Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Science3 STC-QC 3rd Trimestral Exam
Încărcat de
MarilouSodeVillaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Science3 STC-QC 3rd Trimestral Exam
Încărcat de
MarilouSodeVillaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Science
3
rd
Trimestral Exam
Identification.
_________________1. a gentle wind.
_________________2. the varying degree of hotness or coldness is called____.
_________________3. a condition of weather at a place over a period of years.
_________________4. a heavy downpour or rain for a short period of time in a small area.
_________________5. a little stronger air movement.
_________________6. an instrument that tells the direction of the wind.
_________________7. characterized by heavy rain and a very strong wind.
_________________8. when the sun heat cause the water to change into water vapor or gas,
it is called ___________.
_________________9. it measures the air pressure.
_________________10. a condition of atmosphere in a certain place at a certain time.
_________________11.it can indicate the direction and speed of the wind.
_________________12. an instrument that measures the amount of rain fall
_________________13. a mass of condensed water vapor in the sky.
_________________14. it measures the amount of water vapor or humidity in the air.
_________________15. a cloud that is close to the ground. When it is thick it is hard to see
the surroundings.
_________________16. is any moisture that falls from the air to the ground. In the
Philippines the major form of this is rain.
_________________17. A strong, fast, moving wind. It rotates upward. When it is very
strong, it can destroy huts, crops and light structure.
_________________18. a cycle when water vapor is cooled, it changes to drops of water. this
drops became larger and heavier, they cannot float in the sky
_________________19. the rain clouds.
_________________20. the highest clouds.
_________________21. measures the force or speed of the air.
_________________22. a low clouds.
_________________23. process of producing artificial rain.
_________________24. temperature is measured by _____.
_________________25. big heaps of white fluffy clouds are called _____. It also indicates
fair weather.
Multiple choice: Encircle your correct answer.
1. PAGASA stands for____.
a. Philippine Atmospheric Geology and Astronomy Services Administration
b. Philippine Atmosphere Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
c. Philippine Atmospheric Geology and Astronomical Services Administration
d. Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
2. When carbon dioxide in air traps heat and allows energy from the sun to enter/absorb and hold, it
formed a heat blanket around the earth. It is called_______.
a. Red House Effect c. House Effect
b. Green House Effect d. Earth Effect
3. Anything that has mass and volume and occupies space is called.
a. weight c. gravity
b. matter d. molecules
4. The weight of an object is the ______.
a. size and mass of an object
b. pull of gravity on the object
c. space occupied by the object
5. All objects are made up of _______.
a. energy
b. molecules
c. particles
6. Some solids dissolve quickly in water. Which of these solids does not dissolves in water?
a. salt
b. rice
c. sugar
7. Some solids quickly change to gas without passing through the liquid state. Which of the following are
examples of this.
a. ice and sugar
b. naphthalene balls and dry ice
c. salt and margarine
8. It is the amount/substance of matter that an object contains. It is not affected by gravity.
a. weight c. matter
b. mass d. volume
9. It involves change in form or appearance.
a. Physical change
b. Chemical Change
c. Property of matter
10. When water and oil are mixed in a container, the oil stays on the surface, this shows
that _________________.
a. Oil is lighter than water.
b. water is lighter than oil
c. oil always stays on the surface
11. Which of these liquids evaporates quickly?
a. paint
b. butter
c. alcohol
12. Which of these sentences is not true?
a. Water is a form of liquid
b. Water has weight
c. Water is solid
13. Which changes to liquid when heated?
a. ice
b. water
c. oil
14. An example of Physical change is _______, while _______shows chemical change.
a. rusting of iron; cooking food
b. sugar melts; fruit ripens
c. digesting food; rusting of iron
15. the space occupied by matter or the size of an object is called.
a. weight c. gravity
b. matter d. volume
16. Three phases of matter .
A: density, volume and weight
B: solid, liquid, and gas
C: water, metal and gases
17. The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas.
A: Freezing point
B: Melting point
C: Evaporation point
D: Condensation point
18. The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a solid
A: Freezing point
B: Melting point
C: Evaporation point
D: Condensation point
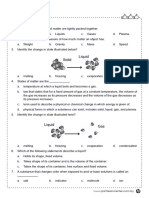
Tell whether each is a solid, liquid, or gas.
1. milk - ________________________ 2. cookie - _________________________
3. oxygen - _____________________ 4. fish - ___________________________
5. pencil - ______________________ 6. maple syrup - _____________________
7. shampoo - ____________________ 8. carbon dioxide - ___________________
9. ice cube - ____________________ 9. paint - ___________________________
10. oil - ________________________ 10. salt - ___________________________
11. water vapor - _________________ 12. gasoline - _______________________
13. helium - _____________________ 14. sand - _________________________
Complete each sentence with the word solid, liquid, or gas.
A ____________________________ has a definite shape. It does not take the shape of its
container. It also has a definite volume because it can be measured.
A ____________________________ does not have a definite shape. It takes the shape of its
container. It does have a definite volume because it can be measured.
A ____________________________ does not have a definite shape. It sometimes takes the shape of
its container and sometimes flies freely around you. These particles are not connected to each other and
takes up whatever space is available.
Identify the PHYSICAL CHANGES
Write
CO-condensation
H-heating
F-freezing
S-sublimation
E-evaporation
1.liquid to gas=________
2.gas to liquid=________
3.liquid to solid=________
4.solid to gas=________
5.liquid to solid/liquid to gas=________
Write
CO-condensation
H-heating
F-freezing
S-sublimation
E-evaporation
1.boiling water=________
2.water dew in the morning
3.alcohol on your palm
4.morning dew=________
5.napthaline balls to gas=________
6.gasoline on a running car=________
7.car freshener=________
8.moth balls to gas=________
Make a Bar Graph:
Make a Line Graph:
DAY
TEMPERATURE
M 25
T 28
W 30
TH 34
F 31
S 24
S 26
DAY
TEMPERATURE
M 27
T 28
W 30
TH 34
F 31
S 24
S 26
Match the description in Column A with the items on Column B. Write only the letter of your
answer on the line before each number.
Column A Column B
____1. Absorbs all colors a. Opaque materials
____2. Produce shadows b. Leaves of plants
____3. Reflects lights c. White colors
____4. Source of light d. black
____5. Reflect green lights e. transparent materials
____6. Reflects all colors f. mirror
____7. Pure water g. translucent materials
h. fire
Column A Column B
____8. Heat from the sun is felt on the earth a. water becomes ice
____9. Heat is removed from water b. 45C
____10. An instrument that measures temperature c. radiation
____11. Temperature of boiling water d. conduction
____12. Heat is transferred from a frying pan to e. 38C
the scrambled egg. f. thermometer
____13. Temperature of human body with fever g. 100C
Choose the option to answer each question or complete each statement.
____1. It is our main source of light and heat.
a. electricity
b. moon
c. sun
____2. Our great grandparents used this object to light their homes at night.
a. flashlight
b. fluorescent lamp
c. oil lamp
____3. Campers gather around this source of light at night.
a. bonfire
b. oil lamp
c. torch
____4. It has chemicals which makes bulbs produce light energy.
a. battery
b. flashbulb
c. incandescent bulb
____5. It changes electricity into heat energy.
a. gas stove
b. wood stove
c. electric stove
____6. It changes chemical energy to heat energy to cook our food.
a. gas stove
b. electric stove
c. microwave
____7. This kind of object allows some light to pass through.
a. opaque object
b. transparent object
c. translucent object
____ 8. This kind of object blocks light.
a. opaque object
b. translucent object
c. transparent object
____9. This is an example of a translucent object.
a. wood
b. hot coffee
c. frosted glass
____10. Which statement is true?
a. Light is always absorbed.
b. Light travels in a straight line.
c. Light passes through all kinds of objects.
____11. Which shows the bad effect of sunlight?
a. dries cloths
b. help plants grow
c. burns skins
____12. Which of these will scatter the color of light?
a. object
b. raindrop
c. rainbow
____13. How can we produce fire without a match?
a. rub two sticks together
b. rub our palms together
c. rub a stone with our hand
____14. Why do objects expand?
a. heat is applied.
b. Heat is removed.
c. they are cooked.
____15. Why do people wear sunglasses when they travel during hot weather?
a. everybody wears sunglasses.
b. they want to look glamorous
c. they need to protect their eyes.
____16. A hooting sound is to a/an ________as a squeaky sound is to a/an ______.
a. bird, mouse
b. owl, mouse
c. frog, mouse
____17. Pitch is the same as the loudness of a sound.
a. True
b. False
____18. Sounds are produced when objects _________.
a. move
b. vibrate
c. are reflected
____19. Which of these animals can hear more sounds better?
a. dog
b. eagle
c. rabbit
____20. Which of these makes a high-pitches sound?
a. drum beats
b. galloping horses
c. an ambulance siren
____21. Which among these voices produces the highest pitch?
a. alto
b. bass
c. soprano
____22. What do people do so they can hear better?
a. cover their ears
b. Ask the other person to shout
c. Cup their hands around the ear
____23. Which of the following may cause damage to our hearing?
a. speaking softly
b. blowing the nose gently
c. setting the radio at full volume
____24. In what medium does sound travel the slowest
a. gas
b. liquid
c. solid
____25. Which is the best conductor of sound?
a. gas
b. liquid
c. solid
____26. The Philippine lies east of the ______.
a. Celebes Sea
b. Pacific Ocean
c. South China Sea
____27. The smallest body of water that is surrounded by land is the _____.
a. bay
b. lake
c. pond
____28. Which of these makes the soil in the woods fertile?
a. heavy rains
b. overflowing rivers
c. decaying plants and animals
____29. Volcanic soil is fertile because of the ______.
a. decayed plants and animals
b. minerals in the molten rocks
c. hot mud coming from the crater
____30. What can be used for building purposes?
a. sand
b. gravel
c. both a and b
____31. Which of these helps prevent soil erosion?
a. crop rotation
b. cover cropping
c. regular harvesting
____32. The presence of too many chemicals in the soil and in water will _________.
a. reduce the yield of the harvest
b. slow down the growth of plants
c. both a and b
____33. Watering the plants with the use of a can or a dipper instead of a garden hose during
summer is recommended because _______.
a. it is cheaper
b. it saves water
c. it is easier to hold
____34. Soil is composed of _______.
a. small bits of broken rocks
b. decayed plants and animals
c. both a and b
____35. What makes the hot water and steam in geyser shoot up in the air?
a. a pull of gravity
b. rocks pushing up water
c. extreme heat and pressure deep in the earth
____36. What is a cheap and easy way to enrich or fertilize the soil in the garden?
a. Lessen the numbers of plants.
b. Put cut vegetable or other plant parts and fish entrails (gills and intestines) in open
pits and cover them with moist soil.
c. both a and b
____37. It is not safe to get drinking water from open wells and streams or rivers because of
the presence of ________.
a. small pieces of broken glass and metals
b. bacteria and other organisms that cause diseases
c. both a and b
____38. To make drinking water really safe during the rainy season, it should be _____.
a. filtered
b. boiled for about 20 minutes
c. left standing or kept in a water container for a long time
____39. Which of these practices will help conserve water?
a. turning off faucets tightly
b. watering plants with a garden hose
c. leaving dripping faucets unattended
____40. Which are renewable resources?
a. animals
b. plants
c. both a and b
____41. The sun is very important to people because it aids in ________.
a. heating our food
b. food-making in plants
c. drying up the oceans and rivers
____42. The sun is actually made up of ________.
a. millions of stars
b. a falling hot rock
c. hot, glowing gases
____43. Sun spots are _______.
a. spots in the sun
b. glowing gases from the sun
c. dark areas on the suns surface
____44. Which is true of the suns rotation? It rotates _______.
a. fastest at the poles
b. fastest at the equator
c. slowest at the equator
____ 45. It takes the earth _________ to make one complete rotation.
a. 1 day
b. 1 month
c. 365 days
____46. The moon is not seen from the earth during _______.
a. full moon
b. new moon
c. first quarter
____47.The moon takes _____to make one revolution around the earth.
a. 1 day
b. 28 days
c. 365 days
____48. The telescope that is used to study the suns corona and prominence is the ____.
a. coronagraph
b. radio telescope
c. sundial
____49. The moon is Earths _______.
a. meteor
b. satellite
c. twin
____50. There is life on the moon
a. Yes
b. No
c. Sometimes
____51. What are Armstrong, Collins, and Aldrin known for? They _____.
a. discovered the moon
b. were the first to land on the moon
c. were the first men who landed on Mercury
____52. The sun seems to rise in the east and set in the west because _____.
a. the sun moves at great speed
b. the sun has fixed place in outer space
c. Earth spins or rotates on its axis in a counterclockwise direction.
____53. When the earth rotates from the dark side toward the lighted side, _____ occurs.
a. day
b. eclipse
c. night
____54. We see a bright round disk during a ____ moon.
a. full
b. half
c. new
____55. A galaxy is composed of ____.
a. a group of stars
b. a group of planets
c. a group of meteors
Write T if the statement is true and F if it is false.
_____1. Curtains are good conductors of sound.
_____2. Some animals can hear better than people.
_____3. The pitch of the first note of the first line in the song Joy to the World is higher
than the last note.
_____4. Sound travels faster in air than in water.
_____5. The sound of a bird singing is noise.
_____6. Sound can be heard on the moon.
What do we do to each object to make it produce sound?
1. gong _____
2. flute _____
3. rattle _____
4. drum _____
5. guitar _____
pluck hit beat
blow shake
Match the description in Column A with the items on Column B. Write only the letter of your
answer on the line before each number.
Column A Column B
____1. the ability to do work a. air
____2. the bending of light b. echo
____3. bouncing of sound c. energy
____4. a push or pull d. force
____5. it makes work easier and faster e. machine
____6. needed by living things to breathe f. prism
____7. It separates light into different colors g. reflection
____8. formed when light cannot pass through h. refraction
an object i. shadow
____9. Allows light to pass through j. sound
____10. it is produced when things vibrate. k. translucent
____11. materials that allow little light l. transparent
to pass through m. friction
____12. the bouncing of light when it n. malleability
strikes an object o. brittleness
____13. a great English physicist and p. strength
mathematician who proved q. elasticity
that light is composed of several colors. r. hardness
____14. a force that opposes motion. s. luminous sources
____15. heat travels through liquid or gas t. non-luminous objects
____16. to break easily when enough force is applied u. pitch
____17. It returns to its original shape v. lever
after an applied force is removed w. screw
____18. that can make some solid so thin x. inclined plane
without breaking y. convection
____19. to resist being stretched z. Sir Isaac Newton
____20. to resist breaking
when stretched, twisted or bend
____21. produce their own light
____22. do not produce light but they become
visible because they reflect light
____23. highness and lowness of sound
____24. a mechanical fastening device consisting
essentially of an inclined plane.
____25. a slanted surface like a ramp.
____26. a rigid bar or plank with a central point
Choose the right answer.
_______________1. An inclined plane that wraps around a shaft
_______________2. A stiff rod that rotates around a pivot point
_______________3. Made of two inclined planes put together
_______________4. Uses grooved wheels and a rope, belt or chain
_______________5. A modification of a pulley
_______________6. A straight slanted surface.
Lever Wedge Pulley
Inclined Plane Screw Wheel and Axle
Write P in the blank if the object has potential energy and K if it has kinetic energy
_____1. rolling ball
_____2. ball string
_____3. diving board
_____4. moving marble
_____5. lava flowing down a mountain side
_____6. pendulum
_____7. cart
_____8. running boy
_____9. swinging baseball bat
_____10. parked car
Push or Pull.
_____1. squeezing a sponge
_____2. keys on the piano to make a sound
_____3. pick up a shopping bag
_____4. drag along a toy car by a string
_____5. picking flowers in the garden
_____6. getting out of the car
_____7. getting in the car
_____8. closing the cabinet door
_____9. opening a letter
_____10. putting the dirty clothes in a laundry basket
Solve for the volume. Write the correct measuring units.
A. Volume of a regular Solid
4 cm
3 cm
2 cm
1. What is the length?__________
2. What is the height?__________
3. What is the width?___________
4. What is the numerical statement?____________________________
5. What is the volume? ____________________________________
B. Volume of Irregular Solid
Water in the graduated cylinder reads after the marble was dropped 125 ml. But the
initial volume was 75 ml. Find the volume of the marble?
1. initial volume - _________________
2. final volume - __________________
3. Write the numerical statement - ___________________________________
4. What is the volume? _____________________________________________
Matching Type: Write the letter of the correct answer.
a. globe s. terracing
b. crust t. Milky Way Galaxy
c. continents u. corona
d. mountain v. prominences
e. Mt. Everest w. Erosion
f. volcano x. soil
g. crater y. clay
h. lava z. sand
i. hill aa. Loam
j. plateau bb. Humus
k. plain cc. Gravel
l. Rice Granary of the Philippines dd. Renewable Resources
m. valley ee. nonrenewable resources
n. island ff. strip cropping
o. archipelago gg. contour farming
p. delta hh. cover cropping
q. isthmus ii. stubble mulching
r. peninsula jj. quartz
_____1. top solid layer of the earth
_____2. a group of island like the Philippines and Japan.
_____3. the highest landform
_____4. a flat wide lowland. A wide flat land
_____5. an opening of the volcano
_____6. The Central Plain of Luzon is known as _____.
_____7. the process by which top soil is washed away
_____8. different plants are planted in alternating rows of land.
_____9. a kind of soil which is made from bits of rocks.
_____10. a small model of the earth
_____11. a mountain with an opening which lava and fiery rocks are thrown out
during an eruption.
_____12. a big family of stars in which the solar system belongs.
_____13. an elevated land with a broad and flat top. a high, wide , flat land.
_____14. A landform that is completely surrounded by water.
_____15. a land formation at the mouth of a river.
_____16. the outermost layer of the suns atmosphere
_____17. a landform that is much lower than a mountain
_____18. it is made up of very fine rock particles. a soil that is sticky when wet and
hard when dry.
_____19.it is easily replaced after being consumed
_____20. the largest land masses
_____21. a rich soil material formed from decayed plants and animals
_____22. it takes million of years to be replaced
_____23. a farming method where wide steps are made around the slopes of the hills.
_____24. a method of farming where the furrows follow the shape of the field.
_____25. a method of preventing soil erosion in which the uncut part of the plants are left on
the ground.
_____26. The highest mountain in the world
_____27. A lowland between two mountains or hills.
It is also a flat land but surrounded by high lands.
_____28. a farming method where fields are planted with low growing crops to protect the soil
from being washed away by wind and rain.
_____29. a fertile soil which consists of clay, sand and decayed matter.
_____30. a small grains of rocks
_____31. a mixture of pebbles and small rocks usually used for construction purposes.
it is also found along river banks or other bodies of water.
_____32. a thin layer of loose materials found on the surface of the earth
_____33. a hot glowing gas from the edge of the sun which shoots into space.
_____34. molten rocks
_____35. a piece of land with one narrow strip connected to the mainland and the other sides
bordered by water.
_____36. a narrow strip of land joining two large land masses.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Statement or Answers The Question. Write Your Answer On A Separate Sheet of PaperDocument4 paginiStatement or Answers The Question. Write Your Answer On A Separate Sheet of PaperJabsTheKnightÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Test-Chapter 1 MatterDocument5 paginiScience Test-Chapter 1 MatterRentika SiahaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Worksheet Grade 5 - Topic: Solid Liquid Gas Name: - Date: - A. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) - Tick The Correct AnswerDocument7 paginiScience Worksheet Grade 5 - Topic: Solid Liquid Gas Name: - Date: - A. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) - Tick The Correct AnswerLaura Linn LattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer 3Document2 paginiReviewer 3christinejoysalvador0919Încă nu există evaluări
- Third Quarterly TestDocument34 paginiThird Quarterly TestReynalyn AbadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- T F T T T: Name: - DateDocument5 paginiT F T T T: Name: - DateSamantha NortonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matter QuizDocument5 paginiMatter QuizduhyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weekly Test (Science)Document3 paginiWeekly Test (Science)AlfredoDoriaJrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative - Consumer Chemistry 9 - 1.1Document2 paginiSummative - Consumer Chemistry 9 - 1.1Gabriela FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- THIRD SUMMATIVE TEST in SCIENCE Grade 3-6Document9 paginiTHIRD SUMMATIVE TEST in SCIENCE Grade 3-6EpiTaffsÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE 3-6 Third SUMMATIVE TESTDocument9 paginiSCIENCE 3-6 Third SUMMATIVE TESTLyrendon CariagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top Test Format For SY 2022-2023 - Chapters 1 and 2Document4 paginiTop Test Format For SY 2022-2023 - Chapters 1 and 2Alea PrillyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 5.revisionDocument3 paginiWorksheet 5.revisionAli monaemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Test 1 Grade 4Document7 paginiUnit Test 1 Grade 4Alexius BaghiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 6 ExaminationsDocument21 paginiScience 6 ExaminationsLucille Gacutan AramburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st QT Science ReviewerDocument5 pagini1st QT Science ReviewerCheryl Walker100% (1)
- 1st QT Science 5Document4 pagini1st QT Science 5Lilibeth Tejano LaderaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Worksheet MatterDocument5 paginiRevision Worksheet MatterScience Teacher100% (1)
- Education Gate International School 2: Name: - Grade: 6Document8 paginiEducation Gate International School 2: Name: - Grade: 6Lama AldailamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE 5 TestDocument3 paginiSCIENCE 5 TestMaricris KrisantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7 Science TestDocument4 paginiUnit 7 Science Testapi-404448001Încă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCEDocument4 paginiSCIENCEAira JamsaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1ST Summative Test Science 4 Q1Document1 pagină1ST Summative Test Science 4 Q1Kristy HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choose The Letter of The Best Answer.: Summativeno. 1 Quarter 1Document3 paginiChoose The Letter of The Best Answer.: Summativeno. 1 Quarter 1Janjan ToscanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choose The Letter of The Best Answer.: Written Work No. 1 Quarter 1Document3 paginiChoose The Letter of The Best Answer.: Written Work No. 1 Quarter 1Russel Valentine OliverosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Test Name: - ScoreDocument3 paginiSummative Test Name: - ScoreJOECEL MAR AMBIDÎncă nu există evaluări
- States of Matter WorksheetDocument1 paginăStates of Matter WorksheetBernie InocieteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st QTR - 2nd Summative TestDocument2 pagini1st QTR - 2nd Summative TestRichel AcebuchiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3RD Quarter AssessmentsDocument6 pagini3RD Quarter AssessmentsLorraine DonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questioner For The Long Quiz (Grade 8)Document3 paginiQuestioner For The Long Quiz (Grade 8)Novie Mae ReambonanzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ST Science 3 No. 1Document2 paginiST Science 3 No. 1Kennedy EscanlarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 1 EliDocument12 paginiWorksheet 1 EliAngge CatembungÎncă nu există evaluări
- EarthScie Summq2Document1 paginăEarthScie Summq2Jeralyn Vallecer-AbelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerDocument3 paginiChoose The Letter of The Best AnswerRovieda ButacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Exam - SampleDocument9 paginiScience Exam - SampleKristine PinpinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Science MatterDocument3 pagini3 Science Matterputri choerunissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Periodical Test in Science-5 by Mam Noemi ClementeDocument3 paginiFirst Periodical Test in Science-5 by Mam Noemi ClementeMary Christine Lasmarias CuevasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choose The Letter of The Best Answer.: Written Work No. 1 Quarter 1Document3 paginiChoose The Letter of The Best Answer.: Written Work No. 1 Quarter 1Jazzele LongnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- QUARTER 3 Summative Test G8Document6 paginiQUARTER 3 Summative Test G8Angelita MenesesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 8 Science Summative TestDocument7 paginiGrade 8 Science Summative Testzerleigh dream pagal75% (4)
- 1 Quarter Written Task in Science 5Document3 pagini1 Quarter Written Task in Science 5dianne perezÎncă nu există evaluări
- RM Grade 3 AclcDocument2 paginiRM Grade 3 AclcHANIFAH DalumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- G4 ScienceDocument2 paginiG4 SciencepauloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matter Unit PretestDocument4 paginiMatter Unit Pretestapi-297507006Încă nu există evaluări
- 100 C Vapour Air Steam Easily Heated SolidsDocument18 pagini100 C Vapour Air Steam Easily Heated SolidsSalim DanielaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 78 11 12 Science Physics States of Matter 3Document3 pagini78 11 12 Science Physics States of Matter 3Kung ThanyathornÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Sses Science 1ST PTDocument8 pagini2 Sses Science 1ST PTjwvopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gr. 6 Science First Term Revision 2Document19 paginiGr. 6 Science First Term Revision 2sultan alkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 PRELIM EXAM IN Science/Health - 5: NAMEDocument2 pagini3 PRELIM EXAM IN Science/Health - 5: NAMEJhasper ManagyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 5 ReviewerDocument1 paginăScience 5 ReviewerLorraine CalderonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colegio de Montalban San Jose, Rodriguez, Rizal: Institute of EducationDocument4 paginiColegio de Montalban San Jose, Rodriguez, Rizal: Institute of EducationVOLANTE, EDLYN JOYCEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name 3Document2 paginiName 3marylou austriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Test in ScienceDocument1 paginăSummative Test in ScienceDebz Cay100% (1)
- Summative Test in ScienceDocument1 paginăSummative Test in ScienceDebz CayÎncă nu există evaluări
- G7 ExamDocument4 paginiG7 ExamTaylegendCareyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shanay ScienceDocument6 paginiShanay ScienceDarshini Aaditya JhaveriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: Velcar Elementary School Macabaklay, Gapan City - Ooo-First Periodical Test in Science VDocument4 paginiDepartment of Education: Velcar Elementary School Macabaklay, Gapan City - Ooo-First Periodical Test in Science VMary Ann ManalastasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 3 Q1 MelcDocument2 paginiScience 3 Q1 Melcanaliza balagosa100% (1)
- 3 Periodical Test in Science 9: St. Clare Community Foundation School Inc. Leviste, Laurel, BatangasDocument6 pagini3 Periodical Test in Science 9: St. Clare Community Foundation School Inc. Leviste, Laurel, BatangasChermaine VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading and PhonicsDocument6 paginiReading and PhonicsMarilouSodeVillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Invert I B RatesDocument2 paginiInvert I B RatesMarilouSodeVillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading PrepDocument4 paginiReading PrepMarilouSodeVillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prep WorksheetDocument12 paginiPrep WorksheetMarilouSodeVillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math PrepDocument6 paginiMath PrepMarilouSodeVillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- (2017) Toxicological Effects of Glycyrrhiza Glabra (Licorice) A ReviewDocument16 pagini(2017) Toxicological Effects of Glycyrrhiza Glabra (Licorice) A ReviewicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- S.No. Type Medicine NameDocument6 paginiS.No. Type Medicine Namered petalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Water Chemistry in FreshwasterDocument4 paginiIntroduction To Water Chemistry in FreshwasterpomodoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- TM 10-4930-220-13PDocument133 paginiTM 10-4930-220-13PAdvocateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green Glue Material Safety DataDocument4 paginiGreen Glue Material Safety DatawilldoyeahÎncă nu există evaluări
- HEPA Cleanroom Filter Testing PDFDocument4 paginiHEPA Cleanroom Filter Testing PDFprovaoralÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Promotional Activity of RCF Fertilizers Through Print Media (RCF Sheti PatrikaDocument26 pagini"Promotional Activity of RCF Fertilizers Through Print Media (RCF Sheti PatrikagirishtorawaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Conditioning EquipmentsDocument31 paginiAir Conditioning EquipmentsamarparimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cci Valve 100DSVDocument8 paginiCci Valve 100DSVyg89Încă nu există evaluări
- Ipa18 202 SeDocument15 paginiIpa18 202 SeDimas Suryo WicaksonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hofmeister Series: Ions Franz Hofmeister ProteinsDocument11 paginiHofmeister Series: Ions Franz Hofmeister ProteinsRajeshwari SridharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zatamaru Cjenovnik PregledatiDocument8 paginiZatamaru Cjenovnik PregledatiNemanja StrkicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Who We Are: Case Study-Mahindra ChlorisDocument25 paginiWho We Are: Case Study-Mahindra ChlorisSUNIDHI VERMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nepro PVC PipesDocument11 paginiNepro PVC PipesAhrian BenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydro Silk Fluid Englisch 06 2020Document1 paginăHydro Silk Fluid Englisch 06 2020Saman KhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- MasterCast 140Document4 paginiMasterCast 140robin rezkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12345Document1 pagină12345Praveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- UO-II Chapter 4 (Adsorption)Document27 paginiUO-II Chapter 4 (Adsorption)Ghaydah Hamed Rashid Al-AbriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sae 1025Document6 paginiSae 1025Mada PerwiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic Auto Feed Drilling Machine With Indexing Machine: SynopsisDocument30 paginiPneumatic Auto Feed Drilling Machine With Indexing Machine: SynopsisMaruthi JacsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scale-Up of Protein Purification Downstream Processing Issues PDFDocument13 paginiScale-Up of Protein Purification Downstream Processing Issues PDFCapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sales Contract Bangladesh Complete and Signed by Jolly 22 July 2021Document18 paginiSales Contract Bangladesh Complete and Signed by Jolly 22 July 2021Fantania BerryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxylink - Starting Point Formulation: Acrylic Direct To Metal Coating Based On Posichem PC-Mull AC 16-2Document2 paginiOxylink - Starting Point Formulation: Acrylic Direct To Metal Coating Based On Posichem PC-Mull AC 16-2Thanh VuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 51314-3985-Methanol-Induced Internal Stress CorrosDocument18 pagini51314-3985-Methanol-Induced Internal Stress CorrosMahmoud GamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nafees Nastaleeq v1.02Document2 paginiNafees Nastaleeq v1.02latifshaikh20Încă nu există evaluări
- Bag Tanning IndiaDocument8 paginiBag Tanning IndiaBurhoneySonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Composition and Some Functional Properties of Soluble Fibro-Protein Extracts From Tunisian Date Palm SeedsDocument12 paginiChemical Composition and Some Functional Properties of Soluble Fibro-Protein Extracts From Tunisian Date Palm SeedsSakline MinarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceramic Tile Fixing StatementDocument5 paginiCeramic Tile Fixing StatementAmit KhazanchiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microstructure Examination of SteelDocument8 paginiMicrostructure Examination of SteelArunodha Hettiarachchi50% (6)
- NTSE Stage 1 State Level Model Paper 10Document30 paginiNTSE Stage 1 State Level Model Paper 10Om Prakash100% (1)