Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Design of Concrete Structures
Încărcat de
Armaan GuptaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Design of Concrete Structures
Încărcat de
Armaan GuptaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, Pilani
Pilani Campus
Instruction Division
_
Please Do Not Print Unless Necessary
SECOND SEMESTER 2013-2014
Course Handout Part II
Date: 16- 1-2014
In addition to part -I (General Handout for all courses appended to the time table) this portion gives further specific details
regarding the course.
Course No. : CE C383
Course Title : Design of Concrete Structures
Instructor-in-Charge : SHAMSHER BAHADUR SINGH
Instructors :
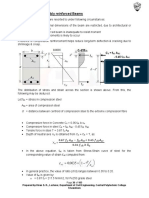
1. Scope and Objective of the Course:
This course deals with analysis and design of Reinforced Concrete (RC) Structures using the Limit State design
methods (Limit State of Strengths and Serviceability). Introduction to various design philosophies used in practice
for design of RC structures will be provided and discussed. Specific structures to be discussed and designed are
beams, slabs, columns, and staircases. In addition, basis for design of isolated footings will be discussed with
example. At the end of this course, the students will be able to design the standard practical reinforced concrete
structures.
2. Text Book (TB):
J. N. Bandhopadhyay, Design of Concrete Structures, PHI Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi, 2008.
P. C. Varghese, Limit State Design of Reinforced Concrete, 2
nd
Edition, PHI Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2011
3. Reference Book (RB):
S U Pillai & Devdas Menon, Reinforced Concrete Design, 3
rd
Edition, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi
Jain, A.K., Reinforced Concrete : Limit State Design, Nem Chand & Bros., Roorkee, 6th ed., 2002
IS 456:2000 Code of practice for Plain and Reinforced concrete, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi
Special Publication (SP)-16, Design aids for reinforced concrete to IS 456:1978, Bureau of Indian Standards, New
Delhi.
Subramanian, N., Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures, Oxford University Press, New Delhi,2013.
Krishna Raju, N., Pranesh, R. N., Reinforced Concrete Design, New Age International Publishers, New Delhi, 2012.
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, Pilani
Pilani Campus
Instruction Division
_
Please Do Not Print Unless Necessary
4. Course Plan:
S.
No.
Topic Learning Objective
Lec.
No.
Ref. to TB
1.
Methods of Design of
Concrete Structures
Introduction, Load factor Method, Limit State Method,
Working Stress Method, Introduction to IS 456-2000 and
SP-16, IS 10262.
02
Ch. 1of TB1 and
TB2
2.
Partial Safety Factors
in Limit State Design
Principles of Limit State Design, Characteristic strengths
and Load, Partial safety factors for loads, and material
strengths, stress-strain characteristics of steel and
concrete
02
Chs. 2-3 of TB1
and Ch. 2 of TB2
3.
Theory of Singly
Reinforced Members
in Bending and Design
Examples
Cover to Reinforcements, Ultimate strengths of RC
Beams, Balanced, Under-Reinforced, and Over-
reinforced sections, Nominal Moment Capacity of
section, Analysis and Design Examples.
04
Ch.4 of TB1
Chs. 3-5 of TB2
4.
Analysis &Design of
Doubly Reinforced
Rectangular Beams:
Rectangular Sections
Assumptions and basic principles, analysis and design of
doubly reinforced concrete beams of rectangular sections,
Strain Compatibility Method, Use of Formulae Steel Beam
Theory, Use of Design Aids SP 16, Specifications
Regarding Spacing of Stirrups in Doubly Reinforced
Beam
03
Ch.5 of TB1 and
Ch. 6 of TB2
5.
Design for Shear,
Limit State of Collapse
in Shear
Type of Shear failures, Design Shear Strength in Concrete
Beams, Design of Stirrups, Rules for Minimum Shear
Reinforcement, Shear in Members subjected to
Compression and Bending.
04
Ch. 7 of TB1 and
TB2
6.
Design of Flanged
Beams
Basis of Design and Analysis of Flanged Beams, T-beam
formulae for Analysis and Design, Limiting Capacity of T-
beams by Use of Design Aids, Tables in SP-24 for Design
of Tea-Beams, Design of Flanged Beams in Shear,
Detailing of Reinforcements
03
Ch. 6 of TB1 and
Ch. 8 of TB2
7.
Design of Bending
Members for Limit
State of Serviceability
Design for Limit State of Deflection, Empirical Method
for Deflection Control in Beams, Empirical Method of
Control of Cracking in Beams, Bar Spacing Rules for
Beams and Slabs, Minimum Percentage of Steel in Beams
and Slabs
03
Ch. 9 of TB1
and TB2
8.
Bond, Anchorage,
Development Lengths
and splicing
Development Lengths of Tension and Compression Bars,
Equivalent Development Length of Hooks and Bends,
splicing of Bars and Curtailment of Bars and their
anchorage
02
Ch. 8 of TB1 and
Ch. 10 of TB2
9. Design of Slabs
Considerations for Design of Slabs, Design for Shear in
one-way slab, Use of Design Aids SP16, Design of Two-
04
Ch. 10 of TB1
and Chs. 11-12 of
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, Pilani
Pilani Campus
Instruction Division
_
Please Do Not Print Unless Necessary
way simply supported slabs, Reinforcement details TB2
10.
Design of
Compression Members
Classification of columns based on slenderness ratio,
reinforcement & loading, Design of rectangular and
circular columns subjected to Axial load, (Axial load +
uni-axial bending) and (Axial load + Bi-axial bending)
05
Ch. 12 of TB1
and Chs. 13-16
of TB2
11. Design for Torsion
Principles of Design for Combined Bending, Shear, and
Torsion by IS 456, Detailing of Torsion Steel in flanged
beams.
02
Ch. 8 of TB1 Ch.
18 of TB2
12. Design of Staircases
Principles of Design, Design of Staircases spanning
transversely and longitudinally. 03
Ch. 11 of TB1
and Ch. 20 of
TB2
13. Design of Footings
Design loads for foundation design, Basis of Design of
Footings, Design of Independent Footing. 03
Ch. 13 of TB1
and Ch. 22 of
TB2
5. Evaluation Scheme:
Component Duration Weightage Date & Time Venue Remarks
Mid-Term Examination 90 mts 30 6/3 4:00- 5:30 PM Open Book
Tutorials/ quizzes/surprise
tests/Computer
Assignment
20
Lab Record and Lab quiz 10
Compre. Examination 3 hours 40 12/5 AN Open Book
6. Chamber Consultation Hour: To be announced in the class by the Instructor.
7. Notice: Notice if any concerning this course will be displayed on the Notice Board of Civil Engineering Deptt.
Instructor-in-Charge (CE C383)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- User Manual SteadyControlDocument57 paginiUser Manual SteadyControlrobiny100% (2)
- Toyota 5L Terminales de EcmDocument9 paginiToyota 5L Terminales de EcmAlfred Nayb Cañoli Ildefonso0% (1)
- Essentials of Civil EnggDocument6 paginiEssentials of Civil EnggAkhilesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced Cement Concrete QuestionsDocument6 paginiReinforced Cement Concrete QuestionsArmaan Gupta89% (9)
- STAAD - Pro Tips and TricksDocument72 paginiSTAAD - Pro Tips and TricksMuam Sayli100% (7)
- Japan Servo CatalogDocument39 paginiJapan Servo CatalogKofaKing100% (1)
- Structural Design - IDocument12 paginiStructural Design - Ikiran sreekumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Handout DoublyReinforcedBeam TheoryDocument2 pagini10 Handout DoublyReinforcedBeam Theorykiran sreekumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Design of Singly Reinforced BeamsDocument16 pagini7 Design of Singly Reinforced Beamskiran sreekumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Properties of Ingredients of ConcreteDocument12 pagini2 Properties of Ingredients of Concretekiran sreekumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Limit State DesignDocument8 pagini5 Limit State Designkiran sreekumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 17 Design For BondDocument15 pagini17 Design For Bondkiran sreekumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Design of Concrete StructuresDocument24 paginiAdvanced Design of Concrete StructuresVarun. hrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15CV51 NOTES Vtu BelDocument77 pagini15CV51 NOTES Vtu BelRavishankar HobannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts of ConcreteDocument19 paginiBasic Concepts of ConcreteSathish SelvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC-I Chapter 2 PDFDocument36 paginiRC-I Chapter 2 PDFWendimu TolessaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two-Way Slab-1Document16 paginiTwo-Way Slab-1sitaramgvsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 Structure Analysis-1Document18 paginiLecture 2 Structure Analysis-1jagmal100% (1)
- Back To Top: Rahul - LeslieDocument12 paginiBack To Top: Rahul - LeslieMukhlish AkhatarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.Engineering-The Effect of Seawater On Shrinkage Properties of Concrete-Amusan Grace ModupeolaDocument12 pagini1.Engineering-The Effect of Seawater On Shrinkage Properties of Concrete-Amusan Grace ModupeolaImpact JournalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loading Action On BuildingsDocument42 paginiLoading Action On BuildingsChi LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCC Unit-1 PDFDocument40 paginiRCC Unit-1 PDFSandeep GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCC SlabsDocument112 paginiRCC SlabsAl-MaroofÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Concrete Structures - I Question PaperDocument3 paginiDesign of Concrete Structures - I Question PaperSourav Sil50% (2)
- Lecture 3Document42 paginiLecture 3Harold Jackson MtyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Design of Steel StructuresDocument43 paginiStructural Design of Steel Structureskiran sreekumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 Design of ColumnsDocument17 pagini19 Design of Columnskiran sreekumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- (LECT-21,22) Prestressed Concrete SlabsDocument22 pagini(LECT-21,22) Prestressed Concrete SlabsSushil MundelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Structural Design - Slab DesignDocument22 paginiAdvanced Structural Design - Slab DesignChamil MahagamageÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1893-Part 1-2016Document44 pagini1893-Part 1-2016Amey GudigarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Design of Buildings Using ETABS (BASIC)Document3 paginiStructural Design of Buildings Using ETABS (BASIC)Mohammed RafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Steel StructuresDocument4 paginiDesign of Steel StructuresprkshdvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prota Engineering StructureDocument22 paginiProta Engineering StructurejewonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 Axially Loaded MembersDocument59 paginiLecture 3 Axially Loaded MembersCyrus HongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Text 01Document325 paginiFull Text 01YashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision of IS 456 & IS 1343 - SummaryDocument3 paginiRevision of IS 456 & IS 1343 - Summaryshiv paa0% (1)
- Effect of Seawater For Mixing and Curing On Structural Concrete PDFDocument10 paginiEffect of Seawater For Mixing and Curing On Structural Concrete PDFtobiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Analysis of Reinforcement &prestressed Concrete BeamsDocument3 paginiComparative Analysis of Reinforcement &prestressed Concrete BeamsTFCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Prestressed ConcreteDocument11 paginiDesign of Prestressed ConcreteMohammed SameerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 (Indeterminte Structures)Document7 paginiChapter 2 (Indeterminte Structures)Hilary WatsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECS318 - Week 2Document26 paginiECS318 - Week 2iskandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 6 Serviceability CriteriaDocument9 paginiCHAPTER 6 Serviceability CriteriaLittleRedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering Project TitlesDocument3 paginiCivil Engineering Project TitlesShamsUlislamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Design - I: 11. Design of Two-Way SlabsDocument10 paginiStructural Design - I: 11. Design of Two-Way Slabskiran sreekumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pavement DesignDocument92 paginiPavement Designpankaj_mbm100% (1)
- Ishwor ChaudharyDocument29 paginiIshwor Chaudharybinud das100% (2)
- Credit Seminar Report - Pushover Analysis FinalDocument29 paginiCredit Seminar Report - Pushover Analysis FinalPalak Shukla100% (1)
- ECG353 Week 10 - 11 Chapter 4Document44 paginiECG353 Week 10 - 11 Chapter 4Muhd MuqhreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Design Steps: Er.T.Rangarajan, B.E, M.SC (Struct - Engg), Consulting Structural EngineerDocument16 paginiSeismic Design Steps: Er.T.Rangarajan, B.E, M.SC (Struct - Engg), Consulting Structural EngineercivilsadiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of A Two Storey Classroom Block Using Design Codes Bs 8110Document58 paginiDesign of A Two Storey Classroom Block Using Design Codes Bs 8110Cholwe Essau Mbilima100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument26 paginiChapter 1 - IntroductionEvo LanzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5.0 - Beam Design (Theory)Document14 paginiChapter 5.0 - Beam Design (Theory)Tikar MengkuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparative Study of Lateral Load Resisting Systems in Tall Structures-Ijaerdv05i0482912Document10 paginiA Comparative Study of Lateral Load Resisting Systems in Tall Structures-Ijaerdv05i0482912Pradeep ChandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- British Problem 5 PDFDocument5 paginiBritish Problem 5 PDFelixnzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 8 CE 806 Behavior of Short ColumnsDocument66 paginiLec 8 CE 806 Behavior of Short ColumnswasimkhaliqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction For RC and Steel DesignDocument14 paginiIntroduction For RC and Steel DesignNur Syaf FiqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Slab DesignDocument18 paginiChapter 6 Slab DesignZAX100% (1)
- Design of Composite BridgeDocument10 paginiDesign of Composite BridgeHarold Jackson MtyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 156 Lecture 1 - Introduction To Steel DesignDocument47 paginiCE 156 Lecture 1 - Introduction To Steel DesignHarvey John ReynonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Steel SectionDocument24 paginiChapter 1 - Introduction To Steel SectionAhmad Ubaidillah Abdul RaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Failure of Short Columns Case Study PrepDocument17 paginiFailure of Short Columns Case Study PrepAsdar AzisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionDe la EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignDe la EverandLecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985De la EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Încă nu există evaluări
- Concrete-Filled Double-Skin Steel Tubular Columns: Behavior and DesignDe la EverandConcrete-Filled Double-Skin Steel Tubular Columns: Behavior and DesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridge Manual 3rd Edition Section 5 PDFDocument23 paginiBridge Manual 3rd Edition Section 5 PDFjpzambranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step 2: Determine The Cube Root: ExamplesDocument2 paginiStep 2: Determine The Cube Root: ExamplesArmaan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced ConcreteDocument1 paginăReinforced ConcreteArmaan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Bored Piles Is 2911-Part 1sec2Document5 paginiDesign of Bored Piles Is 2911-Part 1sec2Armaan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plate Design As Per IS 800-2007Document22 paginiBase Plate Design As Per IS 800-2007Armaan Gupta100% (2)
- Design of Base Slab and Footing of Steel StructureDocument11 paginiDesign of Base Slab and Footing of Steel StructureArmaan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desgin of Steel Structures Comprehensive ExaminationDocument3 paginiDesgin of Steel Structures Comprehensive ExaminationArmaan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On Civil EngineeringDocument48 paginiReport On Civil EngineeringArmaan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desgin of Steel Structures Comprehensive ExaminationDocument3 paginiDesgin of Steel Structures Comprehensive ExaminationArmaan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shortcomings in Structural Design Is 456Document8 paginiShortcomings in Structural Design Is 456yrdgcgf5664Încă nu există evaluări
- Improving Properties of Granular Soil Using Waste MaterialsDocument67 paginiImproving Properties of Granular Soil Using Waste MaterialsArmaan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Outline For PS 2 at DCPLDocument3 paginiProject Outline For PS 2 at DCPLArmaan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Chimney Wind Load ConfigurationDocument2 paginiSteel Chimney Wind Load ConfigurationArmaan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IS 875 1987 Part-3 PDFDocument63 paginiIS 875 1987 Part-3 PDFPrabesh Kc100% (2)
- Lewmar Marine Equipment Guide Ed 14Document224 paginiLewmar Marine Equipment Guide Ed 14Renato Fonseca100% (1)
- Contoh Ringkasan Mengajar Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 2 Dan 3Document2 paginiContoh Ringkasan Mengajar Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 2 Dan 3Izla MajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blender 04Document38 paginiBlender 04Ana Maria100% (1)
- Et154 PDFDocument6 paginiEt154 PDFbytecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gpfsworkshop2010 Tutorial v17 2Document381 paginiGpfsworkshop2010 Tutorial v17 2atretauÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 11Document1 paginăCE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 11Justine Ejay MoscosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GEO ExPro V11i6Document104 paginiGEO ExPro V11i6OsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LS-VINA EHV Cable's CatalogueDocument36 paginiLS-VINA EHV Cable's CatalogueDjar Ndoeth0% (1)
- Giving Constructive Feedback Training Course OutlineDocument3 paginiGiving Constructive Feedback Training Course OutlineJeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- TM - A5ck, CC, CM - y PDFDocument102 paginiTM - A5ck, CC, CM - y PDFslipargolokÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1169a AopDocument12 pagini1169a AopBAYARD BernardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section: Engine MechanicalDocument76 paginiSection: Engine MechanicalcesarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP ABAP ResumeDocument3 paginiSAP ABAP Resumeshakti1392821Încă nu există evaluări
- Drainage CapacityDocument33 paginiDrainage Capacityfan_luc89Încă nu există evaluări
- 3G Video Alarm System User Manual - V4.1Document25 pagini3G Video Alarm System User Manual - V4.1Andres VilloutaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Hydro Thermal SchedulingDocument65 paginiChapter 3 Hydro Thermal Schedulingbik_mesiloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unitrac 80WDocument1 paginăUnitrac 80WprogramacionavanzadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Sheet - Cat Et (Nedg6015-06)Document2 paginiData Sheet - Cat Et (Nedg6015-06)victor.cipriani100% (1)
- Chapter 6 PDFDocument26 paginiChapter 6 PDFDayang Azraa AfeefaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ahu-02 CavDocument7 paginiAhu-02 CavzampacaanasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cabezas de Rotulas-RotulasDocument64 paginiCabezas de Rotulas-RotulasFRANCISCO100% (1)
- About Procurement ConsultingDocument3 paginiAbout Procurement ConsultingBiswadeep SarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis On Turing MachineDocument4 paginiSynopsis On Turing MachineVivek MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Sensors - Nautilus: For Control Circuits, Type XML-F PresentationDocument11 paginiPressure Sensors - Nautilus: For Control Circuits, Type XML-F PresentationxzxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grant Guidelines: Background InformationDocument10 paginiGrant Guidelines: Background Informationmth29Încă nu există evaluări
- 8bit Microprocessor Using VHDLDocument16 pagini8bit Microprocessor Using VHDLTanu Newar0% (2)
- FSP 851Document3 paginiFSP 851RICHIÎncă nu există evaluări