Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Misconduct Disclosure of The Intermediates Using The Trusted Authority
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Misconduct Disclosure of The Intermediates Using The Trusted Authority
Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 03 Special Issue: 07 | May-2014, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 791
MISCONDUCT DISCLOSURE OF THE INTERMEDIATES USING THE
TRUSTED AUTHORITY
N.Vijay
1
, S.Aarthi
2
, M.Pandiyanathan
3
1
N.Vijay PG Scholar, Computer Science and Engineering, M.A.M College Of Engineering, Tamilnadu, India
2
S.Aarthi PG Scholar, Computer Science and Engineering, M.A.M College Of Engineering, Tamilnadu, India
3
M.Pandiyanathan Professor, Computer Science and Engineering, M.A.M College of Engineering, Tamilnadu, India
Abstract
In delay tolerant network which has an certain problem for while transmitting data from source to proper destination due to
traffic or missing data. To solve this problem, motivating the concept of advanced i-trust scheme. The proposed model which
provides solution for that delay tolerant network problem. The game theory approach which has to send an duplicate message
from sender to intermediate node, if anyone node act as malicious node,we can easily predict that node and trusted party who
verify the signature of intermediate node. To provide security while transmitting the data by introducing the concept of Triple des
algorithm.This will provide more security rather than an RSA algorithm.
Keywordsadvanced iTrust, reliable authority, Triple DES, RSA algorithm.
--------------------------------------------------------------------***------------------------------------------------------------------
1. INTRODUCTION
Delay tolerant networks (DTNs) deals with an hetrogeneous
network that may lack in continous network connection.
Routing is the major concern part of the network because
which has to establish the path among all the nodes from the
source node to proper destination node. When an user has to
forward or send the data from one node to next node, we
have to concentrate on two things like route discovery and
maintanence phase. If anyone node doesnt have path from
source node to any other node, create path to all other nodes
from source node by using an discovery mechanism.
2. RELATED WORK
The routing mechanism which has to create path from one
node to another node but it does not send a failure data or
packet from the corresponding node. We need to send an
missing data to the destination node after recovery. By
finding an alternate path if any one node get fails while
forwarding data. If any user wants to send an data or packet
to final node, it requires an intermediate node to reach an
destination or final node.
The intermediate node who has to verify by any other reliable
party to determine whether the corresponding node is good or
not. Because sender and receiver node may not act as thief
node but the intermediate node act as an duplicate node. The
author described in survey paper such as three main
important concepts like packet missing, congestion, dropping
of packets while forwarding the data.
Consider the three nodes which are going to communicate
one by one. Nodes are A,B,C and then if node A wants to
send an data to node C by using an intermediate node B.when
an node A starts sending an data to node B,then the node B
who receives the data or information. Then node B who has
to send the data to node C before that node B has take an
original data. These are all the problems facing while sending
or forwarding data from one node to another node.
Forwarding history to be maintaining each and every node
while sending or forwarding data. The author has to be
introduced several techniques to tolerate this problem but it is
not suitable for solving the network problem. Suppose if any
node act as thief node, the thief node can identify by using an
watch dog technique and path has to calculate by using rater
method.
The misbehaving node history to be find but not properly
eliminating and maintaining duplicate node history or
duplicate node from the network by used an existing method.
To overcome this problem introducing the advanced i-trust
model and triple des algorithm.
And also it has to be find an duplicate node as well as reliable
node to send an original data by using an game theory. This
mechanism which has to send an duplicate message or data to
intermediated node, which node gives an immediate response
to source node that should be considered as reliable node.
3. PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed model which deals with an different strategy
and algorithm to resolve an overall problem identified in
survey. The advanced i-trust model to be identify an
unwanted node present inside the network. The user has to
create the sender and receiver node at initially and then
sender has to select the intermediate nodes to forward the
data by using an proposed model.
The sender who has to collect the participating nodes in the
intermediate side. After collecting the routing nodes details
IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 03 Special Issue: 07 | May-2014, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 792
that information to be passed to reliable person. Then only
sender starts sending an original data to intermediate nodes
and intermediate node who has to create the signature among
all nodes. Because the reliable person to cross verify the
signature of intermediate and reliable node.If it matches with
an original signature then only it will forward the original
data to next node and receiver has to send an receiving
signature to reliable person. Then the reliable person has to
once again verifies the signature then it will forward the data
to receiver side.
3.1 Advantages
Each node should maintain the contact details of all
nodes.
Advanced i-trust introducing an misbehavior
detection scheme in DTNs.
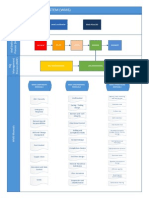
3.2 Architecture
Fig 1. System Architecture
3.3 Proposed Algorithm
create number of nodes to participate n
count from i=1 to n
number starts from 0 to 10n-1
if mi /10n < pb then
all nodes should submit an history
if Detect (i, S,f, [r1, r2], R, D)
Then
Punish the theif nodes
else
payment will not refund back p
end if
else
payment will not refund back p
end if condition
end for condition
3.4 Proposed Modules
There are four modules present in the proposed system. They
are Network Formation, Routing Module, Evidence
Generation phase, Auditing phase
3.4.1 Network Formation
Create number of nodes on the network for the data
transmission process.
The ids are generated for each of the individual
nodes in the network.
There are three algorithms are used, from that
choose any one of the algorithm and use it to
generate keys to all nodes.
The user has to pay for new account creation.
3.4.2 Routing Module
To pick the sender and receiver for the data
transmission.
Routing is the next process for select the
intermediate node.
This intermediate node is used to transfer the data
from the sender to the destination.
The distance of each node is calculated. And then
the path cost is calculated.
Based on this the intermediate is selected.
3.4.3 Evidence Generation Phase
In this the forwarding history evidence is the first
process, this is processed in the sender.
Delegation task evidence is the second process. In
this the signature of the source and the signature of
the intermediate is processed.
Contact history evidence is the third step in the
evidence generation phase.
3.4.4 Auditing Phase
Trust authority plays the vital role in the auditing
phase.
Trust authority sends the investigation request to the
sender, intermediate, and receiver.
The routing history to be sends to reliable person.
Intermediate send the forwarding history to the trust
authority. Receiver sends the contact history to trust
authority.
Based on this the trust authority find the
misbehavior of the intermediate node.
3.5 The Advanced itrust Model
The advanced i-trust model which deals with an reliable
person to verify the signature of the node history. A node
sends an original data to corresponding intermediate nodes
after checking an originality of intermediate nodes.
Based on the node mobility and data size to be fixed on the
intermediate nodes before starting a process. The game
theory method is mainly used for finding an originality of
each node and identify the node speed or immediate response
to source node. After finding an good node we have to
proceed with an new process. And then three different phases
to be maintained and game theory concepts which clearly
identify the original node in the network.
IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 03 Special Issue: 07 | May-2014, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 793
Fig 2. Advanced itrust model
3.5.1 Game Theory Analysis
The game theory is mainly used to identify the duplicate
nodes and reliable nodes in the network. And it also number
nodes to be calculated at source and destination levels by
means of reliable node. The unwanted node doesnt get an
initial payment after finding out.
N = {N0, N1... Nn}
si = {si0 , si1 , si2 , ..., sin } is the strategy set of the
player
i is the payoff of the ith player Ni , and it is
measured by credit earnings.
i has an mixed strategy for player p
3.6 Triple DES Algorithm
The triple des algorithm is mainly used for enforcing security
rather than rsa algorithm..
And then each time which has three rounds and each round
has 56bit.
Two Steps
The plain text which has to converted into ciper text.
And then ciper text process can be again converting to
plaintext after decrypting.
4. CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK
Here we are providing security , integrity as well as data
transmission without network traffic. We implemented
advanced i- trust model to find the unwanted node. The
advanced i-trust model which will provide an greater
efficiency for all kinds of network in future.
REFERENCES
[1] R. Lu, X. Lin, H. Zhu, and X. Shen, SPARK: A New
VANET-based Smart Parking Scheme for Large
Parking Lots, in Proc. of IEEE INFOCOM09, Rio
de Janeiro, Brazil, April 19-25, 2009.
[2] T. Hossmann, T. Spyropoulos, and F. Legendre,
Know The Neighbor: Towards Optimal Mapping of
Contacts to Social Graphs for DTN Routing, in Proc.
of IEEE INFOCOM10, 2010.
[3] Q. Li, S. Zhu, G. Cao, Routing in Selfish Delay
Tolerant Networks in Proc. of IEEE Infocom10,
2010.
[4] H. Zhu, X. Lin, R. Lu, Y. Fan and X.
Shen,SMART: Secure Multilayer Credit-Based
Incentive Scheme for Delay-Tolerant Networks, in
IEEE Transactions on Vehicular
Technology,vol.58,no.8,pp.828-836,2009.
[5] E. Aydayi, H. Lee and F. Fekri,Trust
Management and Adversary Detection for Delay
Tolerant Networks, in Milcom10, 2010.
BIOGRAPHIES
Vijay has successfully received his B.E
computer science degree(2011) from v.s.b
engineering college affiliated to Anna
university, Chennai. He is currently doing
PG scholar at M.A.M college of engineering,
trichy.
Aarthi has successfully received her B.Tech
information Technology degree(2012) from
Kings college of engineering affiliated to
Anna university, Chennai. She is currently
doing PG Scholar at M.A.M College of
engineering, trichy.
Pandiyanathan has received M.Tech from
NIT trichy.He is doing Ph.d affiliated to
anna university, Chennai. He is working as
professor in M.A.M college of engineering,
trichy.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Din 48204Document3 paginiDin 48204Thanh Dang100% (4)
- 3Document76 pagini3Uday ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1: Power and Responsibility: 1. Important Leadership QualitiesDocument6 paginiUnit 1: Power and Responsibility: 1. Important Leadership QualitiesTrần Thanh MinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- TAPPI T 810 Om-06 Bursting Strength of Corrugated and Solid FiberboardDocument5 paginiTAPPI T 810 Om-06 Bursting Strength of Corrugated and Solid FiberboardNguyenSongHaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WDP Process Diagrams v1Document6 paginiWDP Process Diagrams v1Ryan HengÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV TitchievDocument3 paginiCV TitchievIna FarcosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccie R&s Expanded-BlueprintDocument12 paginiCcie R&s Expanded-BlueprintAftab AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ShopDrawings - Part 1Document51 paginiShopDrawings - Part 1YapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Highway Journal Feb 2023Document52 paginiHighway Journal Feb 2023ShaileshRastogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topfast BRAND Catalogue Ingco 2021 MayDocument116 paginiTopfast BRAND Catalogue Ingco 2021 MayMoh AwadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contract 1 ProjectDocument21 paginiContract 1 ProjectAditi BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decision Tree AlgorithmDocument22 paginiDecision Tree Algorithmvani_V_prakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- EceDocument75 paginiEcevignesh16vlsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Project Diary-Wps OfficeDocument4 paginiA Project Diary-Wps OfficeSameer ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shot Blasting Machine ApplicationsDocument7 paginiShot Blasting Machine ApplicationsBhavin DesaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ems Speed Sensor Com MotorDocument24 paginiEms Speed Sensor Com MotorKarina RickenÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1Document53 paginiBIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1lili100% (1)
- Final Project Synopsis 1Document90 paginiFinal Project Synopsis 1Shyam YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 27 Points of Difference Between Personnel Management & HRDDocument2 pagini27 Points of Difference Between Personnel Management & HRDMurtaza Ejaz33% (3)
- Case StudyDocument15 paginiCase StudyChaitali moreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Algorithm Development and Implementation For 3D Printers Based On Adaptive PID ControllerDocument8 paginiThe Algorithm Development and Implementation For 3D Printers Based On Adaptive PID ControllerShahrzad GhasemiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ModelsimDocument47 paginiModelsimKishor KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gol GumbazDocument6 paginiGol Gumbazmnv_iitbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boq Cme: 1 Pole Foundation Soil WorkDocument1 paginăBoq Cme: 1 Pole Foundation Soil WorkyuwonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1207 - RTC-8065 II InglesDocument224 pagini1207 - RTC-8065 II InglesGUILHERME SANTOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Office Administration: School-Based AssessmentDocument17 paginiOffice Administration: School-Based AssessmentFelix LawrenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Python Cheat Sheet-1Document8 paginiPython Cheat Sheet-1RevathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised PARA Element2 Radio LawsDocument81 paginiRevised PARA Element2 Radio LawsAurora Pelagio Vallejos100% (4)
- Analog Electronics-2 PDFDocument20 paginiAnalog Electronics-2 PDFAbhinav JangraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concise Beam DemoDocument33 paginiConcise Beam DemoluciafmÎncă nu există evaluări