Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Electric Power 2
Încărcat de
zidaaan0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări3 pagini: Electric power 2
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest document: Electric power 2
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări3 paginiElectric Power 2
Încărcat de
zidaaan: Electric power 2
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
Electric power is transmitted on
overhead lines like these, and also
on underground high voltage
cables.
Electric power
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is
transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the
watt, one joule per second.
Electric power is usually produced by electric generators, but
can also be supplied by sources such as electric batteries. It
is generally supplied to businesses and homes by the electric
power industry through an electric power grid. Electric power
is usually sold by the kilowatt hour (3.6 MJ) which is the
product of power in kilowatts multiplied by running time in
hours. Electric utilities measure power using an electricity
meter, which keeps a running total of the electric energy
delivered to a customer.
Contents
1 Definition
2 Explanation
2.1 Passive sign convention
2.2 Resistive circuits
2.3 Alternating current
2.4 Electromagnetic fields
3 Electric power supply
3.1 Electricity generation
3.2 Battery power
3.3 Electric power industry
4 See also
5 Notes
6 References
7 External links
Definition
Electric power, like mechanical power, is the rate of doing work, measured in watts, and
represented by the letter P. The term wattage is used colloquially to mean "electric power in
watts." The electric power in watts produced by an electric current I consisting of a charge of Q
coulombs every t seconds passing through an electric potential (voltage) difference of V is
where
Q is electric charge in coulombs
t is time in seconds
Electric power - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_power
1 3 01/09/2014 03:16
Animation showing
electric load
Animation showing
power source
Q is electric charge in coulombs
t is time in seconds
I is electric current in amperes
V is electric potential or voltage in volts
An alternate way to derive this formula is to note that voltage is defined as , the amount
of work that a unit charge (one coulomb) does when it moves between the two terminals, and the
current is defined as , the number of coulombs flowing per second, so
Explanation
Electric power is transformed to other forms of power when electric
charges move through an electric potential (voltage) difference, which
occurs in electrical components in electric circuits. From the standpoint of
electric power, components in an electric circuit can be divided into two
categories:
Passive devices or loads: When electric charges move through a
potential difference from a high voltage to a low voltage, that is
conventional current (positive charge) moves from the positive
terminal to the negative, the potential energy of the charges is
converted to kinetic energy, which performs work on the device.
Devices in which this occurs are called passive devices or loads; they consume electric
power from the circuit, converting it to other forms such as mechanical work, heat, light, etc.
Examples are electrical appliances, such as light bulbs, electric motors, and electric
heaters.
Active devices or power sources: If the charges are forced by an
outside force to move through the device in the direction from a lower
electric potential to a higher, so positive charge moves from the
negative to the positive terminal, work is being done on the charges,
so energy is being converted to electric potential energy from some
other type of energy, such as mechanical energy or chemical energy.
Devices in which this occurs are called active devices or power
sources; sources of electric current, such as electric generators and
batteries.
Some devices can be either a source or a load, depending on the voltage or current through
them. For example, a rechargeable battery acts as a source when it provides power to a circuit,
but as a load when it is connected to a battery charger and is being recharged.
Electric power - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_power
2 3 01/09/2014 03:16
Power triangle: The components of
AC power
Some devices can be either a source or a load, depending on the voltage or current through
them. For example, a rechargeable battery acts as a source when it provides power to a circuit,
but as a load when it is connected to a battery charger and is being recharged.
Passive sign convention
Since electric power can flow in either direction, either into or out of a component, a convention is
needed for which direction represents positive power flow. Electric power flowing out of a circuit
into a component is arbitrarily defined to have a positive sign, while power flowing into a circuit
from a component is defined to have a negative sign. Thus passive components have positive
power consumption. This is called the passive sign convention.
Resistive circuits
In the case of resistive (Ohmic, or linear) loads, Joule's law can be combined with Ohm's law (V =
IR) to produce alternative expressions for the dissipated power:
where R is the electrical resistance.
Alternating current
In alternating current circuits, energy storage elements such as inductance and capacitance may
result in periodic reversals of the direction of energy flow. The portion of power flow that,
averaged over a complete cycle of the AC waveform, results in net transfer of energy in one
direction is known as real power (also referred to as active power). That portion of power flow due
to stored energy, that returns to the source in each cycle, is known as reactive power. The real
power P in watts consumed by a device is given by
where
V
p
is the peak voltage in volts
I
p
is the peak current in amperes
V
rms
is the root-mean-square voltage in volts
I
rms
is the root-mean-square current in amperes
is the phase angle between the current and voltage sine waves
The relationship between real power, reactive power and
apparent power can be expressed by representing the
quantities as vectors. Real power is represented as a
horizontal vector and reactive power is represented as a
vertical vector. The apparent power vector is the hypotenuse
of a right triangle formed by connecting the real and reactive
power vectors. This representation is often called the power
triangle. Using the Pythagorean Theorem, the relationship
among real, reactive and apparent power is:
Real and reactive powers can also be calculated directly from the apparent power, when the
Electric power - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_power
3 3 01/09/2014 03:16
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Eagle PDFDocument6 paginiEagle PDFzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Cobalt MetalDocument6 paginiCobalt MetalzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Butterfly: Butterflies Butterflies Are Part of The Class of Insects in The Order Lepidoptera, Along With The Moths. AdultDocument2 paginiButterfly: Butterflies Butterflies Are Part of The Class of Insects in The Order Lepidoptera, Along With The Moths. AdultzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Antenna: Science and EngineeringDocument1 paginăAntenna: Science and EngineeringzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- PlasterDocument3 paginiPlasterzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Eddy-Current Testing - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument3 paginiEddy-Current Testing - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Electrical Discharge MachiningDocument6 paginiElectrical Discharge MachiningzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- BoronDocument22 paginiBoronzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Eddy-Current Testing - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument3 paginiEddy-Current Testing - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- CNC G-Code Programming Tutorial, Course, Examples, and ProgramsDocument5 paginiCNC G-Code Programming Tutorial, Course, Examples, and Programszidaaan0% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- SulfurDocument20 paginiSulfurzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- ZincDocument29 paginiZinczidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Polarity (Mutual InductanceDocument3 paginiPolarity (Mutual InductancezidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Plasticity (Physics) PDFDocument4 paginiPlasticity (Physics) PDFzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- G CodeDocument16 paginiG CodezidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Difference Between PLC, NC and CNC - QuoraDocument1 paginăWhat Is The Difference Between PLC, NC and CNC - QuorazidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Numerical Control - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 paginiNumerical Control - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediazidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PoundDocument1 paginăPoundzidaaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math ExamDocument4 paginiMath ExamHenry TuganoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IprDocument51 paginiIprRaj Kumar Pathak100% (1)
- Exam021 MIdterm Gen - Phy1Document7 paginiExam021 MIdterm Gen - Phy1Jerome RacalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter OneDocument28 paginiChapter Oneadisu100% (2)
- The Stability and Control of Motorcycles Sharp1971Document14 paginiThe Stability and Control of Motorcycles Sharp1971renoir0079584Încă nu există evaluări
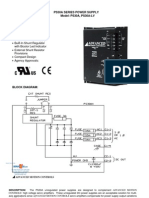
- Advanced Motion Controls PS30ADocument3 paginiAdvanced Motion Controls PS30AServo2GoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- What Is A Demagnetization Curve?: More Than Just Your SupplierDocument2 paginiWhat Is A Demagnetization Curve?: More Than Just Your Suppliersurabhi0706Încă nu există evaluări
- Research Proposal For The Proton BatteryDocument4 paginiResearch Proposal For The Proton BatteryStacey SkibaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magneto Hydro Dynamic Power Generation: EEE Dept The Vazir Sultan College of EnggDocument23 paginiMagneto Hydro Dynamic Power Generation: EEE Dept The Vazir Sultan College of EnggAzghar Ali0% (1)
- Chapter 2Document7 paginiChapter 2Shin Se Kyung100% (1)
- Optimal Design of An In-Wheel BLDC Motor For A Kick Scooter: October 2010Document6 paginiOptimal Design of An In-Wheel BLDC Motor For A Kick Scooter: October 2010Immawan InsaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Overexcitation ProtectionDocument13 paginiOverexcitation Protectionalonso100% (1)
- Pages Printed by Cycle-TempoDocument1 paginăPages Printed by Cycle-TempoBasybelÎncă nu există evaluări
- DARBY - Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics 3edition PDFDocument578 paginiDARBY - Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics 3edition PDFMiguel Zuniga100% (2)
- Inverters - ANTECHDocument21 paginiInverters - ANTECHOG100% (2)
- ELFL003Document27 paginiELFL003Destry YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Submersible SubstationDocument7 paginiSubmersible SubstationWill AchuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 630 Volt and 400 Volt FILM Capacitors Electrolytic & Safety Capacitors MICA and 1000V, 1600V & 6000VDocument8 pagini630 Volt and 400 Volt FILM Capacitors Electrolytic & Safety Capacitors MICA and 1000V, 1600V & 6000VwilfredoinimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- EHVAC-TRANSMISSION-NOTES NewDocument104 paginiEHVAC-TRANSMISSION-NOTES Newpraveenmande100% (1)
- LXP3-6K: SpecificationDocument1 paginăLXP3-6K: SpecificationYopp MismoÎncă nu există evaluări
- End of SemDocument2 paginiEnd of SemyaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit & DimensionsDocument9 paginiUnit & DimensionsRandhir SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transmission Lines-2Document46 paginiTransmission Lines-2Dhruv GolaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Machines 15ME32TDocument8 paginiMechanics of Machines 15ME32TRaghuraj DanadamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverter TrainingDocument66 paginiInverter Trainingkhurazi100% (1)
- CHAPTER 6-CentroidsDocument24 paginiCHAPTER 6-CentroidsYohannes MesfinÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTS9000A Multiple Telecommunication System User Manual Russia Megafone MTS9513A-AD2002Document65 paginiMTS9000A Multiple Telecommunication System User Manual Russia Megafone MTS9513A-AD2002Влад ТолчеевÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso-Tc-213-N-658 PDFDocument71 paginiIso-Tc-213-N-658 PDFFrancisco Manuel Pelaez RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi VerseDocument82 paginiMulti VerseAntito123Încă nu există evaluări
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsDe la EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (19)
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesDe la EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (21)