Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Nomenclature,: Standards
Încărcat de
reacharunk0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
18 vizualizări1 paginăjgjgjgjg
Titlu original
LH(77)
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentjgjgjgjg
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
18 vizualizări1 paginăNomenclature,: Standards
Încărcat de
reacharunkjgjgjgjg
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
STANDARDS, NOMENCLATURE, ABBREVIATIONS 3-9
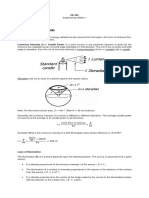
intensity of a lamp or luminaire with angle of emission. See Fig. 5-9b,
page 5-17.
solid of light distribution : a solid the surface of which is such that the
radius vector from the origin to the surface in any direction is proportional
to the luminous intensity of the light source in the corresponding direction.
isocandle line : a line plotted on any appropriate co-ordinates to show
directions in space, about a source of light, in which the candlepower is
the same. See Fig. 8-17, page 8-47.
isolux line: a line, plotted on any appropriate co-ordinates, showing
points of equal illumination. See Fig. 8-20, page 8-49.
coefficient of utilization (of an illumination installation) : the total flux
received by the reference plane divided by the total flux from the lamps
illuminating it. See Fig. 8-19, page 8-48. When not otherwise specified,
the plane of reference is assumed to be a horizontal plane 30 inches
(76 centi-
meters) above the floor. See Table 8-2.
lamp: a light source.
electric filament lamp : a light source consisting of a glass bulb containing
filament electrically maintained at incandescence ; commonly called an
incandescent lamp, an electric light or a light bulb.
electric discharge lamp : a lamp in which light is produced by the passage
of electricity through a metallic vapor or a gas such as mercury, sodium,
neon, argon, and so forth, enclosed in a tube or bulb ; sometimes called a
vapor lamp.
luminaire: a complete lighting unit including lamp, globe, reflector,
refractor, housing, and such support as is integral with the housing. The
term luminaire is used to designate completely equipped lighting fixtures,
wall brackets, portable lamps, and so forth which are removable. It does
not include permanent parts of a building, such as_a-ceiling, or other struc-
tural element ; in street-lighting units the pole, or bracket is not considered
a part of the luminaire.
"~
color: the characteristics of light other than spatial and temporal
inhomogeneities
.
Color
of
an object: the capacity of the object to modify the color of the
light incident upon it.
Colorants: substances used to produce the color of an object.
Dominant wavelength
(of
a color): the wavelength that, combined with
white light (equal energy spectrum) in suitable proportions, matches the
color.
Complementary wavelength: the wavelength that, combined with a sample
color in suitable proportions, matches white light is the sample's comple-
mentary wavelength.
Purity: The relative brightnesses* of the spectrum and white compo-
nents in the mixtures obtained in making a color match determine and are
specified by purity.
Colorimetric purity: the ratio of the brightness of the spectral component
to the brightness of mixture obtained in making a color match.
*
Candancy and luminance have been proposed as being more appropriate terms.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Interior Lighting GlossaryDocument8 paginiInterior Lighting Glossarymena_sky11Încă nu există evaluări
- 5 - IlluminationDocument16 pagini5 - IlluminationDebbieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-2 EE6801Document40 paginiUnit-2 EE6801Thangam MaheshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utilization and Traction: PresentationDocument36 paginiUtilization and Traction: PresentationShailesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lighting Calculations Explained: Lumen Method, Inverse Square Law & MoreDocument56 paginiLighting Calculations Explained: Lumen Method, Inverse Square Law & MoresiddharthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lighting Design Basics and TerminologyDocument22 paginiLighting Design Basics and TerminologyTonoTony100% (1)
- 1.0 Lighting SystemsDocument14 pagini1.0 Lighting SystemsbiddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utilisation of Electrical: EnergyDocument39 paginiUtilisation of Electrical: EnergyGPMoradabad ElectricalÎncă nu există evaluări
- IlluminationDocument41 paginiIllumination20E150 - SOLLARUVI MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lighting: Electrical Energy Equipment: LightingDocument40 paginiLighting: Electrical Energy Equipment: LightingSurajit BondhopadhayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook: E LightingDocument1 paginăHandbook: E LightingreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Electrification Unit 3Document12 paginiBuilding Electrification Unit 3Manik SahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.0 Lighting SystemsDocument20 pagini1.0 Lighting SystemsIgombe IsaacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illumination & Lighting DesignDocument15 paginiIllumination & Lighting DesignMd TabrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-3 Illumination System: Lecture Videos On YoutubeDocument7 paginiUNIT-3 Illumination System: Lecture Videos On YoutubeLavanya LakshmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Power Utilization and Energy Auditing Iveeeviiisem 2 Mark Q & ADocument28 paginiElectrical Power Utilization and Energy Auditing Iveeeviiisem 2 Mark Q & Akailash_singh_7100% (1)
- Electrical Energy IlluminationDocument24 paginiElectrical Energy IlluminationVasavi VaasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aakarshit Jain's notes on accent lighting, halogen lamps, flood lighting and glareDocument15 paginiAakarshit Jain's notes on accent lighting, halogen lamps, flood lighting and glareAakarshit JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Light in Architecture: Energy Comfort and BuildingsDocument27 pagini1.1 Light in Architecture: Energy Comfort and BuildingsParvathy ShekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes Chapter 1 and 2Document37 paginiNotes Chapter 1 and 2Harshal VaidyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3-Lighting Scheme and Bell CircuitsDocument89 paginiChapter 3-Lighting Scheme and Bell CircuitsyeabmotherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lighting Fundamentals Experiment 1: Lamp Types, Metrics, and Measurements (39Document9 paginiLighting Fundamentals Experiment 1: Lamp Types, Metrics, and Measurements (39Dawnill Mar Maturan RegenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lighting TermDocument11 paginiLighting TermJenel TangonanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Illumination FundamentalsDocument24 paginiIntroduction to Illumination FundamentalsMark Laus50% (2)
- PolarizationDocument2 paginiPolarizationapi-323795755Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Installation Ppt1Document27 paginiElectrical Installation Ppt1Abrha Ftsum100% (1)
- Amphitheatre MalabarDocument15 paginiAmphitheatre MalabarniyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 12: BASICS OF LIGHTING (Terms and Concepts)Document7 paginiMODULE 12: BASICS OF LIGHTING (Terms and Concepts)tarlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fafa 3Document10 paginiFafa 3Amsalu SeteyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uee I PDFDocument28 paginiUee I PDFpurushg62Încă nu există evaluări
- Bu 5 - LightingDocument8 paginiBu 5 - LightingSharmaine Danica MarceloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illumination 1 PDFDocument22 paginiIllumination 1 PDFvenkatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of IlluminationDocument8 paginiCalculation of IlluminationEasier Said Than DoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEASURING LIGHT INTENSITYDocument35 paginiMEASURING LIGHT INTENSITYJohn JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring Light: Footcandles, Footlamberts and CandlepowerDocument1 paginăMeasuring Light: Footcandles, Footlamberts and CandlepowerreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter One: IlluminatonDocument50 paginiChapter One: IlluminatonMirkena kebedeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix 10.1Document3 paginiAppendix 10.1Afrim ArtÎncă nu există evaluări
- UEET Assignment #3: I LT F WDocument13 paginiUEET Assignment #3: I LT F Wsophro syneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3Document19 paginiChapter 3Lëlîså DébālkéÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 Fundamentals of IlluminationDocument97 paginiUnit 4 Fundamentals of IlluminationSmarty KalyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IlluminationDocument29 paginiIlluminationadnan faizÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC2353 – ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION NOTESDocument17 paginiEC2353 – ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION NOTESBachu Saee RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Power Utilisation and Energy AuditingDocument14 paginiElectric Power Utilisation and Energy Auditingrpdmohan100% (2)
- Antenna TheoryDocument27 paginiAntenna TheoryDoaa Mahmoud100% (1)
- ElectricalDocument16 paginiElectricalSuresh SaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 26: Polarization-I Lecture 26: Polarization-I: 26.1 Natural RadiationDocument7 paginiModule 26: Polarization-I Lecture 26: Polarization-I: 26.1 Natural RadiationAnoop JenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial LightingDocument13 paginiArtificial LightingPrashna ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lighting or Illumination Is The Use ofDocument23 paginiLighting or Illumination Is The Use ofPrerana RaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- E Lighting: HandbookDocument1 paginăE Lighting: HandbookreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- L IXA: CalculationsDocument1 paginăL IXA: CalculationsreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- ch33 Gelombang EM 118Document25 paginich33 Gelombang EM 118azrilmln21Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Installation GuideDocument111 paginiElectrical Installation GuideDaaniyyee AbdiisaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial Lighting FundamentalsDocument20 paginiArtificial Lighting FundamentalspallaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competitive Questions Advanced Geometry by H.C. RajpootDocument9 paginiCompetitive Questions Advanced Geometry by H.C. RajpootGimi GionesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation All Final PDFDocument121 paginiInstallation All Final PDFmarsilas0% (2)
- LEC 6 - CE333 Illumination DesignDocument5 paginiLEC 6 - CE333 Illumination DesignAndry Eloise JacaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tables for the Energy and Photon Distribution in Equilibrium Radiation Spectra: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 35De la EverandTables for the Energy and Photon Distribution in Equilibrium Radiation Spectra: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 35Încă nu există evaluări
- Intensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleDe la EverandIntensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 paginiProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 paginiProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 paginiProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1464)Document1 paginăEn (1464)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1462)Document1 paginăEn (1462)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocument150 paginiProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- PZU EDUKACJA INSURANCE TERMSDocument19 paginiPZU EDUKACJA INSURANCE TERMSreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- NameDocument2 paginiNamereacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supplement To The Prospectuses and Summary Prospectuses For Investor Shares and Admiral™SharesDocument65 paginiSupplement To The Prospectuses and Summary Prospectuses For Investor Shares and Admiral™SharesreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supplement To The Prospectuses and Summary Prospectuses For Investor Shares and Admiral™SharesDocument65 paginiSupplement To The Prospectuses and Summary Prospectuses For Investor Shares and Admiral™SharesreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergency Response Quick Guide MY: 2014Document2 paginiEmergency Response Quick Guide MY: 2014reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1463)Document1 paginăEn (1463)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1455)Document1 paginăEn (1455)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1459)Document1 paginăEn (1459)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1461)Document1 paginăEn (1461)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- And Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atDocument1 paginăAnd Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1460)Document1 paginăEn (1460)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1458)Document1 paginăEn (1458)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1450)Document1 paginăEn (1450)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1456)Document1 paginăEn (1456)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1453)Document1 paginăEn (1453)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1457)Document1 paginăEn (1457)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1454)Document1 paginăEn (1454)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mate The: (Fig. - VrouldDocument1 paginăMate The: (Fig. - VrouldreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1452)Document1 paginăEn (1452)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1389)Document1 paginăEn (1389)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1451)Document1 paginăEn (1451)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1388)Document1 paginăEn (1388)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1390)Document1 paginăEn (1390)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- En (1387)Document1 paginăEn (1387)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLD of MDB-3 Last Update For Print-ModelDocument1 paginăSLD of MDB-3 Last Update For Print-ModelSharif 087Încă nu există evaluări
- Symbols PDFDocument8 paginiSymbols PDFakhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switch and Types of Switch: What Is A Switch?Document5 paginiSwitch and Types of Switch: What Is A Switch?Swagat PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shutdown SIS: Truck 777D Truck FKR 777D Off-Highway Truck FKR00001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY 3508B EngineDocument3 paginiShutdown SIS: Truck 777D Truck FKR 777D Off-Highway Truck FKR00001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY 3508B EngineGerald BoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Busch-Presence Detectors - Brochure - Rev2018 - EnglishDocument44 paginiBusch-Presence Detectors - Brochure - Rev2018 - EnglishPRABHU SHANKAR MÎncă nu există evaluări
- L-s20 Specification For Road Lighting InstallationDocument82 paginiL-s20 Specification For Road Lighting Installationzamanhuri junidÎncă nu există evaluări
- JVC Av21q3d TV SMDocument10 paginiJVC Av21q3d TV SMtelevizionistulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Combustion Engines MCQ PDFDocument14 paginiInternal Combustion Engines MCQ PDFShakir ullah87% (53)
- Division Category Product Group Item Vendor Item No - Unit Cost Last Purch DateDocument504 paginiDivision Category Product Group Item Vendor Item No - Unit Cost Last Purch Datefawad121Încă nu există evaluări
- KEC Semiconductor Product Guide SMD PDFDocument117 paginiKEC Semiconductor Product Guide SMD PDFaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concave and Convex Mirror ExerciseDocument5 paginiConcave and Convex Mirror ExerciseĐặng Thái Nhật100% (1)
- Drill Press PlansDocument24 paginiDrill Press PlansJose BelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Type-code explanatory notes for spark plugsDocument1 paginăType-code explanatory notes for spark plugsRafael RosasÎncă nu există evaluări
- GENSET PROFILEDocument44 paginiGENSET PROFILEMichał BujaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- RLB Project ConsiderationsDocument3 paginiRLB Project Considerationsகௌதம் வைத்தியநாதன்Încă nu există evaluări
- Mccu 228 Manual T02Document22 paginiMccu 228 Manual T02luismidexÎncă nu există evaluări
- DMG 2007 Technical-CatalogueDocument455 paginiDMG 2007 Technical-CatalogueadasdasasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battery Indicators: PART NO. 910114 2260 SRM 138Document34 paginiBattery Indicators: PART NO. 910114 2260 SRM 138Andrey LuqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instalacion de Cabeza c4.4Document5 paginiInstalacion de Cabeza c4.4Crespo JorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bme MCQ QuestionDocument6 paginiBme MCQ QuestionAbhishek SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Class Etiquette for StudentsDocument22 paginiOnline Class Etiquette for StudentsSUHANEERIYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q Eim-2a (Module)Document20 paginiQ Eim-2a (Module)egagamaosanderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recip Engine Troubleshooting GuideDocument15 paginiRecip Engine Troubleshooting GuideKaung Htet Cho100% (2)
- EASY UPS BV Family Overview Brochure - 120VDocument4 paginiEASY UPS BV Family Overview Brochure - 120VLiliana AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Diag) - Immobilizer SubaruDocument22 pagini(Diag) - Immobilizer SubaruElectronicdeivi DeiviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Small Engine: A Step-By-Step Guide To Maintaining Your Small EngineDocument8 paginiSmall Engine: A Step-By-Step Guide To Maintaining Your Small EngineBez ImenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Insulated SwitchgearsDocument24 paginiGas Insulated Switchgearscody100% (3)
- 6 Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)Document5 pagini6 Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)Srini VasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toll Plaza Boq P 03Document29 paginiToll Plaza Boq P 03SIVA NAGA SUDHEER SIDDANIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maple Terrace E-Brochure PDFDocument18 paginiMaple Terrace E-Brochure PDFouguewayÎncă nu există evaluări