Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
HSL and HSV
Încărcat de
s_paraisoDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
HSL and HSV
Încărcat de
s_paraisoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
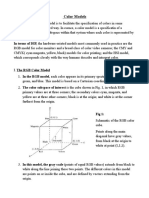
HSL (Hue, Saturation, Lightness)
HSV (Hue, Saturation, Value)
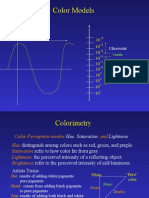
Hue - Variety of any color, caused by approach to or slight
admixture of another
Saturation - colorfulness of a stimulus relative to its own
brightness
Lightness - brightness relative to the brightness of a
similarly illuminated white
Value (Brightness) - attribute of a visual sensation
according to which an area appears to emit more or less light
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
HSL and HSV
- the two most common cylindrical-
coordinate representations of points in
an RGB color model
- developed in the 1970s for computer
graphics applications
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
Their uses include:
- color pickers
- color-modification tools in
image editing software
- less commonly for image analysis and
computer vision
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
Basic principles:
- HSL and HSV are both cylindrical
geometries
- hue, their angular dimension, starting at
the red primary at 0, passing through the green primary at
120 and the blue primary at 240, and then wrapping back
to red at 360
- In each geometry, the central vertical axis comprises
the neutral, achromatic, or gray colors, ranging from black at
lightness 0 or value 0, the bottom, to white at lightness 1 or
value 1, the top
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
Basic Principles:
- In both geometries, the additive primary
and secondary colors red, yellow, green, cyan,
blue, and magenta and linear mixtures between
adjacent pairs of them, sometimes called pure
colors, are arranged around the outside edge of
the cylinder with saturation 1; in HSV these have
value 1 while in HSL they have lightness
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
HSL to RGB:
Given an HSL color with hue H [0, 360), saturation S
HSL
[0, 1], and lightness L [0, 1], we can use the same
strategy. First, we find chroma:
C = (1-|2L-1|) x S
HSL
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
find a point (R
1
, G
1
, B
1
) along the bottom three faces of the
RGB cube, with the same hue and chroma as our color (using
the intermediate value X for the second largest component of
this color):
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
Finally, we can find R, G, and B by adding
the same amount to each component, to
match lightness:
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
HSV to RGB:
- Given a color with hue H [0, 360],
saturation S
HSV
[0, 1], and value V [0, 1], we
first find chroma:
C = V x S
HSV
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
Then we can find a point (R
1
, G
1
, B
1
) along the bottom three
faces of the RGB cube, with the same hue and chroma as our
color (using the intermediate value X for the second largest
component of this color):
HSL and HSV
Color Spaces
Finally, we can find R, G, and B by adding
the same amount to each component, to
match value:
M = V C
(R,G,B) = (R1 + m, G1 + m, B1 + m)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Computer Vision: Spring 2006 15-385,-685 Instructor: S. Narasimhan Wean 5403 T-R 3:00pm - 4:20pmDocument25 paginiComputer Vision: Spring 2006 15-385,-685 Instructor: S. Narasimhan Wean 5403 T-R 3:00pm - 4:20pmshailendrachimadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMC - Chapter 1Document58 paginiCMC - Chapter 1Habete ItfÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Relativity of Color: Josef AlbersDocument9 paginiThe Relativity of Color: Josef AlbersPemburu MusangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color - Color in The Eye: Rods vs. ConesDocument5 paginiColor - Color in The Eye: Rods vs. ConesEdiPánucoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jim Worthey S Locus of Unit Monochromats (Color-Matching)Document11 paginiJim Worthey S Locus of Unit Monochromats (Color-Matching)backvlackoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document86 paginiChapter 2Habete ItfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elcolor LLUM PIGMENT+Història NewtonDocument17 paginiElcolor LLUM PIGMENT+Història NewtonSaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volume and Surface AreaDocument18 paginiVolume and Surface AreaPrabhakar Chowdary ChintalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color AnalysisDocument11 paginiColor AnalysisNirmal BhowmickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hsi - HSL - HSVDocument27 paginiHsi - HSL - HSVspahicdaniloÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSL and HSV - Wikipedia, Th..Document15 paginiHSL and HSV - Wikipedia, Th..ramu.paturi7712Încă nu există evaluări
- Visualization of Complex Functions: Bernd Thaller, University of Graz, Austria SourceDocument23 paginiVisualization of Complex Functions: Bernd Thaller, University of Graz, Austria SourcerobertunpÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCL ColorsDocument12 paginiHCL ColorsSafi BhaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colour Image ProcessingDocument60 paginiColour Image ProcessingkondurukarthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Space: Color Model Colors Tuples RGB Cmyk Absolute Color SpaceDocument20 paginiColor Space: Color Model Colors Tuples RGB Cmyk Absolute Color SpaceDinesh ScorpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Model 1Document20 paginiColor Model 1sharmilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Color Image ProcessingDocument34 paginiChapter 6 Color Image ProcessingGarvit TyagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Image Processing: Prepared by T. Ravi Kumar NaiduDocument60 paginiColor Image Processing: Prepared by T. Ravi Kumar NaiduRavi KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colour (Compatibility Mode)Document30 paginiColour (Compatibility Mode)PradeepvenugopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Map SymbolsDocument15 paginiMap Symbolsgreyproperties88Încă nu există evaluări
- Chap1 2 3Document27 paginiChap1 2 3Hàng Không Mẫu HạmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 8Document73 paginiLect 8Asif FiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Theory: Complementary ColorsDocument2 paginiColor Theory: Complementary ColorsShannara21Încă nu există evaluări
- Q1. Disitinguish Between Random and Raster Scan Display Devices. Ans: Raster ScanDocument4 paginiQ1. Disitinguish Between Random and Raster Scan Display Devices. Ans: Raster ScanahsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Collor IpDocument29 paginiCollor IpMALAKONDA REDDY BOILLAÎncă nu există evaluări
- LightDocument7 paginiLightMegha SahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- RGB (Used in Computer Graphics) Yiq, Yuv or Ycbcr (Used in Video Systems)Document9 paginiRGB (Used in Computer Graphics) Yiq, Yuv or Ycbcr (Used in Video Systems)Mera KaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 15 Colour ModelDocument14 paginiChap 15 Colour ModelShivangi Bansal 204020Încă nu există evaluări
- Color FeatureDocument3 paginiColor Featureart101988Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 8 Color SystemDocument28 paginiLecture 8 Color SystemAbdelRahman MahmoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colour ModelsDocument5 paginiColour ModelsKrishanu Modak100% (1)
- Digital Image Processing, Color ModelsDocument40 paginiDigital Image Processing, Color Modelsk_kunarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Image Processing (EE 4235) Lecture: Color (Part 1)Document23 paginiDigital Image Processing (EE 4235) Lecture: Color (Part 1)Andrew WilcoxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Graphics: Color ModelsDocument35 paginiComputer Graphics: Color Modelsمروة عبدالله محمد علي حبيبانÎncă nu există evaluări
- RGB To HSVDocument2 paginiRGB To HSVnikwplayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color: CSE 320 Graphics ProgrammingDocument34 paginiColor: CSE 320 Graphics ProgrammingIsaac Joel RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV 3Document10 paginiCV 3Bilal KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color ModelsDocument33 paginiColor ModelsAditya PugaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS8092 Computer Graphics and Multimedia Notes WatermarkDocument169 paginiCS8092 Computer Graphics and Multimedia Notes WatermarkRameez NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Theory AdvancedDocument51 paginiColor Theory AdvancedHervis FantiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 Colour Image ProcessingDocument53 paginiChapter 9 Colour Image ProcessingSaikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CGMM 3Document3 paginiCGMM 3nishita patidarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Curves and SurfacesDocument2 paginiLecture Curves and SurfacesHassan .YÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Theory AdvancedDocument51 paginiColor Theory AdvancedThEChArLiE WoRlDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz DIPDocument7 paginiQuiz DIPayesha bashirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color ModelsDocument34 paginiColor ModelsSinduja BaskaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color LectureDocument31 paginiColor LectureM.AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colour Theories & Some ApplicationsDocument51 paginiColour Theories & Some ApplicationsTalha KhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER - 5 FINAL FOR CLASS Color Image ProcessingDocument63 paginiCHAPTER - 5 FINAL FOR CLASS Color Image ProcessingSomeoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Models: UltravioletDocument18 paginiColor Models: UltravioletSyawal Dina SimangunsongÎncă nu există evaluări
- © UW CSE Vision FacultyDocument62 pagini© UW CSE Vision FacultyDuong TheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colouring ModelDocument15 paginiColouring ModelHariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Image ProcessingDocument13 paginiColor Image ProcessingBrijesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSL HSVDocument30 paginiHSL HSVashwaagomaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Good 01 PDFDocument3 paginiGood 01 PDFlegend pereyraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Image Processing: Course WebsiteDocument76 paginiDigital Image Processing: Course WebsiteSmita SangewarÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSI Color SpaceDocument13 paginiHSI Color Spacehuechhoac100% (3)
- Colour TheoryDocument29 paginiColour TheoryHervis FantiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color History TerminologyDocument21 paginiColor History TerminologysefiefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colour Theory PDFDocument37 paginiColour Theory PDFSrinivasa RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CFG PdaDocument68 paginiCFG Pdas_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- C A S U P M: Course Code: CMSC 123 Course Name: Data Structures Credit: Prerequisite: Course DescriptionDocument2 paginiC A S U P M: Course Code: CMSC 123 Course Name: Data Structures Credit: Prerequisite: Course Descriptions_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Models and Color Applications: CMSC 161: Interactive Computer GraphicsDocument25 paginiColor Models and Color Applications: CMSC 161: Interactive Computer Graphicss_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shading Models For Polygonal Objects: CMSC 161: Interactive Computer GraphicsDocument17 paginiShading Models For Polygonal Objects: CMSC 161: Interactive Computer Graphicss_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shading Models For Polygonal Objects: CMSC 161: Interactive Computer GraphicsDocument17 paginiShading Models For Polygonal Objects: CMSC 161: Interactive Computer Graphicss_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 8cDocument29 paginiLecture 8cs_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 8aDocument20 paginiLecture 8as_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distributed Ray TracingDocument22 paginiDistributed Ray Tracings_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visible Surface Determination: CMSC 161: Interactive Computer GraphicsDocument34 paginiVisible Surface Determination: CMSC 161: Interactive Computer Graphicss_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Quest For Visual Realism: CMSC 161: Interactive Computer GraphicsDocument10 paginiThe Quest For Visual Realism: CMSC 161: Interactive Computer Graphicss_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color ModelsDocument15 paginiColor Modelss_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Texture MappingDocument29 paginiTexture Mappings_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- YUVDocument13 paginiYUVs_paraisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure - STAAR Surgical - EVO Visian ICL (Surgeon Brochure) (En)Document12 paginiBrochure - STAAR Surgical - EVO Visian ICL (Surgeon Brochure) (En)Andreea L. MihalceaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensory Dysfunction & AutismDocument15 paginiSensory Dysfunction & AutismDiana DanciuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Image ProcessingDocument49 paginiImage ProcessingJyoti SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pupil Evaluation: Walter Huang, OD Yuanpei University Department of OptometryDocument54 paginiPupil Evaluation: Walter Huang, OD Yuanpei University Department of OptometryRatri Wulandari SusilaningrumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aphakia Vs Contact LensDocument77 paginiAphakia Vs Contact LensSiva LoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 4 Reflex LabDocument3 paginiLesson 4 Reflex LabBritaneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TNBDocument21 paginiTNBAhmad FauziÎncă nu există evaluări
- NetVR Version 1.3 Supported Cameras and EncodersDocument369 paginiNetVR Version 1.3 Supported Cameras and EncodersBraulio Andres Arenas VillavicencioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.7 Visual PathwayDocument70 pagini6.7 Visual Pathwaylovelots1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Anomalous Trichromats: SynonymsDocument4 paginiAnomalous Trichromats: SynonymsFaheem KvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook (Sensory Analysis Workshop)Document103 paginiHandbook (Sensory Analysis Workshop)DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jovs v1 Id1006Document9 paginiJovs v1 Id1006ANIEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Art History - Print - QuizizzDocument3 paginiIntroduction To Art History - Print - QuizizzandieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursery-Faith-Second Periodical ExamDocument17 paginiNursery-Faith-Second Periodical ExamMary Grace FresnediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sense and Sensitivity in Architecture - The Use of Five Senses in Space MakingDocument5 paginiSense and Sensitivity in Architecture - The Use of Five Senses in Space MakingPremier Publishers100% (1)
- Glaucoma Visual Field Testing UpdateDocument8 paginiGlaucoma Visual Field Testing UpdateDrStenÎncă nu există evaluări
- JR - KBR - Scleral Fixation of Single Pieces Foldable IOL Using Double Flanged Technique - Karina AdistiariniDocument23 paginiJR - KBR - Scleral Fixation of Single Pieces Foldable IOL Using Double Flanged Technique - Karina AdistiariniKarina Adistiarini BudijantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- VHIT PAA Oct2017 HillDocument69 paginiVHIT PAA Oct2017 HillDiah Ayu Kusuma DewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Five SensesDocument15 paginiThe Five SensesMy name is傻逼Încă nu există evaluări
- Sensory Processing DisorderDocument6 paginiSensory Processing DisorderScott SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 583 Lecture08Document28 paginiEE 583 Lecture08Nikhil AggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barnett 2011Document7 paginiBarnett 2011Annisa RahayuÎncă nu există evaluări
- RetinaDocument42 paginiRetinaAhmed Omara100% (2)
- BioDocument21 paginiBioShweta katiyarÎncă nu există evaluări
- VT30 Ideal Picture SettingsDocument3 paginiVT30 Ideal Picture SettingsMichael ZengÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Should Every Teacher Know About Visual Impairments?Document10 paginiWhat Should Every Teacher Know About Visual Impairments?asprillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensory Stimulation For Coma PatientsDocument48 paginiSensory Stimulation For Coma PatientsSherry PhippsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychobiology Ch. 6: Vision Lecture NotesDocument23 paginiPsychobiology Ch. 6: Vision Lecture NotesGabriel CardozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cranial NervesDocument65 paginiCranial Nervessarguss14100% (13)
- Refraction by The EyeDocument28 paginiRefraction by The EyeCherry OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări