Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Tense: Affirmative/Negative/ Use Important Notes
Încărcat de
mickeyduranDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Tense: Affirmative/Negative/ Use Important Notes
Încărcat de
mickeyduranDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Tense
Affirmative/Negative/
Question
Use Important Notes
Simple present/
Present Indefinite
A: He writes a letter.
N: He does not write a letter.
Q: Does he write a letter?
1. Universal truth
Sun shines during the day.
2. Habits
She gets up early in the
morning.
3. Instruction or direction
Take this and go to Nasik.
4. Future actions
Well give it to her when she
arrives.
In affirmative statement, use the
first or basic form with first,
second and third person plurals.
But with third person singular,
use s or es with the first or
basic form.
(Add es to verbs ending in s, sh,
x, o, ch.)
In negative and interrogative
sentence, use do- with first,
second and third person plurals
does - with third person singular
Present
Progressive/
Continuous
A: He is writing a letter.
N: He is not writing a letter.
Q: Is he writing a letter.
1. Action taking place in the
moment of speaking.
1. It is raining now.
2. Action taking place only for
a limited period of time.
2. She is working for exam.
3.
3. Action arranged for the
future.
at the
moment, just, just now, Listen!,
Look!, now, right now
4. We are going for picnic
tomorrow.
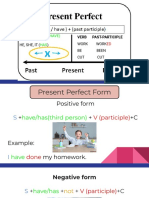
Present Perfect A: He has written a letter.
N: He has not written a letter.
Q: Has he written a letter?
1. Action that stopped recently.
I have just completed my
homework.
2. Indicate an activity began in
the past and continues till the
moment of speaking.
I have waited for you for 3 hrs.
3. A repeated action in an
unspecified period between the
past and now.
We have visited Mumbai
several times.
For and Since
Since and For are very common
time expressions used with the
Present Perfect.
We use For with a period of time,
for example:
I have lived here for 20 years.
When talking about a starting
point, we use Since, for example:
I have lived here since 1960.
Present Perfect
Continuous/
Progressive
A: He has been writing a
letter.
N: He has not been writing a
letter.
Q: Has he been writing a
letter?
Denotes an activity or state that
extends over a period of time that
began in the past and includes the
present and may extend into the
future.
I have been teaching here since
1999.
all day, for 4 years, since 1993,
how long?, the whole week
Simple Past A: He wrote a letter.
N: He did not write a letter.
Q: Did he write a letter?
1. action completed in the past
We gaveher a doll for her
birthday.
2. Situation in the past
I lived in India for 10 years.
(I don't live there anymore).
Time Expression: yesterday, 2
minutes ago, in 1990, the other
day, last Friday
if sentence
type II (If I talked, )
Past Progressive A: He was writing a letter.
N: He was not writing a
letter.
Q: Was he writing a letter.?
1. action going on at a certain
time in the past
The dog was barking.
2. action in the past that is
interrupted by another action
When Bob was painting
windows, it started raining.
3. Actions in progress at the
same time
When I was dancing, she was
playing Chess.
Time Expression: when, while, as
long as
Past Perfect A: He had written a letter.
N: He had not written a letter.
Q: Had he written a letter?
Action happened first in two past
actions.
When I reached their, the bus
had already left.
already, just,
never, not yet,
once, until that day
if sentence type III (If I had
talked, )
Past Perfect
Continuous/
Progressive
A: He had been writing a
letter.
N: He had not been writing a
letter.
Q: Had he been writing a
letter?
Express actions or situations that
were in progress before some
other actions or situations.
Students had been playing for
half an hour when we entered in
the class.
for, since, the whole day, all day
Simple Future A: He will write a letter.
N: He will not write a letter.
Q: Will he write a letter.
When we give information about
the future or predict future events.
I think it will rain.
in a year, next , tomorrow
she will help you.)
assumption I think, probably,
perhaps
Future I Simple
(going to)
A: He is going to write a
letter.
N: He is not going to write a
letter.
Q: Is he going to write a
letter?
We say something is going to
happen when it has already been
planned or decided.
She is going to be a brilliant
student.
in one year, next week, tomorrow
Future I
Progressive
A: He will be writing a letter.
N: He will not be writing a
letter.
Q: Will he be writing a letter?
action that is going on at a certain
time in the future or action that is
sure to happen in the near future
In an hour, I will be sitting in
front of my TV.
To predict or guess about
someone's actions or feelings,
now or in the future:
in one year, next week, tomorrow
Roshan will be getting married
very soon.
Future Perfect A: He will have written a
letter.
N: He will not have written a
letter.
Q: Will he have written a
letter?
action that will be finished at a
certain time in the future
It is often used with a time
expression using by + a point in
future time.
I will have graduated from
university by May.
by Monday, in a week
Future Perfect
Continuous/
Progressive
A: He will have been writing
a letter.
N: He will not have been
writing a letter.
Q: Will he have been writing
a letter?
Express situations that will last
for a specified period of time at a
definite moment in the future.
We also use this tense to express
certainty about the cause of some
future situation.
By 2001 I will have been
living here for sixteen years.
for , the last couple of hours, all
day long ,by tomorrow / 8 o'clock
This year / month / week/ Next
year / month / week
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- FUTURE Tenses - PPTDocument37 paginiFUTURE Tenses - PPTi.diana100% (1)
- At, On and in (Time) - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryDocument7 paginiAt, On and in (Time) - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryKo JiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12) Semantic Categories of AdverbsDocument3 pagini12) Semantic Categories of Adverbsmarcela noemi100% (2)
- Simple Present Present Continuous Simple Past 4. Past ContinuousDocument11 paginiSimple Present Present Continuous Simple Past 4. Past ContinuousArDian PrimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- There Are 12 Tenses in EnglishDocument6 paginiThere Are 12 Tenses in EnglishyrynukaaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 5848263865233574455Document8 pagini4 5848263865233574455Regasa GutemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future Perfect Tense: What Will The Future Bring and When?Document6 paginiFuture Perfect Tense: What Will The Future Bring and When?Jose Jacob Ortiz MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple TenseDocument13 paginiSimple TenseChad HayesÎncă nu există evaluări
- TensesDocument25 paginiTensesrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- TensesDocument5 paginiTensesShruti MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Tenses: A. Simple Present TenseDocument9 paginiSimple Tenses: A. Simple Present TenseJun YuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tense TabloDocument3 paginiTense TabloHosna SalehiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 1 Simple TensesDocument27 paginiGroup 1 Simple TensesRichell Tiong0% (1)
- Time and TenseDocument5 paginiTime and TenseDevanshi BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Notes 11Document29 paginiEnglish Notes 11Abduraman AbubekerÎncă nu există evaluări
- TensesDocument7 paginiTensesdharoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar Lii 2020Document25 paginiEnglish Grammar Lii 2020adjeponehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Introduction To TensesDocument34 paginiBasic Introduction To TensesPriti PritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Simple ContinuousDocument17 paginiPresent Perfect Simple ContinuousLiliana RaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Tense Vs ContinuousDocument2 paginiPresent Perfect Tense Vs ContinuousMonja DjukicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition of The Present Perfect TenseDocument20 paginiDefinition of The Present Perfect TenseSelebriti Rafiq ChikidotÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Tense Timeline QuerformatDocument3 paginiEnglish Tense Timeline QuerformatqkhaiproÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIMBA ENGLEZA 2 Id Anul 1 L. Andrei-CocartaDocument43 paginiLIMBA ENGLEZA 2 Id Anul 1 L. Andrei-CocartaEvelina AnileveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Putri Raneta.D - 3336200012 - Bclass - EnglishDocument8 paginiPutri Raneta.D - 3336200012 - Bclass - EnglishPutri RanetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Tenses: Present Perfect TenseDocument3 paginiEnglish Tenses: Present Perfect TenseKatarina Perčobić100% (1)
- Verb TensesDocument49 paginiVerb TensesHazel GaylanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Tense: Present, Past and Future TenseDocument15 paginiTypes of Tense: Present, Past and Future TenseBirhanu Getachew BelayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses: Shivani M. (PDP Dept.)Document21 paginiTenses: Shivani M. (PDP Dept.)Sandeep SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 1 Verb TensesDocument29 paginiClass 1 Verb TensesWallace SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect - ContinuousDocument23 paginiPresent Perfect - ContinuousAlexander HidalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Listed Below Are Uses With Examples, and The Structure of The Present Simple TenseDocument6 paginiListed Below Are Uses With Examples, and The Structure of The Present Simple TenseUma KalyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRESENT Tenses UsageDocument4 paginiPRESENT Tenses UsageSkruzdelyte MielaÎncă nu există evaluări
- B1 Week 1 and 2Document41 paginiB1 Week 1 and 2wendypo97Încă nu există evaluări
- OW ONG: Affirmative Statements Negative Statements QuestionsDocument1 paginăOW ONG: Affirmative Statements Negative Statements QuestionsyoureslteacherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses in EnglishDocument16 paginiTenses in EnglishSandeep Goud KalalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Simple & ContinuousDocument20 paginiPresent Perfect Simple & Continuousbuendia8986% (7)
- TensesDocument7 paginiTensesmanikarthikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Past Future TensesDocument14 paginiPresent Past Future TensesamitjkjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses Bridge CourseDocument6 paginiTenses Bridge CourseJacintha RohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indefinite Tenses (Examples)Document9 paginiIndefinite Tenses (Examples)statsenkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- JWJWJWDocument26 paginiJWJWJWShankSoham MohantyÎncă nu există evaluări
- HND Year 1 IsaDocument51 paginiHND Year 1 Isabsonleader5Încă nu există evaluări
- Verb TenseDocument21 paginiVerb TenseNara BnÎncă nu există evaluări
- English ReportDocument31 paginiEnglish ReportAfrica Santiago MataÎncă nu există evaluări
- TensesDocument35 paginiTensesMarianÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Unit 1 Grammar - Perfect Aspect - TheoryDocument11 paginiA. Unit 1 Grammar - Perfect Aspect - TheoryVerónica Pérez MadrigalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Parts of Speech TableDocument6 pagini8 Parts of Speech TableAnonymous UadvwxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect ContinuousDocument16 paginiPresent Perfect ContinuousNabila ClaudyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Errors Based On TensesDocument56 paginiErrors Based On TensesSan DeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caroline Grammar + TestsDocument127 paginiCaroline Grammar + TestsanhxuanqbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Only THE TENSESDocument8 paginiOnly THE TENSESMIRZA IBRAHIM ALI BAIGÎncă nu există evaluări
- DoneDocument7 paginiDoneYasmin Putri MaharaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Verb Tenses Structure (Compatibility Mode)Document21 pagini12 Verb Tenses Structure (Compatibility Mode)Briggette QuijijeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engleski Gramatika Sva VremenaDocument13 paginiEngleski Gramatika Sva VremenaMirjana BrčićÎncă nu există evaluări
- TENSESDocument19 paginiTENSESAryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- All TensesDocument21 paginiAll TensesDaniela DiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Tense Exercises With AnswersDocument13 paginiPresent Tense Exercises With Answersanwarofswat100% (1)
- Reviewing Verb TensesDocument21 paginiReviewing Verb Tensesapi-290529183100% (1)
- Present Perfect - For - SinceDocument10 paginiPresent Perfect - For - SinceCarlos SuarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present PerfectDocument2 paginiPresent PerfectGheorghe HorgosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 101 Present Perfect Continuous Tense Sentences: TenseDe la Everand101 Present Perfect Continuous Tense Sentences: TenseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjectives and Adverbs Class 9Document53 paginiAdjectives and Adverbs Class 9Hien BuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepositional Phrases: AdjectivesDocument5 paginiPrepositional Phrases: AdjectivesSuzanne LauÎncă nu există evaluări
- PrepositionDocument11 paginiPrepositionWong Jia MingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orientation Kit-EnglishDocument19 paginiOrientation Kit-EnglishThe HackerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Middle English: Adjective and AdverbDocument10 paginiMiddle English: Adjective and AdverbИван ПаламаренкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjective Unac 2019bDocument6 paginiAdjective Unac 2019bKevin Villavicencio LoaizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silabo de Ingles Segundo SemestreDocument61 paginiSilabo de Ingles Segundo SemestreOber Mayer Villegas MiguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predicate Adjective or NotDocument2 paginiPredicate Adjective or Notfany3dÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Study Korean Lesson 22Document11 paginiHow To Study Korean Lesson 22Avicenna Zahara BungaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upstream For Bulgaria Part 1 Part 2 Variant 2 504b864e84256Document7 paginiUpstream For Bulgaria Part 1 Part 2 Variant 2 504b864e84256Daniel Rosenov AsenovÎncă nu există evaluări
- NOUNSDocument17 paginiNOUNSShahReza Hanifi Shahrom100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 8 (Final Examination)Document17 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in English 8 (Final Examination)Joyce AgraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SENTENCE PATTERN PronounDocument6 paginiSENTENCE PATTERN PronounDhittaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taller InglesDocument5 paginiTaller Inglesoscar rodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Reflexive Pronouns Fun Activities Games - 48630Document1 paginăPersonal Reflexive Pronouns Fun Activities Games - 48630Qurratulain rasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9th of MayDocument13 pagini9th of MayAndreea RanettiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infinitives and Verbs + Ing Forms PDFDocument10 paginiInfinitives and Verbs + Ing Forms PDFStevenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duolingo 1Document3 paginiDuolingo 1Daliborka BurtićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Passive VoiceDocument26 paginiActive Passive VoiceAman BeriwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grosarium From Week 1 Until Week 17 - Dilla Nurul Khafidah - 2104411071Document49 paginiGrosarium From Week 1 Until Week 17 - Dilla Nurul Khafidah - 2104411071Dilla NurulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adverbs and Expressions of OpinionDocument4 paginiAdverbs and Expressions of Opinionkitty2911100% (1)
- Complete The Sentences Using ManyDocument9 paginiComplete The Sentences Using ManyNova AnggrainyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morphology 2Document18 paginiMorphology 2Azlan TaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- FOG4 Grammar ChartDocument36 paginiFOG4 Grammar ChartGino HuamánÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spanish Dict PDFDocument2 paginiSpanish Dict PDFBharat NarumanchiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ele Unit7 Revision PDFDocument2 paginiEle Unit7 Revision PDFJeny ZuñigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arabic GrammerDocument90 paginiArabic GrammerEmir Asad100% (2)
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument2 paginiAdjectives and AdverbsAshwin Josiah SamuelÎncă nu există evaluări