Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Struct2 Lecture Notes #4 PDF
Încărcat de
Lowie Torres Tonio0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
40 vizualizări5 paginiTrusses are deformed by the Method of Virtual Work. External Virtual Work equals internal virtual strain in all truss members. WORK is understood as the sum of internal work (strain energy) Ui and external work (i.e. Work performed by loads and reactions) Ue.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Struct2 Lecture Notes #4.pdf
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentTrusses are deformed by the Method of Virtual Work. External Virtual Work equals internal virtual strain in all truss members. WORK is understood as the sum of internal work (strain energy) Ui and external work (i.e. Work performed by loads and reactions) Ue.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
40 vizualizări5 paginiStruct2 Lecture Notes #4 PDF
Încărcat de
Lowie Torres TonioTrusses are deformed by the Method of Virtual Work. External Virtual Work equals internal virtual strain in all truss members. WORK is understood as the sum of internal work (strain energy) Ui and external work (i.e. Work performed by loads and reactions) Ue.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 5
Notes in Structural Analysis II Glenn M.
Pintor / De La Salle University
Deflection of Trusses by Virtual Work Method
Deflections of Trusses by the Method of Virtual Work
! Method of Virtual Work: Trusses
o 1 external virtual unit load acting on the truss joint in the stated direction of !
o n internal virtual normal force in the truss member caused by the external virtual unit
load
o ! external joint displacement caused by real loads on the truss
o N internal normal force in the truss member caused by the real loads
o L length of the member
o A cross-sectional area
o E modulus of elasticity
" External virtual unit loads creates internal virtual forces
" Real loads cause the truss joints to be displaced ! in the same direction as the
virtual unit load
" Each member is displaced NL/AE in the same direction as its respective n force
" External virtual work 1!! equals the internal virtual work (or internal virtual
strain) in all truss members
! Method for determining displacements and slopes
o Semi-graphical methods: for beams subjected to simple loadings
o Energy methods (conservation of energy principle): for complicated loadings, for
trusses & frames
! Conservation of energy principle: External work and stain energy
o Work done by external forces U
e
is transformed into internal work (strain energy) U
i
developed when structure deforms
! PRINCIPLE OF WORK: Necessary condition for equilibrium
A SYSTEM OF FORCES ACTING ON A GIVEN STRUCTURE IS IN EQUILIBRIUM if and only if
the WORK performed by these forces is zero for any consistent state of deformation of the
structure.
WORK is understood to mean the sum of internal work (i.e. work performed by internal forces) Ui
and external work (i.e. work performed by loads and reactions) Ue.
! Virtual Work vis--vis Real work
o Work: physical quantity defined as the product of force times a conjugate displacement,
i.e., a displacement in the same direction as the force we are considering.
o Real work, i.e., the product of a real force and a real displacement, i.e., a force and a
displacement that both actually occur.
o A real force is a force that corresponds to a state of equilibrium due to actions that correspond
to the design requirements of a given structure. For example, real forces include the loads,
reactions, and internal forces (moments, shear forces, and axial forces) due to conditions such
as dead load, live load, wind load, etc. Real forces are the forces that a given structure will
Notes in Structural Analysis II Glenn M. Pintor / De La Salle University
Deflection of Trusses by Virtual Work Method
actually experience during its service life, or forces that represent a limit state (such as ultimate
limit state) that must be checked to ensure safety and serviceability.
o A real displacement of a given structure is a displacement that corresponds to the response of
the structure to real forces. For example, a beam subjected to dead load will deflect downward.
The deflection at a given point along the span is a real displacement because it corresponds to
a state of equilibrium defined by real forces.
" extend the concept of real work to a definition of virtual work, which is the
product of a real force and a conjugate displacement, either real or virtual.
" compute the virtual work corresponding to this virtual displacement by
summing the products of real forces times conjugate virtual displacements.
" introduce unknown sectional forces at those locations where we have cut the
structure to create the virtual displacement.
introduced bending moment at the base, Mb.
For completeness, introduce a shear force V and an axial force N at the
base of the column, but, there is no component of virtual displacement
conjugate to these forces. They have therefore not been shown in the
example.
Notes in Structural Analysis II Glenn M. Pintor / De La Salle University
Deflection of Trusses by Virtual Work Method
o 1 external virtual unit load acting on the truss joint in the stated direction of !
o ! external displacement caused by real loads
o u internal virtual loading acting on the element in the direction of dL
o dL internal deformation of the element caused by the real loads
! Sample problems
Notes in Structural Analysis II Glenn M. Pintor / De La Salle University
Deflection of Trusses by Virtual Work Method
Notes in Structural Analysis II Glenn M. Pintor / De La Salle University
Deflection of Trusses by Virtual Work Method
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Stability of Buildings Part 4 Moment FramesDocument57 paginiStability of Buildings Part 4 Moment Framesalextse100% (4)
- Worked Example To Eurocode 2 Vol. 1Document224 paginiWorked Example To Eurocode 2 Vol. 1vbisketi100% (25)
- ANSYS and Cable Stayed BridgeDocument22 paginiANSYS and Cable Stayed BridgeZain SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detail Section: (R.C. Gutter)Document1 paginăDetail Section: (R.C. Gutter)Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fallingwater by Gerard Feldmann1 PDFDocument5 paginiFallingwater by Gerard Feldmann1 PDFdanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 11Document37 paginiLecture 11mj03127477706Încă nu există evaluări
- Virtual Work Method: Clifford Jay C. Ansino Theory of Structure Ii 5-BSCE-BDocument6 paginiVirtual Work Method: Clifford Jay C. Ansino Theory of Structure Ii 5-BSCE-BKhen CatayasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 08 (B)Document46 paginiLecture 08 (B)businessw025Încă nu există evaluări
- ECS556 OCT 2020 - Topic 1 - RevisionDocument18 paginiECS556 OCT 2020 - Topic 1 - RevisionThevaneyan KrishtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 09Document46 paginiLecture 09Leo KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cse30301 3 2015Document57 paginiCse30301 3 2015王嵐Încă nu există evaluări
- Struct2 Lecture Notes #2 (Truss Analysis & Deflection) PDFDocument12 paginiStruct2 Lecture Notes #2 (Truss Analysis & Deflection) PDFLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual WorkDocument15 paginiVirtual WorkYishak AmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bhairav Thakkar MosDocument33 paginiBhairav Thakkar MosAnonymous bg4BXjfrJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment of Strength Material WORDDocument10 paginiAssignment of Strength Material WORDasisha mostÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Virtual WorkDocument15 pagini3 Virtual WorkMekuannint DemekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pushover AnalysisDocument62 paginiPushover AnalysisRakesh7770100% (2)
- Intro To Strength of Materials LessonDocument26 paginiIntro To Strength of Materials LessonMichaela Vernice PeñarubiaÎncă nu există evaluări
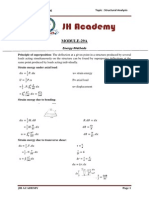
- Module-29A: Energy MethodsDocument2 paginiModule-29A: Energy MethodsjhacademyhydÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthquake EngineeringDocument24 paginiEarthquake EngineeringYuoyung tin100% (1)
- Structural AnalysisDocument220 paginiStructural AnalysisMohamedSajeerMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural ANalysisDocument291 paginiStructural ANalysispairilioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tos III Lesson 3Document18 paginiTos III Lesson 3Kendi KoomeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual Work MethodDocument4 paginiVirtual Work MethodBehar AbdurahemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of MaterialsDocument114 paginiStrength of MaterialsVivek SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-Mechanics of Material - I (Mid Term)Document134 pagini1-Mechanics of Material - I (Mid Term)irum,Încă nu există evaluări
- Ce-318 01Document46 paginiCe-318 01Azmat NaseemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 3Document47 paginiLec 3彭宇鑫Încă nu există evaluări
- StructureDocument43 paginiStructurehasan bishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Strength of Materials Arki 3EDocument26 paginiIntro To Strength of Materials Arki 3EMichaela Vernice PeñarubiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work and Energy ModuleDocument18 paginiWork and Energy ModuleKarl CordialÎncă nu există evaluări
- LP 1 Es 10 FinalDocument31 paginiLP 1 Es 10 FinalWalwal WalwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Oscar Victor M. Antonio, JR.: Prepared byDocument37 paginiDr. Oscar Victor M. Antonio, JR.: Prepared byheherson juanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE6501 Structural Analysis I PDFDocument164 paginiCE6501 Structural Analysis I PDFtuuheey100% (1)
- Chapter 2 (Part 2)Document35 paginiChapter 2 (Part 2)muhammadtalhabilal6666Încă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Dynamics of Structures 1Document39 paginiAdvanced Dynamics of Structures 1Halil ZeyrekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Materials NotesDocument88 paginiStrength of Materials NotesprasanthprpÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument16 paginiUntitledGanesh KeskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test The Strength of Structural Members: Learning Activity #2Document28 paginiTest The Strength of Structural Members: Learning Activity #2nandishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanic of Material Lab ReportDocument28 paginiMechanic of Material Lab ReportMuhd Farhan Bin Ibrahim50% (2)
- ENR202 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 1B Slides and Notes: Slide 1Document29 paginiENR202 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 1B Slides and Notes: Slide 1jimyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Moment Equation PaperDocument9 paginiThree Moment Equation PaperAkash SoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forces and StructureDocument24 paginiForces and StructureMay Myat Mon KyawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Design and Inspection-Principle of Virtual Work: by Dr. Mahdi Damghani 2019-2020Document48 paginiStructural Design and Inspection-Principle of Virtual Work: by Dr. Mahdi Damghani 2019-2020Aniruddh PansambalÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTPPT6 - Virtual Work Method PDFDocument32 paginiMTPPT6 - Virtual Work Method PDFKris To PherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me 212 Mechanics of Material - I: Credit Hours: Theory 3 Hrs Lab 1 HR Contact Hours: Theory 3 Hrs Lab 3 HrsDocument22 paginiMe 212 Mechanics of Material - I: Credit Hours: Theory 3 Hrs Lab 1 HR Contact Hours: Theory 3 Hrs Lab 3 HrsKifayat UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction and Review: W WW T .V O UW D RL Om .CDocument2 paginiIntroduction and Review: W WW T .V O UW D RL Om .CMohammed ImranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 Displacement (External Load)Document40 pagini2.1 Displacement (External Load)Adron Lim33% (3)
- CHAPTER 6 - ReviewerDocument18 paginiCHAPTER 6 - ReviewerEdgiecylin S. GALENOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Internal LoadingsDocument33 paginiChapter 1 - Internal LoadingsYoon Pwint YamoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bending MomentDocument5 paginiBending Momentlisan2053Încă nu există evaluări
- Strength Simple Stresses 1Document14 paginiStrength Simple Stresses 1Richmon Lazo BorjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 001 Lec. 1 Stress Analysis (ME 276)Document25 pagini001 Lec. 1 Stress Analysis (ME 276)IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Strain Energy MethodsDocument35 paginiChapter 3 - Strain Energy MethodsPAULUS MAONGOÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME211Document28 paginiME211TayyabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Materials: Selected Topics ONDocument76 paginiStrength of Materials: Selected Topics ONSodik KarimovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ae8008 Unit-I BasicsDocument17 paginiAe8008 Unit-I BasicsGEZHILMARANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statics Week 1 - 2019Document11 paginiStatics Week 1 - 2019Qazi Muhammed FayyazÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Simple Stresses and StrainDocument25 pagini1 Simple Stresses and StrainRakshith MirajkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionDe la EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionEvaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (4)
- Tonio, Lowie Jay - Assignment No. 1Document35 paginiTonio, Lowie Jay - Assignment No. 1Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A 15 PDFDocument1 paginăA 15 PDFLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantages of Agile Project ManagementDocument12 paginiAdvantages of Agile Project ManagementLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 048 RMP Board Exam 1Document8 pagini048 RMP Board Exam 1Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A 14 PDFDocument1 paginăA 14 PDFLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Front Elevation: Bureau of DesignDocument1 paginăFront Elevation: Bureau of DesignLowie Torres Tonio100% (1)
- 043 Practical Problems ... Part 2Document14 pagini043 Practical Problems ... Part 2Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 042 Practical Problems ... Part 1Document16 pagini042 Practical Problems ... Part 1Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A 4 PDFDocument1 paginăA 4 PDFLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- P E R S P E C T I V E: Bureau of DesignDocument1 paginăP E R S P E C T I V E: Bureau of DesignLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Left Side Elevation Right Side Elevation Cross Section: Bureau of DesignDocument1 paginăLeft Side Elevation Right Side Elevation Cross Section: Bureau of DesignLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A 4aDocument1 paginăA 4aLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ground Floor Plan: Bureau of DesignDocument1 paginăGround Floor Plan: Bureau of DesignLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Material Hauling CostDocument2 paginiUnit Material Hauling CostJose LeuterioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-19 Acceptance Item 311Document1 paginăA-19 Acceptance Item 311Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Office of The SecretaryDocument150 paginiOffice of The Secretaryaj100% (9)
- P E R S P E C T I V E: Bureau of DesignDocument1 paginăP E R S P E C T I V E: Bureau of DesignLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular No. 2017 11 Re 2017 Midyear ConventionDocument1 paginăCircular No. 2017 11 Re 2017 Midyear ConventionLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Calculations For 10x24 MPBDocument29 paginiStructural Calculations For 10x24 MPBLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Daily Activity Log Date: Weather: Day: ManpowerDocument2 paginiProject Daily Activity Log Date: Weather: Day: ManpowerLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-18 Acceptance Item 310Document1 paginăA-18 Acceptance Item 310Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-17 Acceptance Item 300Document1 paginăA-17 Acceptance Item 300Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Office of The SecretaryDocument9 paginiOffice of The SecretaryLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do 003 S2015Document1 paginăDo 003 S2015Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-16 Acceptance Item 201Document1 paginăA-16 Acceptance Item 201Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do 003 S2015Document1 paginăDo 003 S2015Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do 158 S2015Document6 paginiDo 158 S2015Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- B-14 Insulation Resistance Test - MDP (IRT)Document2 paginiB-14 Insulation Resistance Test - MDP (IRT)Lowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department Orders SummaryDocument15 paginiDepartment Orders SummaryLowie Torres TonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stainless Steel Structure Design HandbookDocument20 paginiStainless Steel Structure Design Handbookgnino2Încă nu există evaluări
- BeamsDocument1 paginăBeamsneelimasudhirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lee Shoemaker CompressedDocument78 paginiLee Shoemaker CompressedczapatachueÎncă nu există evaluări
- K. B. Construction 12.3.19 - 13 Pages.Document13 paginiK. B. Construction 12.3.19 - 13 Pages.AmitChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Beams and Frames: Theory of Structure - IDocument20 paginiAnalysis of Beams and Frames: Theory of Structure - IMuhammad UsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced Concrete Analysis and Design PDFDocument556 paginiReinforced Concrete Analysis and Design PDFSuhas MangaloreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ratliperl: The Modern Solution For Energy Efficient BuildingDocument1 paginăRatliperl: The Modern Solution For Energy Efficient BuildingAdhil RamsurupÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSD Task 2 NotesDocument16 paginiPSD Task 2 Notesmuhfil MuhfilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12 Retaining WallDocument100 paginiChapter 12 Retaining WallLiu ZhenguoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cement Replacing MaterialsDocument9 paginiCement Replacing MaterialsAnish PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flexural Design of PC Elements Ch4iDocument22 paginiFlexural Design of PC Elements Ch4inagham tariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- RoofsDocument45 paginiRoofsWhiskey /Încă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Building, Design of Steel Structure Part 2, Types of LoadsDocument36 paginiIndustrial Building, Design of Steel Structure Part 2, Types of LoadsRaju Sharma100% (3)
- SDS Prequalification Document R2 - OptDocument59 paginiSDS Prequalification Document R2 - Optmohd sumerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manhole Comparison For Type I and IIDocument2 paginiManhole Comparison For Type I and IIMesfinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Criteria - School BuildingDocument2 paginiDesign Criteria - School BuildingAlfie Angelo Reyes100% (1)
- Efficient Assumption of Design Variables For Stress Ribbon FootbridgesDocument11 paginiEfficient Assumption of Design Variables For Stress Ribbon FootbridgesJORGE BARRERAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methodical Approach To Repair BuildingsDocument12 paginiMethodical Approach To Repair BuildingsSri vaishnavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced Concrete Design - Palestine Ii - ACI 318M-08Document282 paginiReinforced Concrete Design - Palestine Ii - ACI 318M-08EVER GUZMAN BALCASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Result of Concrete Cube Quality Control Laboratory, Road Div SiwanDocument2 paginiTest Result of Concrete Cube Quality Control Laboratory, Road Div SiwanB k RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab - Frame 06 6210110355Document6 paginiLab - Frame 06 6210110355A ArtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe LineDocument75 paginiPipe Linekiran raghukiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- CementDocument4 paginiCementAlecx Marie G. Llamas100% (1)
- Mini ProjectDocument45 paginiMini Projectmanohar manuÎncă nu există evaluări
- BOQ Proposed Completion of Three Storey Building For Isolation RoomsDocument12 paginiBOQ Proposed Completion of Three Storey Building For Isolation RoomsJake CanlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- DR - Nurul ImamDocument11 paginiDR - Nurul Imamnadimalam78692Încă nu există evaluări
- Hooks in Beams Stirrups: Column Tie Hook DetailsDocument1 paginăHooks in Beams Stirrups: Column Tie Hook DetailsDesign explorer olomizanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- KTP PPVCDocument55 paginiKTP PPVCShumei ZhouÎncă nu există evaluări