Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Math 2 Makiling
Încărcat de
Annabelle Poniente HertezDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Math 2 Makiling
Încărcat de
Annabelle Poniente HertezDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
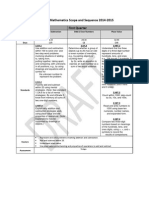
MATHEMATICS II (Gifted)
Content
Content Standards Performance Standards Learning Competencies
Numbers and Number Sense
A. Comprehension of whole
numbers
demonstrates
understanding of the
relationships between
numbers and place value
of whole numbers up to
1000 and beyond and of
ordinal numbers up to 20
th
and beyond
.
number notation and
place value, cardinal
and ordinal numbers,
and comparing and
ordering numbers up to
10,000.
explores the concepts
of numbers up to 1000
and beyond
reads and writes these
numbers
The learner
visualizes and identifies numbers from
1000 and beyond
explore the concept of cardinal
numbers up to 1,000 and beyond and
compare these numbers in various
contexts
Explore the concept of ordinal numbers
from 31
st
to 100
th
and beyond
associates numbers with sets having
100 obects and beyond
associates numbers with sets having !01
up to 1000 obects and give the number of
obects.
1.1 "ssociates numbers with sets having
1,001 up to 10,000 obects#things.
counts and groups obects in ones, tens,
and hundreds. (lifted from K to 12)
counts numbers by 10s, !0s and 100s.
1.2 $%ip counts by 3s, &s through 1000
1.3 $%ip counts by !0s through 10,000
reads and writes numbers from 101
through 1000 in symbols and in words.
2. 'eads and writes numbers from 1,001
through 10,000 in symbols and in words
reads and writes numbers through 1000 in
symbols and in words.
2.1 'eads numbers from 1,001 through
10,000 in symbols and in words
2.2 (rites numbers from 1,001) 10,000 in
symbols and in words
gives the place value of each digit in a
three)digit number.
2.3 *ives the place value and value of each
digit in a 3 to ! digit number
2.3.1 +rom the smallest#biggest to ! digit
number
2.3.2 'ound numbers to nearest 10s,
100s, 1000s and 10,000s
identify ordinal numbers
through 100th.
writes three)digit numbers in expanded
form.
2.& (rites 3)! digit numbers in expanded
form
2.&.1 (rites the missing digits of numbers
in the expanded form
e.g 3!&, 300 - !0 - &, 300 - &0 - .... ,
300 - ..... - &
compares numbers using /, 0 and ,.
orders numbers up to 10,000 from least to
greatest and vice versa. (lifted from K to 12 &
enhanced)
2.! 1ompares numbers using /, 0 and ,
2.2 'ounds number to the
2.2.1 nearest tens, hundreds and
thousands
2.2.2 nearest ten thousands
2.3 4ifferentiates odd from even numbers
with 2 to &) digit numbers
2.5 6dentifies odd#even 2)&) digit numbers
visualizes and identifies the 1st through the
20th obect of a given set from a given point of
reference. (lifted from K to 12)
3. 'eads and writes ordinal numbers through
compute sums and solve
addition problems involving
numbers of up to 1000.
100
th
in symbols and words
reads and writes ordinal numbers from 1st
through the 20th.
3.1 6dentifies 31
st
through 100
th
obect in
given sets from a given point of reference
3.2 6dentifies ordinal numbers up to the
100
th
identifies and uses the pattern of naming
ordinal numbers from 1st to the 20th.
3.3 6dentifies the pattern of naming ordinal
numbers e.g 21
st
, 22
nd
, 23
rd
, 2&
th
, etc.
3.& 7ses the pattern of naming ordinal
numbers beyond100th
&. 'eads and writes centavos and pesos
through 1,000
!. 8ells how many 9100 bills are in 91,000:
9!0 bills are in 91,000
2. 1ompares values of different
denominations of 9hilippine coins and paper
bills through 91,000 using the relation
symbols
3. Expresses 'oman numbers in e;uivalent
<indu)"rabic through 1 and vice versa
3.1 'eads and writes 'oman =umerals
through 1 in <indu)"rabic numbers and vice)
versa through>
a. repetition ?e.g 66@
b. subtraction (e.g IV)
the concept of the four
operations of whole numbers and
the identity and zero properties of
multiplication.
c. addition (VI)
7.2 Solves simple addition problems
using Roman numerals
C!"R#$#%SI% & '((I)I%
adds numbers with sums up to 1000
without and with regrouping> 2 digit and 3)
digit.
1. "dds 2)& digit numbers with sum up to
A,AAA without or with regrouping
uses the following properties of addition in
computing for sums of up to 1000>
zero#identity property of addition, commutative
property of addition, associative property of
addition.
1.1 $hows the commutative property of
addition
1.2 $hows the associative property of
addition
adds numbers with sums up to 1000
without and with regrouping> 3 digit and 3)
digit.
use mental strategies to *nd sums to 1+
and di,erences -rom 1+ or less
mentally adds 1) to 2)digit numbers with
sums up to 100. (lifted from K to 12)
mentally adds 3)digit numbers by ones ?up
to A@.
mentally adds 3)digit numbers by tens
?multiples of 10 up to A0@.
mentally adds 3)digit numbers by hundreds
?multiples of 100 up to A00@. (lifted from K to
12)
1.3 "dds 3 to & digit numbers with sums up
to 10,000 with regrouping
1.3.1 without regrouping in short form
1.3.2 with regrouping in tens #hundreds
place
1.& "dds 2)& addends digit numbers with
zero in any of the addends without and with
regrouping with sums up to A,AAA
1.! Estimates sums using front)end and
rounding off techni;ues
1.2 "dds ;uantity of money up to 9!00
without regrouping
1.3 "dds mentally 1 to 2 digit numbers
having 2)3 addends with sums up to 100
2. "pplication of addition
2.1 $olves word problems involving addition
of 2 to & digit numbers including money with
sums up to A,AAA without and with regrouping
2.1.1 'eads and understand the problem
2.1.1.1 8ells>
) what is as%ed
) what is#are given
) the word clue#s
) the operation to be used
2.1.2 9lans what to do and do it
2.1.3 4raws a picture to represent the
word problem
2.1.& 8ransforms word problem into a
number sentence
2.1.! $olves the determined operation
2.1.2 "nswers the ;uestion
2.1.3 1hec%s the answer
2.2 $olves mentally 1) step word problems
involving addition with sums up to AAA
2.3 1reates 1)step word problems involving
addition of whole numbers up to A,AAA
including money with or without regrouping
analyzes and solves word problems
involving addition of whole numbers including
money with sums up to 1000 without and with
regrouping.
compute differences and
solve subtraction problems
involving numbers of up to
1000.
1BC9'E<E=$6B= B+ $7D8'"186B=
subtracts 2) to 3)digit numbers with
minuends up to AAA without and with
regrouping.
1. $ubtracts 1 to 3 Edigit numbers from 3 to !
digit numbers with minuend up to A,AAA
without and with regrouping and with zero
difficulty
1.1 6llustrates how subtraction is used
when>
1.1.1 ta%ing away from the given set
1.1.2 comparing two sets
1.1.3 finding a missing part
1.2 $ubtracts 1 to 3 digit numbers from 3 to
& digit numbers without regrouping
1.3 $ubtracts 1 to 3 digit numbers from 3 to
& digit numbers with regrouping
1.& $ubtracts 1 to 3 digit numbers from 3 to
& digit numbers having zero difficulty with
regrouping
1.! Estimates the difference of two
numbers without regrouping using the front)
end and rounding techni;ue in estimation
1.2 $ubtracts ;uantity of money with
minuend through 9!00.00
1.3 $ubtracts mentally 1 to 2 digit numbers
with minuends up to 100 without regrouping
mentally subtracts 1)digit numbers from 1
to 2)digit numbers with minuends up to !0.
mentally subtracts 3)digit by ones without
regrouping. (lifted from K to 12)
mentally subtracts 3)digit by tens without
regrouping. . (lifted from K to 12)
mentally subtracts 3)digit by hundreds
without regrouping. . (lifted from K to 12)
2. "pplication of $ubtraction
2.1 $olves 1)step word problems involving
subtraction of &)digit numbers including
money with minuends up to A,AAA
8ell>
) (hat is as%ed
) (hat are given
) 8he word clue#s
) 8he operation to be used
4raws a picture#diagram#table#graph to
represent the word problem
) 8ransforms the word problem into
a number sentence
) $tates the complete answer
) 4oes the answer ma%e senseF
(hyF
analyzes and solves one)step word
problems involving subtraction of whole
numbers including money with minuends up
to1000 without and with regrouping.
compute for sums and
differences and solve
problems involving both
addition and subtraction of
numbers.
performs order of operations involving
addition and subtraction of small numbers.
3. "pplication of addition and subtraction
3.1 $olves 2)step word problems involving
addition and subtraction of whole numbers
including money
8ells>
) (hat is as%ed
) (hat are given
) 8he word clue#s
) 8he operation to be used
4raws a picture #diagram#table#graph to
represent the word problem
) 8ransforms the word problem into
a number sentence
) $tates the complete answer
3.2 1reates 1 to 2)step word problems
including money
solves two)step word problems involving
addition and subtraction of 2) to 3)digit
numbers including money using appropriate
procedures.
explore and illustrate the
concept of multiplication of
whole numbers.
1BC9'E<E=$6B= B+ C7G869G61"86B=
illustrates multiplication as repeated
addition, arrays, counting by multiples, and
e;ual umps on the number line. (lifted from K
to 12)
writes a related e;uation for each type of
multiplication> repeated addition, array,
counting by multiples, and e;ual umps on the
number line. (lifted from K to 12)
1. Cultiplies 1 to 2 digit numbers by 1)digit
numbers up to A without and with regrouping
in all places with products up to 51
1.1 8ransforms an addition sentence with a
multiplication sentence and vice)versa
1.2 6dentifies the parts of a multiplication
sentence
illustrates the property of multiplication that
any number multiplied by one ?1@ is the same
number.
illustrates the property of multiplication that
zero multiplied by any number is zero.
1.3 $hows that a number multiplied by 1 is
the same number
illustrates the commutative property of
multiplication. (lifted from K to 12)
1.& $hows that zero multiplied by a
number is zero
1.! Cultiplies 1 to 2 digit numbers by 1)
digit numbers up to A without regrouping
1.2 Cultiplies 1 to 2 digit numbers by 1)
digit numbers up to A with regrouping
1.3 *ives the pairs of factors of a given
number up to AA
1.5 6dentifies the multiples of a given
number
1.A *ives the least common multiple ?G1C@
of two numbers
1.10 Cultiplies mentally 1)2 digit numbers
with products up to 51 with correction
1.11 Cultiplies 1)digit numbers up to A by
multiples of 10 and 100.
compute products of
numbers involving 2, 3, &, !
and 10 and solve problems
involving multiplication of
these numbers.
constructs and fills up the multiplication
tables of 2, 3, &, ! and 10. (lifted from K to 12)
multiplies mentally to fill up multiplication
tables of 2, 3, &, ! and 10. (lifted from K to 12)
2. "pplication of multiplication
analyzes and solves one)step word
problems involving multiplication of whole
numbers including money.
.
2.1 $olves 1)step word problems involving
multiplication of whole numbers including
money with products through 51.
8ells>
) (hat is as%ed
) (hat are given
) 8he word clue#s
) 8he operation to be used
4raws a picture #diagram#table#graph to
represent the word problem
) 8ransforms the word problem into
a number sentence
) $tates the complete answer
2.2 1reates word problems involving
multiplications of whole numbers including
money
3. "pplication of multiplication and any of the
fundamental operations
analyzes and solves two)step word
problems involving multiplication of whole
numbers as well as addition and subtraction
including money
3.1 $olves 2)step word problems involving
multiplication of whole numbers including
money and any of the fundamental operations
learned
3.1.1 8ells>
) (hat is as%ed
) (hat are given
) 8he word clue#s
) 8he operation to be used
4raws a picture #diagram#table#graph to
represent the word problem
) 8ransforms the word problem into
a number sentence
) $tates the complete answer
3.2 1reates a 2)step word problems
involving multiplication of whole number
including money and any one of the two
fundamental operations learned.
explore and model the
concept of division of whole
numbers.
1BC9'E<E=$6B= B+ 46H6$6B=
1. 4ivides whole numbers with dividends
through 51 by 1 digit divisor
represents division as e;ual sharing,
repeated subtraction, e;ual umps on the
number line, and formation of e;ual groups of
obects.
1.1 $hows division as repeated subtraction
1.2 6dentifies the parts of a division
sentence namely, dividend, divisor, and
;uotient
models and describes division situations in
which sets are separated into e;ual parts.
(lifted from K to 12)
1.3 6llustrates division
) Dy partition ?dividing a number
into e;ual parts@
) Dy distribution ?finding how
many times a number is
contained in a given number
) "s inverse of multiplication
)
writes a related e;uation for each type of
situation> e;ual sharing, repeated subtraction,
e;ual umps on the number line, and
formation of e;ual groups of obects.
1.& 'elates multiplication sentence to a
division sentence
1.! 8ransforms a division sentence into a
multiplication sentence and vice versa
2. 4ivides 2 to 3 digit numbers with zero#s in
the dividend by 1)digit number without
remainder
3. 4ivides 2 to 3 digit numbers by multiples of
10 up to A0
&. 4ivides 2 to 3 digit numbers by 1 digit
numbers with remainder
compute ;uotients of
numbers found in the
multiplication tables involving
2, 3, &, ! and 10 and solve
problems involving division of
these numbers.
!. "pplication of 4ivision
divides numbers found in the multiplication
tables of 2, 3, &, !, and 10.(lifted from K to 12)
mentally divides numbers found in the
multiplication tables of 2, 3, &, ! and 10. (lifted
from K to 12)
!.1 $olves 1)step word problems involving
division of whole numbers including money
with dividends up to 51.
analyzes and solves one)step word
problems involving division of numbers found
in the multiplication tables of 2, 3, &, !, and
10. (lifted from K to 12)
2. "pplication of 4ivision and any 1 of the 3
fundamental operations learned.
2.1 $olves 1)step word problems involving
division of whole numbers including money
and any 1 of the other fundamental operations
learned.
2.1.1 8ells>
) (hat is as%ed
) (hat are given
) 8he word clue#s
) 8he operation to be used
4raws a picture or a diagram to
represent the word problem
) 8ransforms the word problem into
a number sentence
) $tates the complete answer
.
Rational Numbers unit fractions, proper fractions
and similar fractions, and
identification of money value
through 100.
explore the concept of unit
fractions and other fractions
less than 1 and compare
these fractions
1BC9'E<E=$6B= B+ +'"186B=$
visualizes and identifies unit fractions with
denominators 10 and below. (lifted from K to
12)
visualizes and identifies other fractions less
than one with denominators 10 and below.
visualizes and identifies similar fractions
?using group of obects and number line@.
reads and writes similar fractions.
compares similar fractions using relation
symbols.
orders similar fractions.
reads and writes unit fractions. (lifted from
K to 12)
compares unit fractions using relation
symbols. (lifted from K to 12)
orders unit fractions. (lifted from K to 12)
1.=ames some or all e;ual parts of a whole
e.g 1#3, 2#3, 3#3: I, 2#&, J, &#&
2. $eparates a whole or group of obects into
halve, thirds, fourths, fifths, sixths, eights
3. 1ompares fractions with similar
denominators by different numerators using
relation symbols
e.g 2#3 0 3#3, J / I, 2#! 0 &#!
&. Hisualizes fractional parts of a number from
halves to eights through !0
e.g 2#3 of 2 ) 2#3 K 2 , 2 K 2 , 12 , &
3 3
<ow many parts are shaded , 12 , & parts
3
3 of 5 )) 3 K 5 , 3 K 5 , 2& , 2
& & & &
!. +inds the fractional parts of a number
2. $olves word problems involving finding
fractional part of a given sets#numbers
including money
3. 1reates word problems involving finding
fractional part of a given number including
money
Enrichment
'educes fractions to simplest forms
e.g 2#& # 2#2 , L 4ivide both numbers by
their *1+
apply number concepts on
problem situations involving
money.
reads and writes money with value through
1000. (lifted from K to 12 and enhanced)
counts and tells the value of a set of bills or
a set of coins through 1000 in peso ? coins
only, bills only and coins and bills@. (lifted from
K to 12 and enhanced)
counts and tells the value of a set of bills or
a set of coins through 1000 in centavo ?coins@.
(lifted from K to 12 and enhanced)
counts and tells the value of a set of bills or
a set of coins through 1000 in combinations of
pesos and centavos ?9eso and centavo coins
only, bills and centavo coins, coins and bills@.
(lifted from K to 12 and enhanced)
reads and writes money in symbols and in
words through 1000.
(lifted from K to 12 and enhanced)
compares values of different
denominations of coins and paper bills
through 1000 using relation symbols /, 0 and
,. (lifted from K to 12 and enhanced)
Geometry
the basic properties of
geometric shapes, simple
tessellations and symmetry.
visualize and model half)
circles and ;uarter circles as
well as other common
shapes.
Comprehension of Geometry
visualizes, identifies, classifies and
describes half)circles and ;uarter circles.
(lifted from K to 12)
1. 6dentifies different shapes common in the
home and in school
2. classifies shapes according to number of
sides and corners
constructs s;uares, rectangles, triangle,
circles, half)circles and ;uarter circles using
cut)outs and s;uare grids. (lifted from K to 12)
&. +orms simple symmetrical designs from
given shapes
identifies shapes#figures that show
symmetry in a line
.
&.1 6dentifies lines of symmetry
&.2 6dentifies figures with lines of symmetry
explore the concept of
symmetry. creates figures that show symmetry in a
line. (lifted from K to 12)
visualize, model and
represent tessellations.
recognizes shapes that can tessellate.
(lifted from K to 12)
tessellates a surface using triangles and
s;uares. (lifted from K to 12)
3. 8essellates a surface using triangles and
s;uares
explore the concept of
lines, curves and surface on
3)dimensional obects.
identifies straight lines and curves, flat and
curved surfaces in a 3)dimenional obect.
(lifted from K to 12)
explains the differences between straight
lines and curved lines, flat surfaces and
curved surfaces.
(lifted from K to 12)
Patterns and Algebra
patterns on numbers and
geometric obects.
argue and ustify patterns. identifies and explains simple repeating
patterns.
determines the next term ?figure#number@ in
a given se;uence and give a reason.
apply their understanding
and strategies in completing
patterns.
finds and completes patterns according to
one or two of the following attributes> shape,
size, color, orientation.
Measurement
the concept and application of
time and of using standard units
in measuring length, mass, area
and capacity.
compute for measures of
time and solve problems
involving time.
".1 1omprehension of 8ime Ceasure
1.1 6ndicates the time to the nearest
minute and second
1.2 8ells time when the minute hand is at !
minute position
e.g 1>0!, 1>3!, 1>!!
1.3 'eads time as shown on the different
%inds of time pieces ?wristwatches, cloc%s@ in
figures and words
1.& 1onverts measures of time
e.g hours to minutes: minutes to hours:
seconds to minutes
2. "pplication of time measure
2.1 $olves 1)step word problem involving
time measure such as determining elapsed
time and ending time using the steps in
problem solving
2.2 1reates word problems involving time
measures
D)1. 1omprehension of linear measures
1.1 Ceasures obect using standard units of
linear measure i.e centimetre, meter
1.1.1 "pproximates and measures the
length, width, height and distance
of obects in metres and
centimetres
1.1.2 8ells the relationship between
metres and centimetres
1.2 +inds the perimeter of a given figure
using grid
2. "pplication of linear measure
2.1 $olve 1) step word problems involving
linear measure using any of the fundamental
operations
2.2 1reate word problems involving linear
measure
1)1 1omprehension of "rea
1. Hisualizes area of plane figures in s;uare
units
2. +inds the area of plane figures in s;uare
units
4)1 1omprehension of mass measure
1.1 Ceasures mass of obect using
standard units of mass measure such
as gram and %ilogram
1.2 1onverts standard units of mass
measure to lower or higher units
1.3 "pproximates measurement of mass
1.& 6nvestigates accuracy in measuring
mass and ;uantity of things bought
e.g weighing sac% of rice
2. "pplication of Cass Ceasures
2.1 $olves word problems involving mass
measures using any of the four fundamental
operations
E.1 1omprehension of 1apacity
1.1 Ca%es measurement using standard
units of capacity measure e.g litre,
millilitre
1.21onverts standard units of capacity
measures from lower to higher units
1.3 "pproximates capacity of containers
2."pplication of 1apacity Ceasures
2.1 $olves word problems involving units of
capacity using the steps in problem solving
+)1 1omprehension of 8emperature Ceasure
1.1 6dentifies the parts of a thermometer
1.2 'eads body#weather thermometer using
1elsius degrees
2."pplication of temperature measure
2.1 $olves word problems involving
body#weather temperature
tells and writes the time in minutes
including a.m. and p.m. using analog and
digital cloc%s.
finds the duration of time elapsed using
calendar, analog and digital cloc%s.
solves simple word problems involving
time.
identify and compare the
standard units centimeter and
meter.
shows and uses the appropriate unit of
length to measure a particular obect and their
abbreviations cm and m.
compares length in meters or centimeters.
estimate and compute for
lengths of obects and solve
problems involving lengths
using centimeter and meter.
measures obects using appropriate
measuring tools in m or cm.
estimates and measures length using
meter or centimeter.
solves simple word problems involving
length.
identify, use and compare shows and uses the appropriate unit of
the standard units gram and
%ilogram.
mass to measure a particular obect or
situation and their abbreviations g and %g.
compares mass in grams or %ilograms.
estimate and compute for
the mass#weight of an obect
and solve problems involving
mass#weight.
measures obects using appropriate
measuring units in g or %g.
estimates and measures mass using gram
or %ilogram.
solves simple word problems involving
mass.
explore and illustrate the
concept of area.
illustrates area as a measure of how much
surface is covered or occupied by plane
figure.
shows the area of a given figure using
s;uare tile units, i.e. number of s;uare tiles
needed.
estimate and compute for
the area of a plane figure.
estimates the area of a given figure using
any shape.
finds the area of a given figure using
s;uare tile units i.e. number of s;uare tiles
needed.
measure capacity. shows and finds capacity using appropriate
measuring tools, e.g. amount of li;uid needed.
Statistics and Probability
pictographs with scale
representations and the idea of
li%elihood.
organize and interpret
data.
collects and organizes data using tables
and pictures.
reads and interprets data in a given
pictograph.
represent data using
scales
forms scale representation of obects from
the data collected.
ma%es pictographs using scale
representation.
ma%e conectures and
educated guesses about the
li%elihood of events
ma%es a guess on whether an event is less
li%ely, more li%ely, e;ually li%ely or unli%ely to
happen based on facts.
!aps and .rap/s
&1 collect and organi0e data
&2 interpret and create
concrete and picture grap/s
&1 interpret and create
pictograp/s and s2mbolic
grap/s
&3 pose oral 4uestions in
relation to conducting
surve2s and5or
". 1omprehension of graphs
1. 'eads and interprets data on a bar graph
and a pictograph
1.1 =ames the parts of a pictograph and
bar graph
a. title
b. legend
c. label
1.2 8ells the function of each part
2. 1ollects and organizes data for graphs
3. 'eads and interprets data presented in
interpreting data pictograph and bar graph
D. 1omprehension of maps
1. 8ells the position of certain obect or
place using the primary and secondary
directions
1.1. =ames the secondary directions
1.2 Gocates the secondary directions
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Effects of The Environment On The Life Cycle of Organisms: Worksheet in Science IvDocument2 paginiEffects of The Environment On The Life Cycle of Organisms: Worksheet in Science IvAnnabelle Poniente Hertez100% (1)
- Kinesiology For The Martial Arts PDFDocument50 paginiKinesiology For The Martial Arts PDFB'MAZ100% (4)
- Gad Legal Mandate1Document87 paginiGad Legal Mandate1LGU PadadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDFDocument258 paginiPDFfathy MoghiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stages in The Life Cycle of Organisms: Worksheet in Science IvDocument2 paginiStages in The Life Cycle of Organisms: Worksheet in Science IvAnnabelle Poniente Hertez0% (1)
- Binary Numbers OverviewDocument9 paginiBinary Numbers OverviewHolsworth WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap-01 Maths 6Document25 paginiChap-01 Maths 6Tarikh KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composite Function Worksheet-02Document4 paginiComposite Function Worksheet-02Marcus Maccoy AcordaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tle Agri - NurseryDocument52 paginiTle Agri - NurserylizÎncă nu există evaluări
- PFR Assignment Parental AuthorityDocument14 paginiPFR Assignment Parental AuthorityAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- PFR Assignment Parental AuthorityDocument14 paginiPFR Assignment Parental AuthorityAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Structures That Help Animals Adapt and Survive: Worksheet in Science IvDocument2 paginiBody Structures That Help Animals Adapt and Survive: Worksheet in Science IvAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Structures That Help Animals Adapt and Survive: Worksheet in Science IvDocument2 paginiBody Structures That Help Animals Adapt and Survive: Worksheet in Science IvAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educational Planning (Felipe)Document102 paginiEducational Planning (Felipe)Felipe Beranio Sullera Jr.100% (4)
- Principle of AssessmentDocument43 paginiPrinciple of AssessmentAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sworn Statement ERFDocument4 paginiSworn Statement ERFAnnabelle Poniente Hertez100% (1)
- IB Source CatalogDocument145 paginiIB Source Catalogeibsource100% (2)
- Sek. Keb. Sungai Rambai 14000 Bukit Mertajam Yearly Plan Mathematics Year 6Document4 paginiSek. Keb. Sungai Rambai 14000 Bukit Mertajam Yearly Plan Mathematics Year 6adiskylineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Core Math Standards 1516Document2 paginiCommon Core Math Standards 1516api-191125030Încă nu există evaluări
- Digit NoteDocument13 paginiDigit NoteAttah FrancisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0475804Document144 pagini0475804Hassan BareachÎncă nu există evaluări
- BW - Mathematics 2Document6 paginiBW - Mathematics 2Remelyn Monares Dela Cruz IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Budget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterDocument8 paginiBudget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterLea Garcia MagsinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Template Q1 Summative Assessment Results - XLSX - MathDocument6 paginiSchool Template Q1 Summative Assessment Results - XLSX - MathJaremie AyonkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Convert A Number To WordsDocument20 paginiHow To Convert A Number To WordsdanieldotnetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commoncoremathcheatsheets 2 NDDocument1 paginăCommoncoremathcheatsheets 2 NDapi-288064681Încă nu există evaluări
- Budget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterDocument8 paginiBudget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterEnteng ODÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEARNING MATERIALS IN MTHT 2062021 22 FinalDocument38 paginiLEARNING MATERIALS IN MTHT 2062021 22 FinalLowela Joy AndarzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Draw The Number Line Showing 0 To 10 Numbers and Answer The FollowingDocument3 paginiA. Draw The Number Line Showing 0 To 10 Numbers and Answer The FollowingSnehal PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- PT Q1 MATH3.docx-BAGALAYOSDocument11 paginiPT Q1 MATH3.docx-BAGALAYOSANNALYN VINESÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2007 Mathematics Standards by ProgressionDocument27 pagini2007 Mathematics Standards by ProgressionElaine EricksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 4 TosDocument2 paginiMath 4 TosIVYÎncă nu există evaluări
- BINARY NUMBER SYSTEM Unit1Document3 paginiBINARY NUMBER SYSTEM Unit1Charu PathakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Miscellaneous: I. Binary Numbers: A DiscussionDocument9 paginiMiscellaneous: I. Binary Numbers: A Discussionghoshtapan4321Încă nu există evaluări
- K To 12 Basic Education Curriculum Learning Competencies (Grade 1) Numbers and Number SenseDocument6 paginiK To 12 Basic Education Curriculum Learning Competencies (Grade 1) Numbers and Number SenseMitch CasticonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6NV PDFDocument54 pagini6NV PDFMahendarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st To 4th Least LearnedDocument1 pagină1st To 4th Least LearnedVINA ARIETAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Electronics: Kwame Oteng Gyasi Lecture 2: Number SystemDocument28 paginiDigital Electronics: Kwame Oteng Gyasi Lecture 2: Number SystemOperation ResearchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conveconvconverting Between Decimal (Base 10) and Binary (Base 2)Document26 paginiConveconvconverting Between Decimal (Base 10) and Binary (Base 2)Himanshu VohraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Competencies (Grade1 - Grade 3)Document9 paginiLearning Competencies (Grade1 - Grade 3)Godwin BabaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secondary Maths 6Document77 paginiSecondary Maths 6Dav Gua67% (3)
- Lres 125Document123 paginiLres 125vijay kumar GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lovely Professional University Phagwara (Punjab) Binary Number SystemDocument5 paginiLovely Professional University Phagwara (Punjab) Binary Number Systemshailesh singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number System OperationsDocument9 paginiNumber System OperationsPascal chadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.number SysDocument7 pagini1.number SysindianmuserprinceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number SystemsDocument7 paginiNumber SystemsAna DshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document32 pagini1vanessa.livaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number System: Chapter - 3Document16 paginiNumber System: Chapter - 3lvsaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sig Fig Handout PDFDocument4 paginiSig Fig Handout PDFAadarsh BalireddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics: (Philippine Elementary Learning Competencies) Basic Education CurriculumDocument34 paginiMathematics: (Philippine Elementary Learning Competencies) Basic Education CurriculumNel ManjaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- STLD Course File Geethanjali-19-83Document65 paginiSTLD Course File Geethanjali-19-83Slim ShadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decimal Number SystemDocument17 paginiDecimal Number SystemmeenuÎncă nu există evaluări
- DT1 ArmietDocument16 paginiDT1 Armietap549640Încă nu există evaluări
- Whole NumbersDocument6 paginiWhole NumbersShakeel vPEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number SystemsDocument35 paginiNumber SystemshasithrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-Number & AlgebraDocument90 pagini1-Number & AlgebrafadilrahmatullahmÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAO Unit-2 Entire NotesDocument106 paginiCAO Unit-2 Entire NotesBhumireddy ChandanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numbers 0 To 10: Understand Addition As Combining Two Groups of ObjectsDocument12 paginiNumbers 0 To 10: Understand Addition As Combining Two Groups of ObjectsAnonymous r1vPtxUrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 02 Prelim ActDocument15 paginiMath 02 Prelim ActJohn kevin AbarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number All LevelsDocument4 paginiNumber All LevelsMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Binary SystemsDocument5 paginiBinary SystemsalihalawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information and Technology ManagmentDocument18 paginiInformation and Technology ManagmentKuldeep Singh ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Number SystemsDocument30 paginiUnit 1 Number SystemsAnurag GoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class-4 Handouts of Unit-1Document6 paginiClass-4 Handouts of Unit-1Priyansh GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 2Document17 paginiCH 2kaibrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Binary SystemDocument5 paginiThe Binary SystemOgbo IsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Csa SummaryDocument10 paginiChapter 2 Csa Summarycsa94Încă nu există evaluări
- First Quarter and 2nd Quarter Scope and Sequence MathDocument2 paginiFirst Quarter and 2nd Quarter Scope and Sequence Mathapi-234156613Încă nu există evaluări
- Data RepresentationDocument9 paginiData RepresentationMeet PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Y1-6 Maths Statements - Number - Number & PVDocument3 paginiY1-6 Maths Statements - Number - Number & PVAndy BrookeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Outcome Years 5Document6 paginiLearning Outcome Years 5Ardent HatredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numeration System PDFDocument6 paginiNumeration System PDFCriziaClaire CosmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 NdgrademathcurriculummapDocument4 pagini2 Ndgrademathcurriculummapapi-318489536Încă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan JUNE 2021Document7 paginiDepartment of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan JUNE 2021Annabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan MAY 2021Document8 paginiDepartment of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan MAY 2021Annabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Reporting Log APRIL 2021Document18 paginiDepartment of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Reporting Log APRIL 2021Annabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan MAY 2021Document8 paginiDepartment of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Plan MAY 2021Annabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Use of Organic FertilizerDocument15 paginiThe Use of Organic FertilizerAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Reporting Log APRIL 2021Document18 paginiDepartment of Education: School Head'S Technical Assistance Reporting Log APRIL 2021Annabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: Monthly Supervisory Accomplishment Report November 2020Document4 paginiDepartment of Education: Monthly Supervisory Accomplishment Report November 2020Annabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reporter: Nove Joy L. Deleña Bsed-Bio - Sci. IiiDocument7 paginiReporter: Nove Joy L. Deleña Bsed-Bio - Sci. IiiAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Template Business PlanDocument5 paginiTemplate Business PlanAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cookies (100pcs) Quantity Price/Quantity Total AmountDocument3 paginiCookies (100pcs) Quantity Price/Quantity Total AmountAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSP Plastic Container PlantersDocument5 paginiBSP Plastic Container PlantersAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Template Business PlanDocument5 paginiTemplate Business PlanAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Plan DETAILDocument4 paginiBusiness Plan DETAILAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL - Science 4 - Q4 - W1Document4 paginiDLL - Science 4 - Q4 - W1Nie EbarleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cookies (100pcs) Quantity Price/Quantity Total AmountDocument3 paginiCookies (100pcs) Quantity Price/Quantity Total AmountAnnabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sworn Statement - 2016Document1 paginăSworn Statement - 2016Annabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MedicalCertificate For Boxing 2Document1 paginăMedicalCertificate For Boxing 2Annabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Las Science4 q2w2Document2 paginiLas Science4 q2w2Annabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ghies Teachers Study Notebook LDM Module Course 2Document45 paginiGhies Teachers Study Notebook LDM Module Course 2Annabelle Poniente Hertez100% (1)
- Affidavit 2016Document5 paginiAffidavit 2016Annabelle Poniente HertezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edible Cell WorksheetDocument3 paginiEdible Cell Worksheetm_frajman100% (4)
- User fc20 PDFDocument34 paginiUser fc20 PDFjesus diasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uci Xco Me Results XDocument4 paginiUci Xco Me Results XSimone LanciottiÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Engineering SurveyingDocument5 paginiWhat Is Engineering SurveyingHui EdroxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Github & SourceTree Manual - 15831Document6 paginiGithub & SourceTree Manual - 15831Jose Cristian Cañaveras VelezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Float Sink Lesson Plan 2Document3 paginiFloat Sink Lesson Plan 2api-388627256Încă nu există evaluări
- History 541gDocument21 paginiHistory 541gkarl1802Încă nu există evaluări
- Tesla Case PDFDocument108 paginiTesla Case PDFJeremiah Peter100% (1)
- Duncan Reccommendation LetterDocument2 paginiDuncan Reccommendation LetterKilimanjaro CyberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master of Business Administration - MBA Semester 3 ProjectDocument2 paginiMaster of Business Administration - MBA Semester 3 ProjectAnkur SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ca DLL Week 2 - 2023 2024Document6 paginiCa DLL Week 2 - 2023 2024YVIE WRITZ ARZAGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anomalous Worldwide SEISMIC July 2010Document130 paginiAnomalous Worldwide SEISMIC July 2010Vincent J. CataldiÎncă nu există evaluări
- W3: Assess 2 On Self-PerceptionDocument2 paginiW3: Assess 2 On Self-PerceptionGielyn Camilo100% (1)
- Curriculum: (R. A. 10533/ K-12 EBEP)Document16 paginiCurriculum: (R. A. 10533/ K-12 EBEP)Diyonata KortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue Assessment Analysis of Offshore Structures With Application To An Existing Platform in Suez Gulf, EgyptDocument21 paginiFatigue Assessment Analysis of Offshore Structures With Application To An Existing Platform in Suez Gulf, EgyptthuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct 3 DDocument406 paginiDirect 3 Dxlam99Încă nu există evaluări
- Art of First DueDocument32 paginiArt of First DuedadaditdahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampling With Automatic Gain Control 4Document31 paginiSampling With Automatic Gain Control 4anandbabugopathotiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNC Unit 1Document4 paginiCNC Unit 1chandiran88Încă nu există evaluări
- Manual To KivyDocument2 paginiManual To KivyvalkmaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Improve Your MemoryDocument2 paginiHow To Improve Your MemoryAlejandro GalvisÎncă nu există evaluări
- C Shock Press KitDocument10 paginiC Shock Press KitSusan LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProceedingDocument7 paginiProceedingnoor hafizzatul izzahÎncă nu există evaluări
- William "Bill" Labov Born December 4, 1927 Age 89 Born in Rutherford, New Jersey,)Document2 paginiWilliam "Bill" Labov Born December 4, 1927 Age 89 Born in Rutherford, New Jersey,)Jesus VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation of MIL-STD-1553 Data BusDocument5 paginiImplementation of MIL-STD-1553 Data BusIJMERÎncă nu există evaluări