Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Web Technology and Business Processes: Outline
Încărcat de
SagarChheda0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
25 vizualizări5 paginiIntranets business Network Transform ERP SCM CRM Intranet Uses Similar to Internet concepts, technologies, Protocols as i.e. Client-server TCP / IP, HTTP, SMTP, FTP Private computer network internal communication and collaboration Securely share organization's information or operational systems Intranet examples corporate initiatives, events, blogs, chat, employee feedback, Sr. Mgmt. Connect Time and productivity Employees can 'pull' information they required rather than 'push' information through
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
05.WebTechBizEnv
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentIntranets business Network Transform ERP SCM CRM Intranet Uses Similar to Internet concepts, technologies, Protocols as i.e. Client-server TCP / IP, HTTP, SMTP, FTP Private computer network internal communication and collaboration Securely share organization's information or operational systems Intranet examples corporate initiatives, events, blogs, chat, employee feedback, Sr. Mgmt. Connect Time and productivity Employees can 'pull' information they required rather than 'push' information through
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
25 vizualizări5 paginiWeb Technology and Business Processes: Outline
Încărcat de
SagarChhedaIntranets business Network Transform ERP SCM CRM Intranet Uses Similar to Internet concepts, technologies, Protocols as i.e. Client-server TCP / IP, HTTP, SMTP, FTP Private computer network internal communication and collaboration Securely share organization's information or operational systems Intranet examples corporate initiatives, events, blogs, chat, employee feedback, Sr. Mgmt. Connect Time and productivity Employees can 'pull' information they required rather than 'push' information through
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 5
1
Web Technology and
Business Processes
By Joscelyn Dias
Outline
Intranets
Business Network Transform
ERP
SCM
CRM
Intranet
Uses Similar to Internet concepts,
technologies, Protocols as i.e. client-
server TCP/IP, HTTP, SMTP, FTP
Private computer network
Internal communication and collaboration
Securely share organization's
information or operational systems
Intranet examples
Intranet
Communication
Corporate initiatives, events, blogs, chat, employee feedback, Sr. mgmt. connect
Time and productivity
Employees can pull information they required rather that push information
through email
Based on roles and responsibilities
Content and multi-media
News-letters, media release, industry news, bulletins
Publishing of corporate knowledge
Policies(IT,IS,Quality), procedure manuals,knowledge mgmt.
Applications for business operations
Webmail, HR processes, Payroll, Taxation, Leave mgmt., R&R, Standards
compliance, Expenses claims
Training
Online methodology, multi-media, feedback and evaluation, quality
Cost savings on printing, updates
Employee directory, internal phone list, holiday calender, schedules,
Requisition forms (facilities, stationery, security, transport)
Intranet Application examples
2
Selecting Intranet web projects
Material taking advantage of hyperlinks
Material more valuable with frequent updates
Complete substitution for hard-copies
Reduced admin, print and handling costs
Criteria: 1) Users have Intranet access, 2) Low
graphics 3) Few pages of information
Inter-department workflow organisation
processes
Authentication and authorization
User shared documents
Intranet Application examples
Intranet Application examples
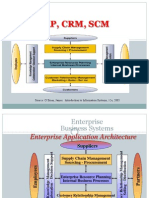
Network Transform: ERP,SCM, CRM
Business Network Transform
Transforming the network of
Suppliers
Business partners
Customers
Radical change with partners
Close alliance, trust, sharing info
Competitive advantage, across Value chain
Network Transform made possible by
IT, Telecom networking
The Internet and Web Technologies
Enterprisewide Resource Planning
ERP Goals:
Streamline business processes
Improve performance of organizations' resource
planning, management and operational control.
Requires re-engineering of current business
processes.
Integrates activities across functional
departments, from product planning, parts
purchasing, inventory control, product
distribution, to order tracking.
ERP software - multi-module application
software
3
ERP Implementation
ERP systems implementation
UNIX, Win NT/2K, Linux, OS of Legacy ERP
Involves Integration
Information together in a single system of applications
Internal and external information systems
Discard all legacy systems at once, install ERP
system
Acceptance by staff, department skills, comfort and
speed of legacy applications, Cost
From independent ERP installations to Single
Instance
ERP Implementation
Integration is key issue
Web Services and SOA
Integrates standalone systems, best-of-breed
solutions
Avoid cost of single instance ERP
But,
Still immature technologies, require complex planning
Require programming and IT architectural talents
Implementation time and cost.
Integration layer in ERPs
ERP software part of a service SOA, using
middleware as integration software.
Provide Web services; customers can link to
link ERP with other software in architecture
But..
Middleware offered only with latest upgrades
Extra fee charge for middleware
ERP Cos. dominance over the software
acquisition process of clients
Single Instance vs. Integration layer
Single instance if...
Have fairly commonplace business processes that
extend across all divisions
Have older systems that need to be replaced
Have multiple ERP instances from a single vendor
Integration layer if...
Have divisions with unique business processes that
cant be changed
Consider an existing investment in best-of-breed
solutions a competitive advantage
Want an environment in which it is easy to integrate
new applications
ERP SCM, CRM
Customers, suppliers demand information
accessed by co. employees
ERP systems info e.g.. order status, inventory
levels through co. websites
E-commerce : New channels of access into ERP
For suppliers and partners (B2B); inventory levels,
etc.
For customers (B2C); order status, billing information
Building links between ERP and the Web
ERP vendor may provide if experienced, cost savings
Else custom integration internally through
IT/consultants
ERP SCM
Reliant upon ERP kind of information
SCM systems benefit from ERP software
as single major source of up-to-date
information.
Top 5 SCM vendors only 34% market (2005
data)
SAP 12%, Oracle 10%, Manhattan
Associates 4%, Infor (SSA, Baan etc.)
SCM not as standard as other software
4
SCM Supply Chain Mgmt.
Business system of enterprise strategies,
business processes and information
technologies
To Improve the planning, execution and
collaboration of material flows, information
flows, financial flows and workforce flows
in the supply chain.
SCM
Supply chain visibility when companies share at
least some data with SCM partners
Suppliers dont have to guess how many raw
materials to order
Manufacturers wouldn't have to order more than they
need from suppliers, Make sure they have enough on
hand if demand for their products unexpectedly goes
up
Retailers would have fewer empty shelves if they
shared the information they had about sales of a
manufacturer's product in all their stores with the
manufacturer.
Generally win-win for all sides of the transaction
Key issues: Collaboration, trust, domination
SCM
Modular software applications
integrate activities across organizations, from demand
forecasting, product planning, parts purchasing,
inventory control, manufacturing, product assembly to
product distribution
Boundary of SCM and E-Com systems
Suppliers, partners, distributors, even customers
Cos extend control they get from ERP
software out to their suppliers and channel
partners
Internet, connectivity, B2B explosion
B2B
Electronic trade or partnering between
organizations.
Share in E-Com (B2B90%, B2C10%)
Private SCM software for procurement.
B2B exchanges function to Manage
procurement of row materials and
coordinating with suppliers.
Customer Relationship Mgmt.
CRM is a business system that consists of
enterprise goals, business strategies, business
processes and enterprise information systems.
CRM helps business increase revenues by
providing services and products that are exactly what
your customers want
offering better customer service
cross selling products more effectively
helping sales staff close deals faster
retaining existing customers and discovering new
ones
CRM
Use technology and human resources to gain insight into
the behavior of customers and the value of those
customers
Cos interact with customers different ways
Mail campaigns,
Web sites
Brick-and-mortar stores
Call centers
Mobile sales force staff
Marketing and advertising efforts.
CRM systems link up customer contact points.
CRM software systems automate many customer-related
business tasks.
5
CRM software system
1. Customer contact management
2. Sales automation
3. Direct marketing
4. Helpdesk module.
5. Call center applications
Sales automation
Auto-management of stages in sales process
Online product building / customization e.g. Dell
Integration with contact management and other
departments
CRM software
Direct Marketing
Directly target customers based on criteria with
promotional activities
Generate direct mails, class and analyze response
Help-desk
E-mail notification, inbound, outbound
Web-based Search support knowledge base for
answer online without calling a support representative
Web Chat to ask more specific questions for support.
CRM Technologies
Online CRM or Web-based CRM
Web pages as the UI (user interface)
Access Enterprise apps through Web-browser, no
deployment of client software
E.g.. Online services, Customer profiles
Hosted CRM
Online, CRM backend systems are hosted at data
centers in ASP model
No in-house deployment, no client installation
Mobile CRM
Handheld / wireless device with browser based UI
Mobile middleware sometime used
E.g. Mobile check-in by airlines, bill payments, credits
CRM issues
Safety
More customer data better analysis better
customer service
Secure databases of customer info : personal,
financial, credit card
Privacy
Willingness of customer to give / leave info. Egg. Fill
web forms with personal info, cookies
Use of study of customer behavior, shopping patterns
Misuse / sale of contact information
Trust of the customer is most important
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ERP and SCMDocument14 paginiERP and SCMrohit_z2kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 Enterprise Business SystemsDocument6 paginiChapter 8 Enterprise Business SystemsErfan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Information SystemsDocument60 paginiTypes of Information SystemsPrateek BhatnagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - 6 Current TrendsDocument45 paginiUnit - 6 Current TrendsPIYA THAKURÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 - ERP and CRM PDFDocument35 pagini4 - ERP and CRM PDFBabak ZeynalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gaya ErpDocument12 paginiGaya ErpGayathri VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Miserp - Unit Ii PNRDocument81 paginiMiserp - Unit Ii PNRDr. Potu Narayana100% (1)
- E-Crm & Erp: Sanjay KeharDocument39 paginiE-Crm & Erp: Sanjay KeharNitin SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Achieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise ApplicationsDocument25 paginiAchieving Operational Excellence and Customer Intimacy: Enterprise ApplicationsArbab Ashraf100% (1)
- ERP Implementation FundamentalsDocument35 paginiERP Implementation FundamentalsVibhas MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIS Final Exam NotesDocument9 paginiMIS Final Exam NotestyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment - MBA 610Document16 paginiAssessment - MBA 610Vishal PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sim Chapter 9Document29 paginiSim Chapter 9nenidsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Customer Relationship Management Systems Help Firms Achieve Customer Profiling and PersonalizingDocument13 pagini1 Customer Relationship Management Systems Help Firms Achieve Customer Profiling and PersonalizingPrafulla Man PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management Information System Chapter 10 NotesDocument5 paginiManagement Information System Chapter 10 Notesgut78Încă nu există evaluări
- Iem Unit 6Document12 paginiIem Unit 6vamsibuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument23 paginiEnterprise Resource PlanningasbahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enterprise Resource Plannin 2Document7 paginiEnterprise Resource Plannin 2haridineshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8Document6 paginiChapter 8ShohagÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5a - CRM, ERP, SCMDocument32 pagini5a - CRM, ERP, SCMPrakriti ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 1 Introduction To Enterprise Resource Planning SystemsDocument20 paginiCH 1 Introduction To Enterprise Resource Planning SystemsPurdianta YoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIS Chapter 2Document36 paginiAIS Chapter 2Ashenafi ZelekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ERP Assignment 1Document29 paginiERP Assignment 1Jaya BharneÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 1 Enterprise SystemsDocument33 paginiUNIT 1 Enterprise SystemsURVASHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT Role SCMDocument36 paginiIT Role SCMManoj Kumar ParasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software and Information Technology Glossary of TermsDocument19 paginiSoftware and Information Technology Glossary of TermsBusiness Software Education CenterÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Challenges That Enterprise Applications Pose, and How Are Enterprise Applications Taking Advantage of New Technologies?Document5 paginiWhat Are The Challenges That Enterprise Applications Pose, and How Are Enterprise Applications Taking Advantage of New Technologies?Agung WidiyantoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM 2010 TrendsDocument26 paginiCRM 2010 TrendsMohammed Al-GhannamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantages and Disadvantages of ERPDocument3 paginiAdvantages and Disadvantages of ERPAmol Kasture0% (1)
- Lecture 6 - Enterprise Applications - Thien Nguyen - V2Document43 paginiLecture 6 - Enterprise Applications - Thien Nguyen - V2Huong Nguyen Thi XuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 ERP SystemsDocument19 pagini4 ERP Systems2205611Încă nu există evaluări
- Enterprise Resource PlannningDocument153 paginiEnterprise Resource PlannningSuraj PrakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- ERP - Marketing / Sales Strategies of Tata Consulting ServicesDocument56 paginiERP - Marketing / Sales Strategies of Tata Consulting ServicesShashank ShettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SystemInteg2 1Document10 paginiSystemInteg2 1Jerlon ZuñigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept of Customer Relation Management. Study of Total Quality Management. To Know About Intellectual Property RightDocument12 paginiConcept of Customer Relation Management. Study of Total Quality Management. To Know About Intellectual Property RightBharath CrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No. 7 Aim: Study of Enterprise Resource Planning and Its ApplicationsDocument4 paginiExperiment No. 7 Aim: Study of Enterprise Resource Planning and Its ApplicationsYogesh KandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- E-Business: Nijaz N Lecturer - ISMSDocument45 paginiE-Business: Nijaz N Lecturer - ISMSVijesh V KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management Information System Lect 3-Cross-Functional Enterprise SystemDocument26 paginiManagement Information System Lect 3-Cross-Functional Enterprise SystemSagar100% (4)
- Enterprise Resource Planning-Crm: by - Anvita, Kenneth, Priyanka, Ritu and SupalDocument57 paginiEnterprise Resource Planning-Crm: by - Anvita, Kenneth, Priyanka, Ritu and SupalAnvi NiftianÎncă nu există evaluări
- PrintDocument10 paginiPrintDella CharistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Process ManagementDocument13 paginiBusiness Process ManagementRashil ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- ERP + E-BUSINESS An Emerging Relationship: Himanshu Sharma, Dolly Lavania, Nidhi GuptaDocument9 paginiERP + E-BUSINESS An Emerging Relationship: Himanshu Sharma, Dolly Lavania, Nidhi GuptaHaya Ali JoudehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enter Prose Management SystemDocument15 paginiEnter Prose Management Systemsimply_cooolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top ERP Requirements Checklist PDFDocument6 paginiTop ERP Requirements Checklist PDFGangadhar YerraguntlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Information Systems: Week 1Document16 paginiManaging Information Systems: Week 1raziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week-4-5 - Lesson 4-5Document13 paginiWeek-4-5 - Lesson 4-5Jhoneuri BaniquedÎncă nu există evaluări
- ErpcrmscmDocument31 paginiErpcrmscmYogesh BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- EprDocument7 paginiEprSaleh AlgdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument13 paginiEnterprise Resource PlanningCarlos Oreste Cruz MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- What's Next For CRM?Document5 paginiWhat's Next For CRM?Venu NaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- MisqaDocument3 paginiMisqaHazanal Rashid KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM Unit - 5Document22 paginiCRM Unit - 5AUCBM - Placement CellÎncă nu există evaluări
- MGT 1272 Management Information System Mid-Term NotesDocument10 paginiMGT 1272 Management Information System Mid-Term NotesYvonne ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Managemet:: SCM On ItDocument3 paginiSupply Chain Managemet:: SCM On ItbadushamsmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erp System: AdvantagesDocument4 paginiErp System: AdvantagesAnand Thorat100% (1)
- What Is CRM (Customer Relationship Management) ?Document77 paginiWhat Is CRM (Customer Relationship Management) ?Muhammad UbaidullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benefits of A CAAT Audit Are:: 1) What Is Computer-Assisted Audit Technique?Document24 paginiBenefits of A CAAT Audit Are:: 1) What Is Computer-Assisted Audit Technique?Chaitali KambleÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDI and ERPDocument26 paginiEDI and ERPIsaac Owusu100% (1)
- 09 WebSpaceAndITAct2000Document2 pagini09 WebSpaceAndITAct2000SagarChhedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Need To Know For IT Manager About:: What Is Secured Web Application?Document3 paginiNeed To Know For IT Manager About:: What Is Secured Web Application?SagarChhedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04.WebTech WebApps FrameworksDocument3 pagini04.WebTech WebApps FrameworksSagarChhedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Outline: Advances in Web TechnologiesDocument5 paginiOutline: Advances in Web TechnologiesSagarChhedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-Matic 14 - User Manual 15Document169 pagini3-Matic 14 - User Manual 15Oliver RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Loss PreventionDocument20 paginiData Loss Preventiondeepak4315Încă nu există evaluări
- Layer 3 Managed 8 10G Port Switch Controller: RTL9303-CGDocument55 paginiLayer 3 Managed 8 10G Port Switch Controller: RTL9303-CG박윤지100% (1)
- Projek Rekabentuk Walkwaybridge 2014 - 15Document6 paginiProjek Rekabentuk Walkwaybridge 2014 - 15HambaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analisis Dan Perbandingan Jaringan Wifi Dengan Frekuensi 2.4 GHZ Dan 5 GHZ Dengan Metode QosDocument19 paginiAnalisis Dan Perbandingan Jaringan Wifi Dengan Frekuensi 2.4 GHZ Dan 5 GHZ Dengan Metode QosNoltujuh Nollapan (Congyang)Încă nu există evaluări
- ABAP On HANA Interview QuestionsDocument26 paginiABAP On HANA Interview QuestionsNagesh reddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sampling PowerpointDocument21 paginiSampling PowerpointMuhammad Furqan Aslam AwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC IT SyllabusDocument32 paginiBSC IT Syllabusஜூலியன் சத்தியதாசன்Încă nu există evaluări
- ShapiroDocument34 paginiShapiroTanuj ShekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRM Ass1Document3 paginiHRM Ass1asdas asfasfasdÎncă nu există evaluări
- People/Occupancy Rules of Thumb: Bell - Ch10.indd 93 8/17/07 10:39:31 AMDocument8 paginiPeople/Occupancy Rules of Thumb: Bell - Ch10.indd 93 8/17/07 10:39:31 AMPola OsamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Licensed Practical Nurse, LPN, Nurse Tech, Nurse Aide, Nursing ADocument4 paginiLicensed Practical Nurse, LPN, Nurse Tech, Nurse Aide, Nursing Aapi-121395809Încă nu există evaluări
- Thermo King Tool Catalog Part 2Document53 paginiThermo King Tool Catalog Part 2Alb NewgateÎncă nu există evaluări
- MC 10226555 0001Document7 paginiMC 10226555 0001Hema IbraÎncă nu există evaluări
- REID CatalogDocument54 paginiREID Catalogzhaoye maoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pivacare Preventive-ServiceDocument1 paginăPivacare Preventive-ServiceSadeq NeiroukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To GlobalizationDocument17 paginiIntroduction To Globalization21100959Încă nu există evaluări
- PETRO TCS Engineering Manual 682Document44 paginiPETRO TCS Engineering Manual 682paulm3565Încă nu există evaluări
- Geotechnical Design MannulDocument828 paginiGeotechnical Design MannulJie ZhouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tamil Nadu Industrial Establishments (Conferment of Permanent Status To Workman Act, 1981Document12 paginiTamil Nadu Industrial Establishments (Conferment of Permanent Status To Workman Act, 1981Latest Laws TeamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form DVAT 27A: Intimation of Deposit of Government DuesDocument2 paginiForm DVAT 27A: Intimation of Deposit of Government DueshhhhhhhuuuuuyyuyyyyyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Navi Mumbai C.A. ListDocument48 paginiNavi Mumbai C.A. ListManish Shetty67% (9)
- CV Rafi Cargill, GAR, MCR, AM GROUP and Consultancy EraDocument6 paginiCV Rafi Cargill, GAR, MCR, AM GROUP and Consultancy EranorulainkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3a. Systems Approach To PoliticsDocument12 pagini3a. Systems Approach To PoliticsOnindya MitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security Enhancement in 2016 SQL ServerDocument21 paginiSecurity Enhancement in 2016 SQL ServerAtul SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taller Sobre Preposiciones y Vocabulario - Exhibición Comercial SergioDocument5 paginiTaller Sobre Preposiciones y Vocabulario - Exhibición Comercial SergioYovanny Peña Pinzon100% (2)
- Impact of Wrongful Termination On EmployeesDocument4 paginiImpact of Wrongful Termination On EmployeesAvil HarshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Motion ProblemsDocument4 paginiCircular Motion ProblemsGheline LexcieÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPI vs. Posadas, G.R. No. L - 34583, 1931Document8 paginiBPI vs. Posadas, G.R. No. L - 34583, 1931Nikko AlelojoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Grants Community Assessment FormDocument3 paginiGlobal Grants Community Assessment Formlalitya xavieraÎncă nu există evaluări