Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 5 (Teacher)
Încărcat de
ajakazDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 5 (Teacher)
Încărcat de
ajakazDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
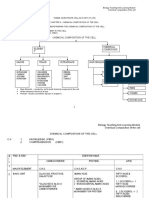
Biology Teaching and Learning
Module
Cell
Division
Chapter 5 : Cell Division
(ANSWERS)
Theme : Investigating Cell As a Basic nit o! "i!e
"S n#erstan#ing $itosis
5%&%& The necessit' !or the pro#(ction o! ne) cells in organisms
List down the need for producing new cells in life (significance of mitosis)
1. produces new cells for growth
2. repair and replaces cells that are dead or damage.
3. to increase the number of unicellular organisms
4. ensure that the offspring/new cells are genetically identical to the parent
5. mitosis preseres the diploid number of chromosomes
5%&%* The necessit' !or the pro#(ction o! ne) cells i#entical to parent cells
List down the necessity for the production of new cell identical to parent cells
1. !pecies surial
2. presere the diploid number of chromosomes
3. presere the genetic information
4. to presere the parent characteristics
5%&%+ De!inition o! $itosis
" type of cell diision which inoles the diision of the nucleus to produce two daughter
cells# each contain same number and same $ind of chromosomes as the parent cells.
Operational-definition based on observation
%he produce of two daughter cells which is a loo$ li$e the parent cell with the diision of
nucleus
&laces where the mitosis occur during the diision of cell
- all somatic (in animal) cells which are all body cells e'cept gametes
- meristem cells ( in plant) at the end of the shoots# the end of roots and cambium
1
Biology Teaching and Learning
Module
Cell
Division
5%&%, The cell c'cle
%he cell cycle is the period that e'tends from the time a new cell is produced until the time
the cell completes a cell diision. %he cell cycle can be diided into two ma(or phases )
interphase and mitotic cell diision or the * phase. *itotic cell diision consists of mitosis
(nucleus diision) and cyto$inensis (cytoplasmic diision)
+n the cell cycle diagram below# identify the phases and e'plain what happen during each
phase.
2
(,2) -asa 2 ) %enaga dihasil$an
(!) !ynthesis phase )
./" replication occur
(1) &hase 1 ) +rganelle are synthesi0ed
and biochemical substances (en0ymes)
are produced
(*) *itosis
(,2) &hase 2 ) 1nergy is produced
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
5%&%5 $itosis -rocess
*itosis inoled of diision of nucleus from the parent cell to produced two new daughter cells
which are genetically identical to the parent. 2efore mitosis occur cell is in the interphase leel
and after mitosis the cyto$inesis occur.
Cell c'cle . Interphase / $itosis / C'to0inesis
Activity 1 !atching the ani"ation phases in "itosis
Activity # $dentify phases of "itosis
+n the diagram below# identify phases of mitosis which hae been labeled
3 ) 1arly prophase
L ) *etaphase
* ) 4nterphase
/ ) Late telophase
+ ) 1arly anaphase
& ) Late anaphase
5 ) Late prophase
6 ) 1arly telophase
3
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
Activity % Arrange the various stages of "itosis in the correct se&uence and
e'plain the "itosis and cyto(inesis
!tages of cell diision of mitosis process.
"naphase
4nterfasa
"naphase
4
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
$nstruction Cut the phases of division cell of "itosis above and paste the appropriate pictures
in the bo' provided in the ne't page in correct order) *'plain +hat happen during each stage
in the bo'es provided)
!tages of cell diision of mitosis process.
.iagram 1'planation
4nterphase
%he chromosomes are not isible but appear as
thread7li$e structures called chromatin
/ucleus is large and prominent
4noles synthesis of protein and organelles#
replication of ./"#
&rophase
8hromosomes in the nucleus condense and become
more tightly coiled.
%he chromosomes appear shorter and thic$er and
are isible.
1ach chromosome now consists of a pair of sister
chromatids (oined together at the centromere.
*etaphase
&rophase *etaphase
Late %elophase
1arly %elophase
5
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
%he spindle fibres begin to form and e'tend between
the centrioles.
%he chromatids are attached to the spindle fibres by
their centrioles
"t the end of the prophase# the nucleolus disappears
and the nuclear membrane disintegrate.
*etaphase
2egins when the centromeres of all chromosomes
are lined up on the metaphase plate.
1nds when the centromeres diide
.iagram 1'planation
"naphase
%wo sister chromatids of each chromosome separate
at the centromere.
%he sister chromatids are pulled apart to the
opposite poles by the shortening of the spindle fibres
+nce separated# the chromatids are referred to as
daughter chromosomes
2y the end of anaphase# the two poles of the cell
hae complete and e9uialent sets of chromosomes
1arly %elophase
2egin when the two sets of chromosomes reach the
opposite poles of the cell.
%he chromosomes start to uncoil and reert to their
e'tended state (chromatin).
%he chromosomes become less isible under the
microscope.
:
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
Late %elophase
%he spindle fibres disappear and a new nuclear
membrane forms around each set of chromosomes
%he nucleolus also re7forms in each nucleus.
8yto$inesis is the diision of the cytoplasm. 4n animal cell a cleaage furrow is formed while in plant
cell a cell plate is formed.
1'plain the cyto$inesis process in the table below.
.iagram 1'planation
"nimal cell
4n animal cell# actin filaments in the
cytoplasm contracts to pull a ring of plasma
membrane inwards
-orming a grooe called a cleaage furrow
&lant cell
;
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
4n plant cell# membrane7enclosed esicles
gather at a plant cell<s e9uator between the
two nuclei
%he esicles fuse to form a cell plate.
%he cell plate grows outwards until its edges
with the plasma membrane of the parent
cell.
5%&%1 Application o! 2no)le#ge on $itosis
Activity Collect infor"ation) Do an article about the application of (no+ledge "itosis
according to the topic belo+) $n your article you can include tabled data, picture and other
suitable techni&ue +hich is necessary)
a) Tiss(e c(lt(re
=
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
3) Cloning : A#vantages an# Disa#vantages
A#vantages Disa#vantages
1nsure the continuity of hereditary
traits from the parent to the clones.
4ncrease the rate of production and the
9uality of the products
%he resistance of the clones towards
diseases and pests is the same. 4f a clone is
infected with a disease or attac$ed by pests
then all the clones will also affected and die.
.iagram
1'planation
1. >ash the tomato plant tissue with hypochloric solution.
2. %omato tissue are cultured in a sterile medium rich in nutrients
3. "fter the callus is formed# transfer the tissue culture to a new sterile medium rich in nutrients
which contain growth hormone.
4. "fter the shoots is formed# transfer them into the plant pod
%omato plant
tissue
8allus
root
!hoots
?
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
,ood 9ualities of the plants and
animals can be selected and
maintained in the clones
*any clones are produced in a short
time
8an be carried out any time of the year.
5%&%4 The Importance o! Controlle# $itosis
1'plain the importance of controlled mitosis.
1. mitosis @ increase the number of cells and repair damage cells. 4t happens in animal
and plant in growth# presere the normal body tissues for surial of life.
2. meiosis @ produce haploid gametes to maintain the number of chromosomes in
organisms
5%&%5 The A!!ect o! ncontrolle# mitosis in living things
1'plain the affect of uncontrolled mitosis (cancer)
1A
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
1. *itosis occur because the changes of gene which control the cell cycle.
2. %his condition happen because of certain irus# to'ic chemical substances# e'pose to the
direct and strong ultra iolate rays.
3. %he cells diide ery fast and unregulated. %his abnormal cell are called tumour.
2enign tumour @ abnormal cells remain at the original site. .o not cause serious problems
and can be remoed by surgery.
*alignant tumour @ the tumour becomes inasie and spread to neighbouring tissues. %his
is cancer.
11
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
"S * : n#erstan#ing $eiosis
5%*%& Inheritance in o!!spring
&rocess of producing new indiiduals is celled se'ual reproduction.
!e'ual reproduction inoled two parents male and female. *ale and female produce
gametes. 1ach gamete has half the number of chromosome compare to the parent. ,amete is
produced during meiosis process.
*ale gamete (haploid) and female gamete (haploid) will combined to form a 0ygote (diploid)
and grow to form a new indiidual.
%he new indiidual which is produced will inherit the characteristic from both parents.
%he number of chromosomes diploid must be maintained from one generation to another
generation so that the characteristic of the species and the number of chromosome can be
maintained. "ny changes regarding the number of chromosome will effect the healthy growth
(syndrome)
1ach species has different number of chromosomes diploid.
5%*%* De!inition o! $eiosis
*eiosis is the process of nuclear diision that reduces the number of chromosomes in new
cells to half the number of chromosomes in the parent cell and produce four daughter cell.
&laces where the meiosis occur )
4n the testes (male) @produce sperms and oaries (female) @ produce oum
"nther of flowers @ produce male gamete in pollen and oaries of the flowers @
produce egg cell as oules
5%*%+ The Stages o! $eiosis
*eiosis consist of two separate diisions. %hey are *eiosis 4 and *eiosis 44.
1ach stage include the prophase# metaphase# anaphase and telophase.
Activity 1 Arrange the stages of "eiosis process and e'plain each stage)
12
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
Stages o! $eiosis -rocess%
$nstruction Cut the phases of division cell of "itosis above and paste the appropriate pictures in the
bo' provided in the ne't page in correct order) *'plain +hat happen during each stage in the bo'es
provided)
*etaphase 4
"naphase 44
*etaphase 44
%elophase 44
&rophase 4
Late &rophase 4
"naphase 4
&rophase 44
13
Biology Teaching and Learning
Module
Cell
Division
The Stages o! $eiosis -rocess
$EI6SIS I
7ig(re E8planation
1arly &rophase 4
Late &rophase 4
8hromosomes begin to condense and shorter
Bomologous chromosomes come together to form
bialents through a process called synapsis.
/on7sister chromatids e'change segments of ./" in
a process $nown as crossing oer.
%he points at which segments of chromatids cross
oer are called chiasmata
/ucleolus and nuclear membrane disappear
8entrioles migrate to the opposite poles of the cells
!pindle fibres strate to form.
*atephase 4
%he homologous chromosomes are lined up side by
side on the metaphase plate.
14
Biology Teaching and Learning
Module
Cell
Division
7ig(re E8planation
"naphase 4
Bomologous chromosomes moe to the opposite
poles of the cell.
%elophase 4
8hromosomes arrie at the poles
1ach pole now has haploid daughter nucleus
because it contains only one set of chromosomes.
!pindle fibres disappear
/uclear membrane nucleolus reappears
$EI6SIS II
&rophase 44
/uclear membranes of the daughter cells
disintegrate again.
%he spindle fibres reform in each daughter cell.
15
Biology Teaching and Learning
Module
Cell
Division
7ig(re E8planation
*etaphase 44
8hromosomes are lined up on the metaphase plate
"naphase 44
%he centromeres of the sister chromatids finally
separated and moe towards the opposite poles of
the cell.
%elophase 44
%he nucleoli and nuclear membranes re7form
%he spindle fibres disappear
8yto$inesis occur and four haploid daughter cells are
formed
1ach contain half the number of chromosomes and it
genetically different from the parent diploid cell.
4t will deelop into gametes
1:
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
5%*%, Comparison Bet)een $eiosis I an# $eiosis II
8omplete the table below regarding the similarities and differences between *eiosis 4 and
*eiosis 44.
Stage $eiosis I $elosis II
-rophase
!imilarities )
7 !pindle fibres are formed
7 1nd when chromosomes reach the metaphase plate.
.ifferences )
7 !ynapsis occur
7 8rossing oer occur
$etaphase
!imilarities )
7 8hromosomes are lined up on the metaphase plate
.ifferences )
7 Bomologous
chromosomes are lined up
on the metaphase plate.
.ifferences )
7 8hromosomes are lined up
on the metaphase plate.
Anaphase !imilarities )
7 8hromosomes / chromatids moe to the opposite poles started
with the centromere
.ifference
7 &aired homologous
chromosomes separate
and moe to the opposite
poles.
7 /o separation of
centromere
.ifference
7 !eparation of chromatids
7 Bae separation of
centromere
Telophase !imilarities
7 /uclear membrane appear
.ifference
7 %he chromosomes of
daughter cell are double
heli' bond
7 %wo daughter cells are
formed
.ifference )
7 %he chromosomes of
daughter cell are single
heli' bond
7 -our daughter cells are
formed
1;
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
5.2.5 Comparison Bet)een $itosis an# $eiosis
7 +ccur in * phase in cell cycle
7 %he diision inoled nucleus and cytoplsm
-or growth# maintenance
and repair of body tissue
!omatic cell
/o cross oer
.augther cells are
genetically identical to
the parent
2
!ynapsis occur
Bas same number of
chromosomes as the
parent cell (diploid)
Bas half the number of
chromosomes of the
parent cell (haploid)
!ynapsis occur
4
.augther cells are
genetically non7identical
to the parent cell
8ross oer occur
&roduce gamete
6eproductie organ
Similarities
Di!!erences
-lace occ(r
The role o! cell #ivision
Crossing over happen or
not 9
:enetic composition o!
#a(gther cells
N(m3er o! #a(gther cell
S'napsis o! homologo(s
chromosomes
N(m3er o! chromosomes
in #a(gther cells
1=
Biology Teaching and Learning Module
Cell Division
5%*%1 The movement o! Chromosomes #(ring $itosis an# $eiosis
a) >hy the moement of chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis should be regulated in
a precise mannerC
1. *eiosis @ to ensure gametes are haploid and each gametes genetically different
from each other
2. *itosis @ to ensure daughter cells has the same number of chromosomes as the
parent cell.
b) %here are many substances which can interrupt the moement of chromosomes during
mitosis and meiosis. /ame the substances and the effect of the process
!ubstances which can interrupt the moement of chromosomes
1. 6adioactie rays
2. D rays
3. EF rays
4. 8arcinogens
"ffect
1. 8ause gene mutation @ cancer
2. homologous chromosomes fail to separate @ produce abnormal chromosomes
c) Bow can we aoid the interruption of moement of chromosomes during mitosis and
meiosis.
1. Bealthy way of life @ not smo$ing
2. Bae a balanced diet
3. &ractise healthy social actiities
4. aoid e'posure to carcinogenic substances
1?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- 3.2 The Principles and Mechanism of InheritanceDocument6 pagini3.2 The Principles and Mechanism of InheritanceajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measured Drawing ReportDocument6 paginiMeasured Drawing ReportEvon LowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fish Vegetable Siomai Doooooneeeee Version EditedDocument35 paginiFish Vegetable Siomai Doooooneeeee Version EditedLoyd Dyrus100% (4)
- Chapter 4 (Teacher)Document19 paginiChapter 4 (Teacher)ajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Human ExcretionDocument26 paginiChapter 3 - Human ExcretionajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Transport System in HumansDocument54 paginiChapter 2 - Transport System in HumansajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Human Breathing MechanismDocument24 paginiChapter 1 - Human Breathing MechanismajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry STPM Sem 3 MSAB Pre Trial Answer PDFDocument2 paginiChemistry STPM Sem 3 MSAB Pre Trial Answer PDFajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 (Teacher)Document32 paginiChapter 6 (Teacher)ajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 12661391789916231 PDFDocument34 pagini5 12661391789916231 PDFkingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.3 Analysing Concentration of Acids and Alkalis: How Do You Prepare A Copper Sulfate Solution? Cuso Cuso (Aq) H ODocument12 pagini7.3 Analysing Concentration of Acids and Alkalis: How Do You Prepare A Copper Sulfate Solution? Cuso Cuso (Aq) H OajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElectrochemistryDocument86 paginiElectrochemistryajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.3 Analysing Concentration of Acids and Alkalis: How Do You Prepare A Copper Sulfate Solution? Cuso Cuso (Aq) H ODocument12 pagini7.3 Analysing Concentration of Acids and Alkalis: How Do You Prepare A Copper Sulfate Solution? Cuso Cuso (Aq) H OajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and Bases Are Found in Food, Things That We Use and Can Be Found in Our EnvironmentDocument19 paginiAcids and Bases Are Found in Food, Things That We Use and Can Be Found in Our EnvironmentajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and Bases (Topic 7) : Designed, Prepared and Edited By: Chemistry Unit Mara Junior Science College Jasin Sept 2005Document13 paginiAcids and Bases (Topic 7) : Designed, Prepared and Edited By: Chemistry Unit Mara Junior Science College Jasin Sept 2005ajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElectrochemistryDocument86 paginiElectrochemistryajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction Oxidising Agent Reducing AgentDocument4 paginiReaction Oxidising Agent Reducing AgentajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Look at This Picture: Man or Woman Cannot Stay Alone To Form The Stability.Document44 paginiLook at This Picture: Man or Woman Cannot Stay Alone To Form The Stability.ajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Matter 1. Diagram 1 Shows Pictures ofDocument17 paginiChapter 3 - Matter 1. Diagram 1 Shows Pictures ofRozaini Othman100% (15)
- Form 1 Chapter 7 HeatDocument12 paginiForm 1 Chapter 7 HeatajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topical Test 8: Salts: Ujian Topikal 8: GaramDocument9 paginiTopical Test 8: Salts: Ujian Topikal 8: GaramajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1&2Document4 paginiWeek 1&2ajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 1 Chapter 2Document7 paginiForm 1 Chapter 2ajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElectrolysisDocument14 paginiElectrolysisajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre TestDocument2 paginiPre TestajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topical Test 9: Manufactured Substances in Industry: Ujian Topikal 9: Bahan-Bahan Dalam IndustriDocument7 paginiTopical Test 9: Manufactured Substances in Industry: Ujian Topikal 9: Bahan-Bahan Dalam IndustriajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topical Test 5: Chemical Bonds: Ujian Topikal 5: Ikatan KimiaDocument7 paginiTopical Test 5: Chemical Bonds: Ujian Topikal 5: Ikatan KimiaajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Itchemf4topicaltest2bl 121017213209 Phpapp02Document8 paginiItchemf4topicaltest2bl 121017213209 Phpapp02Sharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- Itchemf4topicaltest6bl 121017214639 Phpapp02Document10 paginiItchemf4topicaltest6bl 121017214639 Phpapp02ajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topical Test 7: Acids and Bases: Ujian Topikal 7: Asid Dan BesDocument8 paginiTopical Test 7: Acids and Bases: Ujian Topikal 7: Asid Dan BesajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Itchemf4topicaltest3bl 121017213243 Phpapp02Document6 paginiItchemf4topicaltest3bl 121017213243 Phpapp02ajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 (Teacher)Document24 paginiChapter 9 (Teacher)ajakazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Plants That Dye Hair PDFDocument23 paginiChapter 5 Plants That Dye Hair PDFJoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TINDUKADocument7 paginiTINDUKAShantu ShirurmathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas B, Inggris, Varietas Tanaman Kacang Tanah (Makalah)Document8 paginiTugas B, Inggris, Varietas Tanaman Kacang Tanah (Makalah)aldi al iqsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bean Productions Problems of Phaseolus VulgarisDocument415 paginiBean Productions Problems of Phaseolus Vulgarisherodo100% (3)
- Aditya M Pattewar Et Al 2012Document7 paginiAditya M Pattewar Et Al 2012jsrajoyd_224488661Încă nu există evaluări
- Bescherelle Book SmallDocument175 paginiBescherelle Book Smallnedux100% (3)
- Summit Catalog NoPrc Aug2017 SDocument130 paginiSummit Catalog NoPrc Aug2017 S1 Stop100% (1)
- Utilization of Discarded Onion Skin Into DyeDocument17 paginiUtilization of Discarded Onion Skin Into DyeMarco Barberan73% (11)
- MangoDocument55 paginiMangoMomina UlangkayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Singh 2015Document7 paginiSingh 2015khadijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProGreen Ag - Lawn & GardenDocument16 paginiProGreen Ag - Lawn & GardenProGreenAgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Lesson 2: Plant Defense Responses: BiologyDocument7 paginiChapter 3 - Lesson 2: Plant Defense Responses: BiologyIvimina Jack DinglasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tailam UsesDocument168 paginiTailam UsesHiramandalam PatanjaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Problem: Goose Grass or EI (Paragis), Generally Considered An Adventitious Species, IsDocument16 paginiThe Problem: Goose Grass or EI (Paragis), Generally Considered An Adventitious Species, IsTata Duero LachicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 PDFDocument172 pagini12 PDFAlfaraby100% (2)
- Foods High in Uric AcidDocument12 paginiFoods High in Uric AcidAndrelyn Macadaeg100% (1)
- Biodiversity of Plantae and Animalia (Sbu1023)Document15 paginiBiodiversity of Plantae and Animalia (Sbu1023)Arvind RaveeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Task 8Document6 paginiPerformance Task 8Aj MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 Inhibitory Activities of Indonesian Medicinal PlantsDocument7 paginiCYP3A4 and CYP2D6 Inhibitory Activities of Indonesian Medicinal PlantsMahira Ulfa100% (1)
- Ayurvastra Application in The Herbal TextilesDocument10 paginiAyurvastra Application in The Herbal TextilesSunil TalekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contagion Novalis by David KrellDocument330 paginiContagion Novalis by David KrellSimon OliaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 281 Practical RecordDocument97 pagini281 Practical RecordDr.Eswara Reddy SiddareddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Columbian Exchange ArticleDocument7 paginiThe Columbian Exchange Articleapi-294034727Încă nu există evaluări
- Athena Holiday Catalog I I I 2016Document84 paginiAthena Holiday Catalog I I I 2016Jennie WattersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicinal Plants and Their Traditional Uses in Kabylia Tizi Ouzou AlgeriaDocument16 paginiMedicinal Plants and Their Traditional Uses in Kabylia Tizi Ouzou Algeriakamy-gÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phytochemical Analysis of Tamarix Ericoides Rotti (Tamaricaceae) - A Medicinally Important Plant of West Vidarbha RegionDocument3 paginiPhytochemical Analysis of Tamarix Ericoides Rotti (Tamaricaceae) - A Medicinally Important Plant of West Vidarbha RegionthesijÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crop Watch Growth SummaryDocument1 paginăCrop Watch Growth SummaryHooky1979Încă nu există evaluări
- De 1700 Sinergias EsencialesDocument260 paginiDe 1700 Sinergias EsencialesCurso ExÎncă nu există evaluări