Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Jetking Training Cum Placement Project
Încărcat de
DakshtaPhulpagarDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Jetking Training Cum Placement Project
Încărcat de
DakshtaPhulpagarDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
placementcellfinal15.docx (Size: 2.
58 MB / Downloads: 299)
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 ABSTRACT
This project is aimed at developing an application for the Training and
Placement Department of the College. The system is an application that can
be accessed throughout the organization with proper login provided. This
system can be used as an application for the Training and Placement Officers
(TPO) of the college to manage the student information with regard to
placement. Students logging should be able to upload their information in
the form of a CV. The key feature of this project is that it is a onetime
registration. Our project provides the facility of maintaining the details of the
students. It also provides a requested list of candidates to recruit the
students based on given query. Administrator logging in may also search
any information put up by the students. This project will aid colleges to
practice full IT deployment. This will also help in fast access procedures in
placement related activities.
1.2 ABOUT THE PROJECT
This project is to facilitate students in college to register, search and apply
for jobs. The users can access easily to this and the data can be retrieved
easily in no time. In the main page there are options for a new register, a
registered student to directly login using username and password, submit
resume. In the student registration form, we can give personal details,
educational qualifications, and professional skills and upload resume. The job
details of the placed students will be provided by the administrator. The
administrator plays an important role in our project. They provide approval
of student registration and updating.
OBJECTIVES OF THE PROJECT
Computers and information technology has a major influence on the society
and the society is becoming more and more dependent on technology. Going
on is an era of simplifying almost all complicated works using computers.
The last few years have witnessed a tremendous increase in the capabilities
and use of computers. Manual processing makes the process slow and other
problems such as inconsistency and ambiguity on operations. The proposed
system intends user-friendly operations which may resolve ambiguity. By
considering all this factors, the applications produced, which performs the
social service simply and effectively.
Objectives of the Software
Help in fast access procedures in placement related activities
The facility of maintaining the details of the students
This project will aid colleges to practice full IT deployment.
2. REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS
System analysis is a detailed study of various operation performed by a
system and the relationship within and outside of the system. One aspect of
analysis is defining the boundaries of a system and determining whether or
not a candidate system should consider other related system. Analysis
begins when a user or manager begins a study of the programs using an
existing system. System analysis is an application of system approach to the
problem solving using computers. The ingredients are the system elements,
process and technology.
During analysis data is collected on the various files, decision points and
transactions handled by the present systems. This means that to do system
works, one is to understand the system concepts and how the organizations
operate as a system and the design appropriate computer based system and
that will make the organization requirements. It is actually customized
approach to the use of computer problem solving. Analysis can be defined as
the separation of a substance into parts for study an interpretation, detailed
examination. System development revolves around a life cycle that being
with the recognisation of user names. The critical phase of managing system
project is planning. To launch a system investigation, we need a master plan
detailing steps taken, the people to be questioned and outcome expected.
System analysis can be categorized into four parts:
System planning and initial investigation
Information gathering
Analyzing tools for structured analysis
Feasibility study
Cost Benefit Analysis
System study or system analysis is the first among the four life cycle phases
of a system. System analysis begins when a user or manager request a
studying of a program in either an existing system or a project one. It
involves studying the base of the organization currently operating, retrieving
and processing data to produce information with goal of determining how to
make it work better. System analysis itself breaks down into stages
preliminary and detailed. During preliminary analysis, the analyst and the
user list the objectives of the system. To arrive at a preliminary report, the
analyst interviews key personnel in the organization and scheduling
meetings with the users and management.
The objective of analysis phase of the system analysis and design exercise is
the establishment of the requirement for the system to be acquired,
developed and installed. In brief analysis of the system helps an analyst to
make a clear view of an existing system and thereby give suggestions for
the improvement of the new system information about the organizations,
policies, goals, objectives and structure explains the kind of environment
that promotes the introduction of the computer based system. It is
necessary that the analyst must be familiar with the objectives, activities
and functions of the organizations.
2.1 FEASIBILITY STUDY
Once you define a problem you have to analyze whether this is feasible or
not, because all possible solutions are not feasible and feasible one is not
always possible. The detailed studies carried out to check the work ability of
proposed system. A feasibility study is a test of system proposal regarding to
its work ability, impact on the organization ability to meet user needs an
effective use of resources. Thus when a new application is proposed it
normally goes through a feasibility study before it is approved for
deployment.
Thus during feasibility analysis for this project, following primary areas of
interest are to be considered. Investigating the existing system in the area
under investigation and generating ideas about a new system does this.
(a) Technical Feasibility
A study of resource availability that may affect the ability to achieve an
acceptable system. This evaluation determines whether the technology
needed for the proposed system is available or not.
It will avoid multiple file handling
Report generation is very easy
The new system provides full security of confidential data
(b) Economical Feasibility
Computer Services Department will develop the proposed system. The
system will be developed and operated in the existing hardware and
software infrastructure. So there is no need for procuring additional
hardware and software for the system. The proposed will replace the hectic
cost and man power involved in the existing system. The employs will be
trained in using and operating the system, thus eliminating the need for
recruiting employees. Thus the project is economically feasible for the
development for the company
Scheduled Feasibility
An evaluation of the time, which is to be taken in the development of the
project. The time scheduled required for the development for this project is
very important since more development time affects machine time, cost and
cause delay in the development of other systems so the project is concerned
should be completed within a fixed scheduled time as the company is
concerned. Besides this, the project is assigned to the student as an
academic exercise to complete within a fixed schedule of time.
Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD)
Peter Chen originally proposed Entity- Relationship Diagram (ERD) for the
design of relational data base system. The E-R Database model is based on
a perception of real world that consist of a set of basic objects called entities
and relationships among these objects. Sets of primary components
identified for the ERD ; Data objects, attributes, relationships and various
type indicators. The ERD enables us to identify data entity and relationships
using a graphical notation. This model consist of three interrelated pieces of
information.
Entity (Data Object)
A Data Object is a representation of any composite information that must be
understood by software
Attributes
It defines the properties of an entity and takes on one of three different
characteristics. They can be used to name an instance of the data object,
describe the instance and make references to another instance in another
table.
Relationships
Entities are connected to one another in a variety of different ways
Cardinality
Modality
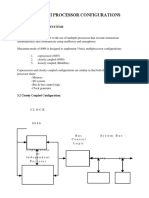
2.2 EXISTING SYSTEM
The existing system is doing all the processes manually. The personnel
should refer all the records kept for years ago to simply know details. This so
tedious and time consuming. This process is so difficult when the number of
users increases.
Drawbacks of Existing System
There are a lot of limitations for the existing systems
Time consuming
Not accurate
Error prone
Large amounts of records are to be kept
Complicated procedure
May not complete in time
Paper work is very tedious
Report production is very slow
All the registers are kept for a long period
Searching for a file or record is very difficult
Due to all this reasons we are moving for the proposed system
Reference: http://seminarprojects.com/Thread-project-on-training-and-
placement-cell#ixzz3ApeiPd6N
TNP Final Report.doc (Size: 1.54 MB / Downloads: 821)
Abstract
Training & Placement Portal aims at providing the Facility to automate
and simplify the process of registration and list generation of eligible
students for placement. This System provide facility to TPO to do all
their Work Regarding Placement like Collecting Student Records,
Registering the Suitable Students, to check the number and
percentage of placed & unplaced students, and important
announcements to other departments. The whole work is automated
as well as on intranet.
INTRODUCTION
1.1 PURPOSE:
Computer based information system are designed to improve existing
system. Whatever the information, TPO has to pass to the student and
he or she can inform online. Improve accuracy in result. It has user
friendly interface having quick authenticated access to documents. It
provides the facility of maintaining the details of the students. It will
reduce the paper work and utilize the maximum capabilities of the
Setup and organization as well as it will save time and money which
are spending in making reports and collecting data. It can be accessed
throughout the organization and outside as well with proper login
provided. This system can be used as an application for college to
manage the student information with regards to placement.
1.2 PROBLEM STATEMENT:
Now a days, Student joins the college for the placement as well as for
better training for their future. But there is manual training has going
on there might be lot of problem student as well as placement
manager has to face. All the transactions are done manually. Fake
entries can be there. System is more error - prone & time consuming.
Difficulty in managing data of students. Large piles of records are to be
maintained. TPOs have to collect the information of various companies
who want to recruit students and notify students time to time about
them. It is a time consuming activity of managing , updating and
informing specific student for specific company requirements.
1.3 PROJECT OBJECTIVE
In order to avoid above existing problem we are design existing
system as online Training and Placement system, so that whatever the
information, TPO has to pass to the student and he or she can inform
online. All the resume send by the student which can be maintain in
the database . It reduce the paper work and storage area. Save time &
work load for TPC Staff and students. Easy to access. Avoid fake Entry.
Only Eligible students get chance. Improve accuracy in result. It has
user friendly interface having quick authenticated access to
documents.
1.4 SCOPE AND LIMITATIONS:
Project has a big scope to do. We Students can maintain their
information and can update it. Notifications are sent to students about
the companies. Students can access previous information about
placement. This system has scope of improvement / amendments. In
future, sector can communicate with each other online. All currently
active enquires can also be added in the website to view if online. This
application can be modified from time to time as per the changing
requirement of the user with lesser cost also the backend of the
application can be changed as per the storage requirement of the
application and to provide more security level features. The limitation
with the application can also be looked into and enhancement can be
made as per user requirement .
All though this project is made only for a particular institute and
supports a particular operating system platform , the wide application
area of the project surpasses this small drawback. Hence proving its
worth.
Reference: http://seminarprojects.com/Thread-project-on-training-
and-placement-cell#ixzz3ApfacZqP
Upload
Log in
Sign up
Browse
<iframe height="0" src="//www.googletagmanager.com/ns.html?id=GTM-ZWF6"
style="display:none;visibility:hidden" width="0"></iframe>
Download
Standard view
Full view
1
of 128
Save to My Library
Look up keyword
Like this
Share on social networks
171Activity
Share to your social networks.
Tweet
Embed
23425541 25778233
1409030889 8ObZSyIPca+c0A
0 of .
Results for:
No results containing your search query
COMPLETE Project on Networking
Ratings:
(1)|Views: 8,222 |Likes: 218
Published by ISHAN CHAUDHARY
for any other project contact me at ishanoo_dxanoo@yahoo.co.in
for any other project contact me at ishanoo_dxanoo@yahoo.co.in
More info:
Categories:Types, Research, Math & Engineering
Published by: ISHAN CHAUDHARY on Dec 01, 2009
Copyright:Attribution Non-commercial
Availability:
Read on Scribd mobile: iPhone, iPad and Android.
download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Flag for inappropriate content|Add to collection
See more
See less
SWAMI PARMANAND COLLEGE OFENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
SIX MONTHS INDUSTRIAL TRAINING REPORT
ON
NETWORKING (MCSE & CCNA)
AT
JETKINGSEC 34 , CHANDIGARH
SUBMITTED AS A PART OF COURSE CURRICULUM
BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY
IN
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Under the Guidance of
Mr. Baljit singhMr. Inder GulatiSubmitted To: Submitted By:
E r . H a r p r e e t K a u r ( H O D ) S a r o j
D o g r a ( 6 9 7 0 4 1 9 1 7 )
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS &COMMUNICATION ENGINEERINGSWAMI
PAMANAND COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING &TECHNOLOGY, DERA BASSI,
MOHALI
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I f eel deepl y i ndedt ed t o Mr . Bal j i t Si ngh, Mi cr os of t t r ai ner who
del i ver ed val uabl elesson on MCSE, his indepth knowledge about the subject
helped me understand thes ubj ect i n bet t er wa y. Hi s met hod of t eachi ng t he
mi nut e det ai l s hel ped me a l ot t oacquire the insight into the subject.I am also
grateful to Mr. Inder Gulati, CCNA trainer for giving best knowledge
aboutCCNA.the way he instilled knowledge of the subject was undoubtly praise
worthy andvaluable.I am also thankful to Jetking institution as a whole that is doing
yeomans service byteaching the learner avreast with the computer , networking and hardware
knowledge thatis the need of the day.I will be failing in my duty if I do not acknowledge my
husband Mr. Nardev Singh Ranawho always stood by my side during my studies. I am
indepted to my sons AnirudhRana and Romil Rana who never clamed my time and get bore
by my long absence rather silent.Last but not the least, I thank all my classmates at
Jetking for extending kindco-operation.
1. INTRODUCTION
This project report pertains to six months industrial training that I had underwentat JETKING,
Chandigarh as part of curriculum of degree in Bachelor of technology inElectronics
and Communication engineering as required by Swami Parmanand College of engineering and
technology (affiliated to Punjab Technical University, Jalandhar) .I l ear nt a l ot f r om
pr of es s i onal manager s and s ki l l ed engi neer s . I had a gr eat learning experience
as trainee in this firm. I learnt a lot about how different networks arecontrolled in the industry or
any department with the help of networking processes, under MCSE and CCNA.I have learnt
about different type of servers like DHCP Server, DNS Server, NATServer. Also I have
learnt how to control the LAN and MAN networks under MCSE(Microsoft Certified
System Engineers) and how to control MAN and WAN networksunder CCNA (CISCO
Certified System Engineers).Justification cannot be done to whatever I have learnt in these six
months within afew pages but I have still tried my best to cover as much as possible in this
report. In thisreport I have tried to sum up the technical knowledge I have gained in my six
months of training.
1.1
Company Profile
Jetking is an organization came into establishment in1947. Jetking is Indiasnumber
one Computer Hardware and Networking Institute.
Birth and Evolution
It took a lot of failure before mankind tasted technological success. Jetking evolved intune with
the changing face of technology. During 55 years in the field of
electronictechnology. Jetking successfully trained thousands of students to
overcome failure for high paying careers.
1 9 4 7 B i r t h 1 9 6 2 P i o n e
e r e d D o - I t - Y o u r s e l f K i t s i n
I n d i a 1 9 7 2 I n t r o d u c e d A s i a - 7 2 , F a i r c h i l d a n d
W i l d c a t t r a n s i s t o r s 1 9 8 6 B e c a m e a P u b l i c
L i m i t e d C o m p a n y a n d a l s o
i n t r o d u c e d ent er t ai nment el ect r oni cs pr oduct - T. V s et s , Two- i n-
ones andamplifiers.1 9 9 0 L a u n c h e d J e t k i n g S c h o o l o f
E l e c t r o n i c s T e c h n o l o g y 1 9 9 3 N e t w o r k o f
J e t k i n g t r a i n i n g c e n t e r s s p r e a d a l l o v e r
I n d i a 1 9 9 4 O p e n i n g o f J e t k i n g ,
C h a n d i g a r h 1 9 9 5 T i e - u p w i t h H e a t h k i t
E d u c a t i o n a l S y s t e m ( U . S . A . ) 1 9 9 6 I n t r o d u c e d
a d v a n c e d c o u r s e s o n P e n t i u m , N o t e b o o k s ,
M o d e m s , Email/Internet, LAN 4.X1 9 9 7 N o v e l l
E d u c a t i o n A c a d e m i c
P a r t n e r 1 9 9 8 R e p r e s e n t a t i v e f o r
I n t e r n a t i o n a l C o r r e s p o n d e n c e S c h o o l ( I C S ) , USA
in India1 9 9 9 A d d e d c y b e r t e c h n o l o g y t o t h e
c u r r i c u l u m 2 0 0 3 I S O 9 0 0 1 - 2 0 0 0 c o m p a n y a n d
A u t h o r i z e d M i c r o s o f t o n l i n e t e s t i n g centre (VUE) for MS,
CISCO, MCSA, MCSE, CCNA, A+ etc.Mr. Suresh G. Bharwani is the CHAIRMAN and
MANAGING Director of Jetking Infotrain Ltd. Indias leading Computer Hardware and
Networking Institute. Withthe vision to promote and the conviction to deliver the widespread
propagation of comp-uter hardware and networking education across the nation, Mr. Bharwani
was the first toset up an training institute offering innovative courses in computer
hardware in 1990.Jetkings core competency lies in providing complete training and
developing hardwareengineers and professionals with sound technical knowledge. It
focuses on the overalldevelopment of personality of an individual with emphasis on
personality development, presentation and communication skills, leadership skills etc.Jetking has
established more than 125 operational centers and 250 faculties acrosst he count r y and has
t r ai ned over 3, 50, 000 s t udent s who have move ont o t he cr ave
success- full career. With its alumni placed in the best of organizations in India and
someabroad,J et ki ng, s vocat i onal t r ai ni ng and pl acement pr omi s es has hel ped
bui l d t he car eer prospects of many young boys and girls.The company has been
awar ded t he I SO 9000: 2000 cer t i f i cat i on i n 2003. Thecompany has been
awarded the Maharashtra IT Award for a key role in manpower activities in year
2006-07,it was felicitated with Franchise Award as Best Franchisor for the year 2007-
08.Also,ranked 4
th
in the list of 26
th
hot franchises as per outlook moneymagazine.Mr. Suresh Bharwani was awarded with
Pikes Peak Award by the Bob PikeGroup USA for effective implementing smart lab plus for
making technical training fun,faster and easier for non- technical person.Acr os s al l t he
s ect or s , i ndus t r i es ar e upgr adi ng t hei r i nf or mat i on t echnol ogysystem.
Industries ranging from plastics, chemicals, textiles and power to the automotiveand telecom
sector are now IT savy. Government and public sectors are going hi-techwith EDI and
computer networks. The IT industry, software companies, data centers, IT-enabled services
providers are all equipped with advance IT system and networks. Theincreasing
number of call centers, BPOs etc., have given a further boost to the hardwareand networking
industry.The courses in jetking comprises lecture and theory session, with a great focus onactive
participation through smart lab plus ,that focuses on audio visual and learning withhands - on
t r ai ni ng and equi ps s t udent s wi t h an i n dept h domai n knowl edge t hat
i s technical; it also equips students with soft skills ,to face the multi-faceted
challenges of corporate world.PLACEMENT: Jetking is the first and only institute that
promises the 100% j obs guar ant ee t o i t s s t udent s . The compani es t hat have
r ecr ui t ed j et ki ngs s t udent s include:Samsung, Sun Micro system, IBM, Canon,
Siement, reliance, TATA, Compaq HPinvent, IT-T solutions, Videsh Sanchar Nigam
Limited, D-Link, Novell, Dell, Wipro, LG,ICIC Infotech and several other MNCs.
Any student who has qualified his or her HSC/SSC examination is eligible to takeup a course at
jetking. The one year program Jetking certified hardware and networking professionals give 680
hours of in-depth knowledge to a student in Basic electronics andcomputer applications.
Computer hardware and peripherals, window 2003 administrator and network administrator
(soon it will be replaced with window server 2008).Apartframe technical knowledge
there are personality development sessions which groom thestudents personality, their ability to
perform better.Jetking, Indias leading hardware and networking training institute has
trainedover 3,00,000 students from its 125 centers spread across India. With its alumni placed
int he bes t of or gani z at i ons i n I ndi a and s ome abr oad, J et ki ng vocat i onal
t r ai ni ng and placement promises has helped build the career prospects of many young boys
and girls.Jetking has partnered with some of the worlds most renowed names in networkingto
provide you with cutting edge courses and technologies. With academic
partnershipswith Microsoft, Comp TIA,LINUX, NOVELL, and person VUE .Jetking
Chandigarh is a division of Hi-Tech point. Hi-Tech point is an ISO 9001-2 0 0 0 I T
c o mp a n y . I t wa s e s t a b l i s h e d i n y e a r 1 9 9 3 a n d r u n b y a c o mp a n y o f
I T professionals. Jetking Chandigarh branch is considered to be the best centre
among allcenters. It has bagged number 1 center award consecutively for last 7 years. Here
trainingon var i ous f i el ds i s goi ng on l i ke Bas i c El ect r oni c, Har dwar e,
Net wor ki ng, J CHNPAnalog and Digital electronics and Hardware, RHCE, RHCSS, MNA,
MCSE (MicrosoftSys t em Engi neer s ) , MCI TP, MNA, CCNA ( CI SCO Cer t i f i ed
Net wor k As s oci at e) , CCNP(CISCO Certified Network Professional).Partnership with
industry leaders like Microsoft and Red Hat Jetking ensure itsstudents authentic
courseware and technology.
2
. LITERATURE RIEVIEW
Computer Networking is a very vast project in the present developing era of
electronicsa n d c o mmu n i c a t i o n . No w a d a y s , c o mp u t e r s a r e u s e d i n a
wi d e r r a n g e . Al l t h e organizations are using multiple computers within their
departments to perform their dayto day work. Computer network allows the user to share data ,
share folders and files withother users connected in a network. Computer Networking has bound
the world in a verysmall area with it wide networking processes like LAN, MAN, WAN.The
courses in jetking comprises lecture and theory session, with a great focus on
active par t i ci pat i on t hr ough s mar t l ab pl us , t hat f ocus es on audi o vi s ual
and l ear ni ng wi t hhands - on t r ai ni ng and equi ps s t udent s wi t h an i n dept h
domai n knowl edge t hat i s technical; it also equips students with soft skills ,to
face the multi-faceted challenges of corporate world.
3. NETWORKING
3 . 1 I n t r o d u c t i o n t o n e t w o r k i n g
Networking is a practice of linking of two or more computing devices such asPCs,
printers, faxes etc., with each other Connection between two devices is
through physical media or logical media to share information, data and resources.
Networks aremade with the hardware and software.Cable/media
Fig 1: computer network
3.1.1 Models of Networking
Model means t he connect i vi t y of t wo comput er s . We have many t ypes
of networking models.(i) Client Server Model(ii) Peer to Peer Model (Workgroup
Model)( i i i ) D o m a i n M o d e l
(i) Client Server Model
In a Client server model we have one server and many clients. A Client can sharethe resources of
server, but a server cannot share the resources on clients.On t he poi nt of vi ew of
admi ni s t r at or i t s ver y eas y t o cont r ol t he net wor k becaus e we combi ne
wi t h t he s er ver al s o at s ecur i t y poi nt of vi ew. I t i s ver y us ef ul because it uses
user level security in which users have to remember only one password toshare the resources.
(ii) Peer to Peer Model (Workgroup Model)
In Peer to Peer networking model all computers are in equal status, that is wecannot
manage centralization, administration secutity. In Peer to Perr networking clientuse operating
system like Window 98, Window XP, Window 2000, Window Vista.
(iii) Domain Model
It is a mixture of client server and peer-to-peer model. In this clients can sharetheir
resources as peer-to-peer but with the permission of the server as in client
server model therefore it is commonly used model because in this security is more as we can
putrestriction on both server and clients.
Difference between Workgroup & Domain
Table
1W o r k g r
o u p
D o m a i n 1. It is a
peer to peer networking model.2. There is no client and no server. All thecomputers are in equal
status.1. It is a server based networking model.2. Ther e i s a cent r al i zed dedi cat ed
s er ver computer called domain controller which
3. This model is recommended for smallnetworks, upto 10 computers.4. Ther e i s no
cent r al i z ed admi ni s t r at edseparately.5 . I n t h i s m o d e l , l o w g r a d e
O S l i k e 2000/XP professional, WIN 98 etc. can beused.6. Users accounts are created in
each PCand are called as Local Users.controls all other computers called clients.3. Thi s
model i s r ecommended f or l ar genetworks.4. There is centralized administration
andeach PC can be administrated and managedfrom the server.5. i n t hi s model hi gh
gr ade OS l i ke WI N2000/2003 Server can be used.6. Users accounts are created on the
server side and are called Domain Users.
3.1.2 Categories of network
Net wor ks can be cat egor i z ed as per geogr aphi cal ar ea t o be cover ed by
t henet wor k. Comput er net wor k ar e di vi ded i nt o f our cat egor i es i ncl udes :
Local Ar ea Network (LAN), Campus Area Network (CAN), Metropolitan Area Network
(MAN) andWide Area Network (WAN).
3.1.2.1 Local Area Network (LAN)
LAN is a computer network that is used to connect computers and work station toshare data
and resources such as printers or faxes. LAN is restricted to a smallarea such as home,
office or college. Devices used in LAN are : HUB and switch.Media for LAN is UTP cables.
Figure 1.2 shows how all work stations, server and printer are interconnected with the help of the
network device.
Fig 2: Local Area Network Types of LAN
I n LANs , dat a can be t r ans f er r ed us i ng t echni ques l i ke t oken pas s i ng. As
per techniques used for data sharing, LANS are classified into Ethernet, Token Bus, TokenRing
and Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI).Figure 3.3 shows LAN classification.
Fig 3: LAN classification
Advantages of LAN
a). Provides communication in smaller networks, easy to install and configure. b). many users
can share data or network elements at the same time which resultsin fast work.
Disadvantages of LAN
a). limited number of computers are connected in a LAN. b). LAN cannot cover large area.c).
Network performance degrades as the number of users exceeds.
3.1.2.2 Campus Area Network (CAN)
Campus Area Network is a computer network made up of two or more LANswithin a limited
area. It can cover many buildings in an area. The main feature of CAN i s t h a t a l l o f t h e
c o mp u t e r s wh i c h a r e c o n n e c t e d t o g e t h e r h a v e s o me relationship to each
other e.g. different buildings in a campus can be connectedusing different CAN. It
will help to interconnect academic departments, libraryand computer laboratories. CAN
is larger than LAN but smaller than WAN.Figure 3.4 shows a CAN network.
Fig 4: Campus Area Network
Devices used in CAN are : HUB, Switch, Layer-3 switch, Access Point .And the
mediaused for CAN is Unshielded twisted pair of cables and Fiber Optics Cable.
3 . 1 . 2 . 3 Me t r o p o l i t a n Ar e a Ne t wo r k ( MAN)
MAN is the interconnection of networks in a city. MAN is not owned by a singleorganization.
It act as a high speed network to allow sharing resources with in acity. MAN can
also be formed by connecting remote LANs through telephonelines or radio links. MAN
supports data and voice transmission. The best exampleof MAN is cable T.V network in a city.
Fig 5 : Metropolitan Area Network
3 . 1 . 2 . 4 Wi d e A r e a N e t w o r k ( WA N )
WAN covers a wide geographical area which include multiple computers or LANs.
It connects computer networks through public networks like, telephone
system,microwave, satellite link or leased line.Most of the WANs use leased lines for internet
access as they provide faster data transfer.WAN helps an organization to establish network
between all its departments and officesl ocat ed i n t he s ame or di f f er ent ci t i es . I t
al s o enabl es communi cat i on bet ween t heorganization and rest world.Devices used in
WAN is only Router
3.2 IP ADDRESSES and MAC Addresses
It is also called as logical addresses. IP is a 32 bit long and it is divided into 4octets
and dot (.) is used to separate one octet from another. It is represented in theform of
decimals. There are two versions of IP addresses:- IPv4- IPv6
Table 2 Comparison between IPv4 and IPv6
3.2.1 IP Address Classes
IP address is a 32 bit address. It is divided into various classes namely Class A, ClassB, Cl as s
C, Cl as s D and Cl as s E. TCP/ I P def i nes Cl as s D f or exper i ment al
pur pos e. TCP / I P addr es s cont ai ns t wo addr es s es embedded wi t hi n one I P
addr es s ; Net wor k address and host address as shown in figure
3.1 NETWORK ADDRESSHOST ADDRESS0 bits 31
bits I P v 4
I P v 6 - I t
i s 3 2 b i t l o n g . - I t i s d i v i d e d i n t o 4 o c t e t s . - I p v 4
p e r f o r m s b r o a d c a s t i n g , multicasting and unicasting.- I P v 4 i s
d i v i d e d i n t o 5 c l a s s e s : A to E.IPv4 is in decimal form.- I t i s 1 2 8 b i t
l o n g . - I t i s d i v i d e d i n t o 1 6 o c t e t s . - I P v 6
d o e s n t s u p p o r t b r o a d c a s t i n g , i t
p e r f o r m s multicasting and unicasting.- I p v 6 d o e s n t s u p p o r t c l a s s e s . -
I P v 6 i s i n h e x a d e c i m a l f o r m .
Class A consists of 8-bit network ID and 24-bit host ID. Class B consists of 16- bit network ID
and 16-bit of host ID. And Class C consists of 24-bit of network ID and 8-bit of host ID.
Address ClassesTable 3: Address Classes
` AddressClassStartingBits(first-byte)Ra n g e o f F i r s t OctetM a s k
V a l u e V a l i d H o s t s C l a s s
A 0 1 t o
1 2 7 2 5 5 . 0 . 0 . 0 2 5 6
* 2 5 6 * 2 5 6 -
2 = 16,777,214C l a s s B 1 0 1 2 8 t o
1 9 1 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 0 . 0 2 5 6 * 2 5
6 - 2 = 6 5 , 5 3 4 C l a s s C 1 1 0 1 9 2
t o 2 2 3 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 0 2 5 6 -
2 C l a s s D 1 1 1 0 2 2 4 t o
2 3 9 R e s e r v e d f o r
m u l t i c a s t i n g C l a s s E
1 1 1 1 2 4 0 t o 2 5 5 R e s e r v e d
f o r r e s e a r c h a n d development
3.2.1.1 How to Assign IP Address to Computer
An IP address assigned to a computer may either be permanent address or addressthat is assigned
to a computer on a time lease or for temporary basis. Hence, the addressgranted to computers
is divided into two categories Dynamic IP addresses and Staticaddresses.
Dynamic IP Addresses
Dy n a mi c I P a d d r e s s e s a r e a s s i g n e d t o t h e d e v i c e s t h a t r e q u i r e
t e mp o r a r y connectivity to the network or non-permanent devices such as portable
computer. Themos t common pr ot ocol us ed f or as s i gni ng Dynami c I P
addr es s i s DHCP al s o cal l ed
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. The DHCP grants IP address to the computer onlease
basis.
Static IP Addresses
Static IP addresses are assigned to the device on the network whose existence inthe
network remains for a longer duration. These static IP addresses are semi-permanentIP addresses
which remain allocated to a specific device for longer time e.g. Server.
3.2.1.2 How to Configure IP Address in window 2003
Right click on
My Network Places
-
properties
right click on
working LAN card
-
properties
select
internet protocol (TCP/IP)
-
properties
Tick on-
Use the following IP addresses
- now f i l l t he I P addr es s e. g
10.0.0.1
Tick on
Use the following DNS server address
Fill the
preferred DNS server
10.0.0.1
Ok
Close
Now check the connectivity of computer with itself with command
Start-run-cmd-ping 10.0.0.1
3.2.2 MAC Addressing
MAC address is a hardware address that is embedded in the NIC card. It is also
knownas hardware address or physical address. Every NIC card has a unique MAC
addressas s i gned by I EEE. MAC addr es s i s us ed t o i dent i f y t he nodes at
l ower l evel s of OSI model. The MAC address operates at the data link layer of the OSI
model.MAC address is a 12 digit hexadecimal number (48 bit address). It is made up
of numbers from 0-9 or a letter from A-F. MAC address can be written in any one of
theformats: MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS
MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SST o identify the MAC address in window:
Click
Start Run
Enter
cmd
in the
Open
text book
Type
ipconfig /all
Press
Enter
The 12 digit MAC address will be shown as say
00:11:11:EA:8D:F6
3.3 NETWORKING MEDIA
To do networking we need to use some type of media. There are many types of media.(i) Coaxial
Cable(ii) Fiber optic cable( i i i ) T w i s t e d P a i r o f
C a b l e s ( i v ) M i c r o - w a v e ( i v ) S a t e l l i t e
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable consists of an insulated copper conductor surrounded by a tubeshaped
copper braid outer copper tune and the inner conductor have the same axis
of curvature hence it called coaxial cable. It is basically of two types:( i ) B a s e
B a n d C a b l e ( R G 5 9 ) ( i i ) B r o a d B a n d C a b l e
( R G 5 8 ) We used Base Band signal cable in Networking of Computers, It is so called
becauseit carries single frequency. Its speed is 10 Mbps and impedance is 50 . Where as Broad
Ba n d Ca b l e s c a r r i e s mu l t i p l e f r e q u e n c i e s . Co n n e c t o r u s e d f o r
Co a x i a l c a b l e i s BNC(British Novel Connector) connector. ARCnet uses RG-62
coaxial cable. It has ani mpedance of 93 and has a compar at i vel y l es s er
at t enuat i on, hence yi el d gr eat er distances. These cables are expensive and provide high
propagation factor.
Fiber Optical Cable
Fiber optic cable consists of a very fine fiber made from two types of glass, one for
theinner core and the other for the outer layer. Here signal is transmitted in the form of
light.Different varieties of fiber optics is used depending on the size of the network.
Singlemode fiber optics is used for networks spanning longer distance. Fiber Optics has
lower propagation factor than coaxial cable. It is a costly but more secure transmission media.
Twisted Pair Cable
There are two wires, which are twisted with each other to avoid EMI
(ElectroMagnetic Induction).these cables are easy to terminate. However they have
a slightlyhigher value of attenuation value and hence have limited distance covering
capacity.Connect or used for Twisted Pair of Cable is (Registered Jack) RJ-45 and
RJ-11. Thereare two types of twisted pair of cables:
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair)
:
In this an extra wire which is called shielded wire is wrapped over the inner cover whi ch
hol ds copper i n pai r s . Thi s pr ot ect i on i s us ed t o pr ot ect s i gnal f r omexternal
noise.
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)In this type of wire no shielded cover is there for extra protection
from noise.There are different categories of UTP cables:
Categories of UTP Cables
Table 4: Category and Speed of UTP cables
C a t e g o r y S p e e d
CAT-1CAT-2CAT-3CAT-4CAT-5CAT-6CAT-756 Kbps4 Mbps10 Mbps16-20 Mbps100
Mbps1Gbps1Gbps
3.3.1 Ethernet Cabling
There are three types of Ethernet cables:
Straight cable
Crossover cable
Rolled cable
3.3.1.1 Straight cable
It is used when we have to connect
PC TO Switch
PC to Hub
Hub to Router
Switch to Router
Colour Coding for straight Cable
TABLE 5
568A(one end) (other end)568B(one end) (other
end)Green/whiteGreenOrange/whiteBlueBlue/whiteOrangeBrown/whiteBrownGreen/whiteGree
nOrange/whiteBlueBlue/whiteOrangeBrown/whiteBrownOrange/whiteOrangeGreen/whiteBlueB
lue/whiteGreenBrown/whiteBrownOrange/whiteOrangeGreen/whiteBlueBlue/whiteGreenBrown
/whiteBrown
3.3.1.2 Crossover Cable
It is used when we have to connect:
PC to PC
Hub to Hub
Switch to switch
Router to Router
PC to Router
Hub to Switch
Colour Coding for Crossover cable
Table 6
Colour Coding for Crossover cable
(one end) (other end)
Orange/whiteOrangeGreen/whiteBlueBlue/whiteGreenBrown/whiteBrownGreen/whiteGreenOra
nge/whiteBlueBlue/whiteGreenBrown/whiteBrown
3.3.1.3 Rollover Cable
Rollover cable isnt used to connect any Ethernet connections together, butRollover cable can
be used to connect a host to a router console serial communication(com) port.NOTE:
Straight cable and Cross cables are used for data transfer but Rollover cables are not
used for data transfer.There are two methods for manufacturing Rollover cables:
Table 7
Colour Coding for Rollover Cable
568A(one end) (other end)568B(one end) (other end)
Green/whiteGreenOrange/whiteBlueBlue/whiteOrangeBrown/whiteBrownBrownBrown/whiteOr
angeBlue/whiteBlueOrange/whiteGreenGreen/whiteOrange/whiteOrangeGreen/whiteBlueBlue/
whiteGreenBrown/whiteBrownBrownBrown/whiteGreenBlue/whiteBlueGreen/whiteOrangeOra
nge/white
3.4 OPERATING SYSTEM
3.4.1 Types of Operating Systems
( i ) DOS ( De s k t o p Op e r a t i n g S y s t e m) ( i i ) NOS ( Ne t wo r k
Op e r a t i n g S y s t e m)
Table 8: Operating Systems
DOS
1. It is a desktop operating system.2. It is used in small networks.3. In this OS, there is less
security.4. In this OS, all computers are clients.5. I n t hi s OS, MS- DOS, GUI
packageWin3.1, Win 95, Win 98, Win ME comes.
NOS
1. It is a network operating system.2. It is used for large networks.3. In this OS, there is more
security.4 . I n t h i s O S , t h e r e a r e s e r v e r s a n d clients.5. In this OS Win NT,
Win 2000, Win2003, LI NUX, UNI X, Novel l andMAC comes.
3.4.1.1 Introduction to Window 2003 Server
Window server 2003 (also referred to as WIN 2k3) is a server operating system produced by
Microsoft. Introduced in 24
th
April 2003 as the successor to window 2000 server, it iscons i der ed by Mi cr os of t t o be
t he cor ner s t one of i t s wi ndow s er ver s ys t em l i ne of bus i nes s s er ver
pr oduct s . An updat e ver s i on Wi ndow Ser ver 2003 R2 was
r el eas edmanufacturing on 6
th
dec, 2005. its successor window 2008 was released on 4
th
feb, 2008.Ac c o r d i n g t o Mi c r o s o f t , wi n d o w s e r v e r 2 0 0 3 i s mo r e
s c a l a b l e a n d d e l i v e r b e t t e r performance than its predecessor window 2000.
Features of Window 2003
( i ) A s i g n i f i c a n t i mp r o v e d v e r s i o n o f I n t e r n e t I n f o r ma t i o n S e r v i c e
( I I S ) ( i i ) I n c r e a s e d d e f a u l t s e c u r i t y o v e r p r e v i o u s v e r s i o n d u e t o
t h e b u i l t i n f i r e wa l l and having most services disabled by default.( i i i ) Ma n a g e
y o u r s e r v e r - a r o l e ma n a g e me n t a d mi n i s t r a t i v e t o o l s t h a t a l l o w
a n administrator to choose what functionality the server should
provide.( i v ) I m p r o v e m e n t t o A c t i v e D i r e c t o r y . ( v ) I mp r o v e me n t t o
Gr o u p P o l i c y h a n d l i n g a n d Ad mi n i s t r a t i o n . ( v i ) P r o v i d e s a Ba c k u p
s y s t e m t o r e s t o r e l o s t f i l e s . ( vi i ) I mpr oved di s k management , i ncl udi ng
t he abi l i t y t o Backup f r om s hadows of files, allowing the Backup of open
files.( v i i i ) I mp r o v e d s e c u r i t y a n d c o mma n d l i n e t o o l s wh i c h a r e p a r t
o f Mi c r o s o f t initiative to bring a complete command shell to the next version of
window.( i x ) S u p p o r t f o r a h a r d b a s e d Wa t c h Do g T i me r , wh i c h c a n
r e s t a r t t h e s e r v e r i f the operating system does not suspend with in a certain amount of
time.
Removed Features
The ability of creating server disk automated system recovery (ASR) is usedinstead .
Edition of Window 2003
Wi ndow s er ver 2003 comes i n a number of edi t i ons , each t ar get ed t owar ds
a particular size and type of business. In general, all variant of window server 2003
have t he abi l i t y t o s har e f i l es and pr i nt er s , act as appl i cat i on s er ver and
hos t mes s age queue, pr ovi de emai l s er vi ces , aut hent i cat e us er s , act as an
X. 509cer t i f i cat e s er ver , pr ovi de LDAP ( Li ght Wei ght Di r ect or y Acces s
Pr ot ocol ) services, serve streaming media, and to perform other server-oriented functions.
3.5 DNS SERVER
DNS stands for domain name system. DNS system is a standard technologyfor managing the
names of websites and other internet domains. DNS techniques allowsyou to type names into
your web browser like computer networking, about computer andallow your computer to
automatically find that address on internet. DNS is the resolutionmechanism used by
Window Server 2003
clients to find other computers and servicesrunning on those computers for
computers in a window 2003 network infrastructure totalk to one another, one of the key
ingredients is the DNS server .Host name alone do notcommunicate globally but communicate
locally, but if domain name is added along withit then the host name can communicate globally.
DNS is use for name reservation i.e. toconvert IP address to host name and host name to IP
address or the function of DNS is toresolve host name such aswww.yahoo.comto an IP
address. User identify only user friendly name and all computers and technologies identify
IP address and MAC addressDNS is use to solve this problem because DNS is used to convert
host name FQDN (fullyqualified domain name) to IP address and IP address to host name .
3.5.1
PARTS OF DNS SYSTEM
(i) Host name(ii) Domain name
(iii) FQDN(iv) Namespace(v) DNS server
3.5.1.1 HOST NAME
Host name is a computer name and is also called is NetBIOS (network basicInput/ output
system) name. NetBIOS is actually an application layer protocol that canuse the transport
services of TCP/ IP when used in routed network. A NetBIOS name is16- byte
addresses that identify a NetBIOS resource on the network.
3.5.1.2 DOMAIN NAME
Domain name is used to identifies the internet site one can identifies the locationwithout having
to remember the IP address of every location e.g. yahoo.com or gmail.com
3 . 5 . 1 . 3 F Q D
FQDN means fully qualified domain name which represents a hostname appended to the parent
name space in hierarchy. Also in fully qualified domain name different levels
of names pace ar e vi s ual i z e as i n f i g bel ow t hi s hi er ar chy i s vi s ual i z ed
t he r oot l evel namespace, top level domain, and so on, in use throughout the internet today.
Left most portion of the FQDN is the host portion of the name. A host name is alias
we give to anIP address.
Fig 6:To find location of a computer using FQDN
FQDN is a unique name in the computer on the network. We can identify host id andlocation of
a computer as in fig above. Suppose we want to find location of pc1 withIP address 20.0.0.1,
which is in lab2, 2
nd
floor in the organization center. The FQDNfor this is
Pc1.row3.lab2.floor2.center.com
But this address is very lengthy to locate pc1 so to simplify this we use c
nametechnique as:
Pc1.center.com=20.0.0
.1
3.5.1.4 Domain Namespace
DNS o p e r a t e s i n wh a t i s k n o wn a s DNS n a me s p a c e . T h e DNS
n a me s p a c e i s a n organized, hierarchical division of DNS names. Domain namespace
enable users to easilyl ocat e t he net wor k s er vi ces and r es our ces . The domai n
names pace i ncl ude t he r oot d o ma i n , t h e t o p l e v e l d o ma i n o f t h e
o r g a n i z a t i o n a n d o r g a n i z e t h e s e d o ma i n i n a hierarchical tree structure.
Namespace works on the hierarchical tree structure of rootdomain. There are total 13
root domain working in the internet, they are A, B, C, D, E, F,G, H, I, J, K, L and M. There
is one root domain, which acts as the starting point of the
full y qualified domain names. This root domain is designated with a dot (.). Fig
6.2shows the tree structure or domain namespace.
Fig 7: Tree structure or Domain Namespace3.5.1.5 DNS server
Any computer providing domain namespace is a DNS server. DNS server is used
toconvert host name FQDN into IP address and IP address into host name FQDN. To storethe
name-to-IP-addresses mappings so crucial to network communication, name
server uses zone files.
3.5.2 DNS Zone
Zone is the part of DNS database that contain record of domain or multiple domain.If the
domains represents logical division of the DNS namespace, zones represents
the physical separation of the DNS namespace. In other words information about records of the
resources within DNS domain is stored in a zone files, and this zone files exist
onhard drive of server. Zone files are divided into one of two basic types:
Forward lookup zone:
Provides host-name-to-IP-address resolution
Reverse lookup zone:
Provides IP-address-to-host-name resolution
3.5.2.1 Resource record stored in a zone file
Each record stored in a zone file has a specific purpose. Some of the records set the behavior of
the name server, others have the job of resolving a host name or service intoan IP table.
( i ) N S ( N a m e S e r v e r ) :
These specify the name servers that are authoritative for a given portionof DNS namespace.
These records are essential when DNS servers are performingiterative queries to
perform name resolution.
( i i ) S O A ( S t a r t o f A u t h o r i t y ) :
This resource record indicates the name of origin for the zone contains the nameof the server that
is the primary source for information about the zone. The information ina n S OA r e c o r d
a f f e c t h o w o f t e n t r a n s f e r o f t h e z o n e a r e d o n e b e t we e n
s e r v e r s aut hor i t at i ve f or t he zone. I t i s al s o us ed t o s t or e ot her pr oper t i es
s uch as ver s i oninformation and timings that affect zone renewal or expiration.
( i i i ) C N A M E ( C a n o n i c a l N a m e ) :
CNAME can be used to assign multiple names of a single IP address.
For example, the server hosting the sitewww.abc.comis probably not named www, but
aCNAME record exist resolution of www to an IP address all the same. The
CNAMErecord actually points not to an IP address, but to an existing A record in the zone.
3.5.2.2 Steps to Install and configure DNS server
Start control panel add and remove program
Add remove window components
Select
networking services
and click on
detail button
Check box of
DNS server
Ok
and
finish
3.5.2.3 Creating a Forward Lookup Zone
Statically fill the IP address
Start administrator tools
DNS
right click on
forward lookup zone
New zone next
Select
primary zone next
Enter
zone name (abc.com) next
Tick
Allow both secure and non secure updates and secure dynamicupdated
next next
now click on
created zone (abc.com)
new host
ent er hos t name f or gl obal l evel ( i . e by ent er i ng www) f i l l I Paddress of the
web server , click on
add
button
enter another host name, a blank host with same IP i.e do not fill its host name
steps to change SOA and NS records
Right click on
SOA records properties
Fill primary server e.g (www.abc.com) responsible person
host master.abc.com apply ok
right click on
NS records
click on
add button
enter FQDNwww.abc.com
resolve ok apply ok
Now go to start menu
ping abc.com
On Client Side To access DNS server fill IP address of server then use ping commande.g
pingwww.abc.com3 . 5 . 2 . 3 C r e a t i n g a R e v e r s e L o o k u p Z o n e
Right click on
reverse lookup zone
New zone next
select
primary zone next
fill
Network ID next next
Select
allow both non secure and non secure dynamic updates
Finish
Right click on created reverse zone
new pointer
enter
host IP number
e.g (50.0.0.50)
enter
FQDN (www.chd.com)3.5.2.4 Some DNS Commands
(i) c:>tracertwww.yahoo.com
command i s us ed t o check t he pat h , a dat a packet f ol l ow f r om one
r out er to another router.
(ii) c:>nslookup
command display the domain name with IP (works only when reverse lookupzone is set up).
( i v ) c : > i p c o n f i g / a l l
This command display FQDN, IP address, MAC address.
(iv) c:>ipconfig /flushdns
This command flush or clear all the information in the cache that is retrievedfrom DNS server.
(v) c:>ipconfig /displaydns
Display the current contents or entries in the cache.
( v i ) c : > i p c o n f i g / r e g i s t e r
register any DNS name
3.6 DHCP SERVER
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a protocol that allocates IP address tocomputer
on a network. DHCP centralized the management of IP address allocation andreduces human
error associated with manual IP configuration. DHCP server supplies allthe necessary
networking param-eters. Two things are always handed out as a part of DHCP
conf i gur at i on: I P addr es s and s ubnet mas k. Fur t her DHCP wi l l
f r equent l yconfigure clients with optional values, such as a default gateway, DNS
server address,and the address of a Window Internet Naming Server, if one is present.
Scenario showingDHCP server IP address allocation.
3.6.1 Working of DHCP Server
( i ) D H C P S c o p e ( i i ) D H C P S u p e r
S c o p e ( i i i ) E x c l u s i o n I P R a n g e ( i v ) D H C P L e a s e
T i m e ( v ) I P R e s e r v a t i o n
DHCP Scope
Scope having the range of IP address for providing dynamic IP address to other computer. A
group of IP address within a scope is called as DHCP scope.
DHCP Super Scope
A super scope is used to combine two or more scopes each serving different subnets, andcan
make t he admi ni s t r at i on of s ever al s copes on wi ndow 2003 DHCP s er ver
mor emanageable. Using super scope you can group multiple scopes as a single administrative
entity that allows the client to lease from either one. With this feature, a DHCP
server can:
Suppor t DHCP cl i ent s on a s i ngl e phys i cal net wor k s egment wher e
mul t i pl elogical IP networks are used. When more than one logical IP network is
used oneach physical subnet or network, such configuration is called multinets.
Support DHCP clients located on the far side of DHCP and BOOTP relay agent.
In multinet configuration, DHCP superscope can be used to group and
activateindividual scope ranges of IP addresses used on your network. In this way ,
aDHCP server computer can activate and provide leases from more than one scopeto clients on a
single physical network.
Exclusion IP range
If you want to reserve some IP for any computer i.e if we want that from the series
of 192. 168. 0. 2 t o 192. 168. 0. 100 i f we want t hat a s er i es of I P addr es s es
mus t not beassigned automatically then at can be done using exclusive IP range.
DHCP Leased Time
DHCP l eas e t i me i s val i di t y of I P addr es s . By def aul t DHCP l eas e t i me i s
8 da ys minimum,1 day maximum 999 days, 23 hours to53 day.With in 8 days:-After 80% of
day clients demand new IP some times server refuse the client request.After 87.5%
of days it will retry, and if the server did not give the new IP address thenthe client
will receive APIPA address (Automatic Private IP Address).When a DHCP client is unable to
locate a DHCP server, the client picks out a random IPaddress from the private APIPA
address range of 169.254.*.*, with a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0. The 169.254.*.* IP
range is private because that network number is not inuse on the internet, it is random because
the client generates an arbitrary host number for that network.The significance of APIPA is that
DHCP client computers that cannot find aDHCP server can still be assigned an IP address and
communicate with other computerson the same subnet mask that also cannot find DHCP
server. It allows communication
when DHCP server is down or just plain not there. Note that APIPA does not assign
adefault gateway, and therefore it cannot communicate with any computer that lives on theother
side of a router.
IP Reservation
There are some DHCP clients that you want to be the DHCP clients, but you will
alsowa n t t o ma k e s u r e t h a t t h e y g e t s a me I P a d d r e s s e v e r y t i me .
T h i s c a n b e d o n e b y statically filling the IP address. We can reserve IP address with the
help of MAC addressfor a particular computer.3.6.2
Installation Steps of DHCP Server
start control panel
add and remove program add and remove window components
select
networking services
and click on
detail button
check box of
DHCP server
ok finish
3 . 6 . 2 . 1 S t e p s To Co n f i g u r e DHCP S e r v e r
start program administrative tool
select
DHCP
create new scope in action menu new scope next
give
scope name
next
give
IP address range
next
add
exclusion name next
check
lease duration next finish
After DHCP server is configured, it is required to be authorized and DHCP
scopeshould be active. For that select DHCP server and click on authorize in action
menu.Then right click on scope name and click on active.
3 . 6 . 2 . 2 O n C l i e n t S i d e
Go to
LAN card properties
select
TCP/IP protocol properties
Select
obtain IP address automatically
Go to
command prompt (cmd)
Give
command
3 . 6 . 2 . 3 B a c k u p o f D H C P S e r v e r
We c a n t a k e b a c k u p o f a l l t h e c o n f i g u r a t i o n i n D H C P s e r v e r
w i t h t h e h e l p o f administrator. Backup means to export the DHCP database
to another system, as it ishel pf ul i n cas e due t o any r eas on our dat a i s
cor r upt ed or del et ed, we can t ake our database from the place where it is stored.
Steps of taking backup :
Stop the DHCP server and disable the DHCP server services
Copy the DHCP server directory to a temporary location, say pen drive or on a new DHCP
server.
3. 6. 3DHCP Rel ay Agent
The DHCP relay agent is a software that listen DHCP discover packet and forward
toDHCP server. In window 2003 server system the DHCP relay agent can be enabled as a part of
Routing and Remote Access (RRAS).
3.6.3.1 Steps To Configure DHCP Relay Agent
Set the network, fill the IP address and select two LAN cards
Open
Routing and Remote Access enable Routing and Remote Access
Right click on
general new routing protocols
Select
DHCP relay agent
New interface
Select
LAN card which is to be connected to the cross cable i.e L1
Ok
Right click on
relay agent properties
Enter IP address of DHCP server
add apply ok
3.7 ACTIVE DIRECTORY
With the release of Windows 2000, Microsoft introduced Active Directory, a
scalable,robust directory service. Active Directory is used to create server based
networking.Active Directorys job is to store and make available a Directory database i.e
informationabout the user, its class, name, address, mails, phone numbers, location.Active
Directory is a technology created by Microsoft that provides a variety of n e t wo r k s e r v i c e s
l i k e Di r e c t o r y S e r v i c e s , DNS b a s e d n a mi n g a n d o t h e r
n e t wo r k i nf or mat i on. Act i ve Di r ect or y al s o al l ows admi ni s t r at or t o
as s i gn pol i ci es , depl oysoftware and apply critical updates to an organizations. Active
Directory was previewedin 1999, released first with window 2000 server edition and revised to
extend functionallyand improve administration in Window 2003. Additional
improvements were made inWindow server 2003 and Window server 2008.The
f undament al bui l di ng bl ock of Mi cr os of t s Di r ect or y s er vi ces cont i nues t o
be adomain. A domain is logically grouping of network resources, including shares,
printers,groups and users accounts. The user account represents the individual to
domain, andallows for different type of access and different types of tasks. Every
users account isunique. It has uniqueness of the user account that allows administrator to
control accessfor every member of domain.There are two types of users accounts: local account
and domain account. Localaccounts are maintained in the local database of a computer
and cannot be used to grantaccess to network resources. Local users are primarily used to
administer a computer or to allow several people to share a single computer that is not
a member of a domain.Whereas domain users accounts are much more widely used
in organizations that localuser accounts because they allow for central
administration and user can log onto anycomputer in the domain. Domain users accounts
are stored in Active Directory.
3. 7. 1Act i ve Di rect ory Servi ces
A computer network can be divided logically into two networking models.
Workgroup
Domain
Difference Between Workgroup and Domain
Table 9W o r k g r o u p
D o m a i n 1. I t i s a peer - t o- peer
net wor ki ngmodel.2. Ther e i s no cl i ent and no s er ver . All computers are in equal
status.3. Thi s model i s r ecommended f or small networks (upto 10 pcs).4. Ther e i s
no cent r al i z ed Admi n- i s t r a t i o n a n d e a c h P C
i s administrated separately.5.In this model, low grade operatings ys t em l i ke 2000/ xp
pr of es s i onal , win 98 etc can be used.6. Wor kgr oup can be gi ven names like sales,
HR, accounts etc.1. It is a server based networking model.2.there is a centralized dedicated
server c o m p u t e r c a l l e d d o m a i n c o n t r o l l e r (DC)which controls all other
computerscalled clients.3. This model is recommended for largenetworks.4. Ther e i s
cent r al i z ed admi ni s t r at i onand each PC can be admi ni s t r at ed andmanaged
from the server.5 . I n t h i s mo d e l h i g h g r a d e o p e r a t i n g s ys t em , l i ke
wi n2000/ 2003 s er ver ar eused.6 . Do ma i n c a n a l s o g i v e n n a me s
l i k e abc.com, xyz.com etc.
7 Users accounts are created in eachP C a n d a r e c a l l e d a s Lo c a l
Us e r s . 7 . Us e r s a c c o u n t s a r e c r e a t e d o n s e v e r s i d e D C a n d a r e
c a l l e d a s D o m a i n Users.Active Directory uses domain to hold objects, each domain
has security boundary.Users must authenticates to the domain in which their users account
resides before theycan acces s r es our ces , s uch as a s har ed f ol der s . Act i ve
Di r ect or y al s o l i nks r el at eddomains in a hierarchical structure and users can access
resources in any of the domain inwhich their user account resides. The hierarchical structures of
related domain is called atree, and all domains in the tree share the same Domain Name System
(DNS) namespace.All the domains and the trees in a single organization are called a forest. All
domains inthe forest share same schema.
3 . 7 . 1 . 1 T y p e s o f D o m a i n
Domain Forest
Domain Tree
Organization unit
Domain Forest
A f o r e s t i s c r e a t e d wh e n wi n d o w 2 k 3 s e r v e r c o mp u t e r i s
c o n f i g u r e d a s a d o ma i n controller. A forest is a collection of multiple domain
link together and relationship between the domains.
Domain Tree
A domain tree is made up when there is a parent child relationship between the domainin the
forest. The child domain includes the complete parent domain name. a tree is a setof two or
more domains sharing common namespace e.g we can create a parent domainand
then child domain like mail. yahoo.com; where mail- child domain, yahoo-
parentdomain.
Fig 8: Structure of domain forest and domain treeOrganization Unit (OU)
Organization unit is the smallest unit in a domain network that can contain
users,computer groups, shared folders, printers and group policy object in simple
words. OUmeans department like sale department, accounts department like sales,
accounts in acompany OU can be used to apply different security policies to
computer and users ind i f f e r e n t d e p a r t me n t . OU a l s o h e l p s i n d i v i d i n g
a d mi n i s t r a t i o n a mo n g d i f f e r e n t administrator of managing only computer and users
of sales department.
3 . 7 . 1 . 2 T y p e s o f D o ma i n C o n t r o l l e r
( i ) P D C : P r i m a r y d o m a i n c o n t r o l l e r ( i i ) A D C :
A d d i t i o n a l d o m a i n c o n t r o l l e r ( i i i ) B D C : B a c k u p d o m a i n
c o n t r o l l e r
Primary Domain Controller (PDC)
This is the first domain controller, in this domain all entries are created in it likeusers account,
group policy, Organization unit etc. All FSMO role are done in PDC.
Additional Domain Controller (ADC)
It is a domain network, it is important to have more than one DC so that if oneDC fails, the
other DC will continue serving the client. There is also load balancing of Active
Directory Service if we have more than one DC.The first DC we create is simply called PDC and
if we create an extra DC thent hat DC i s known as ADC. ADC has s ame
conf i gur at i on of AD as pr i mar y domai ncontroller.All domain controllers in a
domain networking are masters. We can make achange in the active directory of any
domain controller and that change is replicated to allother domain controllers. Replication takes
place among all the domain controllers and iti s cont r ol l ed aut omat i cal l y. I f we
cr eat e a us er i n t he f i r s t domai n cont r ol l er , i t i s automatically created in the ADC
because of replication.All the domain controllers in the domain networking are peers and this
model iscalled as multi- master model
.
Fig 9: Multi-Master Model
3.7.1.3 Requirements of Active Directory
( i ) W i n d o w 2 0 0 0 / 2 0 0 3 s e r v e r c o m p u t e r . ( i i ) A t l e a s t
o n e N T F S p a r t i t i o n .
( i i i ) S t a t i c I P a d d r e s s ( i v ) A t l e a s t 1 G B f r e e h a r d d i s k
s p a c e ( v ) L A N c a r d e n a b l e d a n d c o n n e c t e d t o t h e
n e t w o r k ( vi ) I ns t al l DNS, i f not i ns t al l ed of Act i ve Di r ect or y and
conf i gur e i t . I t s h o u l d b e n o t e d t h a t a c t i v e d i r e c t o r y c a n n o t
w o r k w i t h o u t D N S . D N S i s automatically installed and configured during the
Active Directory installation.
3.7.1.4
Installation of Active Directory
First of all fill the static IP address, then install DNS service into it and after
thatinstall the Active Directory
start run dcpromo
Ok
Welcome to active directory
next next
Select domain controller for a new domain e.g
(gmail.com)
Next
Domain NETBIOS name (gmail.com)
Next
Data folder, folder new tech directory service
next
(SYS VOL)
Next
Click on install and configure the DNS server on this computer to use thisDNS server
as its preferred DNS server.
Tick on permission compatible only with window server
Next
Enter the restore mode and the password
next next finish
now restart computer Command used for the removal of Active Directory
start run dcpromo
This command is also used to remove active directory, if after this command theactive directory
is not removed then type
startrun
cmddcpromo /forceremoval
Ok
How to identify Active Directory installation
Start administrator tool
After that if three options specified if come, it means that Active Directoryhas been installed
Active Directory domain and trusts Active Directory sites and services
Active Directory users and computer Open DNS console by
Administrator toolsDNS
Forward lookup zone msdcs.exam.edu
start of authority (SOA)
name server (NS) Now ping active directory with domain name like
start run ping gmail.com
Backup of Active Director
Active Directory backup
come in use when there is some problem in active directory. If there is any problem in
active directory then remove it and restore the backup.
Start runntbackupok
Select advance mode and untick that is already ticked
Select backup
Selsct system state
Change backup path browse keep in your hardware and then send it to the pen drive
D:\
adbackup
3 . 7 . 2 CHI LD DOMAI N
A domain is created say xyz.com. this domain is known as parent domain or theroot domain.
Now chd.xyz.com will be the child domain or the sub domain of xyz.com.
Fig 10 : parent-child relationship model
A child domain is created to ease administration in a very large domain network. We cancreate
the parent domain in the head office of the company and the child domain in
the branch offices.Each branch office will have its own administrator to manage the
users of thechild domain present in the branch office.A true relationship is automatically
created between the parent domain and thechi l d domai n. Thi s means us er s i n t he
chi l d domai n can acces s t he f i l e s er ver of t he
parent domain. Moreover users of either domain can use clients of either domain
for l oggi ng i n t he domai n but a us er can al ways l ogon onl y i n t he domai n
i n whi ch hi s account resides, though he physically can use client pc of parent or client
domain. Usersof either domain can logon its own domain from either side but only when it use
its owndomain name. users of parent domain can communicate with child domain but
he has touse its domain name for that.
3 . 7 . 2 . 1 S t e p s t o c r e a t e c h i l d d o ma i n
First of all install the active directory on pc1 i.e on the parent domain. Now make
Tomuser on it. On pc2 create the child domain, then make users on it, user- RamBelow are the
steps to cerate child domain.
Fill the IP address in the child domain
Now ping to the parent domain with the domain name (xyz.com)
Run dcpromo ok
next
select domain controller for a new domain
next
select child domain and existing domain name (mcse.com)
next
enter username, password and domain name
enter user parent domain name also enter child domain name
enter complete DNS name i.e xyz.mcse.com
next next next next
it should be noted that parent domain can logon into child domain but on the
other hand child domain cannot logon to the parent domain. Also parent domain can
apply policies or security on the child domain.Make the client member by entering particular
user with its domain name.
First right click on
My Computer
Properties
Computer name
Change
Write domain name ok Now logoff start and then write user name - TomDomain name -
mcse.comAgain logoff and check the other user Start-user name- abcDomain name
mail.mcse.com
3.8 INTERNET SHAREING
We can share a single internet connection to multiple computers with the help
of networking or internet sharing. There are four ways to share
internet.( i ) D i r e c t s h a r i n g ( i i ) I C S I n t e r n e t
c o n n e c t i o n s h a r i n g ( i i i ) W i n P r o x y ( i v ) N A T
N e t w o r k A d d r e s s T r a n s l a t i o n
3.8.1 Direct Sharing
Internet sharing can be done between computers directly, just by taking
internetconnection directly from ISP (Internet Server provider), then it is provided
to ADSLmodel , ADSL modem i s connect ed t o t he I SP t hr ough RJ - 11
connect or . Then i t i s
connected to the switch with RJ-45 connector. Switch, further connects computers thosehave to
be provided with internet connection. The scenario for direct sharing is as shownin figure:
Fig: 11: Direct Sharing Scenario
ADSL modem has IP address 192.168.1.1. All the PCs are assigned with a
DNS(Domain Name Server) and GW (gateway) -192.168.1.1. Also DHCP (Dynamic
HostCo mmu n i c a t i o n P r o t o c o l ) i s e n a b l e d wh i c h wi l l p r o v i d e I P
a d d r e s s e s t o t h e P Cs automatically.
3.8.2 ICS (Internet Connection Sharing)
Internet Connection sharing provides an alternate way to provide Internet Sharing.ICS requires
a server with two network interfaces, one for the private internal
network conf i gur ed wi t h I P 192. 168. 0. 1 addr es s and an adapt er f or publ i c
connect i on. I CSrequires two connections in order to work: one public and one
private i.e. ICS server
requires two LAN cards, Internal (Private) and External (Public). Internal LAN card usesLocal
LAN card (L2) and External LAN card (L1) is used by Internet. ICS is designed to be as
simple as possible. ICS works on following windows: XP, Vista, 2K3 Server,
2k3Server SP1.it doesnt work on the server in which AD+SP1 is present. The
scenario for ICS is shown below:
Fig 12: ICS scenario
No t e : - Wh e n we c o n f i g u r e I CS t h e n t h e l o c a l c a r d d e t e c t
1 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 0 . 1 a d d r e s s automatically.
How to configure ICS
Open
network and sharing center
Network- Properties
Click on
Manage network connections
Right click on
LAN Card
which is used for internet-
Properties
Click on
sharing
Enable ICS
Ok
yes
3.8.3 Win Proxy Server
Win Proxy is a third party software which is used for sharing internet and we canalso block the
web site with the help of win proxy. WIN Proxy supports all the threeclasses A, B, C
also it is supported by all operating systems. The scenario for WIN proxyis shown below:
Fig 13: scenario of win proxy server
In win proxy as shown in the scenario above we can share internet. First of all a ADSLmodem
is connected to the ISP (Internet Service Provider) by a RJ-11 connector andother
end of ADSL modem is connected to the PC1 through RJ-45. Assign IP address192. 168. 1. 1
t o t he ADSL modem al s o enabl e t he DHCP s er ver and s et t he s t ar t
I Paddress of 192.168.1.2 and end IP address of 192.168.1.254. Then after ADSL
modemconnect PC1, assign GW 192.168.1.1 and
3.8.4 NAT (Network Address Translation)
If we have to connect many computers with a single IP address then we will use NAT. NAT
exchange IP packet between local network and internet. The routing and
remoteaccess server of window 2K3 server provide us with a component known as
NAT. Byenabling NAT on a Server 2003 system, you allow connected users on a private
system to
share a single connection to access a public network such as the internet i.e. NAT
enablemultiple client computer to connect the internet through a single publicly
registered IPaddress. A NAT server translate private IP address to public addresses. NAT
eliminatesthe need for large number of IP addresses by mapping externally assigned IP
addresses.
Fig 14: NAT server
When deploying NAT, it is needed to configure setting on both the client sideand the server
side. On the server side of NAT fill the IP address statically.
3.8.4.1 Steps to enable NAT server
Open
internet
Tools
Internet options
connections
LAN settings
untick the
IP and port address
ok
ok
give site name. On t he cl i ent s i de of NAT, cl i ent s i de i s conf i gur ed t o
obt ai n I P addr es s es aut omat i cal l y and t hen r es t ar t t he cl i ent s ys t em.
As s umi ng NAT i s us ed f or addr es s assignment, the client system will receive TCP/IP
information from the NAT server. Theclient information includes:
IP address from 192.168.0.0 private addressing range
Subnet mask (255.255.255.0)
DNS server address, which would be the address of the NAT interfaceon the
server.With the client side configured, there are few things to do on NAT server:
The first step to configure NAT server is to actually install the Routing and
RemoteAccess Services. To do this, start the Routing and Remote Access Service Setup
Wizard.
Start
administrator tools
Routing & Remote Access
Right click on
My Computer
right click on
computer name
Select option
Configure and enable routing & remote access
Welcome to routing
next
next
Select
NAT
next
Select
LAN card
which is to be connected to internet
next
next
From any of the four methods of internet sharing only method is used at atime to
remove the other method
go to
start
setting
add & remove
change/ remove
, tick on
remove.
3.9 VIRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORK (VPN)
A virtual private network is used to convert public network address to
privatenet wor k. Al l t he cl i ent s of VPN di al t o publ i c I P addr es s of VPN
s er ver and r ecei ve pr i vat e I P f r om vi r t ual VPN dynami c hos t pr ot ocol
( DHCP) . i n VPN one can havemultiple virtual connections to a single IP address. This
way ,one network card can hostseveral inbound connections, rather than require a
modem and telephone line for eachsimultaneous remote user.
Fig 15 : scenario of VPN server
Using VPN server we can connect many private networks to internet services i.e
theremote connection. We can create a private network through public network, we can
usefirewall for security and data encryption in VPN server.
3 . 9 . 1 VPN c o mp o n e n t s
( i ) V P N s e r v e r ( i i ) V P N
C l i e n t s ( i i i ) W A N O p t i o n ( i v ) S e c u r i t y
O p t i o n s
VPN Server
VPN server, serve as the end points of a VPN connection. When configuring aVPN
server, you can allow access to just that server, or pass traffic through VPN server so that the
remote user gain access the resources of the entire network.
VPN Client
VPN clients establish connection to VPN server. They can also be routers thatobtain
the router-to-router secure connection. VPN client software is included in all
themodern window operating systems, including Window 2003 server. Router-to
router VPN connection can be made from computers running server2003 and
Windows 2000
running Routing and Remote Access. Additionally, any client that support PPTP
or L2TP connections can be VPN clients of a window server 2003 system.
WAN Options
These provide the physical mechanism for passing data back and forth.
Theseconnections typically include such similar network technologies such as T1or
framerelay. In order for VPN connections to be successful, the VPN client and VPN
server must be connected to each other using either permanent WAN connection or
by dialinginto an internet server provider (ISP).
Security Options
Since a VPN uses a network that is generally open to the public, it is
importantt h a t t h e d a t a p a s s e d o v e r t h e c o n n e c t i o n r e m a i n
s e c u r e . T o a i d w i t h s e c u r e communication routing and remote access
supports such security measure as logon anddomain security, data encryption, smart cards,
IP packet filtering and caller ID.
3 . 9 . 2 T y p e s o f V P N
( i ) P P T P ( P o i n t t o P o i n t T u n n e l i n g P r o t o c o l ) ( i i ) L2 T P
( La y e r 2 T u n n e l i n g P r o t o c o l ) a c c o r d i n g t o CCNA.
Point to Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
PPTP is Microsofts legacy protocol for supporting VPN. It was developed
inconjunction with other communications companies such as Robotics as an
extension tothe PPP protocol. PPTP encapsulates IP or IPX packets inside of PPP
datagrams. Thismeans that you can remotely run programs that are dependent upon
particular network pr ot ocol s . One of t he keys t o r emember about PPTP i s
t hat t he pr ot ocol pr ovi des encr ypt i on capabi l i t i es , maki ng i t much s af er t o
s end i nf or mat i on over nons ecur e networks.
Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
L2 T P i s a s t a n d a r d b a s e d e n c a p s u l a t i o n p r o t o c o l wi t h r o u g h l y t h e
s a me functionality as a Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). One of the key differences
bet ween Wi ndow s s er ver 2003 i mpl ement at i on of L2TPand i t cous i n
PPTP i s t hat L2TPis designed to run natively over IP networks only. This
implementation of L2TPdoes not support native tunneling over X.25, frame relay, or ATM
networks. Like PPTP,L2TPencapsulates Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) frames, which
then encapsulate IP or IPX protocols, allowing users to remotely run programs that
are dependent on specificnetwork protocols . But unlike the PPTP protocol, L2TP
does not provide encryption of t he dat a. For dat a s ecur i t y L2TPr el i es on t he
s er vi ces of anot her s t andar ds - bas ed protocol, IPSec.
3. 9. 3 How t o conf i gure VPN
startadministrative tools
Routing and Remote access
Right click on
computer name configure and enable Routing and Remoteaccess
next
select
remote access (dial up or VPN)
next VPN next
select LAN card which is connected to internet
(172.15.15.50)
public IP
disable enable security next
from a specific range of address
nextnew
enter the required range
oknext no radius
next finish
3. 9. 4 Creat e us ers i n VPN s erver
open user
properties dial in allow access
apply ok
3.9.5
Working on Client Side
Right click on
My Network Places properties
Double click on
New Network Wizard next
Connect to network
at my work place next
Virtual private network connection next
Enter company name (ab
c
)
next
Enter public IP address of VPN server
next
Any one use
next
finish
3.10
ROUTING
It is a process of transferring information through an inter network i.e from
onenetwork to another. Routing connect different networks having ID help in
process of routing. The dial-in properties also allow for specific IP address to be assigned to a
user.This is the only way in Window Server 2003 that you can assign a specific IP to
a user.To assign a specific IP to a user, check the box next to assign A Static IP
Address andenter a valid IP in the space provided. Static routing can also be specified as per
user. Bydefining static routes, users can be limited to only specific parts of networks.I n an
i nt er net wor k a r out er mus t t hen about al l t he net wor ks pr es ent i n t he
f or effort websites, there are hardware routers like CISCO. Even win 2003 server
computer configured as router. In simple words Router is a computer with two
network cards.These two network cards, then, are attached to two different logical
IP networks. Therouting table helps direct traffic that is passed through the router. No w
wh e n t h e r e i s a r o u t e r , a l s o t h e r e i s a r o u t i n g t a b l e , t h e r e i s a
n e e d t o configure the router in order for that router to pass along traffic to the
proper network.Ther e ar e t wo wa ys t he r out i ng t abl e can be bui l t and
modi f i ed: ei t her manual l y or automatically.
3.10.1 Types of Routing
( i ) S t a t i c R o u t i n g ( i i ) D y n a m i c R o u t i n g
3.10.1.1 Static Routing
In this routing information required for routing is manually entered into the router by
administrator.
How to configure LAN routing
Enter the static IP in the router
Administrator tools
Routing and Remote access
Right click on computer name (pcc1)
Configure and enable routing and remote access
next custom configuration
select
LAN routingnext finish
yes
and logon to see IP table routeEnable LAN routing enable LAN routingInterface WAN Interface
WAN 10.0.0.0IP 172.15.0.0 IP 10.0.0.0SNM 255.255.0.0 SNM 255.0.0.0GW 20.0.0.2 GW
20.0.0.1
Fig 16 : scenario for LAN routing
How to configure static routing
At Router R1:
enable LAN routing
right click on
static route
interface WAN
destination 172.15.0.0
mask 255.255.0.0
GW 20.0.0.2At Router R2:
Enable LAN routing
Right click on
static route
Interface WAN
Destination 10.0.0.0
Mask 255.0.0.0
GW 20.0.0.1
Fig 17 : static routing
3.10.1.2 Dynamic Routing
The other way to manage a router routing tables is to let the computer do itfor you. Just like
DHCP allocate IP addresses, configuring the dynamic routing protocol usually
means less errors due to human error, and less administrativeoverhead.In dynamic
routing, routing information is automatically entered in ther out er us i ng pr ot ocol s
l i ke RI P AND OSPF. Thes e r out i ng pr ot ocol s us ed byWindow Server 2003
use one of two kinds of algorithms to determine the best possible path for a packet
to get to its destination, either distance vector or link state. RIP is used for small
networks where as OSPF is used for large networks.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
T h e d i s t a n c e v e c t o r p r o t o c o l i n u s e o n Wi n d o w 2 0 0 3 i s
c a l l e d R o u t i n g Information Protocol (RIP) for IP. This protocol was designed for the
exchange of the routing information within a small to medium size IP network.When Router is
enabled on Window 2003 machine, the routing table includesentries only for the networks that
are physically connected. When RIP is enabledfor an interface, the router will
periodicall y send an announcement of its routingtable to inform other RIP routers of the
networks it can reach. RIP version1 uses broadcast packets for its announcement. RIP version2
offers an improvement andc a n b e c o n f i g u r e d t o u s e e i t h e r
m u l t i c a s t o r b r o a d c a s t p a c k e t s w h e n communicating with other
routers. Also, RIP version2 offers more flexibility insubnetted and classless inter domain
routing (CIDR) environments.The biggest advantage of RIPis its simplicity. With a few clicks in
the Routingand Remote Access Server and MMC console, you can deploy RIP. With the
RIPdynami c r out i ng pr ot ocol i ns t al l ed on Wi ndow s Ser ver 2003, you get
t hefollowing features: ( i ) RI P v e r s i o n 1 a n d v e r s i o n 2 , wi t h t h e a b i l i t y t o
c o n f i g u r e i n d i v i d u a l network cards with separate versions.( i i ) Ca l c u l a t i o n s
u s e d t o a v o i d r o u t i n g l o o p s a n d s p e e d r e c o v e r y o f t h e network whenever
topology changes occur.
( i i i ) Ro u t e f i l t e r s ; y o u c a n c o n f i g u r e RI P t o e x c e p t i n f o r ma t i o n
f r o monly certain networks, and also choose which routes will be sharedwith RIP
routers.( i v) Peer f i l t er s , whi ch al l ow cont r ol over whi ch r out er
announcement s are accepted.( v ) S i m p l e p a s s w o r d a u t h e n t i c a t i o n
s u p p o r t . But there are significant drawbacks, which makes RIP a poor, if not
unusablesolution for large networks. For example, the maximum hop count used for
RIP routersis15, making network 16 hops away (or more) unreachable where RIP is concerned.
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
Where RIP is built to work to work in smaller networks, the Open Shortest PathFirst
(OSPF) routing protocol is designed for large or very large networks. The goal is thes ame:
i nf or mat i on about connect i on t o ot her net wor ks i s s har ed f r om one r out er
t oanother. It offers several advantages over RIP, especially significant in large
networks:( i ) R o u t e s c a l c u l a t e d w i t h O S P F a r e a l w a y s l o o p
f r e e . ( i i ) O S P F c a n s c a l e m u c h m o r e e a s i l y t h a n
R I P . ( i i i ) Reconf i gur at i on f or net wor k t opol ogy changes i s f as t er . The biggest
reason OSPF is the choice in large networks is its efficiency; insteadof changi ng r out i ng
t abl e vi a br oadcas t t he wa y RI P does , OSPF conf i gur ed r out er s mai nt ai n a
map of t he net wor k. The mappi ng i s cal l ed t he l i nk s t at e dat abas e,
OSPFrouters keep the link state database up to date. Once changes have been made to link
statedatabase, an OSPF routers link state database is recalculated.As the networks start to
multiply, the size of the link state database increases, anda corresponding hit on router
performance results. To combat this, OSPF sub divide thenetwork into smaller
sections, called areas. Areas are connected to each other through a backbone area,
with each router only responsible for the link state database for thoseareas connected
to the routers. Area Border Routers (ABRs) then connect one backbonearea to another.
The biggest drawback of OSPF is its complexity; OSPF requires proper planningand
is more difficult to configure and administer.
3.11 EXCHANGE SERVER
Exchange server is a mail server, we can send and receive mail from one user to another user.
Exchange server is the mail server of Microsoft.
3.11.1 Elements of Exchange Server
Mail Server
A server which helps to the users to send and receive mail is called mail server.
Mail Box
A storage place where senders and receivers mails are stored.3.11.2
Exchange Version
Table 10: Exchange Server with different operating systemsE x c h a n g e
V e r s i o n O p e r a t i n g S y s t e m Exchange Server 5.5Exchange
Server 2000Exchange Server 2003Exchange server 2007WIN NT or 2000 server (without
SP).WI N N T o r 2 0 0 0 s e r v e r ( S P 3 , S P 4 ) without (SP).WI N 2000 Ser ver
or WI N2003 s er ver (SP4) without SP.W I N 2 0 0 3 s e r v e r o r R 2 / W I N
2 0 0 8 server with SP1. Wher e SP s t ands f or Ser vi ce Pack. Ser vi ce Pack ar e
t he s er vi ces whi ch ar e l oadedexternally to remove some bugs that come during
installation of server CD.
3.11.3 Requirements for Exchange ServerProtocols Required
POP3 (Post Office Protocol)
This protocol is used for receiving e- mails.
IMAE4 (Internet Messaging Access Protocol)
This protocol is advance version of POP, this is also used to receive mail.
LMTP (Local Mail Transfer Protocol)/SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
This protocol is used to send mails.
NNTP (Network News Transfer protocol)
This protocol is used for transferring messages on internet.
Hardware Requirements
Processor: min. 133MHz Rec. 733MHz
RAM: min. 256MB Rec. 512MB
Other Requirements
OS: 2k or 2k3 Server
NTFS partition
Static IP address
Active Directory
DNS installation with AD zone
IIS installed with ASP.net, SMTP, NNTP and www service
3.12 Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model
OSI model is the layer approach to design, develop and implement network.
OSI provides following advantages: -( i ) D e v e l o p m e n t o f n e w t e c h n o l o g y
w i l l b e f a s t e r . ( i i ) De v i c e s f r o m mu l t i p l e v e n d o r s c a n
c o mmu n i c a t e wi t h e a c h o t h e r .
( i i i ) I mpl ement at i on and t r oubl es hoot i ng of net wor k wi l l be eas y.
3.12.1 Description of Different Layers
Application Layer
Application layer accepts data and forward into the protocol stack. It creates
user interface between application software and protocol stack.
Presentation Layer
This layer decides presentation format of the data. It also able to performs other function like
compression/decompression and encryption/decryption.
Session Layer
This layer initiate, maintain and terminate sessions between different applications.Due to this
layer multiple application software can be executed at the same time.
Transport Layer
Tr ans por t l ayer i s r es pons i bl e f or connect i on or i ent ed and connect i on
l es s communication. Transport layer also performs other functions like( i ) E r r o r
c h e c k i n g ( i i ) F l o w
C o n t r o l BufferingWindowingMultiplexing( i i i ) S e q u e n c i n g ( i v )
P o s i t i v e A c k n o w l e d g e m e n t ( v ) R e s p o n s e (vi)
Network Layer
T h i s l a y e r p e r f o r m s f u n c t i o n l i k e l o g i c a l a d d r e s s i n g
a n d p a t h det er mi nat i on. Each net wor ki ng devi ce has a phys i cal addr es s
t hat i s MACaddress. But logical addressing is easier to communicate on large size
network. Logical addressing defines network address and host address. This type of addressing
is used to simplify implementation of large network. Some
examples of logical addressing are: - IP addresses, IPX addresses etc. Network layer has
different routing protocols like RIP, EIGRP, BGP, andARP et c. t o per f or m t he pat h
det er mi nat i on f or di f f er ent r out i ng pr ot ocol . Network layer also perform other
responsibilities like defining quality of service,fragmentation and protocol identification.
Data Link Layer
The functions of Data Link layer are divided into two sub layers
Logical Link Control
Media Access Control( i ) Lo g i c a l Li n k Co n t r o l d e f i n e s t h e e n c a p s u l a t i o n
t h a t wi l l b e u s e d b y t h e NIC to delivered data to destination. Some examples
of Logical Link Control are ARPA (Ethernet), 802.11 wi-fi.( i i ) Me d i a Ac c e s s
Co n t r o l d e f i n e s me t h o d s t o a c c e s s t h e s h a r e d me d i a a n d establish the
identity with the help of MAC address. Some examples of Media Access Control are CSMA/CD,
Token Passing.
Physical Layer
Physical Layer is responsible to communicate bits over the media thislayer deals with the
standard defined for media and signals. This layer may also performmodulation and
demodulation as required.
3.13 ROUTERS
13.13.1 Router Architecture and its Key Component
IncompleteIOSIOSStartup Configuration
Fig 18 : Architecture of routerProcessor
Speed: - 20 MHz to 1GHzArchitecture: - RISCReduce Instruction set computer Manufacturers: -
Motorola, IBM, Power PC, Texas, Orion, Intel.
Flash RAM
Flash memory is just like a hard copy of the computer. Flash RAM is the permanent
read/write memory. This memory is used to store one or more copiesof router O/S.
Router O/S is also called IOS (Internetwork Operating System).Thesize of Flash RAM in the
router is 4MB to 256MB. This memory is ElectricallyErasable Programmable Read Only
Memory (EEPROM).
NVRAM
NVRAM is a Non Volatile Random Access Memory. It is used to storethe startup
configuration of the Router. It is on chip RAM, its size is 32kb.Processor MemoryController
BIOSROM NVRAMRAMFlashRAMO/SI/OController LANWANPorts
RAM (Random Access Memory)
It is a volatile memory. All the activities we do are stored in RAM,this means thatit holds the
running configuration. RAM of the router is divided into two logical parts.
Primary RAM
Shared RAM
Primary RAM
Primary RAM is used for: -( i ) R u n n i n g c o p y o f
I O S . ( i i ) R u n n i n g c o n f i g u r a t i o n ( i i i ) R o u t i n g
t a b l e ( i v ) Ad d r e s s Re s o l u t i o n P r o t o c o l ( ARP ) t a b l e ( I P a d d r e s s
t o MACaddress)( v ) P r o c e s s o r & o t h e r d a t a s t r u c t u r e
Shared RAM
S h a r e d RAM i s u s e d a s a b u f f e r me mo r y t o s h a r e d t h e d a t a
r e c e i v e d f r o mdifferent interfaces. Size of RAM in a router may vary from 2 MB
to 512 MB.The types of memory that may be present in a RAM are:( i ) D R A M -
> D y n a m i c R A M ( i i ) E D O R A M - > E x t e n d e d D a t a
O u t R A M ( i i i ) S D R A M - > S y n c h r o n o u s D y n a m i c R A M
ROM (Random Access Memory)
It has four components:
POST (Power on Self Test
)
It performs hardware testing.
BOOT StrapBoot strap specifies from where and which inter operating system is to
beloaded.
Mini IOSCisco 2500, 1600
ROM MOW
333333
Router Interfaces & Ports
Interface is used to connect LAN networks or wan networks to the
router. I n t e r f a c e w i l l u s e p r o t o c o l s t a c k s t o s e n d / r e c e i v e d a t a .
P o r t s a r e u s e d f o r t h e configuration of routers. Ports are not used to connect
different networks. The primary purpose of port is the management of router.
33333333
Router Interface
Table 11: Router interfaces and connectors
AUI Attachment Unit InterfaceEPABX Electronic Private Automatic BranchPSTN Public
Services Telephone Network
3.13.2.2 Router Ports
Table 12: Router Ports
333333
Modes of Router
When we access router command prompt the router will display different modes.According to
the modes, privileges and rights are assigned to the user.
User mode
Router>
I n t h i s mo d e , we c a n d i s p l a y b a s i c p a r a me t e r a n d s t a t u s o f t h e
r o u t e r we c a n t e s t connectivity and perform telnet to other devices. In this mode
we are not able to changeand save router configuration.
Privileged mode
Router#
In this mode, we can display all information, configuration, perform administration
task,debugging, testing and connectivity with other devices. We are not able to perform
hereconfiguration editing of the router.The command to enter in this mode is enable.
We have to enter enable password or enable secret password to enter in this mode. Enable
secret has more priority
than enable password. If both passwords are configured then only enable secret
willwork.
Global configuration
Route(config)#
This mode is used for the configuration of global parameters in the router. Global parameters
applied to the entire router. All the changes are performed in this mode. Buthere we
cannot see and save the changes.For e.g: - router hostname or access list of router, password,
Banner, Routing, Security.The command to enter in this mode is configure terminal
Line configuration mode
I n t hi s mode we can s et t he pas s wor d of t he us er mode, i . e t o s et us er
mode password .This mode is used to configure lines like console, vty and auxiliary. There
aremain types of line that are configured.(i) Console
Router(config)#
line console 0(ii) Auxiliary
Router(config)#
line aux 0(iii) Telnet or vty
Router(config)#
line vty 0 4
Interface configuration mode
I n t hi s mode we can s et i p addr es s es of t he i nt er f aces . Thi s mode i s us ed
t oconfigure router interfaces. For e.g:- Ethernet, Serial, BRI etc.
Router(config)#
interface <type> <number>
Router(config)#
interface serial 1
Routing configuration mode
This mode is used to configure routing protocol like RIP, EIGRP, OSPF etc.
Router(config)#
router <protocol> [<option>]
Router(config)#
router rip
Router(config)#
router eigrp 10
333333
Configuring Password
There are five types of password available in a router
Console Password
router#configure terminalrouter(config)#line console 0router(config-line)#password
<word>router(config-line)#loginrouter(config-line)#exitTo erase password do all steps with no
command.
Vty Password
router>enablerouter#configure terminalrouter(config)#line vty 0 4router(config-line)#password
<word>router(config-line)#loginrouter(config-line)#exit
Auxiliary Password
router#configure terminalrouter(config)#line Aux 0router(config-line)#password
<word>router(config-line)#loginrouter(config-line)#exit
Enable Password
router>enablerouter#configure terminal
router(config)#enable password <word>router(config)#exit
Enable Secret Password
E n a b l e P a s s w o r d i s t h e c l e a r t e x t p a s s w o r d . I t i s s t o r e d a s
c l e a r t e x t i n configuration where as enable secret password is the encrypted
password.Router>enableRouter#configure terminalRouter(config)#enable secret
<word>Router(config)#exit
Encryption all passwords
All passwords other than enable secret password are clear text password.
Thecommand to encrypt all password areRouter#configure terminalRouter(config)#service
password-encryption
3.13.5 Managing Configuration
There are two types of configuration present in a router (i) Startup Configuration(ii) Running
ConfigurationStartup configuration is stored in the NVRAM. Startup configuration is
used tosave settings in a router. Startup configuration is loaded at the time of
booting in to thePrimary RAM.Runni ng Conf i gur at i on i s pr es ent i n t he Pr i mar y
RAM wher ever we r un acommand for configuration, this command is written in the
running configuration.
To save configuration
Router#copy running-configuration startup-configurationOr Router#write
To abort configuration
Router#copy startup-configuration running-configuration
To display running-configuration
Router#show running-configuration
To display startup configuration
Router#show startup-configuration
Configuring Host Name
Router#configure terminalRouter(config)#hostname <name><name>#exit or end or
/\zRouter#config terminalRouter(config)#hostname r1R1(config)#
Configuration Interfaces
I n t e r f a c e s c o n f i g u r a t i o n i s o n e o f t h e mo s t i mp o r t a n t p a r t o f t h e
r o u t e r configuration. By default, all interfaces of Cisco router are in disabled mode. We have
touse different commands as our requirement to enable and configure the
interface.Router#configure terminalRouter(config)#interface <type> <no>Router(config-if)#ip
address <ip> <mask>Router(config-if)#no shutdownRouter(config-if)#exit
To display interface status
Router#show interfaces (to show all interfaces)Router#show interface <type> <no>This
command will display following parameters about an interface( 1 ) S t a t u s
( 2) Mac addr es s ( 3) I P addr es s ( 4) Subnet mas k (5) Hardware type /
manufacturer ( 6) Bandwi dt h( 7) Rel i abi l i t y( 8 ) D e l a y (9) Load ( Tx load Rx
load)( 1 0 ) E n c a p s u l a t i o n ( 1 1 ) A R P t y p e ( i f
a p p l i c a b l e ) ( 1 2 ) K e e p a l i v e
Configuring optional parameter on WAN interface
Router#configure terminalRouter(config)#interfac <type> <no>Router(config-if)#encapsulation
<protocol>Router(config-if)#clock rate <value>Router(config-if)#end
Command displaying history of Router
To display commands present in history
Router#show history
To display history size
Router#show terminal
To change history size
Router#config terminalRouter(config)#line console 0Router(config-if)#history size <value(0-
256)>Router(config-if)#exit
Configuring Banners
Banners are just a message that can appear at different prompts according to the
type.Different banners are: -
Message of the day (motd)This banner appear at every access method
LoginAppear before login prompt
ExecAppear after we enter to the execution mode
IncomingAppear for incoming connections
Syntax:-
Router#config terminalR o u t e r ( c o n f i g ) # b a n n e r < t y p e > < d e l i m a t i o n
c h a r > T e x t Ma s s a g e <delimation char>Router(config)#
Example
Router#config terminalRout er ( conf i g) #banner mot d $ Thi s r out er i s
di s t r i but i on 3600 r out er connected to Reliance $Router(config)#
To set time in router
We can configure router clock with the help of two methods:( i ) C o n f i g u r e
c l o c k l o c a l l y ( i i ) Co n f i g u r e c l o c k o n NT P s e r v e r ( Ne t wo r k
T i me P r o t o c o l ) Router does not have battery to save the clock setting. So that
clock will reset to thedefault on reboot.
To display clock
Router#show clock
To configure clock
Router#clock set hh:mm:ss day month year Router#clock set 7:15:10 9 June 2009
To configure clock from NTP server
Router#config terminalRouter(config)#ntp server <IP address>Router(config)#exitC:\>ping
pool.ntp.orgTo get ntp server ip from internetC:\>route print
3.14 SUBNETTING
Subnetting is a process or a technique to divide large and complex networks
intosmaller parts or smaller networks and each network is called as subnet.
Subnetting isdone to reduce the wastage of IP addresses ie instead of having a single huge
network for an organization smaller networks are created within a given huge
network. Subnettingallows the user to create multiple logical networks within a single Class
A, B or C basednetworks.In subnetting, the IPv4 address is broken into two parts;
network id and host id.This process borrows bits from the host id field. In this process, the
network size does notshrink but the size of hosts per network shrinks in order to include sub-
networks withinthe network.
333333
Advantages of subnetting
Size of the physical networks is reduced and hence easy to manage.
Reduce network traffic.
Easy to troubleshoot.
Reduce the wastage of IP address.
Subnet Mask
A subnet mask specifies the part of
IP address that is to be used for identifying asub network. A subnet mask when logically
ANDed with IPaddress provides a 32- bitnetwork address. This binary address gives the
first address in the subnet block specifiedin the large network.
Default Mask
Cl a s s f u l l a d d r e s s e s c o n s i s t s o f t h r e e c l a s s e s ; Cl a s s A, Cl a s s B,
Cl a s s C u s e d f o r subnet.Each class has a default subnet mask C lass A consists of eight
1s in the network address field and 24 0s in remaining field, Class B consists of 16 1s
in network addressfield and 16 0s in remaining field, and Class C cointains 24 1s in
the network addressfield and remaining 8 bytes as 0s. the default address mask in binary and
dotted-decimalis shown in the tableTo Calculate the Subnet Mask 1.Identify the class of
address assigned. For this example the class of IP addressis Class B.
2 . c h e c k t h e d e f a u l t a d d r e s s ma s k f o r t h e a p p r o p r i a t e c l a s s a n d
c o n v e r t i t t o binary format .for this example the default address mask is
255.255.0.0 andthe equivalent binary format is;
11111111.11111111.00000000.000000003.check the no. of 1s in the default mask. E.g
this address contains 16 1s in classB, 16 bits 2 octat are for net id and the last 16 bits 2
octates are for host id.4. now i f we need 9 s ubnet s . Thi s no. 9 i s not a power of
2. t he next no. t hat i s power of 2 and greater than 2 is 16. So, we require 4 extra
4 extra 1s in thenetwork field which has to be borrowed from the host id field.5. t he t ot al
no. of 1s i s 16+4=20, as 16 1s ar e f r om net wor k i d and 4 1s ar e of additional
bits required for subnetwork. The no. of 0s in the n/w is 32-20=12.which defines whole
address.6. hence addr es s i s gi ven as 11111111. 11111111. 11110000. 00000000
and i ndecimal format can be given as 255.255.240.0
Table 14: decimal and binary values of subnet mask
DecimalBinary01281922242402482522542550000000010000000110000001110000011110000
11111000111111001111111011111111
333333
Types of Subnetting
Fixed Length Subnet Mask (FLSM)
Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM)
Steps of Subnetting for FLSM
For IP address 192.168.10.0 (Class C)Step 1:
Identify the total no. of subnets 2^n = no.of subnets
Where n are the no.s and borrowed bytes from host ID portion. Let we are giventhat
we have to make 4 subnets. Therefore 2^n =4 i.e n=2Step 2:
To idettify the total no. of the valid hosts for each subnet.
2^m-2= no.of valid hosts. Where m are the remaining no. of bits in host ID 2^6-
2=62Step 3:
Calculate the subnet mask and range
S u b n e t m a s k f o r n / w
1 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 1 0 . 0 / 2 6
i s 11111111.11111111.11111111.1100000000 ie 255.255.255.192
range=> 256-192=64step 4:
Identify the total no of subnets, no. of valid hosts and the broadcast address.
Table 15: showing subnet mask, valid hosts, broadcast addressS u b n e t w o r k
V a l i d H o s t B r o a d c a s t A d d r e s s
192.168.10.0192.168.10.64192.168.10.128192.168.10.1921 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 1 0 . 1
t o 192.168.10.631 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 1 0 . 6 5 t o 192.168.10.1261 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 1 0 . 1 2 9
t o 192.168.10.1901 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 1 0 . 1 9 3
t o 192.168.10.254192.168.10.63192.168.10.127192.168.10.191192.168.10.255
VLSM
I n VLSM t o al l ocat e I P addr es s es t o s ubnet s dependi ng upon t he no. of
hos t s . Thenetwork having more no of hosts is given priority and the one having
least no of hostcomes at last and for each network the subnet is assigned separately.
As in the scenariogiven:
Fig 19: variable subnet mask
3.15 TELNET
Telnet stands for terminal network, telephone network, terminal encapsulation onthe network.
Purpose of Telnet is to access the remote device in order to configure it. It provides
textual access of the remote device. It uses the services of TCP. Telnet service isused where
small bandwidth is low. It provides textual access of the remote device. Portnumber of Telnet is
23.
3.15.1
To Access the Device Remotely
For this purpose we have to assign the IP addresses to the PCs and the interfaces.For Telnet the
Routers are to be configured with RIP version1 , so that the device can ping each
other. Also DCE cable is used to connect the Routers. The serial link shouldhave
the speed of 64K also apply vty password and enable secret password. Set up
theRouters so that they can manage via Telnet.First of all select the PCs and the routers
connect the ports to the router, doubleclick on router, switch off the router if it is on. Then
select the serial port according to therouters, switch on the router. Select the cable to
connect the Routers. Router to Router connections are made by the serial cable, so
go on first Router select the serial port ass0/1/0 in the scenario, then go to the other Router
and connect the serial cable at interfaces1/0. Accordingly connect the third Router with
interfaces s1/1 and s1/2.
Now connect the PCs to the routers, to do this first select the console cable, click on thePC
select RS232 option, then connect it on the Router and select console cable.
Nowselect cross- over cable on the PC select Fast Ethernet option and on the Router
selectf0/0 option now as the PCs and Routers are connected to each other assign IP
addressesto the PCs and the Routers. According to the fig set the IP addresses of the PCs
doublecl i ck on t he PC choos e t he opt i on of des kt op I P conf i gur at i on.
Now s et t he I Paddress, subnet mask, and the default gateway. Like wise set the IP
address of all thePCs. Now set the IP address of the interfaces of router.
3.15.2 Commands to assign IP addresses to the interfaces:
At Router1
:Router>Router>enableRouter#configure terminalRouter(config)#interface f0/0Router(config-
if)#ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Fig 20: scenario of Telnet
Router#Router#configure terminalRouter(config)#interface s0/1/0Router(config-if)#ip address
40.0.0.1 255.0.0.0Router(config-if)#no shutdownRouter(config)#interface s0/1/0Router(config-
if)#clock rate 64000Router(config-if)#no shutdown Now to check the assigned IPaddresses to
the interfaces the command used isRouter#show ip interface brief
At router 2:
Router#configure terminalRouter(config)#interface f0/0Router(config-if)#ip address 20.0.0.1
255.0.0.0Router(config-if)#no shutdownRouter#Router#configure
terminalRouter(config)#interface s1/0Router(config-if)#ip address 40.0.0.2
255.0.0.0Router(config-if)#no shutdownRouter#configure terminalRouter(config)#interface
s1/1Router(config-if)#ip address 50.0.0.1 255.0.0.0Router(config-if)#no
shutdownRouter(config)#interface s1/1Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000Router(config-if)#no
shutdown
At router 3:
Router#configure terminalRouter(config)#interface f0/0Router(config-if)#ip address 30.0.0.1
255.0.0.0Router(config-if)#no shutdownRouter#Router#configure
terminalRouter(config)#interface s1/0Router(config-if)#ip address 50.0.0.2
255.0.0.0Router(config-if)#no shutdown
To Telnet a device from Router
At all the Routers use these commandsRouter(config)#line vty 0 4Router(config-line)#password
cobraRouter(config-line)#loginRouter(config)#enable password cobraRouter(config)#enable
secret cobra1
To telnet a device from router
Router#telnet <IP>Or Router>telnet <IP>
To exit from telnet session
Router#exit
To exit from a hanged telnet session
Ctrl+shft+6Or
Router#disconnect
To display connected session
Router#show sessionsThis command shows those sessions, which are created or connected by
us.I f we want anyone can t el net our r out er wi t hout pas s wor d t hen on t he
l i ne vt y t ypecommand No Login.
3.16 ROUTING
Routing is a process or technique to identify the path from one network toanother. Routers dont
really care about hoststhey only care about networks and the best path to each network.To
route the packet the router must know the following things:
Destination network
Neighbour device from witch it can learn about remote Networking.
Possible number of routers to reach the destination.
Best route to reach the destination.
How to maintain & verify the routing information.
3.16.1 TYPES OF ROUTING
Static routing.
Default routing.
Dynamic routing.
3.16.1.1 STATIC ROUTING
In static routing an administrator specifies all the routes to reach the destination.
Static routing occurs when you manually add routes in each routers routing
table.By default,Static routes have an Administrative Distance (AD) of 1
Features
There is no overhead on the router CPU.
There is no bandwidth usage between routers.
It adds security, because the administrator can choose to allow routing access to
certainnetworks only.
Advantages of static routing
(1) Fast and efficient.(2) More control over selected path.(3) Less overhead for router.(4)
Bandwidth of interfaces is not consumed in routing updates.
Disadvantages of static routing
(1) More overheads on administrator.(2) Load balancing is not easily possible.(3) In case of
topology change routing table has to be change manually.
Syntax for Static Routing
Router
(
config
)#
ip route
<
destination N/w> <Subnet mask> <NextHope- address or exit interface> [<administrative
distance>Permanent].
To check the routing table of router
Router # show ip route
Fig 21: scenario of static routing
Static routing of router (R1)
Router(config)#ip route 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 40.0.0.2Router(config)#ip route 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
40.0.0.2Router(config)#ip route 50.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 40.0.0.2Router(config)#interface
so/1/0Router(config)# clock rate 64000 Router # show ip route
Static routing of router (R2)
Router(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 40.0.0.1Router(config)#ip route 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
50.0.0.2Router#show ip routeRouter(config)#interface s1/0Router(config)# clock rate
64000Router(config)#interface s1/1
Router(config)#clock rate 64000Router#show ip route
Static routing of router (R3)
Router(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 50.0.0.1Router(config)#ip route 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
50.0.0.1Router(config)#ip route 40.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 50.0.0.1Router(config)#interface
s1/0Router(config)# clock rate 64000Router#show ip route
3.16.1.2 DEFAULT ROUTING
Default routing is used to send packets with a remote destination network not in the routing table
to the next-hop route.Default routing is also a type of static routing which reduces the
routingoverhead & default routing is also used with stub networks. Stub networks
are thosehaving a single exit interface. Default routing is also used for unknown destination.A
special address is used to perform the default routing ie 0.0.0.0The scenario for default routing is
same and but the commands used at the routershaving single exit interface like R1 and R3 have
different commands.
At Router (R1)
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 40.0.0.2Router#show ip route
At Router (R3)
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 50.0.0.1Router#show ip route
3.16.1.3 DYNAMIC ROUTING
Dynamic routing is when protocols are used to find networks and updaterouting table on
routers.A routing protocol defines the set of rules used by router when it
communicatesr out i ng i nf or mat i on bet ween nei ghbor r out er s . I n dynami c
r out i ng, we wi l l enabl e arouting protocol on router. This protocol will send its routing
information to the neighbor router. The neighbors will analyze the information and
write new routes to the routingtable.The routers will pass routing information receive from
one router to other router also. If there are more than one path available then routes
are compared and best path is selected. Some examples of dynamic protocol are: -RIP, IGRP,
EIGRP, OSPF
There are two type of routing protocols used in internetwors:
Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs)
I GP s a r e u s e d t o e x c h a n g e r o u t i n g i n f o r ma t i o n wi t h r o u t e r s i n t h e
s a me Au t o n o mo u s S y s t e m( AS ) n u mb e r . Ro u t i n g wh i c h i s p e r f o r me d
wi t h i n a s i n g l e autonomous system is known as interior routing. The protocol
that are used to performthis type of routing are known as IGP(Interior Gateway
Protocol).These protocols are:-( i ) R I P v 1 ( R o u t i n g I n f o r m a t i o n P r o t o c o l
V e r s i o n 1 ) ( i i ) R I P v 2 ( Ro u t i n g I n f o r ma t i o n P r o t o c o l Ve r s i o n
2 ) ( i i i ) E I GRP ( E n h a n c e d I n t e r i o r Ga t e wa y Ro u t i n g
P r o t o c o l ) ( i v ) O S P F ( O p e n S h o r t e s t P a t h F i r s t ) ( v ) I S - I S
( I n t e r me d i a t e S y s t e m t o I n t e r me d i a t e S y s t e m)
Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGPs)
EGPs are used to communicate between different Autonomous System.Protocol that used to do
this type of routing are called exterior gateway protocols.
Aut onomous Sys t em: - An aut onomous s ys t em i s a col l ect i on of net wor ks
under acommon administrative domain, which basically means that all routers sharing the
samerouting table information are in the same AS.
3.16.2 Routing Protocol Basics
( i ) A d m i n i s t r a t i v e D i s t a n c e s ( i i ) R o u t i n g
p r o t o c o l ( i i i ) R o u t i n g L o o p s
Administrative Distances
The Administrative Distance (AD) is used to rate the trustworthiness of
routinginformation received on a router from a neighbor router. An Administrative
Distance isan integer from 0 to 255, where 0 is the most trusted and 255 means no
traffic will be passed via this route.If a router receives two updates listing he sane remote
network, the first thing the router checks is the AD. If one of the advertised routes has
lower AD than the other, then theroute with the lowest AD will be placed in the
routing table.If both advertised routes tothe same network have the same AD, then routing
protocol metrics (such as hop count or bandwidth of the lines) will be used to find the best path
to the remote network. Theadvertised route with the lowest metric will be placed in the routing
table.But if both advertised routes have the same AD as well as the same metrics,
then therouting protocol will load-balance in the remote network.
3.16.2.1 Classes of Routing Protocols
There are three classes of Routing Protocol( i ) D i s t a n c e v e c t o r
p r o t o c o l ( i i ) L i n k s t a t e p r o t o c o l ( i i i ) H y b r i d
p r o t o c o l .
Distance vector protocol
The Distance-vector protocols find the best path to remote network by judging
distance. Each time a packet goes through a router, thats called a hop. The routewi t h t he
l eas t number of hops t o t he net wor k i s det er mi ned t o be t he bes t r out e.
Thevector indicates the direction to the remote network. They send the entire routing table
todirectly connected neighbors.Ex: RIP, IGRP
.
The distance-vector routing algorithm passes complete routing table contents
toneighboring routers.
A router receiving an update from a neighbor router believes the informationabout
remote networks without actually finding out for itself.
Its possible to have network that has multiple links to the same remote network,and if thats the
case, the administrative distance is checked first. If the AD is the
R o u t e
S o u r c e D e f a
u l t A D
C o n n e c t e d
i n t e r f a c e 0 S
t a t i c
R o u t e
1 E I
G R
P 9
0 I
G R
P 1
0 0
O S
P F
1 1
0 R
I P
1 2
0 E x t e
r n a l
E I G R P 1 7 0 U
n k n o w n 2 5 5 T h i s
r o u t e w i l l n e v e r
b e u s e d
same, the protocol will have to use other metrics to determine the best path to useto that remote
network.
Fig 16: Routing table
Converged Network
Fig 23 : Routing table of covered networks
Routing Loops
Distance-vector routing protocols keep track of any changes to the internet work by
broadcasting periodic routing updates out all active interfaces. This broadcast includesthe
complete routing table.Routing loops can occur because a every router isnt updated
simultaneously.
Routing Loops Example
Router ARouter BRouter DR o u t e r
C R o u t e r
E N e t w o r k
3 N e t w o r k
4 N e t w o r k 5
Fig 24: Routing loops
The interface to Network 5 fails. All routers know about Network 5 from Router E. Router A, in
its tables, has a path to Network 5 through Router B.When Net wor k 5 f ai l s , Rout er E
t el l s Rout er C. Thi s caus es Rout er C t o s t opr out i ng t o Net wor k 5 t hr ough
Rout er E. But Rout er s A, B, and D don t know about Network 5 yet, so they
keep sending out update information. Router C will eventuallysend out its update
and cause B to stop routing to Network 5, but Routers A and D arestill not updated.
To them, it appears that Network 5 is still available through Router Bwith a metric
of 3.The problem occurs when Router A sends out its regular 30-secondHello, Im
still herethese are the links I know about message, which includes theability to
reach Network 5 and now Routers B and D receive the wonderful news
that Ne t wo r k 5 c a n b e r e a c h e d f r o m Ro u t e r A, s o Ro u t e r s B a n d D
t h e n s e n d o u t t h e
information that Network 5 is available. Any packet destined for Network 5 will go
toRouter A, to Router B, and then back to Router A. This is a routing loop.
Link state protocol
Al s o cal l ed s hor t es t - pat h- f i r s t pr ot ocol s , t he r out er s each cr eat e
t hr ees epar at e t abl es . One keeps t r ack of di r ect l y at t ached nei ghbor s , one
det er mi ne s t hetopology of the entire internet work, and one is used as the routing
tables. Link staterouters know more about the internet work than any distance-
vector routing protocol. Li nk s t at e pr ot ocol s s end updat es cont ai ni ng t he
s t at e of t hei r own l i nks t o al l ot her routers on the network Ex: OSPF
Hybrid protocol
Hybrid protocol use aspects of both distance-vector and link state protocol.Ex: EIGRP
3 . 1 6 . 3 R I P ( R o u t i n g I n f o r m a t i o n P r o t o c o l )
Routing Information Protocol is a true distance-vector routing protocol. Itis an IGB (Inter
Gateway Protocol). It sends the complete routing table out to all activeinterfaces
every 30 seconds to its immediate neighbour. This is slow convergence meansthat one router
sends a request to other about its route or network get networks which arenot assigned to it after
all thee three routers have same networks, this process is repeatedto send and receive request so
it is called slow convergenceRIP only uses hop count to determine the best way to remote
network, butit has a maximum allowable hop count of 0-15 by default, meaning that
16 is deemedunreachable.RIP version 1 uses only class full routing, which means that all
devices inthe network must use the same subnet mask.RIP version 2 provides something
called prefix routing, and does sendsubnet mask information with the route updates. This is
called classless routing.
Hop Count
It is a way of measurement. Hop count limit is15.This routing supports only
15routers, if there is one more router in the network then this routing will fails.
Default administrative distance (120)
Timers of RIP
( i ) U p d a t e t i m e r s . ( i i ) H o l d
t i m e r s . ( i i i ) I n v a l i d t i m e r s . ( i v ) F l u s h o u t
t i m e r s .
Route update timer
Rout er updat e t i mer s et s t he i nt er val
30 seconds
between periodic routingu p d a t e s , i n wh i c h t h e r o u t e r s e n d s a c o mp l e t e
c o p y o f i t s r o u t i n g t a b l e o u t t o a l l neighbors.
Router invalid timers
A router invalid timer determines the length of time that must elapse
180 seconds
before a router determines that a route has become invalid. It will come to this conclusionif it
hasnt heard any updates about a particular route for that period. When that happens,thee router
will send out updates to all its neighbors letting them know that the route isinvalid.
Hold-down timer
This sets the amount of time during which routing information is
suppressed.Rout er s wi l l ent er i nt o t he hol d- down s t at e when an updat e
packet i s r ecei ved t hat indicated the route is unreachable. This continues until entire an
update packet is receivedwith a better metric or until the hold-down timer expires. The default is
180 seconds.
Route flush timer
Route flush timers sets the time between a route becoming invalid and its intervalfrom the
routing table
240 seconds
. Before its removed from the table, the router notifiesits neighbors of that routes impending
demise. The value of the route invalid timer must be less than that of the route flush timers.
Difference between RIPV1 & RIPV2
Steps to do routing (version 1)
At router 1
Router(config)# router ripRouter(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0Router(config-router)#network
40.0.0.0
Router#show ip route
At router 2
Router(config)# router ripRouter(config-router)#network 20.0.0.0Router(config-router)#
network 40.0.0.0Router(config-router)# network 50.0.0.0Router#show ip route
At router 3
Router(config)# router ripRouter(config-router)#network 30.0.0.0Router(config-router)#
network 50.0.0.0Router#show ip route
3.16.4 IGRP ( Interior Gateway Protocol)
Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) is a Cisco-proprietary distance-vector r out i ng
pr ot ocol . To us e I GRP, al l your r out er s mus t be Ci s co r out er s . I GRP has
amaximum hop count of 255 with a default of 100. IGRP uses bandwidth and delay of theline by
default as a metric for determining the best route to an internetwork. Reliability,load, and
maximum transmission unit (MTU) can also be used, although they are notused by
default.
Table 18 : Difference between IGRP and
RIPI G
R P
R I
P
C a n b e u s e d i n l a r g e i n t e r n e t w o r k s W o r k s b e s t
i n s m a l l e r n e t w o r k s Us es an aut onomous s ys t em number
f or activationDoes not yse aytibiniys system numbersGi ves a f ul l r out e t abl e updat e
ever y 90secondsGi v e s f u l l r o u t e t a b l e u p d a t e e v e r y 3 0 seconds
H a s a n a d m i n i s t r a t i v e d i s t a n c e o f 1 0 0 H a s a n a d m i n i s t r a t i v e
d i s t a n c e o f 1 2 0 Us es bandwi dt h and del ay of t he l i ne as met r i c ( l owes t
compos i t e met r i c) , wi t h amaximum hop count of 255Uses only hop count to
determine the best p a t h t o a r e mo t e n e t wo r k , wi t h 1 5 h o p s being the
maximum
IGRP Timers
To control performance, IGRP includes the following timers with default settings:
Update timers
Thes e s peci f y how f r equent l y r out i ng- updat e mes s ages s houl d be s ent .
Thedefault is 90 seconds.
Invalid timers
These specify how long a router should wait before declaring a route invalid if itdoesnt receive a
specific update about it. The default is three times the update period.
Hold down timers
These specify the hold down period. The default is three times the update
timer period plus 10 seconds.
Flush timers
These indicate how much time should pass before a route should be flushed fromthe routing
table. The default is seven times the routing update period. If the update timer is 90 seconds by
default, then 7 90 = 630 seconds elapse before a route will be flushedfrom the route table.
At Router 1
R1(config)#router igrp 10R1(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0R1(config-router)#network
40.0.0.0R1#show ip route
At Router 2
R2(config)#router igrp 10R2(config-router)#network 40.0.0.0R2(config-router)#network
20.0.0.0R2(config-router)#network 50.0.0.0R2#show ip route
At Router 3
R1(config)#router igrp 10R1(config-router)#network 30.0.0.0R1(config-router)#network
50.0.0.0R1#show ip route3.16.5
EIGRP(Enhanced Interior Routing Protocol)
Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a classless, enhanced distance-vector protocolt hat gi ves us a
r eal edge over I GRP. Li ke I GRP, EI GRP us es t he concept of anautonomous
system to describe the set of contiguous routers that run the same routing protocol and share
routing information. But unlike IGRP, EIGRP includes the subnetmask in its route updates.
The advertisement of subnet information allows us to useVLSM and summarization
when designing our networks.EIGRP is sometimes referred to as a hybrid routing protocol
because it hascharacteristics of both distance-vector and link-state protocols. It sends
traditionaldistance-vector updates containing information about networks plus the cost
of reaching them from the perspective of the adverting router. EIGRP has a
maximumhop count of 255.
Powerful features that make EIGRP a real standout from IGRP
Support for IP, IPX, and AppleTalk via protocol-dependent modules Consideredclassless (same
as RIPv2 and OSP
Support for VLSM/CIDR
Support for summaries and discontiguous networks
Efficient neighbor discovery
Communication via Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP)
Best path selection via Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL)Cisco calls EIGRP a distance vector
routing protocol, or sometimes anadvanced distance vector or even a hybrid routing
protocol. EIGRP supports different Network layer protocols through the use of
protocol-dependent modules (PDMs). EachEIGRP PDM will maintain a separate series of
tables containing the routing informationt h a t a p p l i e s t o a s p e c i f i c p r o t o c o l . I t
me a n s t h a t t h e r e wi l l b e I P / E I GRP t a b l e s , IPX/EIGRP tables, and
AppleTalk/EIGRP tables.
Neighbor Discovery
Before EIGRP routers are willing to exchange routes with each other, they
must b e c o me n e i g h b o r s . T h e r e a r e t h r e e c o n d i t i o n s t h a t mu s t b e
me t f o r n e i g h b o r s h i p establishment:
Hello or ACK received
AS numbers match
Identical metrics (K values)To maintain the neighborship relationship, EIGRP routers
must also continuer e c e i v i n g He l l o s f r o m t h e i r n e i g h b o r s . E I GRP
r o u t e r s t h a t b e l o n g t o d i f f e r e n t autonomous systems (ASes) dont automatically
share routing information and they dont become neighbors.The only time EIGRP advertises its
entire routing table is when it discovers a newneighbor and forms an adjacency with it
through the exchange of Hello packets. Whenthis happens, both neighbors advertise
their entire routing tables to one another. After
each has learned its neighbors routes, only changes to the routing table are
propagatedfrom then on.EIGRP maintains three tables containing information about the
internetworks.(i) Neighbor TableRecords information about routers with whom neighborship
relationshipshave been formed.(ii) Topology TableStores the route advertisements about
every route in the internetwork receivedfrom each neighbor.
EIGRP Metrics
Another really sweet thing about EIGRP is that unlike many other protocols thatuse a single
factor to compare routes and select the best possible path, EIGRP can use
acombination of four:
Bandwidth
Delay
Load
Reliability3.16.6
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
is an open standards routing protocol thats beenimplemented by a wide variety of network
vendors, including Cisco. This works by usingthe Dijkstra algorithm. First, a shortest path tree is
constructed, and then the routing tableis populated with the resulting best paths. OSPF converges
quickly, although perhaps notas quickly as EIGRP, and it supports multiple, equal-cost routes to
the same destination.But unlike EIGRP, it only supports IP routing.OSPF is an IGP protocol.
It is a link state routing protocol. It is supported bymany operating systems. Its default
AD is 110, hop count limit is unlimited.
It is classless routing protocol, supports VLSM/CIDR. By default the highest IP addressof
interface will be elected as Router id.
OSPF provides the following features
Consists of areas and autonomous systems
Minimizes routing update traffic
Allows scalability
Supports VLSM/CIDR
Has unlimited hop count
Allows multi-vendor deployment (open standard)OSPF is supposed to be designed in a
hierarchical fashion, which basically meansthat you can separate the larger internetwork into
smaller internetworks called areas. Thisis the best design for OSPF.The reasons for creating
OSPF in a hierarchical design include:
To decrease routing overhead
To speed up convergence
To confine network instability to single areas of the network Each r out er i n t he net wor k
connect s t o t he backbone cal l ed
area 0,
o r t h e
backbone area
. OSPF must have an
area 0
, and all routers should connect to this area if at all possible. But routers that connect
other areas to the backbone within an AS arecalled
Area Border Routers (ABRs).
Still, at least one interface must be in area 0.OS P F r u n s i n s i d e a n a u t o n o mo u s
s y s t e m, b u t c a n a l s o c o n n e c t mu l t i p l e autonomous systems together. The router
that connects these
ASes
together is called an
Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR).
OSPF Terminology
Link
A l i nk
is a network or router interface assigned to any given network. When aninterface is
added to the OSPF process, its considered by OSPF to be a link.
Router ID
The Router ID (RID)
is an IP address used to identify the router. Cisco choosesthe Router ID by using the
highest IP address of all configured loopback interfaces. If nol oopback i nt er f aces ar e
conf i gur ed wi t h addr es s es , OSPF wi l l choos e t he hi ghes t I Paddress of all
active physical interfaces.
Neighbors
Neighbors
a r e t w o o r m o r e r o u t e r s t h a t h a v e a n i n t e r f a c e o n a
c o m m o n network,such as two routers connected on a point-to-point serial link.
Adjacency
An adjacency
is a relationship between two OSPF routers that permits the directexchange of route updates.
OSPF is really picky about sharing routing information unlike EIGRP, which
directly shares routes with all of its neighbors. Instead, OSPFdirectly shares routes only
with neighbors that have also established adjacencies. And notall neighbors will become
adjacentthis depends upon both the type of network and theconfiguration of the routers.
OSPF Topologies database
T h e t o p o l o g y d a t a b a s e
c o n t a i n s i n f o r m a t i o n f r o m a l l o f t h e L i n k S t a t e Ad v e r t i s e me n t
p a c k e t s t h a t h a v e b e e n r e c e i v e d f o r a n a r e a . T h e r o u t e r u s e s
t h e information from the topology database as input into the Dijkstra algorithm that
computest he s hor t es t pat h t o ever y net wor k. LSA packet s ar e us ed t o updat e
and mai nt ai n t hetopology database.A Link State Advertisement (LSA)
is an OSPF data packet containing link-stateand routing information thats shared
among OSPF routers. There are different types of LSA packets. An OSPF router
will exchange LSA packets only with routers to which ithas established adjacencies.A
designated router (DR)
is elected whenever OSPF routers are connected to thesame multi-access network. A prime
example is an Ethernet LAN.
A backup designated router (BDR)
is a hot standby for the DR on multi-accesslinks The BDR receives all routing
updates from OSPF adjacent routers, but doesntflood LSA updates.
OSPF areas
An OSPF area is a grouping of contiguous networks and routers. All routers in thesame area
share a common Area ID.
Broadcast (multi-access)
Broadcast (multi-access) networks
s uch as Et her net al l ow mul t i pl e devi ces t oconnect to (or access) the same network,
as well as provide a
broadcast
ability in which asingle packet is delivered to all nodes on the network. In OSPF, a DR and a
BDR must beelected for each broadcast multi-access network.
Non-broadcast multi-access
Non-Broadcast Multi-Access (NBMA)
networks
are types such as Frame Relay, X.25, and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). These
networks allow for multi-access, but have no broadcast ability like Ethernet. So, NBMA
networks require special OSPFconfiguration to function properly and neighbor relationships
must be defined.
Point-to-point
Point-to-point
r e f e r s t o a t y p e o f n e t wo r k t o p o l o g y c o n s i s t i n g o f a d i r e c t connection
between two routers that provides a single communication path. The point-to- point connection
can be physical, as in a serial cable directly connecting two routers, or itcan be logical.
Point-to-multipoint
Point-to-multipoint refers to a type of network topology consisting of a series
of connections between a single interface on one router and multiple destination routers. Allof
the interfaces on all of the routers sharing the point-to-multipoint connection belong tothe same
network. As with point-to-point, no DRs or BDRs are needed.
SPF Tree Calculation
Within an area, each router calculates the best/shortest path to every network inthat
same area. This calculation is based upon the information collected in the
topologydatabase and an algorithm called shortest path first (SPF)OSPF uses a metric
referred to as
cost
. A cost is associated with every outgoinginterface included in an SPF tree. The cost
of the entire path is the sum of costs of theoutgoing interfaces along the path.Cisco uses
a simple equation of 10
8
/ bandwidth.The bandwidth is the configured bandwidth for the interface. Using this rule,
a 100Mbps Fast Ethernet interface wouldhave a default OSPF cost of 1 and a
10Mbps Ethernet interface would have a cost of 10.An interface set with a bandwidth of
64,000 would have a default cost of 1563.
Benefits of OSPF
( i ) M i n i m u m r o u t i n g u p d a t e s . ( i i ) P r i o r i t i e s o n a l l t h e
C I S CO r o u t e r s t h e p r i o r i t y i s 1 . ( i i i ) T h e r o u t e r s h a v i n g h i g h e s t I P
a d d r e s s b e c o me BRD( Bo r d e r De s t i n a t i o n Router)
Steps to apply OSPF
Syntax:
Router(config)#router ospf <ospf process id>Router(config-router)#network <network address>
<wild card mask> area<area number>
Fig 25: OSPF Scenario
At Router r1
Router(config)#router ospf 1Router(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area
0Router(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0Router(config)#interface
s0/1/0Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000Router#show ip route
At Router r1
Router(config)#router ospf 2R o u t e r ( c o n f i g - r o u t e r ) # n e t w o r k 2 0 . 0 . 0 . 0
0 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 a r e a 0 Router(config-router)#network 40.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area
0Router(config-router)#network 50.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0Router(config)#interface
s0/1/0Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000Router#show ip route
At Router r3
Router(config)#router ospf 1Router(config-router)#network 30.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area
0Router(config-router)#network 50.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0Router#show ip route
3.17 LAN SWITCHING
3.17.1 SWITCH
Switches are generally used to segment a large LAN smaller segments. Smaller s wi t ches
s uch as t he Ci s co Cat al ys t 2924XL have 24 por t s capabl e of of cr eat i ng
24different network segment for the LAN. Larger switches such as the Cisco Catalyst 6500can
have hundreds of ports. Switches can also be used to connect LANs with
differentmedi a, f or exampl e, a 10 Mbps Et her net LAN and 100 Mbps
Et her net LAN can beconnected using a switch. Some switches support cut
through switching, witch reduceslatency and delays in the network, while bridges
support only store-and-forward traffics wi t chi ng. Fi nal l y s wi t ches r educe
col l i s i on on net wor k s egment . A s wi t ch i s anetworking device which filters and
forward packets through the network. It is a layer 2device. It is more advanced then hub but not
as advanced as router.The basic function of a switch is to manage the signal flow. When
the switch is open, it allows the signal tof l ow t hr ough i t and when i t i s cl os ed,
i t s t opes t he s i gnal t o f l ow. Swi t ch connect s separate LAN segment. It allows
multiple system to transmit simultaneously. A switch isa har dwar e devi ce t hat f i l t er s
and f or war d dat a packet s bet ween net wor k s egment s . Ethernet switches are
used in LAN to create Ethernet networks. Switches forward thetraffic on the basis of
MAC address. Switches maintain a switching table in which MACaddresses and port numbers
are used to perform switching decision.
WORKING OF SWITCH
When switches receives data from one of connected devices, it forward data onlyto the port on
witch the destinated system is connected.It use the media access Control(MAC)
address of the device to determine the correct port.The MAC address is a
uniqenumber that is programed in to every Network Interface Card(NIC). Concider, device
Awants to send data to device B.When device A passes the data, switch receives it. Switchthan
cecks the MAC address of the destination system. It then transfer data to device B
only instead of brodcasting to all the devices. By forwarding data only to the system towitch the
data is addressed, switch decreases the amount of traffic on each network link.
SWITCHING METHODS
There are three types of switching method:
Store-and-forward switching
The entire frame is received and the CRC is computed and verified
beforeforwarding the frame. If the frame is too short (i.e. less than 64 bytes
including theCRC), too long (i.e. more than 1518 bytes including the CRC), or has
CRC error, itwill be discarded.It has the lowest error rate but the longest latency for switching.
However, for high-speed network (e.g. Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet network),
the latency isnot significant. It is the most commonly used switching method, and is supported
bymost switches.
Cut-through switching
It is also known as Fast Forward switching.
A frame is forwarded as soon ast he des t i nat i on MAC addr es s i n t he header has
been r ecei ved ( t he 1s t 6 byt es following the preamble).
I t h a s t h e h i g h e s t e r r o r r a t e ( b e c a u s e a f r a me i s forwarded without
verifying the CRC and confirming there is no collision) butthe shortest latency for
switching
Fragment-free switching ( Modified Cut-through switching )
A f r ame i s f or war ded af t er t he f i r s t 64 byt es of t he f r ame have
beenreceived. Since a collision can be detected within the first 64 bytes of a
frame,f r agment - f r ee s wi t chi ng can det ect a f r ame cor r upt ed by a col l i s i on
and dr opit.Therefore, fragment-free switching provides better error checking than
cut-through switching.The er r or r at e of f r agment - f r ee s wi t chi ng i s above s t or e-
and- f or war ds wi t c h i n g a n d b e l o w c u t - t h r o u g h s wi t c h i n g . T h e l a t e n c y
o f f r a g me n t - f r e e
s wi t chi ng i s s hor t er t han s t or e- and- f or war d s wi t chi ng and l onger t han
cut - through switching. NOTE:
Bridges only support store-and-forward switching. Most new switch models alsouse store-and-
forward switching. However, it should be noted that Cisco 1900 switchesuse
fragment-free switching by default.
Types of switch based on OSI model
( i ) L a y e r - 2 s w i t c h ( i i ) L a y e r - 3 s w i t c h
Layer-2 Switching
La yer - 2 s wi t chi ng i s har dwar e bas ed, whi ch means i t us es t he
MACaddr es s f r om t he hos t NI C car d t o f i l t er t he net wor k t r af f i c. La yer - 2
s wi t ch can beconsidered as multi- port bridge.Layer 2 switches are fast because they
do not look at the network layer header information, instead it looks at the frames
hardware address before deciding toeither forward the frame or drop it.
Limitations of Layer 2 Switching
With bridge the connected networks are still one large broadcast domain.Layer 2 switch
cannot break the broadcast domain, this cause performance issue whichlimits the size
of your network. For this one reason the switch cannot completely replacerouters in the
internetwork.
3.17.1.1 VLAN (Virtual LAN)
VLAN provides Virtual Segmentation of Broadcast Domain in the network.
Thedevices, which are member of same Vlan, are able to communicate with each other. The
devi ces of di f f er ent Vl an may communi cat e wi t h each ot her wi t h r out i ng.
So t hat different Vlan devices will use different n/w addresses.Vlan provides following
advantages: -
Logical Segmentation of network
Enhance network security
Creating port based Vlan
In port based Vlan, first we have to create a Vlan on manageable switch then wehave to add
ports to the Vlan. A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a broadcast domain created based on the
functional, security, or other requirements, instead of the physical locationsof the devices, on a
switch or across switches. With VLANs, a switch can group differentinterfaces into different
broadcast domains. Without VLANs, all interfaces of a switchare in the same
broadcast domain; switches connected with each other are also in thesame broadcast
domain, unless there is a router in between. Different ports of a switchcan be assigned
to different VLANs. A VLAN can also span multiple switches.
The advantages of implementing VLAN are
It can group devices based on the requirements other than their physicallocations.
It breaks broadcast domains and increases network throughput.
It provides better security by separating devices into different VLANs.
Since each VLAN is a separate broadcast domain, devices in different VLANscannot listen or
respond to the broadcast traffic of each other.
Inter-VLAN communication can be controlled by configuring access controllists on the router or
Layer 3 switch connecting the VLANs.
Types of VLAN
Static VLAN
Assigning VLANs to switch ports based on the port numbers. It is easier to setup and
manage.
Dynamic VLAN
Assigning VLANs to switch ports based on the MAC addresses
of thedevices connected to the ports.A VLAN management application is used to set up a
database of MAC addresses, andconfigure the switches to assign VLANs to the
switch ports dynamically based on theMAC addresses of the connected devices. The
application used by Cisco switches iscalled VLAN Management Policy Server
(VMPS).Cisco switches support a separate instance of spanning tree and a separate bridgetable
for each VLAN.
A VLAN = A Broadcast Domain = Logical Network (Subnet)VLAN Operation
Fig 26: VLAN Operation
Each l ogi cal VLAN i s l i ke a s epar at e phys i cal br i dge. VLANs c a n s p a n
a c r o s s mu l t i p l e s wi t c h e s . T r u n k s c a r r y t r a f f i c f o r mu l t i p l e
VLANs . Tr unks us e s peci al encaps ul at i on t o di s t i ngui s h bet ween
di f f er ent VLANs .
VLAN links
There are two different types of links in a switched network:
Access link
A link from Pc to switch is called as access link or A link that is part of only oneVLAN.
Ther ef or e, a por t connect i ng t o an acces s l i nk can be a member of onl y
oneVLAN. And the mode of port is called as access mode.
Trunk link
A link from switch to switch or switch to router is called as trunk link. A 100Mbps
or 1000 Mbps point-to-point link that connects switches or routers, and
carriesframes of different VLANs . Therefore, a port connecting to a trunk link can be a
member of mul t i pl e VLANs . Al l VLANs ar e conf i gur ed on a t r unk l i nk by
def aul t . VLANTr unki ng, by maki ng us e of f r ame t aggi ng, al l ows t r af f i c
f r om di f f er ent VLANs t otransmit through the same Ethernet link (trunk link) across
switches.VLAN Trunking identifies the VLAN from which a frame is sent by tagging
theframe with the source VLAN ID (12-bit long). This feature is known as frame tagging
or frame identification. When there are multiple switches then we have to use trunk links
toconnect one switch with other. If we are not using trunk links then we have to
connectone cable from each vlan to the corresponding vlan of the other switch.With frame
tagging, a switch knows which ports it should forward a broadcastframe (forward out
the ports which have the same VLAN ID as the source VLAN ID). Italso knows which
bridge table it should use for forwarding an unicast frame (since aseparate bridge table
is used for each VLAN).
A f r ame t ag i s added when a f r ame i s f or war ded out t o a t r unk l i nk, and
i s r emoved when t he f r ame i s f or war ded out t o an acces s l i nk. Ther ef or e,
any devi ceattached to an access link is unaware of its VLAN membership
.
Commands to create Vlan
Switch#vlan databaseSwitch(vlan)#vlan <no.> [name <name of vlan>]Switch(vlan)#exit
Commands to configure ports for a Vlan
By def aul t , al l por t s ar e member of s i ngl e vl an t hat i s Vl an1. we can
change vl anmembership according to our requirement.Switch(config)#interface <type>
<no.>Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan <no.>Switch(config-if)#exit
Commands to configure multiple ports in a vlan
Switch(config)#interface range <type> <slot/port no. (space)(space) port no.>Switch(config-
if)#switchport access vlan <no.>Switch(config-if)#exit
Example: -
Suppose we want to add interface fast Ethernet 0/10 to 0/18 in vlan5Switch(config)#interface
range fastethernet 0/10 18Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 5Switch(config-if)#exit
To display mac address table
Switch#show mac-address-tableV l a n M a c
a d d r e s s t y p e p o r
t s
2 0 0 0 - 0 8 - a 1 6 - a b - 6 a - 7 b d y n a m i c f a 0 / 7
To Display Vlan and port membership
Switch#show vlan brief
Command to make Trunk link
Switch(config)#interface <type> <type number> Note :- Trunk mode should not be a member of
any vlan port.
3.17.1.2 Vlan Trunking Protocol (VTP)
With the help of VTP, we can simplify the process of creating Vlan. In
multiples wi t ches , we can conf i gur e one s wi t ch as VTP s er ver and al l ot her
s wi t ches wi l l beconfigured as VTP client. We will create Vlans on VTP server
switch. The server willsend periodic updates to VTP client switches. The clients
will create Vlans from theupdate received from the VTP server.
VTP Operation
V T P a d v e r t i s e m e n t s a r e s e n t a s m u l t i c a s t f r a m e s . V T P
s e r v e r s a n d c l i e n t s a r e s y n c h r o n i z e d t o t h e l a t e s t r e v i s i o n
n u m b e r . V T P a d v e r t i s e m e n t s a r e s e n t e v e r y 5 m i n u t e s o r
w h e n t h e r e i s a c h a n g e .
VTP Modes
VTP server mode
By default all the switches in this mode are in server mode. VTP server is as wi t ch
i n whi ch we can cr eat e, del et e or modi f y Vl ans . yhe s wi t ch i n t hi s
modeforwords the vlans to next switch. The server will send periodic updates for
VTPclients.
VTP client mode
On VTP client, we are not able to create, modify or delete Vlans. The switchin this
mode creates the vlans that are received from server mode switch.The clientwill
receive and forward vtp updates. The client will create same Vlans as defined invtp update.
VTP Transparent mode
Transparent is a switch, which will receive and forward VTP update. It is ableto create, delete
and modify Vlans locally. A vlan created in this mode cannot beforworded into next
switch. A transparent will not send its own VTP updates and willnot learn any information from
received vtp update.
VTP configuration
At Switch 1:
Creat vlan
Port assignment
Trunk port
Switch vtpSwitch(config)#vtp mode server Switch(config)#vtp domain ciscoSwitch(config)#vtp
password sun
At switch 2:
Switch(config)#vtp mode server Switch(config)#vtp domain ciscoSwitch(config)#vtp password
sun
At switch 3:
Switch(config)#vtp mode server Switch(config)#vtp domain ciscoSwitch(config)#vtp password
sun
Fig 27 : VTP Configuration
To see all the configurations
Switch#show vtp passwordSwitch#show vlan brief Switch#show vtp status
Vtp version
Vtp domain
Vtp mode
Vtp pruning
Vtp reusion number
Maximum vlan supporting
Total no. of vlans
VTP Pruning
Pr uni ng i s t he VTP f eat ur e t hr ough whi ch a t r unk l i nk can be
aut omat i cal l ydisable, for a particular Vlan if neighbor switch does not contain ports in that
Vlan. Vlan1is not prun eligible. I n c r e a s e s a v a i l a b l e b a n d w i d t h b y
r e d u c i n g u n n e c e s s a r y f l o o d e d t r a f f i c E x a m p l e : S t a t i o n
A s e n d s b r o a d c a s t , a n d b r o a d c a s t i s f l o o d e d o n l y
t o w a r d any switch with ports assigned to the red VLAN
Command to configure VTP Pruning
We have to use only one command on VTP server for VTP Pruning.Switch#configure
terminalSwitch(config)#vtp pruningSwitch(config)#exit
Fig 28 : VTP Pruning
Spanning Tree Protocol
When we connect multiple switches with each other and multiple path exist fromone s wi t ch
t o anot her s wi t ch t hen i t may l ead t o t he s wi t chi ng l oop i n t he
net wor k. Multiple paths are used to create redundancy in the network. STP is only required
whenmultiple path exist then there is possibility of loop in n/w.
Problems that occur with redundancy path
(i) Multiple copies of the frame will be received by destination.(ii) Frequent changes in the mac
address table of switch.(iii) A mac address may appear at multiple ports in a switch.(iv) Packets
may enter in the endless loop.
Spanni ng Tr ee Pr ot ocol wi l l s ol ve t hi s pr obl em by bl ocki ng t he
r edundanc yinterface. So that only one path will remain active in the switches. If
the primary pathgoes down then disabled link will become enable and data will be transferred
through that path.
Spanning Tree Protocol Basics
S p a n n i n g T r e e P r o t o c o l o r S TP ( I E E E 8 0 2 . 1 d ) i s u s e d t o s o l v e t h e
l o o p i n g problem. It runs on bridges and switches in a network. It implements a
SpanningTree Algorithm (STA), which calculates a loop-free topology for the network.
STP ensures that there is only one active path between any two network segments b y
b l o c k i n g t h e r e d u n d a n t p a t h s . A r e d u n d a n t p a t h i s u s e d o n l y wh e n
t h e corresponding active path failed. It is not used for load-balancing.
Becaus e STP s ol ves t he l oopi ng pr obl em by bl ocki ng one or mor e l i nks i n
anetwork, the frames traveling between some source / destination devices may not be able to use
the shortest physical path.
Bridges exchange STP information using messages called Bridge Protocol DataUnits
(BPDUs) through Layer 2 multicast.
3.18 Wi-Fi (WIRELESS FIDELITY)
The term "Wi-Fi" suggests "Wireless Fidelity", compared with the long-established
audio recording term "High Fidelity" or "Hi-Fi". The term "Wi-Fi", first usedcommercially in
August 1999. Wi-Fi is an IEEE standard 802.11.
3 . 1 8 . 1 W i r e l e s s L A N
Wi - Fi i s al s o known as wi r el es s LAN. The name of a
popul ar wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to provide wireless high-
speedInternet and network connections. "Wi-Fi works with no physical wired
connection between sender a n d r e c e i v e r b y u s i n g r a d i o f r e q u e n c y ( RF)
t e c h n o l o g y , a f r e q u e n c y wi t h i n t h e electromagnetic spectrum associated with
radio wave propagation. When an RF current is
supplied to an antenna, an electromagnetic field is created that then is able to
propagatethrough space.
The Typical Range of a Wi-Fi LAN
The range of a homeWi-Fi LANdepends on thewireless access point (WAP)or
wirelessrouter being used. Factors that determine a particular WAP or wireless
router' srange are:
the specific 802.11 protocol employed
the overall strength of the device transmitter
the nature of obstructions and interference in the surrounding areaA gener al r ul e of t humb
i n home net wor ki ng s a ys t hat 802.11band802.11g WAPs and routers support a
range of up to 150 feet (46 m) indoors and 300 feet (92 m)o u t d o o r s . A n o t h e r
r u l e o f t h u m b h o l d s t h a t t h e e f f e c t i v e r a n g e o f 802.11a is
approximately one-third that of 802.11b/g.Obstructions in home such as brick walls and
metal frames or siding greatly canreduce the range of a Wi-Fi LAN by 25% or more.
Because 802.11a employs a higher s i gnal l i ng f r equency t han 802. 11b/ g,
802. 11a i s mos t s us cept i bl e t o obs t r uct i ons . Interference from microwave ovens and
other equipment also affects range. 802.11b and802.11g are both susceptible to these.
3.18.2
Wireless Standards
The different wireless standards that are used for IEEE 802.11 standard are
Fig 29: IEEE 802.11 Standards
802.11
It was released in year 1997
.
The standard was original of 802.11. the max. datarate of this is 2Mbps and frequency of this is
2.4GHz and can cover upto 46m.
802.11a
It was modified in year 1999. this is improved version of original standard. Operates
at the frequency of 5GHz, which is less crowded than 2.4GHz where telephonesand microwaves
may cause interference. Although the speed is up to 54Mbps, the rangeis only up to 75 feet or
distance covered is 46m. 802.11a standard is incompatible with both 802.11b and g
because it operates at a different frequency.
802.11b
This standard was released in 1999
.
Operates on the 2.4GHz frequency band andcan transmit data at speeds of up to 11Mbps
within a range of up to 100-150 feet or adistance of 90m.Wireless range can be affected by
reflective or signal-blocking obstacles,such as mirrors, walls, devices and location, whether
indoors or outdoors.
802.11g
This standard was released in 2003. The max. data rate for the standard is 54Mbps.It supports a
frequency range of 2.4GHz, covers a distance of 90m.
802.11n
T h e l a t e s t v e r s i o n o f I E E E 8 0 2 . 1 1 s t a n d a r d t h a t i s s t i l l i n
p r o g r e s s o f devel opment . The next gener at i on of hi gh- s peed wi r el es s
net wor ki ng, capabl e of delivering the range and capacity to support today's most
bandwidth-hungry applicationslike streaming high definition video, voice, and music.
Wireless-n is based on MIMO(Multiple Input, Multiple Output) technology, which
uses multiple radios to transmitmultiple streams of data over multiple channnels.Operates
in two modes of frequency 2.4GHz and 5.6GHz frequency band andcan t r ans mi t
dat a at s peeds of up t o 11Mbps wi t hi n a r ange of up t o 100- 150 f eet
. Wireless range can be affected by reflective or signal-blocking obstacles, such as mirrors,walls,
devices and location, whether indoors or outdoors.
Wi-Fi is supported by many applications anddevices
video game consoles
homenetworks
PDAs
mobile phones
major operating systems
other types of consumer electronics
3.18.3 Wireless Security
A common but unproductive measure to deter unauthorized users is to suppress
theAP'sSSIDbroadcast, "hiding" it. This is ineffective as a security method because
theSSID is broadcast in the clear in response to a client SSID query. Another
unproductivemet hod i s t o onl y al l ow comput er s wi t h knownMAC addressest o
j oi n t he net wor k. MAC address are easily spoofed. If the eavesdropper has the ability to
change his MACaddress, then he may join the network byspoofing an authorized address
.
Wired Equivalent Privacy(WEP) encryption was designed to protect against
casualsnooping, but is now considered completely broken. Tools such
asAirSnort or aircrack can quickly recover WEP encryption keys.
To counteract this in 2002, theWi-Fi AllianceblessedWi-Fi Protected Access(WPA) for
wireless security. Though more secure than WEP, it has outlived its designed lifetime,has known
attack vectors and is no longer recommended.In 2004 the fullIEEE 802.11i(WPA2) encryption
standards were released. If used with a802.1Xserver or in pre-shared keymode with a strong and
uncommon passphrase WPA2 is still considered secure, as of 2009.
4. CONCLUSION
General Conclusion
Comput er Net wor ki ng i s a ver y vas t pr oj ect i n t he pr es ent devel opi ng er a
of electronics and communication. Now a days, computers are used in a wider range. All the
organizations are using multiple computers within their departments to perform their dayto day
work. Computer network allows the user to share data , share folders and files withother users
connected in a network. Computer Networking has bound the world in a verysmall area with it
wide networking processes like LAN, MAN, WAN.
Applications
Communication Field
Industries
Medical Field
Rearch Field
Organisations
School
Colleges
REFRENCES
www.goole.com
www.jetkinginfotrain.com
www.microsoft.com
www.nythimes.com
www.digitech-engineers.com
Network Essentials module
4-in-1 MCSE study material
Introduction to Window Server2003
CISCO Cretified Network Associate
Faruk Husain
Activity (171)
Filters
Add to collectionReview Add NoteLike
Showing
AllMost RecentReviewsAll NotesLikes
You've already reviewed this. Edit your review.
read
Rating 0/5
0
Post notePost reviewPost replyPost note and like
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Zero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionDe la EverandZero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Icemplc ReportDocument8 paginiIcemplc ReportPratik BhoirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tpcell Statement of ProblemDocument14 paginiTpcell Statement of Problemhareeshma hdasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDe la EverandSoftware Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interactive Learning: 1. Introduction and Objectives of The ProjectDocument69 paginiInteractive Learning: 1. Introduction and Objectives of The ProjectThansiya ThansiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gatepass - Aspdotnet - Full DoucmentDocument59 paginiGatepass - Aspdotnet - Full DoucmentS LingeswarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Courier Service SystemDocument84 paginiOnline Courier Service SystemRadheshyam Nayak100% (1)
- Untitled DocumentDocument31 paginiUntitled Documentnahim islamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Job Portal Java Project DocumentDocument92 paginiOnline Job Portal Java Project DocumentMamatha RYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project On Student Management SystemDocument59 paginiProject On Student Management SystemAnuj Singh67% (3)
- Document - Repository and Search Engine For Alumni of CollegeDocument110 paginiDocument - Repository and Search Engine For Alumni of CollegeSminfo Mdu67% (3)
- Courier Project ReportDocument99 paginiCourier Project ReportArchie Srivastava100% (3)
- Banking Documentation of VB ProjectDocument40 paginiBanking Documentation of VB ProjectPaari Malhotra100% (1)
- Project NewDocument18 paginiProject Newhemant1108aranghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Payment Billing System DocumentDocument66 paginiPayment Billing System DocumentUsha AvinashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Payment Billing System DocumentDocument65 paginiPayment Billing System Documentshankar_718571% (7)
- Module 5 - Reading1 - SystemDevelopmentDocument26 paginiModule 5 - Reading1 - SystemDevelopmentChristopher AdvinculaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Caretaker ManagementDocument68 paginiProject Caretaker ManagementChandramathi M100% (2)
- Chapter One: 1.1 Statement of ProblemDocument9 paginiChapter One: 1.1 Statement of ProblemAbuky Ye AmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employee Tracking System: Done byDocument6 paginiEmployee Tracking System: Done byPrakash ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Development of Employee Performance Management - An OverviewDocument57 pagini1.1 Development of Employee Performance Management - An OverviewJothi ManiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Project Report OnDocument92 paginiA Project Report OnMan Mohan ChaurasiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term Paper of Database Management System Topic:-Bus Reservation SystemDocument26 paginiTerm Paper of Database Management System Topic:-Bus Reservation Systemkaruna1240Încă nu există evaluări
- Bank ManagementDocument71 paginiBank ManagementMubariz ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction of ProjectDocument38 paginiIntroduction of ProjectAndrew MeyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employee Survey Feedback System 201: 1.1. ObjectiveDocument32 paginiEmployee Survey Feedback System 201: 1.1. ObjectiveAbhijeet NigoskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- College Management SystemDocument8 paginiCollege Management SystemSunil Sharma50% (2)
- UNIVERSITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Full ReportDocument20 paginiUNIVERSITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Full Reportkumthekarsachin00Încă nu există evaluări
- University PPT - PPT: University Management System Full ReportDocument22 paginiUniversity PPT - PPT: University Management System Full ReportAryan AryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why-Is-A-System-Proposal-So-Crucial-For-System-Design 2Document3 paginiWhy-Is-A-System-Proposal-So-Crucial-For-System-Design 2GlobeÎncă nu există evaluări
- RiportDocument130 paginiRiport720 026 Promita GhoruiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Highlight Add Note Share QuoteDocument4 paginiHighlight Add Note Share QuoteYogesh YogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online TC Generation DocumentationDocument15 paginiOnline TC Generation Documentationravi kumar100% (1)
- College Info and SolutionDocument47 paginiCollege Info and SolutionNilesh Kumar ParjapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BekkkkiDocument6 paginiBekkkkiNimpa JaredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software Engineering Unit 2Document14 paginiSoftware Engineering Unit 2Yogesh PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Two Literature ReviewDocument6 paginiChapter Two Literature ReviewAishah amslahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Employee Management System: A Project ReportDocument54 paginiOnline Employee Management System: A Project ReportMohammad ShoebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employee Management SystemDocument40 paginiEmployee Management SystemMangesh Amant Aure88% (24)
- ERP System Documentation 123Document75 paginiERP System Documentation 123Victor KariukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employee Payroll SystemDocument7 paginiEmployee Payroll Systemsteph_ekeh75% (4)
- Feasibility StudyDocument16 paginiFeasibility StudyMarianne Balita AtienzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Resource Management System: Santhosh Ahul VeerDocument75 paginiHuman Resource Management System: Santhosh Ahul VeerBharathi VaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- University Management System DOCUMENTATIONfinalDocument114 paginiUniversity Management System DOCUMENTATIONfinalKaf Afari44% (9)
- Blantyre International University Systems Analysis & Design Assignment 1Document8 paginiBlantyre International University Systems Analysis & Design Assignment 1aizkorri__1528Încă nu există evaluări
- Capstone Final ReportDocument26 paginiCapstone Final ReportLalit GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Content Management SystemDocument66 paginiContent Management Systemrv0000s50% (2)
- College Library Management System: by Manish Bisht Deepak RajaramDocument42 paginiCollege Library Management System: by Manish Bisht Deepak RajaramNikhil GawadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examination Management SysteDocument87 paginiExamination Management SysteAjeet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Requirement Document For Intern ManagementDocument32 paginiBusiness Requirement Document For Intern ManagementSamAryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report E-CampusDocument21 paginiProject Report E-CampusNikita Jain50% (4)
- Print 3Document60 paginiPrint 3arunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis On Coll MGMTDocument27 paginiSynopsis On Coll MGMTJeffrey ShawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report Student Information SystemDocument110 paginiProject Report Student Information SystemFreeProjectz.com86% (58)
- Synopsis Job PortalDocument16 paginiSynopsis Job PortalAbhishek SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- College Info and Solution": Rajasthan Technical University, KotaDocument24 paginiCollege Info and Solution": Rajasthan Technical University, KotaNilesh Kumar ParjapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment of Design and Analysis of Information SystemDocument8 paginiAssignment of Design and Analysis of Information Systembir5311Încă nu există evaluări
- House RentDocument62 paginiHouse RentfcmitcÎncă nu există evaluări
- HostelDocument48 paginiHostelNaveen Jaswal75% (4)
- Prospekt WT48C-600 enDocument4 paginiProspekt WT48C-600 enshruthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobility Strategy-Lte Wcdma Gsm-V2Document72 paginiMobility Strategy-Lte Wcdma Gsm-V2Pooneh Parvin100% (1)
- CS 540: Introduction To Artificial Intelligence: Final Exam: 5:30-7:30pm, December 17, 2015 Beatles Room at EpicDocument11 paginiCS 540: Introduction To Artificial Intelligence: Final Exam: 5:30-7:30pm, December 17, 2015 Beatles Room at EpicchemchemhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBG ENGs R11.3Document94 paginiMBG ENGs R11.3Manu RTÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCM ApplicationsDocument50 paginiTCM ApplicationsPhúc Hòa PtitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mind ValleyDocument2 paginiMind ValleyAbhinav Goswami0% (1)
- MTU BLUE VISION AdVANCED PDFDocument8 paginiMTU BLUE VISION AdVANCED PDFomar alayash100% (1)
- Rtu2020 SpecsDocument16 paginiRtu2020 SpecsYuri Caleb Gonzales SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powerline Communications For Street Lighting AutomationDocument6 paginiPowerline Communications For Street Lighting AutomationPhú NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fortios - Microsoft Hyper-V CookbookDocument33 paginiFortios - Microsoft Hyper-V CookbookAlejandro BuitragoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web SocketDocument20 paginiWeb SocketakahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellcrypt Enterprise Gateway USA V3.4-A-V2 0Document2 paginiCellcrypt Enterprise Gateway USA V3.4-A-V2 0Pravesh Kumar ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultima Forte Required Data Inputs For ZTE InfrastructureDocument15 paginiUltima Forte Required Data Inputs For ZTE InfrastructureVarun SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi Processor Configurations: 3.1 Multiprocessor SystemsDocument3 paginiMulti Processor Configurations: 3.1 Multiprocessor SystemsAnonymous c75J3yX33Încă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet AWACDocument6 paginiDatasheet AWACfokwoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cube400 Modbus Comms Manual REV5Document18 paginiCube400 Modbus Comms Manual REV5Anonymous qktauX50tsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acronyms of ComputerDocument179 paginiAcronyms of ComputerDhiman NathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fos Rest API Change LogDocument23 paginiFos Rest API Change LogMuhammad HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DCC Micro Project Report On: Title:-Packet Tracer Server and ClientDocument19 paginiDCC Micro Project Report On: Title:-Packet Tracer Server and ClientNoor alam ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bandwidth Controller TutorialsDocument25 paginiBandwidth Controller TutorialsAnank SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- S3030 Portable ReaderDocument2 paginiS3030 Portable ReaderRaymond YambaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charging SYSTEMDocument64 paginiCharging SYSTEMThind MalkeetÎncă nu există evaluări
- I+ME Actia PassThru XS2G Driverpack 2.8.1.14Document7 paginiI+ME Actia PassThru XS2G Driverpack 2.8.1.14Jose AG0% (1)
- Junos Associate JNCIA-Junos Voucher Assessment TestDocument5 paginiJunos Associate JNCIA-Junos Voucher Assessment TestIct labÎncă nu există evaluări
- Java Network ProgrammingDocument21 paginiJava Network Programminghj43usÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yealink SIP-T21 Administrator GuideDocument841 paginiYealink SIP-T21 Administrator GuideAleksey MarmiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Reservation SystemDocument5 paginiOnline Reservation SystemSara AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyderabad Metropolitan Water Supply & Sewerage Board - Online Bill PaymentDocument1 paginăHyderabad Metropolitan Water Supply & Sewerage Board - Online Bill PaymentInnoInfo AdamÎncă nu există evaluări
- LMT Token RingDocument15 paginiLMT Token Ringlakshay187Încă nu există evaluări
- BGP Interview Questions and Answers - Basic and Advanced LevelsDocument6 paginiBGP Interview Questions and Answers - Basic and Advanced LevelsAbdul MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNDe la EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsDe la EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.De la EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsDe la EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301De la EverandCCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301Încă nu există evaluări
- Unlock Any Roku Device: Watch Shows, TV, & Download AppsDe la EverandUnlock Any Roku Device: Watch Shows, TV, & Download AppsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsDe la EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZDe la EverandPHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kali Linux Network Scanning Cookbook - Second EditionDe la EverandKali Linux Network Scanning Cookbook - Second EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionDe la EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksDe la EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Designing and Building Security Operations CenterDe la EverandDesigning and Building Security Operations CenterEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (3)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityDe la EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (13)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxDe la EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (67)
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachDe la EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamDe la EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900De la EverandMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)De la EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)Încă nu există evaluări
- Mastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionDe la EverandMastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamDe la EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringDe la EverandCybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (40)
- CCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationDe la EverandCCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationÎncă nu există evaluări