Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
How To Draft A Geodesic Dome
Încărcat de
Florin Valeriu0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
141 vizualizări9 paginiThis document provides instructions for drafting a geodesic dome using the alternate breakdown method. This involves:
1) Drafting portions of an icosahedron and its circumscribing sphere in two views.
2) Subdividing one face of the icosahedron into a grid by dividing each edge into four equal parts.
3) Projecting the points in the grid radially outward to their locations on the circumscribing sphere.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
38808132 How to Draft a Geodesic Dome
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThis document provides instructions for drafting a geodesic dome using the alternate breakdown method. This involves:
1) Drafting portions of an icosahedron and its circumscribing sphere in two views.
2) Subdividing one face of the icosahedron into a grid by dividing each edge into four equal parts.
3) Projecting the points in the grid radially outward to their locations on the circumscribing sphere.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
141 vizualizări9 paginiHow To Draft A Geodesic Dome
Încărcat de
Florin ValeriuThis document provides instructions for drafting a geodesic dome using the alternate breakdown method. This involves:
1) Drafting portions of an icosahedron and its circumscribing sphere in two views.
2) Subdividing one face of the icosahedron into a grid by dividing each edge into four equal parts.
3) Projecting the points in the grid radially outward to their locations on the circumscribing sphere.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 9
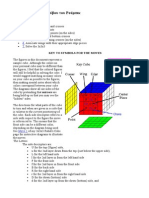
How to Draft a Geodesic Dome
Original Source Spencer Hunter, 1996
(*Permission granted to distribute freel in unaltered form!"
#! How to draft t$e needed portion of an icosa$edron in two %iews
##! How to draft t$e needed portion of t$e circumscribing sp$ere
###! Subdi%iding one face of t$e icosa$edron
#&! Pro'ecting t$e deri%ed points out to t$e circumscribing sp$ere
&! (onnecting t$e pro'ected points
&#! Deri%ing usable templates from t$e drawing
&##! (onstructing a $emisp$erical model
)in*s to public+domain images t$at accompan t$is document ma be found one le%el
bac* in m (ompre$ensi%e ,nticipator Design Science director, or at t$e -.)/
$ttp/00www!u!ari1ona!edu02s$unter0cads!$tml! )in*s to Public Domain #mages
Abstract: one met$od of drafting a geodesic dome, *nown as t$e alternate brea*down, is
to subdi%ide one face of an icosa$edron and pro'ect t$e deri%ed points out to its
circumscribing sp$ere! 3$e points on t$e sp$ere are t$en connected b lines, and
au4iliar %iews and rotations can t$en be performed to obtain t$e desired true si1e of eac$
of t$e triangular surfaces, gi%ing face angles and c$ord lengt$s! 5urt$er rotations and
au4iliar %iews can be produced as needed to get a4ial and di$edral angles, but t$ose
won6t be co%ered $ere!
#f t$e drawing is e4ecuted carefull enoug$, an actual model can be built from it, w$ic$ #
$a%e successfull done wit$ inde4 cards and glue! 7ear in mind, t$oug$, t$at t$is is an
analog tec$ni8ue and is t$erefore imprecise! 5or large+scale construction, eit$er use a
computer aided design program suc$ as ,uto(,D to deri%e precise %alues, or refer to
publis$ed tables of c$ord factors suc$ as t$ose b 9osep$ (linton in Domebook 2!
How to draft the needed portion of an icosahedron in two views.
,n icosa$edron is one of t$e fi%e basic Platonic solids consisting of twel%e
%ertices (twel%e points, surpri1ingl, are t$e most e8uidistant points one can cram
onto t$e surface of a sp$ere" and twent e8uilateral triangular faces! #t $elps to
*now t$at surrounding eac$ %erte4 are fi%e e8uilateral triangles!
,! 3$e top or plan %iew of t$e topmost fi%e triangles of an icosa$edron wit$
its ape4 facing straig$t up, t$en, would be a perfect pentagon! 3$e sides of
t$e pentagon would represent t$e true lengt$ of eac$ edge of t$e
icosa$edron, and t$e edges leading up to t$e ape4 would appear as spo*es
in t$is pentagon to its center!
So, t$e first step in drafting t$e geodesic dome is to construct t$is
pentagon wit$ its spo*es!
1! -sing a compass, draw a circle!
:! Draw a $ori1ontal line t$roug$ t$e center of t$is circle!
;! 7isect t$e distance from t$e left intersection of t$e circle and t$e
center! )abel t$is point m!
<! (onstruct a perpendicular bisecting line to t$e $ori1ontal line
t$roug$ t$e center of t$e circle (not point m"! )abel t$e intersection
of t$e new line wit$ t$e top of t$e circle point 3!
=! >it$ t$e compass point on m, set t$e span to t$e lengt$ from m to
3 and swing an arc down to t$e $ori1ontal line! )abel t$e
intersection point p!
6! >it$ t$e compass point on 3, set t$e span to t$e lengt$ from 3 to
p! 3$is is t$e lengt$ of one side of t$e pentagon! -se t$e compass
to mar* off t$is lengt$ about t$e circumference of t$e circle!
(onnect t$ese new points wit$ straig$t lines to form a pentagon!
?! Draw straig$t lines from eac$ of t$e %ertices of t$e pentagon to t$e
center to form t$e spo*es!
3$e top point of t$is pentagon is 3@ label t$e center ,,O (for A,pe4A of t$e
icosa$edron, and AOriginA or center of its circumscribing sp$ere t$at lies
directl beneat$ t$e ape4 in t$e plan %iew"@ and t$e two points t$at form
t$e base line at t$e bottom of t$e pentagon, from left to rig$t, 7 and (
respecti%el!
7! Be4t, draw in a folding line to t$e rig$t of t$e pentagon parallel to line
3,! 3$is is w$ere t$e side ele%ation %iew will be constructed! Draw
pro'ection lines to t$e rig$t from points 3@ ,,O@ and line 7( perpendicular
to t$e folding line!
(! ,long t$e pro'ection line from ,,O in t$e side ele%ation %iew, arbitraril
select point , t$at is t$e ape4 of t$e icosa$edron! Set our compass span
to t$e lengt$ of one of t$e sides of t$e pentagon in t$e plan %iew, t$en wit$
t$e compass point on , in t$e side ele%ation, draw an arc t$at intersects
t$e pro'ection line from 3 awa from t$e folding line! 3$is intersection is
point 3 in t$e side ele%ation! Draw in line 3, t$at is s$own in true lengt$
in t$e side ele%ation %iew!
D! #n t$e side ele%ation %iew, draw a line perpendicular to t$e pro'ection line
at point 3 straig$t down until it intersects t$e pro'ection line from 7 and
(! )abel t$is point (, 7 (point 7 is $iding be$ind point ( in t$is %iew" t$at
represents t$e line 7( seen straig$t on as a point in t$e side ele%ation!
,gain in t$e side ele%ation, draw a line from , to (, 7 t$at is t$e true
lengt$ of t$e altitude of e8uilateral triangle ,7( and also represents
triangle ,7( seen edge+on as a line in t$e side ele%ation %iew! 3$is is all
of t$e icosa$edron we need to draw in order to draft a geodesic dome!
How to draft the needed portion of the circumscribing sphere.
C! #n t$e side ele%ation %iew, construct a perpendicular bisecting line to line
,3! >$ere t$is line intersects t$e pro'ection line from point ,, O in t$e
plan %iew is point O in t$e side ele%ation!
5! >it$ t$e compass point on point O in t$e side ele%ation, set t$e span to t$e
lengt$ from O to ,, t$e ape4 of t$e icosa$edron, w$ic$ is t$e same lengt$
as O to 3! Swing an arc from , down past point (, 7! 3$is is all of t$e
circumscribing sp$ere we need to draw in order to draft a geodesic dome!
Subdividing one face of the icosahedron.
G! Bow it6s time to arbitraril decide on t$e degree of brea*down, or
fre8uenc, of eac$ e8uilateral face of t$e icosa$edron, w$ic$ will be
pro'ected out to t$e surface of its circumscribing sp$ere to form a dome! #f
ou decide on a fre8uenc of one, we6re doneD Eou $a%e a geodesic dome
consisting of fi%e e8uilateral triangles (awn"! , fre8uenc of two means
to find t$e midpoints of t$e edges of eac$ face and connect t$em to
subdi%ide t$e face into four smaller e8uilateral triangles! , fre8uenc of
A%A means to di%ide eac$ edge of all t$e faces into A%A parts and connect
all t$e resultant points in a triangular grid t$at subdi%ides eac$ face into
A%A+s8uared number of smaller e8uilateral triangles!
H! 5or t$is document, we will set A%A e8ual to four, since t$at fre8uenc ma
be t$e smallest brea*down we can reliabl get awa wit$ using t$is
met$od of construction@ because it produces a %er aest$eticall pleasing
dome@ and per$aps because it6s also t$e fre8uenc 7uc*minster 5uller
c$ose for $is first large+scale commercial dome commissioned b t$e 5ord
Fotor (ompan! 5our is an e%en+fre8uenc brea*down, and all e%en+
fre8uenc brea*downs using icosa$edra allow us to construct
$emisp$erical domes wit$out t$e need to truncate an of t$e surfaces!
#n t$e plan %iew, subdi%ide eac$ edge of triangle ,7( into four e8ual
parts! (onnect all t$e resultant points wit$ straig$t lines to form a
triangular grid t$at s$ould di%ide triangle ,7( into si4teen smaller
triangles!
#! )abel all t$e new points, including t$ose formed b line intersections in
t$e triangular grid! Starting in t$e plan %iew from point ,, mo%e down one
le%el on t$e grid in triangle ,7( and label t$e first two new points a1 and
a:, left to rig$t, respecti%el! Fo%e down to t$e ne4t le%el and label t$e
ne4t t$ree new points b1, b:, and b;, left to rig$t, respecti%el! Fo%e
down to t$e ne4t le%el and label t$e ne4t four new points c1, c:, c;, and
c<, left to rig$t, respecti%el! 5inall, mo%e to t$e bottom le%el of triangle
,7( t$at is line 7(, and label all fi%e points d1, d:, d;, d<, and d=, left to
rig$t, respecti%el! Bote t$at d1 is an alternate label for point 7, and d= is
an alternate label for point (! d:, d;, and d< are t$e new points created
along wit$ t$e triangular grid!
9! Pro'ect all t$e new points into t$e side ele%ation %iew!
a1 and a: pro'ect onto one point along line ,7 in t$e side ele%ation, and
t$at point is labeled a:, a1 (since a1 lies be$ind a: in t$is %iew"! Similarl,
b1, b:, and b; pro'ect onto one point along line ,7 in t$e side ele%ation
and labeled, of course, as b;, b:, b1! c1, c:, c;, and c< pro'ect onto one
point along line ,7 t$at6s labeled c<, c;, c:, c1, and t$e points d1, d:, d;,
d<,and d= pro'ect onto one point at t$e end of line ,7 labeled d=, d<, d;,
d:, d1 (t$at is an alternate label for point (, 7"!
#f ou $ad c$osen a $ig$er fre8uenc, ou would need to label and pro'ect
more points@ $ad a lower fre8uenc been c$osen, fewer points would be
labeled and pro'ected!
Projecting the derived points out to the circumscribing sphere.
Pro'ecting in t$is sense means radiall out from t$e center point O of t$e
circumscribing sp$ere, not t$e usual ort$ograp$ic pro'ection between t$e plan and
side ele%ation %iews wit$ respect to t$e folding line!
G! ! Bote t$at t$e pro'ection lines from point O in t$e plan %iew to points b:
and d; are parallel to t$e folding line! 3$erefore, t$ese lines will appear as
true lengt$ and, more importantl, as true slope in t$e side ele%ation! >e
can t$en draw pro'ection lines out from point O to points b: and d;,
respecti%el, in t$e side ele%ation %iew and e4tend t$em to find out w$ere
t$e intersect t$e circumscribing sp$ere! )abel t$ese new points b:6 and
d;6, respecti%el, t$at trul lie on t$e circumscribing sp$ere! Pro'ect
(ort$ograp$icall" b:6 and d;6 bac* into t$e plan %iew, w$ere t$e lie
along t$e radial pro'ection line from O to b: and d; in t$e plan %iew!
)! ! 3$e radial pro'ection lines from O to most points in t$e triangular grid of
triangle ,7( in t$e plan %iew, $owe%er, are not parallel to t$e folding
line, so we cannot reliabl e4tend t$em to t$e circumscribing sp$ere
s$own in t$e side ele%ation to obtain w$ere t$e would pro'ect!
3$e solution to t$is problem is to rotate an gi%en radial pro'ection line in
t$e plan %iew so t$at it HisH parallel to t$e folding line, determine w$ere it
intersects t$e circumscribing sp$ere in t$e side ele%ation, t$en rotate it
bac* to its original position wit$ t$e deri%ed pro'ected point s$own!
)et6s use point c: as an e4ample! #n t$e plan %iew, e4tend a radial
pro'ection line from O to and slig$tl beond c:! Set t$e compass point on
O and ad'ust t$e span to t$e lengt$ from O to c:! Swing an arc from c:
o%er to t$e e4tension of line 3, and label t$at intersection rc: so t$at line
Orc: is now parallel to t$e folding line! Ort$ograp$icall pro'ect rc: into
t$e side ele%ation! (ircular rotations in t$e plan %iew translate into linear
rotations in t$e side ele%ation (a two+dimensional circle seen from t$e side
is simpl a %ertical line"! 3o find rc: in t$e side ele%ation, draw a line
down from c: in t$e side ele%ation until it intersects wit$ t$e pro'ection
line from rc: in t$e plan %iew! 3$is intersection represents point rc: in t$e
side ele%ation! Be4t, e4tend a radial pro'ection line from O out to rc: in
t$e side ele%ation and e4tend t$e line until it intersects t$e circumscribing
sp$ere! )abel t$is point rc:6 and ort$ograp$icall pro'ect it bac* to t$e
plan %iew w$ere it intersects t$e e4tension of line 3, t$at represents rc:6
in t$e plan %iew! >it$ t$e compass point on O in t$e plan %iew, reset t$e
span to t$e lengt$ of line Orc:6 and swing an arc bac* to t$e original radial
pro'ection line Oc:! 3$e intersection between t$at arc and t$e e4tension of
line Oc: is c:6, t$e radial pro'ection of c: out to t$e circumscribing sp$ere!
#n t$e side ele%ation, rotate rc:6 bac* to t$e original radial pro'ection line
t$at e4tends from O to c: and beond b drawing a line up from rc:6 until
it intersects t$e e4tension of line Oc:, t$at is c:6 in t$e side ele%ation! Eou
can double+c$ec* t$e accurac of our drafting b seeing if c:6 in t$e side
ele%ation does indeed line up c:6 in t$e plan %iew!
,ll t$e ot$er radiall pro'ected points a16, a:6, b16, b;6, c16, c;6, c<6, d:6, and
d<6 can be determined in bot$ %iews b t$is same process! d16 and d=6 are
t$e same as d1 and d=, t$at are t$e same as 7 and (, two points of t$e
original icosa$edron t$at lie on t$e circumscribing sp$ere!
Connecting the projected points.
3$is s$ould be a fairl straig$tforward process in t$e plan %iew!
Simpl connect wit$ straig$t lines t$e pro'ected points as t$e points t$e were
deri%ed from in triangle ,7( are connected!
#n t$e side ele%ation, t$is is a bit more confusing, as a16 is $iding be$ind a:6 and
$ence triangle ,a16a:6 appears edge+on as a line, as does triangle b:6a16a:6,
triangle b:6c:6c;6, and triangle c:6c;6d;6! ,lso, onl $alf of w$at appears in t$e
plan %iew can be seen in t$e side ele%ation, wit$ t$e ot$er $alf consisting of
in%isible lines t$at $ide be$ind %isible lines!
Howe%er, w$en all t$e points are properl connected, ou now $a%e a two+%iew
t$ree+dimensional rendition of 10:It$ of a four+ fre8uenc geodesic sp$ere! #
belie%e computer aided design programs would now gi%e ou precise %alues for
all lengt$s and angles in t$e drawing, but if all one $as are standard drafting tools,
t$ere6s more fun a$ead!
Deriving usable templates from the drawing.
5ortunatel, onl fi%e triangular templates are needed to construct t$e entire ;:I+
triangle geodesic sp$ere, or a beautiful 16I+triangle $emisp$erical dome! 3o
a%oid an furt$er confusion (# $ope", allow me to specif t$ose fi%e triangles wit$
single letter descriptions/
o triangle ,a16a:6 JK triangle ,
o triangle a16a:6b:6 JK triangle 7
o triangle a:6b:6b;6 JK triangle (
o triangle b:6c:6c;6 JK triangle D
o triangle c:6c;6d;6 JK triangle C
#n standard applied descripti%e geometr, one could construct folding lines
parallel to t$e edges of eac$ of t$ese triangles to determine t$eir true lengt$s in
au4iliar %iews, and t$en construct t$e templates on a separate s$eet of paper, but
t$ere is a muc$ simpler wa! Botice t$at triangles ,, 7, D, and C appear edge+on
in t$e side ele%ation! #f we rotate t$ose triangles so t$at t$e are parallel to t$e
folding line and pro'ect t$em bac* into t$e plan %iew, t$e will appear as true si1e
in t$e plan %iew, wit$ all face angles and edge lengt$s s$own in proper
proportion!
3riangle ( is not s$own edge+on, so we need an au4iliar %iew t$at does s$ow it
so! Draw a construction line across triangle ( in t$e side ele%ation parallel to t$e
folding line and pro'ect it bac* into t$e plan %iew, w$ere it is s$own in true
lengt$! (reate a new folding line perpendicular to t$is construction line in t$e plan
%iew and pro'ect triangle ( into t$e new au4iliar %iew, w$ere it s$ould appear
edge+on (since t$e new au4iliar %iew is related to t$e side ele%ation %iew, t$e
distances from t$e new folding line to all points will be t$e same as t$ose from t$e
folding line to all points in t$e side ele%ation"! #n t$e new %iew, rotate triangle (
until it is parallel to t$e new folding line, and pro'ect it bac* into t$e plan %iew
w$ere it will now be s$own in true si1e!
-sable templates can now be created from t$e drawing b simpl coping all fi%e
true+si1e triangles onto a separate s$eet of paper!
Constructing a hemispherical model.
Eou will need t$irt copies of triangle ,, t$irt copies of triangle 7, t$irt copies
of triangle C, ten copies of triangle D, and si4t copies of triangle (! 3riangle (
translates to two different mirror+image triangles in t$e model@ construct t$irt
copies, t$en flip t$e template around to create t$e ot$er t$irt mirror+image copies
if needed! #f a $ig$er fre8uenc was c$osen, t$ere would be more of t$ese mirror+
image triangles to contend wit$!
(areful labeling of all triangles will allow successful construction of t$e model!
(onstantl refer bac* to our drawing to see $ow t$e all fit toget$er!
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Lime Hemp and Rice Husk-Based Concretes for Building EnvelopesDe la EverandLime Hemp and Rice Husk-Based Concretes for Building EnvelopesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geodesic Analysis SampleDocument22 paginiGeodesic Analysis SampleSeaShell_6Încă nu există evaluări
- Sustainable Masonry: Stability and Behavior of StructuresDe la EverandSustainable Masonry: Stability and Behavior of StructuresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydronic Radiant-Floor HeatingDocument8 paginiHydronic Radiant-Floor Heatingkasandra01Încă nu există evaluări
- Is 9901-1 PDFDocument12 paginiIs 9901-1 PDFJGD123Încă nu există evaluări
- McKinsey - Precision Forestry A Revolution in The WoodsDocument11 paginiMcKinsey - Precision Forestry A Revolution in The WoodsJorge NexusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dome BuildingDocument5 paginiDome BuildingReny France100% (1)
- EncripStic Reference Guide Dec 2014Document14 paginiEncripStic Reference Guide Dec 2014Matthew RileyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Mimi CriDocument8 paginiBio Mimi CriYogendra PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- EncryptStick ManualDocument55 paginiEncryptStick Manualhebrew4Încă nu există evaluări
- Manual SG05Document7 paginiManual SG05fabianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aquaponics Fish Production and Stocking Densities - The Aquaponic SourceDocument5 paginiAquaponics Fish Production and Stocking Densities - The Aquaponic SourceSofiene RouisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detail Geo Study of Manali AreaDocument10 paginiDetail Geo Study of Manali AreaSarthak KhatriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kiva's Straw Bale GreenhouseDocument14 paginiKiva's Straw Bale GreenhouseStrawbale100% (1)
- How To Build A Bamboo Bicycle PDFDocument11 paginiHow To Build A Bamboo Bicycle PDFtalltale100% (1)
- Savio Ponds Construction GuideDocument32 paginiSavio Ponds Construction Guidebeggi-ner100% (3)
- Prefabricated BuildingDocument4 paginiPrefabricated BuildingAmulie JarjuseyÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSF ICF Construction Manual PDFDocument77 paginiDSF ICF Construction Manual PDFArnel Pamaos Lopiba MontañezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superinsulated Geodesic DomeDocument32 paginiSuperinsulated Geodesic DomeEnglishTeacherTJ100% (3)
- Guide To Hand SolderingDocument1 paginăGuide To Hand SolderingNICComp100% (1)
- The Dome Builders Handbook PDFDocument113 paginiThe Dome Builders Handbook PDFsersol83% (12)
- Aluminum Geodesic Dome Roof Design Phases 1 PDFDocument10 paginiAluminum Geodesic Dome Roof Design Phases 1 PDFZahra Nser AldeinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eodesic Omes: A Fuller Understanding of Applied GeometryDocument6 paginiEodesic Omes: A Fuller Understanding of Applied Geometrycaravanista1327Încă nu există evaluări
- Hyperself Electrical PDFDocument1 paginăHyperself Electrical PDFSenthilkumar NarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Passive Solar SystemDocument38 paginiApplication of Passive Solar SystemRam Krishna SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydroponic Food FactoryDocument38 paginiHydroponic Food Factorymarandan850% (1)
- ICON (IPX-3200) IPSTAR Satellite Terminal Release 1.1Document18 paginiICON (IPX-3200) IPSTAR Satellite Terminal Release 1.1030929Încă nu există evaluări
- Labour Requirement For Various Construction WorksDocument6 paginiLabour Requirement For Various Construction WorksPrem KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIY Gel Imaging SystemDocument2 paginiDIY Gel Imaging SystemT4urus-VegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Calculations For No-Head, Low-Head Waterwheels... by RuDocument2 paginiDesign Calculations For No-Head, Low-Head Waterwheels... by RuSPYDERSKILL100% (1)
- Passive Low Energy Architecture in Hot and Dry ClimateDocument10 paginiPassive Low Energy Architecture in Hot and Dry ClimatePavithra SuparamanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Far Should LED Grow Lights Be From Plants PDFDocument4 paginiHow Far Should LED Grow Lights Be From Plants PDFdannie gaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On Adopting Groasis Waterboxx For Water Saving Measures at The La PrimaVera CoopDocument22 paginiReport On Adopting Groasis Waterboxx For Water Saving Measures at The La PrimaVera CoopU8x58100% (1)
- Be Main Project 19 FinalDocument75 paginiBe Main Project 19 Finaljuned shaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- PortfolioDocument62 paginiPortfolioAiesya YusopÎncă nu există evaluări
- GeodesicDome ConstructionDocument171 paginiGeodesicDome ConstructiongarcolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chart - Note Completion - Basic 4Document5 paginiChart - Note Completion - Basic 4Mai Anh Le100% (1)
- Green Roof Specifications and StandardsDocument12 paginiGreen Roof Specifications and StandardsCastoroil7Încă nu există evaluări
- Building A DomeDocument3 paginiBuilding A DomeJeff Jassen Ordeniza CasinilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- CADRE (Analysis of Geodesic Dome)Document36 paginiCADRE (Analysis of Geodesic Dome)adityapandey285100% (1)
- Design, Manufacture and Test A Hydraulic Ram: ThesisDocument42 paginiDesign, Manufacture and Test A Hydraulic Ram: ThesisIrfan ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Dug WellsDocument241 paginiHand Dug WellsebadendickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factsheet Straw BaleDocument2 paginiFactsheet Straw BaleBiogasDudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cabin One Minimal House: Pricelist 2019Document9 paginiCabin One Minimal House: Pricelist 2019encrisisxÎncă nu există evaluări
- EasyDomes A4 FaldariDocument17 paginiEasyDomes A4 FaldariMark Gordon L.Încă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Pacific Yurts Color BrochureDocument6 pagini2011 Pacific Yurts Color BrochureNiko DiamesisÎncă nu există evaluări
- OpenSim40 API Guide DevWorkshopDocument24 paginiOpenSim40 API Guide DevWorkshopAndreia NicolauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive Solar Design 90pagesDocument90 paginiPassive Solar Design 90pagesKrystal LambÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agard Corrosion HDBDocument208 paginiAgard Corrosion HDBSyavash EnshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Bottle Wood BurnerDocument13 paginiGas Bottle Wood BurnerGringgo KweeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forests in PermacultureDocument15 paginiForests in Permaculturemariacontabilitate20072105Încă nu există evaluări
- Building Integration WindDocument52 paginiBuilding Integration WindBondBestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Λύση του 5 Χ 5 Χ 5 κύβου του ΡούμπικDocument11 paginiΛύση του 5 Χ 5 Χ 5 κύβου του ΡούμπικTheodore HaralabisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constructing Special ParallelogramsDocument4 paginiConstructing Special ParallelogramsAllen HuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer Key For Anna University - Chennai, Jan 2013-FnDocument12 paginiAnswer Key For Anna University - Chennai, Jan 2013-FnsnvijayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYS 212 Lab: Gauss' Law & Conductors: Lab Activity 1: Debunking Electric Field and Flux "Myths"Document8 paginiPHYS 212 Lab: Gauss' Law & Conductors: Lab Activity 1: Debunking Electric Field and Flux "Myths"Prathyush MarepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faiz Ul HassanDocument5 paginiFaiz Ul HassanFaiz Ul HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Format of Project ReportDocument14 paginiFormat of Project ReportMayankAgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metodos de Construccion de PlieguesDocument23 paginiMetodos de Construccion de PlieguesaracelihinojosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Title of The Paper (Uppercase, Centered, Times New Roman 16 PT, Single Spaced)Document6 paginiTitle of The Paper (Uppercase, Centered, Times New Roman 16 PT, Single Spaced)Georgiana NeaguÎncă nu există evaluări
- TYPO Print Services GuideDocument9 paginiTYPO Print Services GuideFlorin ValeriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recycle SignsDocument2 paginiRecycle SignsFlorin ValeriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP Artwork Details FullDocument1 paginăCP Artwork Details FullFlorin ValeriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pantone Colour ChartDocument10 paginiPantone Colour ChartCT0011100% (1)
- M Dome: Technical SpecificationsDocument1 paginăM Dome: Technical SpecificationsFlorin ValeriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature AB Residential Retaining WallsDocument56 paginiLiterature AB Residential Retaining WallsFlorin ValeriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detoxifierea Ficatului - LIVER CLEANSEDocument1 paginăDetoxifierea Ficatului - LIVER CLEANSEFlorin ValeriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geodesic Dome Tent Construction InstructionsDocument7 paginiGeodesic Dome Tent Construction InstructionsFlorin ValeriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geodesic Dome InfoDocument29 paginiGeodesic Dome InfoMariusProtopopescu100% (2)
- The Hulda Clark Action Plan: ! Your Quick-Start Guide ToDocument41 paginiThe Hulda Clark Action Plan: ! Your Quick-Start Guide ToThomas Carroll100% (9)
- 24 Hour Military Time SWL Zulu Time 24hr Wall ClockDocument1 pagină24 Hour Military Time SWL Zulu Time 24hr Wall ClockFlorin ValeriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quarkxpress 8.5 Mac Keyboard Commands En-UsDocument22 paginiQuarkxpress 8.5 Mac Keyboard Commands En-UsFlorin ValeriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Card Rose Pop UpDocument3 paginiCard Rose Pop UpEutimos Paramatatya67% (3)
- Psihologie Si Teorie CuanticaDocument590 paginiPsihologie Si Teorie CuanticaFlorin ValeriuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Quiz Review Similarity Parallel Lines and MidpointsDocument3 paginiUnit 2 Quiz Review Similarity Parallel Lines and Midpointsapi-334137347Încă nu există evaluări
- Engineering GraphicsDocument166 paginiEngineering GraphicsArun KastwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadrilateral - Always, Sometimes. Never (Answers)Document1 paginăQuadrilateral - Always, Sometimes. Never (Answers)urfriend_jjn0580% (5)
- Chapter 9 II Lines & Planes in 3D ENHANCEDocument21 paginiChapter 9 II Lines & Planes in 3D ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions - Homework - 9th - Maths - 2024-01-16T14:21Document40 paginiQuestions - Homework - 9th - Maths - 2024-01-16T14:21shraddha_mundadadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GE3251 Engineering Graphics Question Bank 1Document6 paginiGE3251 Engineering Graphics Question Bank 1mahathi1628Încă nu există evaluări
- 13-Medians of Triangles ConstructionsDocument4 pagini13-Medians of Triangles ConstructionsAymenÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRANSFORMATIONSDocument8 paginiTRANSFORMATIONSalan miaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Graphics (Code No. 046) CLASS XI-XII (2021-22)Document11 paginiEngineering Graphics (Code No. 046) CLASS XI-XII (2021-22)NavyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angles: (180°) and Go Full (360°)Document10 paginiAngles: (180°) and Go Full (360°)Fons Roxas-ChuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lines and Angles NotesDocument5 paginiLines and Angles NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day 16 - Unit 2 Review Day 2 SolutionsDocument5 paginiDay 16 - Unit 2 Review Day 2 Solutionsapi-253195113Încă nu există evaluări
- Angles in Triangles - Timestar Challenge#Document2 paginiAngles in Triangles - Timestar Challenge#ifrahxoxhotmail.co.uk100% (1)
- Angles Properties in CirclesDocument13 paginiAngles Properties in Circlesjavaria227204Încă nu există evaluări
- Cubes and DicesDocument4 paginiCubes and DicesVinoth KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009 VectorsDocument15 pagini2009 Vectorsfabremil7472100% (2)
- Mec121 - Engineering Graphics Week 4Document43 paginiMec121 - Engineering Graphics Week 4Psalmuel Victor AloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 4properties of Special Parallelograms - PPSXDocument38 pagini6 4properties of Special Parallelograms - PPSXFrances DayondonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identifying Faces of A Solid Figure: Background Information For LearnersDocument4 paginiIdentifying Faces of A Solid Figure: Background Information For LearnersGrace Joy S ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pythogoras Detailed Lesson PlansDocument15 paginiPythogoras Detailed Lesson PlansPh DeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2023 Omu Yos Deneme Ingilizce 1Document24 pagini2023 Omu Yos Deneme Ingilizce 1hala mordaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loci in Two DimensionDocument16 paginiLoci in Two DimensionkalkultaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circle Theorems - CIE IGCSE Maths - Extended Paper 4 2023 (Hard) - Save My ExamsDocument5 paginiCircle Theorems - CIE IGCSE Maths - Extended Paper 4 2023 (Hard) - Save My ExamsTarun PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angle Between Two LinesDocument4 paginiAngle Between Two LinesKashifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Further Vectors WorksheetDocument13 paginiFurther Vectors Worksheetzhiwu2685Încă nu există evaluări
- Class 9 Annual Paper.Document4 paginiClass 9 Annual Paper.Vanshh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Summative 3rd Quarter in MathDocument2 pagini1st Summative 3rd Quarter in MathRemore VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Document5 paginiMaths Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 02Anonymous TvppppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plane GeometryDocument7 paginiPlane GeometryKc CheungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Icse MathsDocument113 paginiIcse MathsJanaki Krishnan100% (1)
- Simplified Organization: Learn to Love What Must Be DoneDe la EverandSimplified Organization: Learn to Love What Must Be DoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eat That Frog!: 21 Great Ways to Stop Procrastinating and Get More Done in Less TimeDe la EverandEat That Frog!: 21 Great Ways to Stop Procrastinating and Get More Done in Less TimeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3225)
- The Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldDe la EverandThe Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (5)
- Clean Mama's Guide to a Healthy Home: The Simple, Room-by-Room Plan for a Natural HomeDe la EverandClean Mama's Guide to a Healthy Home: The Simple, Room-by-Room Plan for a Natural HomeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- House Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetDe la EverandHouse Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gentle Art of Swedish Death Cleaning: How to Free Yourself and Your Family from a Lifetime of ClutterDe la EverandThe Gentle Art of Swedish Death Cleaning: How to Free Yourself and Your Family from a Lifetime of ClutterEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (467)
- Success at Home with ADHD.: Practical Organization Strategies to Make Your Life Easier.De la EverandSuccess at Home with ADHD.: Practical Organization Strategies to Make Your Life Easier.Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (17)
- Root to Leaf: A Southern Chef Cooks Through the SeasonsDe la EverandRoot to Leaf: A Southern Chef Cooks Through the SeasonsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- 100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiDe la Everand100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Wild Witchcraft: Folk Herbalism, Garden Magic, and Foraging for Spells, Rituals, and RemediesDe la EverandWild Witchcraft: Folk Herbalism, Garden Magic, and Foraging for Spells, Rituals, and RemediesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (32)
- Lightly: How to Live a Simple, Serene & Stress-free LifeDe la EverandLightly: How to Live a Simple, Serene & Stress-free LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (12)
- The Joy of Less: A Minimalist Guide to Declutter, Organize, and SimplifyDe la EverandThe Joy of Less: A Minimalist Guide to Declutter, Organize, and SimplifyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (277)
- A Girl and Her Greens: Hearty Meals from the GardenDe la EverandA Girl and Her Greens: Hearty Meals from the GardenEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (7)
- How To Win Friends And Influence PeopleDe la EverandHow To Win Friends And Influence PeopleEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6513)
- How to Keep House While Drowning: A Gentle Approach to Cleaning and OrganizingDe la EverandHow to Keep House While Drowning: A Gentle Approach to Cleaning and OrganizingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (845)
- Mini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreDe la EverandMini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (76)
- Crochet Zodiac Dolls: Stitch the horoscope with astrological amigurumiDe la EverandCrochet Zodiac Dolls: Stitch the horoscope with astrological amigurumiEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Aristotle and Dante Discover the Secrets of the UniverseDe la EverandAristotle and Dante Discover the Secrets of the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2341)
- Minimalism: Minimalism for Beginners. How to Live Happy While Needing Less in This Modern Material WorldDe la EverandMinimalism: Minimalism for Beginners. How to Live Happy While Needing Less in This Modern Material WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (39)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateDe la EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1002)
- Dream Sewing Spaces: Design & Organization for Spaces Large & SmallDe la EverandDream Sewing Spaces: Design & Organization for Spaces Large & SmallEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (24)
- The Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingDe la EverandThe Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (11)
- Crochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!De la EverandCrochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (10)
- The Fitness Mindset: Eat for energy, Train for tension, Manage your mindset, Reap the resultsDe la EverandThe Fitness Mindset: Eat for energy, Train for tension, Manage your mindset, Reap the resultsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (31)
- Crochet with London Kaye: Projects and Ideas to Yarn Bomb Your LifeDe la EverandCrochet with London Kaye: Projects and Ideas to Yarn Bomb Your LifeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- You Need a Budget: The Proven System for Breaking the Paycheck-to-Paycheck Cycle, Getting Out of Debt, and Living the Life You WantDe la EverandYou Need a Budget: The Proven System for Breaking the Paycheck-to-Paycheck Cycle, Getting Out of Debt, and Living the Life You WantEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (421)