Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Laminar Boundary Layer
Încărcat de
KvvPrasadDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Laminar Boundary Layer
Încărcat de
KvvPrasadDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Laminar Boundary layer
Unit#2
(Ref 8.6.2, 8.6.3 Potter)
Boundary layer
Types of boundary layer
- At Re
x
< Re
cr
Laminar layer
- At Re
x
> Re
cr
Turbulent layer
Critical Reynolds number, Re
cr
= 500,000
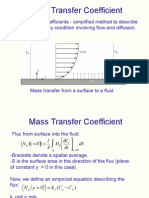
Boundary layer properties is found by either
1. Rigorous solution of Navier Stokes equation or (Blasius)
or
2. Simple Von Karman momentum integral method
Von Karman Integral Method.
It is valid for both laminar and turbulent flow
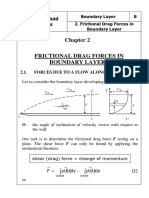
Von Karman Integral Equation for
Force balance on fluid element from previous page
gives the Momentum eqn. in flow direction when dP/dx
=0
Mass balance gives
Neglecting pressure gradient
where is the momentum thickness
[ ]
=
= + + + + +
0 0
2
0
0
) (
) )( ( )
2
(
x U udydx
x
dydx u
x
dx dp
M M M dx d dp p d
dp
p p
top in out
Ud dydx u
x
m m m
in out top
=
= =
0
= =
dy u U u
d
dy u
d
dy U
d
) (
2
dx dx dx
0 0
0
Laminar velocity profile
Assume laminar profile
u = ay + b y
2
+ cy
3
Use boundary conditions
y=0, u=0; u=U,
(du/dy)= 0 at y =
(d
2
u/dy
2
)= 0 at y = 0
It gives laminar velocity
profile
(2)
3
3
2
1
2
3
y y
U
u
=
Find Boundary layer thickness of
Laminar BL using cubic velocity profile
Substitute velocity profile (2) in Von Karman eqn (1)
From the definition of shear stress
Equating above two one gets
.
dx
d U
dy
y y y y
dx
d
U dy u U u
dx
d
2
0
3
3
3
3
2
0
0
139 . 0
2 2
3
1
2 2
3
) ( =
= =
2
3
0
0
U
dy
du
y
=
=
=
x
x
Re
65 . 4
=
Displacement thickness & skin friction (Appx)
Displacement thickness is defined as
Skin friction on the wall is
found by using value of
From the definition of local skin friction coefficient, C
fx
Average skin friction coefficient
0
*
1 dy
U
u
x
fx
U
C
Re
646 . 0 2
2
0
= =
L
L L
x
fx f
L
dx C
L
C
Re
29 . 1
Re
646 . 0 1 1
0 0
= = =
x
U U
dy
du
y
Re
323 . 0
2
3
2
0
0
= =
=
=
Exact solution of Blasius
Blasius through more rigorous solution of BL eqns.
found values of BL thickness, displacement thickness
& local friction coefficient.
He found average skin friction coefficient for the entire
length L
Use these equations for solving problems. Shear stress
;
Re
664 . 0
;
Re
72 . 1
;
Re
5
*
5 . 0
x
x
x
x
C
x x
= = =
L
f
C
Re
33 . 1
=
Laminar boundary layer
[Douglas p-393]
Oil with a free stream velocity of 3 m/s
flows over a thin plate of 1.25 m wide and 2
m long. Determine the boundary layer
thickness and the shear stress at mid-length
and calculate the total, double sided
resistance of the plate (density 860 kg/m3,
kinematic viscosity 10
-5
m
2
/s)
Problem
The floor of the wind tunnel of a model of French
TGV moves with the speed corresponding to that
of the main flow. This prevents a boundary layer
from building up on the floor as the fluid reaches
the turbo-train and more closely resembles the
actual flow relative to a moving train. Find what
would be boundary layer if floor was not moving.
Air velocity is 6 m/s and train is 2.5 m from the
leading edge. Take viscosity 1.55x10
-5
m
2
/s
Model testing of worlds fastest train
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2De la EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- 101 Basic Guitar Chords PDFDocument12 pagini101 Basic Guitar Chords PDFMahendra Setyo Hadi100% (2)
- 101 Basic Guitar Chords PDFDocument12 pagini101 Basic Guitar Chords PDFMahendra Setyo Hadi100% (2)
- Wave Forces On Vertical CylinderDocument22 paginiWave Forces On Vertical CylinderInayatul LailiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics Response Spectrum AnalysisDocument33 paginiDynamics Response Spectrum AnalysisAhmed Gad100% (1)
- Rhodes Solutions Chapter 2Document16 paginiRhodes Solutions Chapter 2niquee9ner78% (9)
- Chapter 3 Flows Around Submerged BodiesDocument65 paginiChapter 3 Flows Around Submerged BodiesPrya Suthan Sathiananthan100% (2)
- Mecanica de Fluidos SolucionarioDocument27 paginiMecanica de Fluidos SolucionarioFrankcTecsiSenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canal DesignDocument26 paginiCanal Designnibas999100% (3)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresDe la EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterDe la EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerodynamics 2 MEC 3706 Exercise Sheet 2 and SolutionDocument18 paginiAerodynamics 2 MEC 3706 Exercise Sheet 2 and SolutionJarvis AsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chen 2610 Faculty CH 7 ADocument17 paginiChen 2610 Faculty CH 7 ASwamy RakeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics II: B.S. Mechanical Engineering 4 SemesterDocument80 paginiFluid Mechanics II: B.S. Mechanical Engineering 4 Semesternaeema_58Încă nu există evaluări
- CL464 Midsem Exam - SolutionDocument4 paginiCL464 Midsem Exam - SolutionAkash Pavan100% (1)
- Boundary Layer Theory - P2Document19 paginiBoundary Layer Theory - P2alphascribeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1Document2 paginiTutorial 1Amal J AdhikaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics II (Chapter 2)Document16 paginiFluid Mechanics II (Chapter 2)Shariff Mohamad FairuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics Tutorial 11-Damped Vibrations-13p PDFDocument13 paginiDynamics Tutorial 11-Damped Vibrations-13p PDFmanfredm6435100% (1)
- Boundary LayerDocument16 paginiBoundary LayerSatyanand ErankiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction IntroDocument13 paginiFriction IntroblozzerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 Example ProblemsDocument4 paginiModule 3 Example ProblemsMark Kevin EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment BL 1Document2 paginiAssignment BL 1RAHUL KUMAR JHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mmems 2 UDocument163 paginiMmems 2 UHardeshkumar KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice QuesDocument6 paginiPractice QuesAndyÎncă nu există evaluări
- P2Document55 paginiP2Abdulla BaderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prestress Concrete (24-30)Document33 paginiPrestress Concrete (24-30)Prantik Adhar SamantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extra WEAR SolutionsDocument7 paginiExtra WEAR SolutionsGiannis MamalakisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Power Fluid B 2011 Final With Model AnsweDocument7 pagini2nd Power Fluid B 2011 Final With Model AnsweS.A. BeskalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prediction of Unsteady Lifts of Oscillating Rectangular Cylinder at Low Reduced Velocities by Large Eddy SimulationDocument13 paginiPrediction of Unsteady Lifts of Oscillating Rectangular Cylinder at Low Reduced Velocities by Large Eddy Simulationebrahem khalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boundary LayerDocument24 paginiBoundary Layerstephaniet0514Încă nu există evaluări
- Mel242 30Document30 paginiMel242 30hmudassir_1Încă nu există evaluări
- Solution: D 883 - 8 2 D 2 B PDocument4 paginiSolution: D 883 - 8 2 D 2 B PIsmail A Ismail100% (2)
- Lectures For ES912, Term 1, 2003.: December 7, 2003Document18 paginiLectures For ES912, Term 1, 2003.: December 7, 2003getsweetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Example of CH-3Document13 paginiSolved Example of CH-3Abubeker AreboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation ProblemsDocument4 paginiPresentation ProblemspangiastikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bounadary Layer TheoryDocument58 paginiBounadary Layer TheorySukrit NarulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NS EquationDocument81 paginiNS EquationRitik ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue of MaterialsDocument40 paginiFatigue of MaterialsnitinÎncă nu există evaluări
- AgainDocument5 paginiAgainComputer Maintainance Hardware and softwareÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 2135E - Fluid Mechanics II - Take Home Test: Time Allocated: 2 Hours To 2 Hours and 30 MinutesDocument5 paginiME 2135E - Fluid Mechanics II - Take Home Test: Time Allocated: 2 Hours To 2 Hours and 30 Minutesrayni46100% (1)
- Assignment 6 With Solutions (2) FM WhiteDocument9 paginiAssignment 6 With Solutions (2) FM WhiteabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illustrates Flow Behaviour of Common Fluids: A. B. C. D. Solution - ADocument17 paginiIllustrates Flow Behaviour of Common Fluids: A. B. C. D. Solution - AJaspreet KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diffusion Equation: Environmental Transport and FateDocument15 paginiDiffusion Equation: Environmental Transport and Fatejohndo3Încă nu există evaluări
- Natural Convection LatestDocument38 paginiNatural Convection LatestPradyumna Dhamangaonkar50% (2)
- Afm bl2Document15 paginiAfm bl2Anonymous ncBe0B9bÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics Tutorial No.4 Flow Through Porous PassagesDocument8 paginiFluid Mechanics Tutorial No.4 Flow Through Porous PassagesvinothenergyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 13 Forced Convection Flat Plate SummaryDocument9 paginiLec 13 Forced Convection Flat Plate Summary82ghost82Încă nu există evaluări
- CHE4162 Set 1 Solutions Ch2 Single ParticlesDocument8 paginiCHE4162 Set 1 Solutions Ch2 Single ParticlesHua KhienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Che 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Document7 paginiChe 4009 Transport Phenomena Assignment # 1Bao-Ngoc HoangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation Cap 6 Heat II BWDocument20 paginiPresentation Cap 6 Heat II BWSean Crespo GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch1 IntroductionDocument33 paginiCh1 Introductiongaith syoofÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Boundary Layer Drag Lift Physical Model Tutorial SolutionDocument20 pagini10 Boundary Layer Drag Lift Physical Model Tutorial SolutionVenkitaraj K PÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEEP 541 - Hardening: Fall 2002 Jake BlanchardDocument41 paginiNEEP 541 - Hardening: Fall 2002 Jake BlanchardezekingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- External FlowDocument81 paginiExternal FlowKasumbi ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set AdrianDocument60 paginiProblem Set AdrianTomas Otero IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pamm 1 - 2009Document2 paginiPamm 1 - 2009Tubaguts1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportDe la EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constructed Layered Systems: Measurements and AnalysisDe la EverandConstructed Layered Systems: Measurements and AnalysisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesDe la Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)De la EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Încă nu există evaluări
- ORDERDocument1 paginăORDERClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Booking PDFDocument1 paginăBooking PDFClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plagiarism PickardDocument19 paginiPlagiarism PickardClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Unlock Hidden FilesDocument1 paginăHow To Unlock Hidden FilesClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document5 paginiAssignment 1Clementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- APA In-Text CitationsDocument3 paginiAPA In-Text CitationsAnonymous dTBdAicJh1Încă nu există evaluări
- Logbook SummaryDocument1 paginăLogbook SummaryIzzudin HusseinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academic Calendar 2016Document2 paginiAcademic Calendar 2016Clementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- OrderDocument1 paginăOrderClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Statement: No Debts/Commitment Estimate CostDocument2 paginiFinancial Statement: No Debts/Commitment Estimate CostClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Year Semester 1 TimetableDocument1 paginăFinal Year Semester 1 TimetableClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Statement: Engineering Team Project: Group 25Document1 paginăProblem Statement: Engineering Team Project: Group 25Clementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13 Introduction To Polymer (Edited)Document36 paginiChapter 13 Introduction To Polymer (Edited)Clementz WS100% (1)
- How Boilers WorkDocument18 paginiHow Boilers Workhozipek5599100% (1)
- How To Close PortsDocument1 paginăHow To Close PortsHashir HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00drug AbuseDocument23 pagini00drug AbuseClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- AssignmentDocument1 paginăAssignmentClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- KuiDocument13 paginiKuiClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Change Your Folders Background PDFDocument1 paginăHow To Change Your Folders Background PDFbkchoudhury1993Încă nu există evaluări
- Concept Matrix Template NanotechnologyDocument3 paginiConcept Matrix Template NanotechnologyClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cheating As The Weapon For SuccessDocument3 paginiCheating As The Weapon For SuccessClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Boilers WorkDocument18 paginiHow Boilers Workhozipek5599100% (1)
- External Flows: Dye StreakDocument8 paginiExternal Flows: Dye StreakClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Paper 2 Section A: by Haslinda MidyDocument31 paginiEnglish Paper 2 Section A: by Haslinda MidyClementz WSÎncă nu există evaluări