI - Cu Coperta in RomanaDocument104 paginiGhidul de Prevenire A Miopiei - de Dr. Kaisu VIIKARI - Cu Coperta in Romanadlucian82Încă nu există evaluări








































![Fatty Liver Diet Cookbook: Triumph Over FLD and Hepatic Steatosis with Scrumptious Low-Fat Recipes, Harness Your Metabolism, and Embrace a Swell-Free Life Naturally [II EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/598276019/149x198/1b7a1779c0/1711328726?v=1)




![No Gallbladder Diet Cookbook: Discover Flavorful and Nourishing Recipes to Revitalize Your Metabolism After Gallbladder Surgery [III EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/591540228/149x198/6ba6cc3b38/1713999276?v=1)