Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
$R4L3P8W
Încărcat de
lightknow0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
22 vizualizări4 paginitimes 100
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documenttimes 100
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
22 vizualizări4 pagini$R4L3P8W
Încărcat de
lightknowtimes 100
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 4
01_Introduction
Suppose you wanted to start a business. What would you need?
First, you would have to decide what products your business would
offer. This decision would influence your view on what premises
(or land) you needed, the kind of machinery required and the type
of labour to be employed. In addition, you would need to find the
money (capital) to pay for setting up all these things.
Factors of Production
Above all, however, you would need organisational skills. In
business terms an ability to organise, together with a willingness to
take risks in pursuit of financial returns, is called enterprise.
Some would consider enterprise to be the most important of the
four factors of production, as poorly run businesses rarely
survive for long.
Land Securities has been at the forefront of the UK commercial
property investment and development industry for over 60 years. It is
a business that combines the factors of production to create returns
for its shareholders. It manages property and generates rental income.
It remains market leader by providing commercial
accommodation and property services to more than 2,000 customers.
Land Securities develops large scale building projects such as
office blocks and retail centres. It then rents out the premises,
providing all the services that tenants require. Land Securities does
not actually build properties itself; but contracts out the building
work to other businesses. It does, however, provide the enterprise
and bears the risk of a development not succeeding.
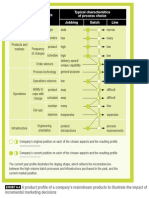
Com bining fact or s of pr oduct ion t o achieve gr owt h object ives
Product
or
Service
Capital
Enterprise
Land
Labour
02_Enterprise and risk
Enterprise refers to all the organisational skills that go into creating a
product or service. It also includes a willingness and ability to take
risks in order to gain rewards and to think up new products or services.
Land Securities manages its risks by making sure it has a balanced
portfolio. The portfolio will contain some developments that carry a
substantial element of risk but which, if successful, will bring high
returns. It will also contain lower risk activities, which ensure a steady
income stream. Land Securities has a well-established risk
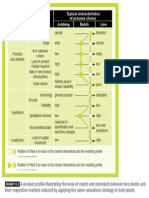
management strategy that follows the six steps shown in the diagram.
Risk Management at Land Securities
1. Identify the business goals and objectives (the reasons why
risks are taken).
2. Identify the risks.
3. Measure the level of risk.
4. Develop action plans to manage the risks.
5. Assess the risks again after they have been managed.
6. Report at each stage.
This company combines this strategy with innovation thinking
up new products and services to meet clients needs. Examples of
these include:
Property outsourcing Land Securities Trillium is the market
leader here.
Additional client services e.g. building maintenance, cleaning,
reception and security.
Landflex - this enables clients to change the size of their
accommodation over time and to have flexible leases on property.
In addition to thinking up new lines of business, Land Securities
must monitor its ongoing activities. It constantly checks its
portfolio of properties and projects to ensure that they are
producing the best possible returns. This involves carefully
managing the other three factors of production.
03_Land and labour
Land in economic and business terms includes earth, sea and sky
and all the natural resources within them. Like nearly all economic
resources, land is scarce there is less of it available than people
want to use, therefore people must pay to own or use it. When
firms use land efficiently, the land rises in value. Land Securities
often puts land to new uses. If the buildings already on it are no
longer serviceable, the company will demolish them and redevelop
the site. If, however, the buildings still have potential, Land
Securities will save resources by refurbishing them.
Taking care of the environment is a big issue in the case of land
use. Land Securities is careful to manage resources sensitively. It
recycles rubble from old buildings into new projects, such as
Heathrows new Terminal 5, which was built using recycled
aggregate. It also works with subcontractors to ensure that
buildings are as energy efficient as possible. Land Securities also
develops brownfieldsites e.g. the Kent Thameside Development
of mixed housing and commercial property. The company seeks to
minimise the effects its suppliers have on the environment. In
particular the Group is looking at all of its sources of paper and
timber. As part of its Land Securities Trillium ISO14001
Environmental Certification, it checks all of its potential suppliers
policies on health, safety and the environment to ensure that its
environmental footprint is as small as possible.
Cur r ent and Pr evi ous Case St udi es
Downl oads Qui zzes Company I nf o Theor y
Investment Portfoilio 31 March 2004 (billion)
Retail
3.20
Retail
Warehouse
1.30
London
Offices
3.00
Industrial
Premises
0.40
1. Goals &
Objectives
2. Identify
6. Report
4. Action
3. Assess 5. Reassess
Labour is the work done by an economys workforce. Different
people do different jobs requiring different skills and attributes.
Labour, therefore, does not just mean physical effort. It refers to all
work done, whether by hand or brain. Land Securities employs
nearly 2,000 people across the UK. They are responsible for the
management of the property portfolio. They also look after the
development and delivery of all the business property services.
The company believes that employees performance, and their
contribution to achieving business objectives, should be rewarded
appropriately. With this in mind it uses pay, incentives and benefits
to help motivate its staff.
The business communicates openly with employees, so that
management and employees can easily exchange ideas or solve
problems. Communication includes:
an intranet that regularly updates employees
regular presentations on business activities and future plans
management and staff away days
email updates
various magazines, both on paper and online, including a
monthly environmental newsletter.
Land Securities also encourages staff to suggest ideas that might
bring benefits to the company. It rewards them for original ideas
that prove capable of being put into practice.
The Group looks to recruit and develop the best people for its
various business roles. It also offers them ongoing comprehensive
training programmes. It sets targets for internal promotion and
constantly monitors staff to ensure that people maximise their
career opportunities. It runs a Values into Action award
programme, which rewards employees for demonstrating in the
workplace the companys core values. These are:
integrity
respect for the individual
customer service
excellence
innovation.
The company also encourages its employees to be involved in
community activities in the areas where they are based. This helps
to build good working relationships between the company and
local communities.
04_Workplace legislation
Labour is an important factor of production and managing labour
effectively involves understanding workplace legislation.
Land Securities looks to comply with all laws relating to the
workplace. These include ensuring that nobody is harassed or
treated differently because of their age, race, colour, disability,
creed, religion, or sexual orientation. The legislation that Land
Securities must follow includes:
Health and Safety at Work Act. Both employers and
employees have a duty to work in as safe and healthy a way as
possible. Some responsibilities rest with the employer e.g. to
provide a safe working environment. Others lie with the
employee e.g. not to act in any way that will endanger
him/herself or any other worker.
Equal Pay Act. Men and women should receive equal pay for
equal work. If a woman is doing the same work as a man, she
should receive the same financial reward. This applies even if a
womans job has a different title, provided she is doing the same
work.
Sex Discrimination Act. This extended the law to include
such matters as recruitment, training, and promotion
opportunities. Employers may not discriminate on grounds of an
employees or applicants gender. The government set up the
Equal Opportunities Commission to enforce the Act.
Race Relations Act. This made it illegal to discriminate
between people on the grounds of race, colour, marital status,
nationality or ethnic group. It also set up the Race Relations
Board to investigate complaints. The Act applies to all aspects of
employment including job advertisements, recruitment processes
such as interviews, and training and promotion opportunities.
Disability Discrimination Act.Employers with 20 or more staff
must not discriminate against applicants or employees on grounds
of disability, providing that the applicant is capable of doing the job.
05_Capital
In the context of factors of production, capital refers to the
buildings, machinery, equipment (including vehicles) and tools
that businesses use to create goods and services. In this context,
capital does not mean money but means the real assets that
businesses purchase or hire, using money. Land Securities operates
in the property market, where capital is a key factor of production.
The companys 2,000 employees manage a portfolio of investment
assets worth around 8 billion.
Businesses like Land Securities have to borrow large amounts of
money because their activities depend so heavily on physical
capital. This borrowing brings them responsibilities to the people
or institutions who have helped to finance them through bank
loans, bond sales and share issues. Land Securities is a public
limited company so it has shareholders who expect a return on
their investment. Land Securities three divisions compete to see
which can generate the best financial performance.
The companys three main divisions are:
Central London- Its 8.9 billion investment portfolio includes
more than 810,000 m
2
of office space in London and substantial
retail holdings in Oxford Street and Tottenham Court Road. The
main driver is to recycle capital in a cyclical market, for example
the selective acquisition of properties with active management
opportunities rather than simple asset accumulation.
Retail - The Group owns 18 shopping centres and 25 retail parks
located across the UK and its vision is to acquire or develop long-
term assets. Land Securities has been selling high street retail, to
enable it to drive higher returns through the active management of
larger assets.
Property Outsourcing - This division manages properties on
behalf of the clients who own them. It offers a complete buildings
management and support service. This leaves the businesses who
occupy the buildings to concentrate on what they are good at. They
no longer have to deal with day-to-day problems such as caretaking,
cleaning and buildings maintenance. Clients for this service include
government departments, the BBC and BT.
In addition to this Land Securities have an Urban Community
Development division, which is overseeing and master planning
one of Europe's largest regeneration schemes in Kent Thameside.
In such a capital-intensivebusiness, the company has to ensure
that it is managing risk and also working to achieve the best returns
for all of its stakeholder groups.
06_Conclusion
Land Securities stated aim is to create sustainable shareholder
returns through good financial management. This relies on careful
management of all four factors of production. Land, Labour and
Capital are all important, but Enterprise is arguably the most
important of all. With its sound organisational and entrepreneurial
skills, Land Securities continues to be the market leader in the UK
property market.
Cur r ent and Pr evi ous Case St udi es
Downl oads Qui zzes Company I nf o Theor y
Glossary
Away days: Training or other opportunities offered away
from the workplace e.g. at a hotel or conference centre.
Brownfield site: Development sites that have been built on
previously. These contrast with greenfield sites, which have
only been used for agriculture and never been built on.
Capital: The physical things necessary for production e.g.
buildings, machines, vehicles, equipment, tools.
Capital-intensive: Using a high proportion of buildings,
machinery, equipment, tools to produce a good or service.
Enterprise: The organisational and risk-taking skills
necessary for a business to continue to exist.
Environmental footprint: The effect a business or
operation has on the environment. Responsible businesses
will try to leave as small an environmental footprint as
possible e.g. by recycling or other good environmental
practice.
Factors of production: The four resources, or inputs,
necessary for the production of a good or service. Land,
Labour, Capital and Enterprise.
Intranet: An internally focused website created on a linked
computer system.
ISO140001: The international standard for good
environmental business practice.
Labour:Human effort, in whatever form.
Land:The worlds natural resources.
Market leader: The business with the largest share of a
particular market.
Portfolio: A collection of investments eg buildings available
for let.
Stakeholder: Any person or group with an interest in a
business. This will include customers, suppliers,
owners/shareholders, directors, employees, communities,
government.
T
h
e
T
i
m
e
s
N
e
w
s
p
a
p
e
r
L
i
m
i
t
e
d
a
n
d
M
B
A
P
u
b
l
i
s
h
i
n
g
L
t
d
2
0
0
5
.
W
h
i
l
s
t
e
v
e
r
y
e
f
f
o
r
t
h
a
s
b
e
e
n
m
a
d
e
t
o
e
n
s
u
r
e
a
c
c
u
r
a
c
y
o
f
i
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
,
n
e
i
t
h
e
r
t
h
e
p
u
b
l
i
s
h
e
r
n
o
r
t
h
e
c
l
i
e
n
t
c
a
n
b
e
h
e
l
d
r
e
s
p
o
n
s
i
b
l
e
f
o
r
e
r
r
o
r
s
o
f
o
m
i
s
s
i
o
n
o
r
c
o
m
m
i
s
s
i
o
n
.
Fo r m o r e i n f o r m a t i o n a b o u t La n d Secu r i t i es
p l ea se b r ow se:
www. landsecur it ies. com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Emphasis On Predictive Costing and Budgeting: 70 A Management Accounting Framework: A TaxonomyDocument1 paginăEmphasis On Predictive Costing and Budgeting: 70 A Management Accounting Framework: A TaxonomylightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- QCH 3Document2 paginiQCH 3lightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- BA 3352: Intro - Strategy QuestionsDocument2 paginiBA 3352: Intro - Strategy QuestionslightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timothy W. Bothell, PH.D.: T P M SDocument1 paginăTimothy W. Bothell, PH.D.: T P M SlightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- BA 3352: Capacity - Layout QuestionsDocument2 paginiBA 3352: Capacity - Layout QuestionslightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- BA3352: Midterm On 29 October 2002 - VERSION BDocument10 paginiBA3352: Midterm On 29 October 2002 - VERSION BlightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Positioning Problems: Colt 45 Malt LiquorDocument2 paginiPositioning Problems: Colt 45 Malt LiquorlightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Figure 7.2 Environment and ResultsDocument1 paginăFigure 7.2 Environment and ResultslightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Example: Tage Ypical EsultsDocument1 paginăCase Study Example: Tage Ypical EsultslightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSR-USA Vs EUDocument5 paginiCSR-USA Vs EUlightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- In Pursuit of A Panacea: Which Three-Letter Acronym Next?: Exhibit 7.1Document1 paginăIn Pursuit of A Panacea: Which Three-Letter Acronym Next?: Exhibit 7.1lightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- $RQC36X2Document12 pagini$RQC36X2lightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- $R8NTTSJDocument1 pagină$R8NTTSJlightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- $R1S589WDocument1 pagină$R1S589WlightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Testing: H M S KDocument1 paginăPerformance Testing: H M S KlightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rearrange Infrastructure: Methodology: The Six StepsDocument1 paginăRearrange Infrastructure: Methodology: The Six StepslightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sales Force Automation Technology: Using The Tools of Interactivity To Build Learning RelationshipsDocument1 paginăSales Force Automation Technology: Using The Tools of Interactivity To Build Learning RelationshipslightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organizing For A Networked, B2B Future: Defining What It Means To Manage TechnologyDocument1 paginăOrganizing For A Networked, B2B Future: Defining What It Means To Manage TechnologylightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Making A Virtual Organization Work: Reprinted From Focus No. 21, Zurich Insurance GroupDocument6 paginiMaking A Virtual Organization Work: Reprinted From Focus No. 21, Zurich Insurance GrouplightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Focusing Operations Around Resources or MarketsDocument1 paginăFocusing Operations Around Resources or MarketslightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exhibit8.1Document1 paginăExhibit8.1lightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tender Document of Internal Control Proc 2007Document21 paginiTender Document of Internal Control Proc 2007lightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exhibit6.1Document1 paginăExhibit6.1lightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exhibit6.4Document1 paginăExhibit6.4lightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exhibit6.5Document1 paginăExhibit6.5lightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exhibit6.3Document1 paginăExhibit6.3lightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exhibit6.2Document1 paginăExhibit6.2lightknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- SHS11Q4DLP 21st CentFinalDocument33 paginiSHS11Q4DLP 21st CentFinalNOEMI DE CASTROÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdverbsDocument10 paginiAdverbsKarina Ponce RiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide To Effective Project ManagementDocument102 paginiA Guide To Effective Project ManagementThanveerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Conditional Sentences YanneDocument3 paginiTugas Conditional Sentences Yanneyanne nurmalitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1stQ Week5Document3 pagini1stQ Week5Jesse QuingaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Chemistry Ramakrishna Mission V. C. College, RaharaDocument16 paginiDepartment of Chemistry Ramakrishna Mission V. C. College, RaharaSubhro ChatterjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DND Homebrew Ideas V1 - The HomebreweryDocument3 paginiDND Homebrew Ideas V1 - The HomebreweryKalazans CardialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process of CounsellingDocument15 paginiProcess of CounsellingSamuel Njenga100% (1)
- The Role of Mahatma Gandhi in The Freedom Movement of IndiaDocument11 paginiThe Role of Mahatma Gandhi in The Freedom Movement of IndiaSwathi Prasad100% (6)
- Quarter 3 Week 6Document4 paginiQuarter 3 Week 6Ivy Joy San PedroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Translation TerminologyDocument7 paginiBasic Translation TerminologyHeidy BarrientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1E Star Trek Customizable Card Game - 6 First Contact Rule SupplementDocument11 pagini1E Star Trek Customizable Card Game - 6 First Contact Rule Supplementmrtibbles100% (1)
- Approved Chemical ListDocument2 paginiApproved Chemical ListSyed Mansur Alyahya100% (1)
- Del Monte Usa Vs CaDocument3 paginiDel Monte Usa Vs CaChe Poblete CardenasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZKAccess3.5 Security System User Manual V3.0 PDFDocument97 paginiZKAccess3.5 Security System User Manual V3.0 PDFJean Marie Vianney Uwizeye100% (2)
- FJ&GJ SMDocument30 paginiFJ&GJ SMSAJAHAN MOLLAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Thinking PDFDocument7 paginiDesign Thinking PDFFernan SantosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daud Kamal and Taufiq Rafaqat PoemsDocument9 paginiDaud Kamal and Taufiq Rafaqat PoemsFatima Ismaeel33% (3)
- Motion To Strike BasedDocument16 paginiMotion To Strike BasedForeclosure Fraud100% (1)
- Hombres Mujeres Cmo Salir Del Camino Equivocado Spanish Edition by Badinter Lisabeth 950557584xDocument5 paginiHombres Mujeres Cmo Salir Del Camino Equivocado Spanish Edition by Badinter Lisabeth 950557584xFernanda Avilés CartagenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contents Serbo-Croatian GrammarDocument2 paginiContents Serbo-Croatian GrammarLeo VasilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sino-Japanese Haikai PDFDocument240 paginiSino-Japanese Haikai PDFAlina Diana BratosinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reith 2020 Lecture 1 TranscriptDocument16 paginiReith 2020 Lecture 1 TranscriptHuy BuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletan Problems in Soccer PlayersDocument5 paginiMusculoskeletan Problems in Soccer PlayersAlexandru ChivaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edc Quiz 2Document2 paginiEdc Quiz 2Tilottama DeoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creative Nonfiction 2 For Humss 12 Creative Nonfiction 2 For Humss 12Document55 paginiCreative Nonfiction 2 For Humss 12 Creative Nonfiction 2 For Humss 12QUINTOS, JOVINCE U. G-12 HUMSS A GROUP 8Încă nu există evaluări
- AASW Code of Ethics-2004Document36 paginiAASW Code of Ethics-2004Steven TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infusion Site Selection and Infusion Set ChangeDocument8 paginiInfusion Site Selection and Infusion Set ChangegaridanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Policarpio Vs Manila Times - Unprotected Speech LibelDocument3 paginiPolicarpio Vs Manila Times - Unprotected Speech LibelStef BernardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term-2 - Grade 8 Science (Biology) Mock Paper-2Document3 paginiTerm-2 - Grade 8 Science (Biology) Mock Paper-2bhagat100% (1)