Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Syllabus 6th Sem
Încărcat de
Pravin Kumar KarumanchiDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Syllabus 6th Sem
Încărcat de
Pravin Kumar KarumanchiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
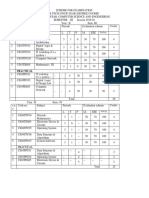
Syllabus for B. E.
Sixth Semester
(Electronics & Communication Engg.)
FIELDS AND RADIATING SYSTEMS
Scheme (Theory: 4 hrs, Tutorial: 1hr.)
Duration : 3 Hr.
College Assessment : 20 Marks
University Assessment : 80 Marks
UNITI:
Guided waves: Waves between parallel planes, TE, TM, TEM waves and their characteristics, Attenuation
in parallel plane guides, wave impedances.
UNIT-II:
Rectangular waveguides: TM, TE waves in rectangular guides and their characteristics, wave velocity,
guide wavelength, wave impedances, field configurations.
UNIT-III:
Transmission lines: Transmission line equations and their solution. Transmission line parameters,
characteristic impedance, propogation constant, attenuation constant and phase constant, waveform
distortion, distortionless transmission lines, loading of transmission lines, reflection coefficient and
VSWR.Equivalent circuits of transmission lines, transmission lines at radio frequency, open and short
circuited lines, smith chart, stub matching.
UNIT-IV:
Scalar and vector potentials, retarded potentials, field due to a current elements, power radiated and
radiation resistance for field due to a dipole, power radiated and radiation resistance, reciprocity theorem
applied to antennas gain and aperture of an antenna, radiation intensity, directivity and antenna gain.
UNIT-V:
Two element arrays and their directional characteristics, linear array analysis, broadside and end-fire
arrays, pattern multiplication, binomial arrays, Design of broadcast array for a specific pattern.
UNIT-VI:
Basic principles of parabolic reflectors, analysis and power pattern, lens antennas, folded dipole, turnstile
and yagi antenna, log-periodic antennas, horn antennas, traveling wave antennas,cassegrain antenna.
Books: -
1. Electromagnetic waves and radiating systems: Edward C.Jordan & Keith G. Balmain
2. Antennas: Krauss.
Reference Book:
1. Communication Electronics: George Kennedy
CONTROL SYSTEM ENGINEERING
Scheme (Theory: 4 hrs, Tutorial: 1hr.)
Duration : 3 Hr.
College Assessment : 20 Marks
University Assessment : 80 Marks
UNIT-I:
Introduction to need for automation and automatic control, use of feedback, Broad spectrum of system
application. Mathematical modelling, Diff.equations, transfer functions, block diagram, signal flow graphs,
Application to elementary system simplifications, Effect of feedback on parameter variation, disturbance
signal, servomechanisms and regulators. Control system components, Electrical. Electromechanical,
hydraulic, pneumatic and other components. Their functional analysis and input, output representation.
UNIT-II:
Time response of the system, first order & second order system, (standard input) concept of gain & time
constant, steady state error, type of control system, approximate method for higher order system.
UNIT-III:
Root location and its effect on time response, elementary idea of Root Locus, effect of adding pole and
zero and proximity of imaginary axis.
UNIT-IV:
Stability of control systems, conditions of stability characteristic equation, Routh Hurwitz criterion, special
cases for determining relative stability.
UNIT-V:
Frequency response method of analysing linear system, Nyquist & Bode Plot, stability & accuracy
analysis from frequency response, open loop & closed loop frequency response.
Nyquist criteria, effect of variation of gain & addition of poles & zeros on response plot, stability margin in
frequency response.
UNIT-VI:
State variable method of analysis, characteristic of system, state choice of state representation of vector
matrix differential equation, standard form, relation between transfer function and state variable.
Text Books:
1. Control system analysis: Nagrath and Gopal
Reference Book:
1. Linear system analysis : D. Azzo & Honpis, 1975
LINE COMMUNICATION & SWITCHING SYSTEM
Scheme (Theory: 4 hrs, Tutorial: 1hr.)
Duration : 3 Hr.
College Assessment : 20 Marks
University Assessment : 80 Marks
UNIT: I
Telegraphy: telegraph codes, morse code, cable code, 7.5 unit code, telegraph speed, baud, morse key,
morse sounder, telegraph relays, polarised and non-polarised relays, operate and release lag, telegraph
distortion. Telegraph circuit: simplex and duplex telegraph ckt, differential duplex ckt, bridge duplex
telegraph ckt, telegraph repeater.
UNIT:II
Teleprinter, teleprinter transmitter receiver, baudat multiplex, telex, fascimile.
UNIT:III
Manual telephony: telephone transmitter and receiver, side tone, strowger exchange, subscribers
telephone set, principles of manual switching system, electronic telephone, transmission bridge, local and
central battery system, telephone relays, trunk exchange, junction working.
UNIT: IV
Automatic telephony: strowger exchange, line switches and selectors, ringing and tone ckt, subscriber
uniselsctor ckt, hybrid coil, line balancing n/w, two and four wire repeaters, trunking diagram, cross bar
switching system, traffic engg, traffic unit, grade of service, calculation of switches and selectors, director
systems, busy hour call attempts(bhca).
UNIT: V
Electronic switching systems: pcm principles, companding, hdba, coding borscht function, subscriber line
interface ckt (slic), trunk side interface, cas, ccs, ccitt no. 7 signalling, cellular telephony, introduction to
isdn.
UNIT: VI
I carrier communication: carrier equipments, attenuator,
Equilizer filters, long haul carrier telephone system, power line carrier communication.
Text Books:
1. Telegraphy by M.B. Bishwas
2. Telephony by N.M. Bishwas
COMMUNICATION ELECTRONICS
Scheme (Theory: 4 hrs, Tutorial: 1hr.)
Duration : 3 Hr.
College Assessment : 20 Marks
University Assessment : 80 Marks
UNIT-I:
Frequency spectrum of electromagnetic waves, their properties, wave propagation etc.Tuned Amplifiers,
gain and bandwidth, neutralization, Noise, types, source, noise figure calculation.
UNIT-II :
AM .modulators, series plate modulated class C amplifier, efficiency and power calculations, SSB
modulation SSS-SC modulations. A.M. Demodulators, square law detector, diode peak detector,
envelope detector, detectors for SSB and SSB-SC AM signals, AM using transistors .
UNIT-III :
Angle Modulation, Frequency modulation spectrum, Reactance tube and FET modulators Armstrong
method, .F.M. transmitters, frequency stabilization methods. FM discriminator .Foster Selly, PLL
detectors, .stereophonic FM.
UNIT-IV:
Pulse modulation, pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), Pulse width Modulation (PWM), Pulse Position
Modulation (PPM), Pulse code modulation (PCM), Delta Modulation DM).
UNIT-V:
Radio Receivers and its measurements: TRF receiver, superhetrodyne receiver. Detailed study of block
schematic and circuits of mixer, RF-stage, I .F stage detector, Automatic gain control (AGC), FM radio
receivers.
Receiver Measurements: Sensitivity, selectivity, image frequency rejection etc. communication Receiver,
block schematic and its special features.
UNIT-VI:
Line telephony: Elementary phone System, central switching, simple exchange, two and four wire
connections, Time division multiplexing, Analog Time division switching, time slot interchanging (TSI),
space array for digital signal, combined space time switching.
Text Books:
1. Communication Electronics: Kennedy, TMH
2. Communication Electronics: Deshpande, TMH
Reference Book:
1. Communication Electronics: Forest Bakeries
2. Radio Communication: Miller
3. Electron Tybe Circuits: Seely
4. Principals of Communication System: Taub and Schilling,PHI
5. Communication Electronics: Roddy and Coolen, PHI
COMPUTER ORGANISATION
Scheme (Theory: 4 hrs, Tutorial: 1hr.)
Duration : 3 Hr.
College Assessment : 20 Marks
University Assessment : 80 Marks
UNIT-I :
Resister Level Design: General characteristic, description languages, combinational and sequential
components, design methods. Processor level design components, design techniques.
UNIT-II:
Processor design : Processor organisation, information representation, number formats. Instruction set,
instruction formats, instruction types, multiplication and division ALU design, floating point arithmetic,
IEEE 754 floating point formats.
UNIT-III:
Control design: Instruction sequencing, interpretation, hard wire control design, methods, multiplier and
CPU control unit. Micro programmed Control: Basic concept, minimizing microinstruction size, multiplier
control unit Micro programmed Computers: CPU control unit. A conventional & inconventional computers.
UNIT-IV:
Memory organisation: Device characteristics, RAM, serial access memories, Virtual memory, concept of
Cache memory & associative memories.
UNIT V:
System Organisation: Local & long distance communication, Input & output system, Interrupts, DMA,
introduction to parallel processing.
UNIT VI:
Concept of parallel processing, pipelining, vector processors, Introduction to RISC
architecture, data flow architecture.
Text Books:
1. A.S Tanen Baum, Structured computer Organisation Third edition, PHI
2. Y. Chu 11 Computer organisation & Microprogramming. Prentice Hall, Englewood Chiffs. N. J
Reference Books :
1. M. H. Mano, Computer system Architecture, Prentice Hall, Engle wood chiffs.N.J
2. C. H. Gear, Computer organisation & Programming, McGraw Hill, N.V.
3. Computer Architecture and Organisation: J.P Hayes, Second edition, PAI.
ELECTRONIC WORKSHOP PRACTISE
Fabrication and testing of small electronics circuit, PCB Design and technical report presentation.
Study of Indian standards in Electronic Industry.
Manufacturing, practices in Electronic Industry.
Reference material:-
PCB Design: Boshar TMH Pub.
Elliot: Integrated circuit Fabrication Technology (TMH)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Processors, Parallel Processing and Virtual MachinesDocument12 paginiProcessors, Parallel Processing and Virtual MachinesSaloni ThapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Unit 3 CSADocument25 paginiUnit 3 CSAyugdevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- R18 B.TECH CSE II Year SyllabusDocument33 paginiR18 B.TECH CSE II Year SyllabusDivyaThalankiVenkataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Computer Organization and Architecture by William StallingDocument34 paginiComputer Organization and Architecture by William StallingFinding_Nemo4Încă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- SEISBIT® 3D: The New Seismic While Drilling Data Acquisition SystemDocument10 paginiSEISBIT® 3D: The New Seismic While Drilling Data Acquisition SystemEugene FrancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- It Skills NotesDocument29 paginiIt Skills Notesjuttahtsham160Încă nu există evaluări
- Sequencing Control Signals in Computer OrganizationDocument48 paginiSequencing Control Signals in Computer OrganizationVenkataramana Bathala0% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Introduction To C++ ProgrammingDocument193 paginiIntroduction To C++ Programmingarjun vijay91% (11)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Co 18cs34 Notes FinalDocument141 paginiCo 18cs34 Notes FinalAshishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Microprocessor Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument15 paginiMicroprocessor Chapter 1 IntroductionKrishna GuragaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- AK47's O Level: Computer Science 2210 April 2030 30 MinutesDocument6 paginiAK47's O Level: Computer Science 2210 April 2030 30 MinutesPC AbdulkarimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sir J.C Bose School of Engineering: Somnath Khamaru Sourish Barman B.Tech Ece 3 Year Student, SkfgiDocument25 paginiSir J.C Bose School of Engineering: Somnath Khamaru Sourish Barman B.Tech Ece 3 Year Student, SkfgiSomnath KhamaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Lab9 VHDLDocument8 paginiLab9 VHDLFasli CoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Fully Prepared Accounts Notes For The Year 2009 - 10 NewDocument167 paginiNew Fully Prepared Accounts Notes For The Year 2009 - 10 NewAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Modle 01 - HPC Introduction To PipelineDocument124 paginiModle 01 - HPC Introduction To PipelineJaideep SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- ResearchDocument4 paginiResearchNikko PatunganÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Design of A General Purpose 8 Bit RISC Processor For Computer Architecture LearningDocument30 paginiDesign of A General Purpose 8 Bit RISC Processor For Computer Architecture LearningGuillermo Esqueda SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Punjab Technical University: Computer ArchitectureDocument2 paginiPunjab Technical University: Computer ArchitecturesandeepaprÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- List of Elective Courses With Syllabus.Document64 paginiList of Elective Courses With Syllabus.neelimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The 8051 Microcontroler Based Embedded SystemsDocument43 paginiThe 8051 Microcontroler Based Embedded Systemsmanishpatel_790% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Syllabus CBCS III IV 27.09.19 PDFDocument51 paginiSyllabus CBCS III IV 27.09.19 PDFहर्ष सौदर्शनÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4FDocument23 paginiChapter 4FPogo Iso100% (1)
- Lorch ROUNDSEAM Rundnahtloesungen en ViewDocument32 paginiLorch ROUNDSEAM Rundnahtloesungen en ViewElina ViolitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Introduction To PIC18Document44 paginiChapter 2 Introduction To PIC18Andy WoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQDocument162 paginiMCQZohaib BukhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- GE6151 Computer Programming NotesDocument152 paginiGE6151 Computer Programming NotesSuryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Göktuğ Karaman 171112023 EEE481 Computer Architecture HW #2 Single-Cycle CPU Control Unit DesignDocument8 paginiGöktuğ Karaman 171112023 EEE481 Computer Architecture HW #2 Single-Cycle CPU Control Unit DesignGoktug KaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- COA Full Syllabus-CSEDocument3 paginiCOA Full Syllabus-CSEAMARTYA KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5) Basic CO and DesignDocument35 pagini5) Basic CO and DesigngobinathÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Offline SCN CodingDocument1 paginăOffline SCN CodingStephenson100% (2)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)