Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
VD Temario PDF
Încărcat de
Jordi_fg0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
69 vizualizări2 paginiCG - wheelbase - track - Ride height - static weight distribution - weight transfer - sprung / unsprung mass - axis / coordinate system - forces on a vehicle - slip angle - tyre characteristics - friction circle (excel model) - steer characteristics (ackermann) All Excel models are made in class, directly based on the theory and Formulae given in class. All ADAMS / ViewModels are passed on to students already made.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
VD temario.pdf
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentCG - wheelbase - track - Ride height - static weight distribution - weight transfer - sprung / unsprung mass - axis / coordinate system - forces on a vehicle - slip angle - tyre characteristics - friction circle (excel model) - steer characteristics (ackermann) All Excel models are made in class, directly based on the theory and Formulae given in class. All ADAMS / ViewModels are passed on to students already made.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
69 vizualizări2 paginiVD Temario PDF
Încărcat de
Jordi_fgCG - wheelbase - track - Ride height - static weight distribution - weight transfer - sprung / unsprung mass - axis / coordinate system - forces on a vehicle - slip angle - tyre characteristics - friction circle (excel model) - steer characteristics (ackermann) All Excel models are made in class, directly based on the theory and Formulae given in class. All ADAMS / ViewModels are passed on to students already made.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
1
Vehicle Dynamics and Simulation
Terminology
- CG
- wheelbase
- track
- Ride height
- static weight distribution
- weight transfer
- sprung/unsprung mass
- axis/coordinate system
- forces on a vehicle
- slip angle
- tyre characteristics
- friction circle (Excel model)
- steer characteristics
- Ackermann (Excel model)
Steady State Handling
- understeer/oversteer
- yaw gain (Excel model - benchmarking vehicle DNA)
- understeer gradient, K and stability margin
Lateral load transfer
- CG migration effect
- Tyre friction vs FZ
- (Excel model)
- (analysis using ADAMS/View model)
Longitudinal load transfer
- weight split and CG height (trade-off long and lat performance)
- traction/power limited accel vs. Weight split and CG height
- (Excel model and ADAMS/View model)
Note: Excel and ADAMS models will be used for understanding/outlining the role of the relevant variables for each case and analyse possible trade-offs.
All Excel models are made in class, directly based on the theory and formulas given in class. All ADAMS/ViewModels are passed on to students already made.
Marks: Exam 50% - Assignent 50%. About the exam: All questions taken directly from VD notes, Formulae handed out in the exam.
Vehicle design mass/inertia relationship:
- packaging and wheelbase
- Dynamic Index (Excel model)
Tyre characteristics
- tyre friction coeff. vs. Lateral acceleration
Tyre modelling pacejka
Slip angle
Slip ratio
Friction circle
FZ vs. tyre deflection
Stiffness
Camber effect
(Excel model)
Feeding back road test data to determine tyre grip
Suspension : introduction
requirements
design considerations
terminology
kinematics/geometry
steering axis
kingpin inclination
castor/castor trail
camber
scrub radius
toe-in
bump steer
bump-camber
motion ratio
2
Suspension: Anti-pitch geometry
anti-dive
anti-squat
(Excel model)
Suspension: Lateral weight transfer anti-roll geometry
roll centre
lateral weight transfer model
(Excel model and ADAMS/View model)
Suspension: design
- The Understeer Budget concept
- Equating all suspension characteristics.
- Tyres (how to use the model optimize to weight split)
- Requirements (Wheel travel, Wheel rate, roll rate, anti-pitch, anti-roll, deg/G)
- springs (suspension stiffness split (for neutral steering), ARB, etc.
- (Excel model)
Damping
Initial setup ( damping ratio vs. wheel vertical speed), low and high
speed damping, motion ratio.
Suspension components
- packaging considerations
- uprights (packaging)
- rockers (kinematics considerations)
- wishbones
- Load cases (worst case scenario and fatigue loads Excel model and
ADAMS/View model)
- applying load cases results to FEA boundary conditions.
- S-N curve
- Steering kinematics (ADAMS/View model)
Gear selection calculations
defining and optimizing calculations
referred inertias
tractive effort/ road loads
constant torque curves
analysis of force-velocity graph
fuel consumption
(Excel model)
Brake proportioning and adhesion utilisation
(Excel model)
Brake system design
(Excel model)
Chassis
- stiffness requirements
- Packaging
- Fabrication type of chassis
- torsional stiffness
- FEA boundary conditions (considerations and effects on results)
- Development method identifying weak areas with FEA
Aerodynamics
Drag and downforce: effect on vehicle balance, cornering
and braking/traction (Excel model)
Determining Cd, Cr and engine torque curve from road tests
(Excel model)
Laptime simulator
(excel model) simple model for analysis of trade-offs and
initial setup
Sensitivity analysis
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Basic Nature of Vehicle Understeer-OversteerDocument36 paginiThe Basic Nature of Vehicle Understeer-OversteerRTCNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belgians Early WarDocument41 paginiBelgians Early WarDenis Diez75% (4)
- 10 K&CDocument95 pagini10 K&COscar Mendoza Quintana100% (1)
- Guide to Load Analysis for Durability in Vehicle EngineeringDe la EverandGuide to Load Analysis for Durability in Vehicle EngineeringP. JohannessonEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Vehicle Roll EstimatorDocument10 paginiVehicle Roll EstimatorRaja Amer AzimÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC Worksheet v016Document82 paginiAC Worksheet v016Игорь БелецкийÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ackerman Erik ZapletalDocument23 paginiAckerman Erik ZapletalMrudula Amar WardeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fvschemes & Fvsolution For Steady State and Transient SimuationsDocument4 paginiFvschemes & Fvsolution For Steady State and Transient SimuationsIsaacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied Vehicle Dynamics Seminar April 7-10, 2017 Sinhgad Technical Education Society - Pune, IndiaDocument2 paginiApplied Vehicle Dynamics Seminar April 7-10, 2017 Sinhgad Technical Education Society - Pune, IndiaPRAVEEN REDDY100% (1)
- Sae Technical Paper Series: T. Amato, F. Frendo and M. GuiggianiDocument10 paginiSae Technical Paper Series: T. Amato, F. Frendo and M. GuiggianiAramis SchultzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chassis Newsletter 2010.8Document3 paginiChassis Newsletter 2010.8Ganesh ShanmugamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling and Validation of Off-Road Vehicle Ride DynamicsDocument17 paginiModeling and Validation of Off-Road Vehicle Ride DynamicsAnderson MoribeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porsche Chassis DevelopmentDocument18 paginiPorsche Chassis DevelopmentArif OthmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development and Experimental Verification of A Parametric Model of An Automotive DamperDocument126 paginiDevelopment and Experimental Verification of A Parametric Model of An Automotive DamperMrudula Amar WardeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Four - Kinematic Steering - 2015 - Essentials of Vehicle DynamicsDocument11 paginiChapter Four - Kinematic Steering - 2015 - Essentials of Vehicle DynamicsJulián AvellaÎncă nu există evaluări
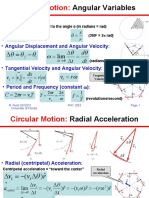
- Math - Circular Motion-AngularDocument9 paginiMath - Circular Motion-AngulardhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of Aerodynamics For A Solar Race CarDocument7 paginiDevelopment of Aerodynamics For A Solar Race CarAmr MagdyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bump SteerDocument5 paginiBump SteerHimanshu RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Senior Project ReportDocument6 paginiSenior Project ReportRoss Bunnell100% (1)
- CG Height Calculator - Automotive Brake System Calculator - BRAKE POWERDocument2 paginiCG Height Calculator - Automotive Brake System Calculator - BRAKE POWERAnonymous QiMB2lBCJLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formula Student 101: A Low Inertia Goes Against Stability But It Does Help With ControlDocument12 paginiFormula Student 101: A Low Inertia Goes Against Stability But It Does Help With ControlLeonardo ColpoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FSAE Data Analysis Day 2 To PrintDocument55 paginiFSAE Data Analysis Day 2 To PrintJorge CorderoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Suspension and Chassis GlossaryDocument9 paginiSuspension and Chassis GlossaryHemantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transient Characteristics of A Hydraulically Interconnected Suspension System PDFDocument12 paginiTransient Characteristics of A Hydraulically Interconnected Suspension System PDFmanteghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tyre Report SampleDocument5 paginiTyre Report SampleArka PatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chassis 23 PDFDocument89 paginiChassis 23 PDFpartizan21Încă nu există evaluări
- Análise de Um Veículo em YAWDocument3 paginiAnálise de Um Veículo em YAWLeonardo ColpoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 253 Suspension Calc ExplainedDocument1 pagină253 Suspension Calc ExplainedholaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Racing Simulation of A Formula 1 Vehicle With Kinetic Energy Recovery SystemDocument15 paginiRacing Simulation of A Formula 1 Vehicle With Kinetic Energy Recovery SystemRodrigo Bob100% (1)
- Automotive Differentials, ReleaseDocument30 paginiAutomotive Differentials, Releasestefanovicana1Încă nu există evaluări
- Find Your Roll CenterDocument20 paginiFind Your Roll CenterchainplatesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composite Effects On Tire MechanicsDocument22 paginiComposite Effects On Tire MechanicsTomislavMatanićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Springs&Dampers Tech Tip 1Document4 paginiSprings&Dampers Tech Tip 1Sankhadeep BhattacharyyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braking DynamicsDocument16 paginiBraking DynamicsSalih Ağın100% (2)
- Baja'18 Problem Statements 1Document2 paginiBaja'18 Problem Statements 1Shubham GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation of Optimized Regenerative Braking in Energy Efficient Driving StrategiesDocument20 paginiImplementation of Optimized Regenerative Braking in Energy Efficient Driving StrategiesBT20MEC120 Jyoti ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roll Center MysteryDocument7 paginiRoll Center MysteryMrudula Amar WardeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Suspension Design by Ravi DeshmukhDocument11 paginiSuspension Design by Ravi DeshmukhsonirocksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ackermann Steering For Performance Race Cars PDFDocument22 paginiAckermann Steering For Performance Race Cars PDFr2d23Încă nu există evaluări
- At2402 NotesDocument7 paginiAt2402 NotesAnonymous ETBwIduGiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tire Force Estimation in Off Road VehiclesDocument119 paginiTire Force Estimation in Off Road VehiclesSantiago Urgiles100% (1)
- Vehicle Suspension Modeling NotesDocument25 paginiVehicle Suspension Modeling Notesahmetlutfu100% (2)
- Torque Vectoring With A Feedback and Feed Forward Controller-Applied To A Through The Road Hybrid Electric VehicleDocument6 paginiTorque Vectoring With A Feedback and Feed Forward Controller-Applied To A Through The Road Hybrid Electric Vehiclesmmj2010Încă nu există evaluări
- 272 Concept Class Mansoura University DR Rev 2Document8 pagini272 Concept Class Mansoura University DR Rev 2Gazzara WorldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Suspension Control of Ground VehicleDocument6 paginiActive Suspension Control of Ground VehicleSanjay MehrishiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autonomous Vehicles On The Edge A Survey On Autonomous Vehicle RacingDocument31 paginiAutonomous Vehicles On The Edge A Survey On Autonomous Vehicle RacingGergely HornyakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Davis Steering Gear Mechanism For Four Wheels and Six WheelsDocument5 paginiAnalysis of Davis Steering Gear Mechanism For Four Wheels and Six WheelsIJIRSTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Time Simulation and Parametric Optimization Applied To Racing Cars The BMW Team Brasil Case PDFDocument47 paginiReal Time Simulation and Parametric Optimization Applied To Racing Cars The BMW Team Brasil Case PDFDebra JacksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Stability ProgramDocument21 paginiElectronic Stability ProgramVinay GirdharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Damper DynoDocument3 paginiDamper DynoEoin MurrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vehicle Dynamics Tutorial - 1Document46 paginiVehicle Dynamics Tutorial - 1Girish ChandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designing Shell Eco Marathon Car Bodies With SolidDocument8 paginiDesigning Shell Eco Marathon Car Bodies With Solidالامير حسنÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulastudent2014 PDFDocument27 paginiFormulastudent2014 PDFDionisis SpiliopoulosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baja SAE Auburn Design Report Cleveland State University 16Document10 paginiBaja SAE Auburn Design Report Cleveland State University 16Noel Mahung Melendez100% (1)
- Sae Baja India 2011 (FDR)Document22 paginiSae Baja India 2011 (FDR)Rahul ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team Teaching Presentation How Car Suspension WorksDocument17 paginiTeam Teaching Presentation How Car Suspension Worksmsaad19103564Încă nu există evaluări
- Braking System Suggested For The AtvDocument9 paginiBraking System Suggested For The AtvAkash SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of Composite Structures for Automotive Applications: Chassis and DrivetrainDe la EverandDesign and Analysis of Composite Structures for Automotive Applications: Chassis and DrivetrainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00-Temari 01 - 18 PDFDocument232 pagini00-Temari 01 - 18 PDFJordi_fgÎncă nu există evaluări
- AckermanDocument11 paginiAckermanC.E. Ishmeet Singh50% (2)
- Vehicle Dynamics Training: Lunes Martes Miércoles Jueves Viernes Sábado DomingoDocument1 paginăVehicle Dynamics Training: Lunes Martes Miércoles Jueves Viernes Sábado DomingoJordi_fgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flex BuildDocument32 paginiFlex BuildJordi_fgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper Trapezius MuscleDocument6 paginiUpper Trapezius MusclejpÎncă nu există evaluări
- 40 KL DesignDocument10 pagini40 KL DesignSung Woong MoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Order of AdjectivesDocument5 paginiOrder of AdjectivesHoney Lou SemblanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Horse Evaluation HandbookDocument34 paginiHorse Evaluation Handbookapi-526186145Încă nu există evaluări
- Birches ExcerptDocument2 paginiBirches Excerptrrivera7396Încă nu există evaluări
- Class - XII Unit - 1Document68 paginiClass - XII Unit - 1XDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxo Aqa16 p9cs xq02 XxaannDocument5 paginiOxo Aqa16 p9cs xq02 Xxaannali mehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 4 - The Skeletal SystemDocument38 paginiLab 4 - The Skeletal SystemNatalie PembertonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charlton 27Document20 paginiCharlton 27gladtan0511Încă nu există evaluări
- The Interesting Facts About Theme ParksDocument11 paginiThe Interesting Facts About Theme ParksArzu TaghiÎncă nu există evaluări
- F1 Mavericks PDFDocument243 paginiF1 Mavericks PDFHector NeriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taneks Brake CatalogueDocument31 paginiTaneks Brake CatalogueeCommerce SAJID AutoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment - Case Studies and ObjectiveDocument3 paginiAssignment - Case Studies and ObjectiveISHAAN GOYALÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Great Is Our God (World Edition) - Chris Tomlin-How Great Is Our God - The Essential Collection - DBDocument3 paginiHow Great Is Our God (World Edition) - Chris Tomlin-How Great Is Our God - The Essential Collection - DBOscar Felipe Guerra VelazcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2wvzq79gvycokolywolffkan 325-Sl Tower Crane NetworkDocument6 pagini2wvzq79gvycokolywolffkan 325-Sl Tower Crane NetworkdjlivuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Results Ews IrelandDocument26 paginiResults Ews IrelandMattÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8100 X-Cess 5W-40: Gasoline and Diesel Engine Oil 100% SyntheticDocument2 pagini8100 X-Cess 5W-40: Gasoline and Diesel Engine Oil 100% SyntheticJmi JobsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Results Final Run RDC Oberhof 2023Document8 paginiResults Final Run RDC Oberhof 2023racementÎncă nu există evaluări
- Folk DanceDocument21 paginiFolk DanceRomeo Nicolas I. NungayÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Different Types of Basketball Scoring Shots: Fundamentals in ShootingDocument14 paginiThe Different Types of Basketball Scoring Shots: Fundamentals in ShootingLore Anne Mhae SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- SBN Product CatalogDocument50 paginiSBN Product CatalogChien Nguyen100% (1)
- PS 200B PDFDocument16 paginiPS 200B PDFLuis Fernando Vasquez RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Punch PowerDocument2 paginiPunch PowerguidocesanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Codex: Blood Angels: WARHAMMER 40,000Document2 paginiCodex: Blood Angels: WARHAMMER 40,000Henrique MiradouroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distant Worlds II BookDocument7 paginiDistant Worlds II BookJoaoPauloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mahindra Scorpio-N Review - Page 2 - Team-BHPDocument13 paginiMahindra Scorpio-N Review - Page 2 - Team-BHPRavi DhingraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chord Guitar Miley CyrusDocument1 paginăChord Guitar Miley CyrusaldifaiezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deku Calisthenics Workout PDFDocument9 paginiDeku Calisthenics Workout PDFAria Yamasaki100% (1)
- 300 BLK WhitepaperDocument28 pagini300 BLK Whitepapereric desentis100% (1)