Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Formula Sheet Geometry
Încărcat de
samuthraraja0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
100 vizualizări2 paginisheet
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentsheet
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
100 vizualizări2 paginiFormula Sheet Geometry
Încărcat de
samuthrarajasheet
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Copyright Regents Exam Prep Center
Geometry Things to Remember!
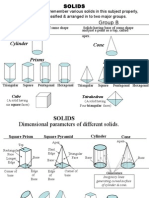
Regular Solids:
Tetrahedron 4 faces
Cube 6 faces
Octahedron 8 faces
Dodecahedron 12 faces
Icosahedron 20 faces
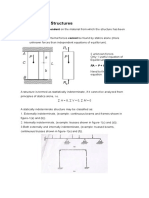
3-D Figures:
Prism: V = Bh
Pyramid:
1
3
V Bh =
Cylinder:
2
V r h = ;
2
2 2 SA r r = +
Cone:
2
1
3
V r h = ;
2
SA s r r = +
Sphere:
3
4
3
V r = ;
2 2
4 SA r d = =
Locus Theorems:
Fixed distance from point.
Fixed distance from a line.
Equidistant from 2 points.
Equidistant 2 parallel lines.
Equidistant from 2
intersecting lines
Polygon Interior/Exterior Angles:
Sum of int. angles = 180( 2) n
Each int. angle (regular) =
180( 2) n
n
Sum of ext. angles = 360
Each ext. angle (regular) =
360
n
Congruent Triangles
SSS
SAS
ASA
AAS
HL (right triangles only)
NO donkey theorem
(SSA or ASS)
CPCTC (use after the triangles are congruent)
Related Conditionals:
Converse: switch if and then
Inverse: negate if and then
Contrapositive: inverse of the converse
(contrapositive has the same truth value
as the original statement)
Triangles:
By Sides:
Scalene no congruent sides
Isosceles 2 congruent sides
Equilateral 3 congruent sides
By Angles:
Acute all acute angles
Right one right angle
Obtuse one obtuse angle
Equiangular 3 congruent angles(60)
Equilateral Equiangular
Exterior angle of a triangle equals the
sum of the 2 non-adjacent interior
angles.
Mid-segment of a triangle is parallel
to the third side and half the length of
the third side.
Inequalities:
--Sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater
than the length of the third side.
--Longest side of a triangle is opposite the largest angle.
--Exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of the
two non-adjacent interior angles.
Pythagorean Theorem:
2 2 2
c a b = +
Converse: If the sides of a triangle
satisfy
2 2 2
c a b = + then the triangle is a
right triangle.
Similar Triangles:
AA
SSS for similarity
SAS for similarity
Corresponding sides of similar
triangles are in proportion.
Mean Proportional in Right Triangle:
Altitude Rule: Leg Rule:
Copyright Regents Exam Prep Center
Parallels: If lines are parallel
Corresponding angles are equal.
m<1=m<5, m<2=m<6, m<3=m<7, m<4=m<8
Alternate Interior angles are equal.
m<3=m<6, m<4=m<5
Alternate Exterior angles are equal.
m<1=m<8, m<2=m<7
Same side interior angles are supp.
m<3+m<5=180, m<4+m<6=180
Quadrilaterals:
Parallelogram: opp
sides parallel
opp sides =
opp angles =
consec. angles supp
diag bis each other
Rectangle: add 4 rt
angles, diag. =
Trapezoid:
Only one set
parallel sides.
Median of trap is
parallel to both
bases and =
sum bases.:
Rhombus: add 4 =
sides, diag. perp, diag
bisect angles.
Square: All from
above.
Isosceles Trap:
legs =
base angles =
diagonals =
opp angles supp
Transformations:
Glide
reflection is
composition
of a reflection
and a
translation.
Isometry
keeps length.
Orientation
label order
Circle Segments
In a circle, a radius perpendicular to a chord
bisects the chord.
Intersecting Chords Rule:
(segment part)(segment part) =
(segment part)(segment part)
Secant-Secant Rule:
(whole secant)(external part) =
(whole secant)(external part)
Secant-Tangent Rule:
(whole secant)(external part) = (tangent)
2
Hat Rule: Two tangents are equal.
Circle Angles:
Central angle = arc Inscribed angle = half arc Angle by tangent/chord = half arc
Angle formed by 2 chords Angle formed by 2 tangents, or 2 secants, or a tangent/secant
= half the sum of arcs = half the difference of arcs
Slopes and Equations:
2 1
2 1
= .
y y vertical change
m
horizontal change x x
1 1
slope-intercept
( ) point-slope
y mx b
y y m x x
= +
=
Coordinate Geometry Formulas:
Distance Formula:
2 2
2 1 2 1
( ) ( ) d x x y y = +
Midpoint Formula:
1 2 1 2
( , ) ,
2 2
x x y y
x y
+ +
=
Circles:
Equation of circle center at origin:
2 2 2
x y r + = where r is the radius.
Equation of circle not at origin:
2 2 2
( ) ( ) x h y k r + = where (h,k) is the
center and r is the radius.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Integral CalculusDocument34 paginiIntegral CalculusMarcelene Justine Dionisio100% (1)
- Geometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes CirclesDocument2 paginiGeometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes Circlesmarko1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Cliff S Notes GeometryDocument2 paginiCliff S Notes GeometryKamal SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formula Sheet GeometryDocument2 paginiFormula Sheet Geometrykssuhasreddy_3743947Încă nu există evaluări
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsDe la EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Angles MeasurementDocument60 paginiAngles Measurementsitaram_akella_1Încă nu există evaluări
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 paginiGeometry and TrigonometryFranc VenturaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extra Exercises - Express and SpecialDocument26 paginiExtra Exercises - Express and Specialdmal88Încă nu există evaluări
- Math (F4) - Straight Line 5.1Document33 paginiMath (F4) - Straight Line 5.1Roszelan MajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pin Vs Fixed Joints in TrussDocument4 paginiPin Vs Fixed Joints in TrussgazzafletchÎncă nu există evaluări
- 425 Serviceability CHP 6 S11Document76 pagini425 Serviceability CHP 6 S11aomareltayeb100% (1)
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 1Document29 paginiMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 1AjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.1 The Geometry of SolidsDocument118 pagini10.1 The Geometry of SolidsCasalta KennethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screw Connections Subject To Tension Pull-Out and Shear ForcesDocument63 paginiScrew Connections Subject To Tension Pull-Out and Shear ForcesSalik TrambooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 Math 13-1Document53 paginiLesson 1 Math 13-1akladffja100% (1)
- Review of Deflections of Structures: Ceng 141Document34 paginiReview of Deflections of Structures: Ceng 141Marcelo AbreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 - 2.3 PDFDocument40 pagini2.1 - 2.3 PDFMuhammad IkhwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Matrix TrussDocument83 pagini05 Matrix TrussSharan BvpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plane & Solid Geometry HandoutDocument14 paginiPlane & Solid Geometry HandoutAngelo Luigi Yasay100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics IV 2020Document17 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics IV 2020FloryVicBarranco100% (9)
- Lecture 2 - Reinforced Concrete - Design of Rectangular BeamDocument44 paginiLecture 2 - Reinforced Concrete - Design of Rectangular BeamChristopher PaladioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7: GEOMETRY: Illustrating PolygonsDocument10 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7: GEOMETRY: Illustrating PolygonsBab Sita100% (1)
- Answ Er Key: Hints & Solutions (Year-2009)Document24 paginiAnsw Er Key: Hints & Solutions (Year-2009)sabhari_ramÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 Matrix FrameDocument72 pagini07 Matrix FrameAminatul Fadillah MarpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 07 PDFDocument16 paginiChapter 07 PDFMohd Aizat NasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper Test - Full: InstructionsDocument18 paginiPaper Test - Full: InstructionsGangadhar BagaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limit State Design of BeamDocument47 paginiLimit State Design of BeamSukhwinder Singh GillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface Area and Volume HandbookDocument3 paginiSurface Area and Volume HandbookOktavianaalf100% (1)
- Shear Forces and Bending Moments in Beams: (Examples)Document13 paginiShear Forces and Bending Moments in Beams: (Examples)Əli KərimovÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATH 9 3rd EXAMDocument13 paginiMATH 9 3rd EXAMNimfa PlazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced RC Week2Document41 paginiAdvanced RC Week2haloÎncă nu există evaluări
- FE Civil CBT Specs With RangesDocument4 paginiFE Civil CBT Specs With RangesSanam AfreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phase Relationships of SoilDocument5 paginiPhase Relationships of Soilmageshm1Încă nu există evaluări
- NM Assignment SolutionDocument146 paginiNM Assignment SolutionBEENAYEK AdHIKARIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defining UBC97 Seismic Analysis in Robot - ExampleDocument5 paginiDefining UBC97 Seismic Analysis in Robot - ExampleSinedpak DufamÎncă nu există evaluări
- tn409 Ps Vibration Ex 053911 PDFDocument6 paginitn409 Ps Vibration Ex 053911 PDFLau Kim HwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions To Fe Exam Review Problems Rev7Document21 paginiSolutions To Fe Exam Review Problems Rev7narjis banoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design For Snow Loading On RoofsDocument4 paginiDesign For Snow Loading On Roofskkozak99Încă nu există evaluări
- Surveying Model QuestionDocument2 paginiSurveying Model QuestionMahesh Kumar K BÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIE 047 - Lesson 1Document56 paginiCIE 047 - Lesson 1Anagen PabecaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2160607-Elementary Structural Design 09012017 040945AMDocument16 pagini2160607-Elementary Structural Design 09012017 040945AMAydinAkhtarpour100% (1)
- Shear CentreDocument2 paginiShear CentrePaulSmile100% (1)
- MCESE 203 Theory of Plates and Shells - Set2Document2 paginiMCESE 203 Theory of Plates and Shells - Set2Tibu ChackoÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Avoid Them: 1) Seismic Design Category ADocument4 paginiHow To Avoid Them: 1) Seismic Design Category ARabindraUpretiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designed and Detailed According To IS 456 As An Ordinary Moment Resisting Frame Also Called Ordinary Concrete FrameDocument3 paginiDesigned and Detailed According To IS 456 As An Ordinary Moment Resisting Frame Also Called Ordinary Concrete FrameAnonymous Gye18jÎncă nu există evaluări
- So You Want To Become A MathematicianDocument11 paginiSo You Want To Become A MathematicianDevontae Bylar100% (1)
- Soil Lab. ManualDocument32 paginiSoil Lab. Manualishaq kazeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trvaerse CairoU Civil Publish TotalDocument43 paginiTrvaerse CairoU Civil Publish TotalMohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes On StaticsDocument121 paginiLecture Notes On StaticsAhmet BenliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cece 4244 - Advanced RC DesignDocument195 paginiCece 4244 - Advanced RC DesignJaya RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- UAE Professional Structural Engineer Test - RequirementsDocument3 paginiUAE Professional Structural Engineer Test - RequirementsMelekeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plastic Analysis of Unbraced Portal Frames of Steel Structures in PDFDocument99 paginiPlastic Analysis of Unbraced Portal Frames of Steel Structures in PDFbiniamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthquake Lateral Force Analysis PDFDocument41 paginiEarthquake Lateral Force Analysis PDFGozai MahoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indetermine StructureDocument8 paginiIndetermine Structuremaloy100% (1)
- Moment of Inertia LectureDocument26 paginiMoment of Inertia LectureMohdmuslim AbdkohaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 D Structures Basic ConceptsDocument42 pagini1 D Structures Basic ConceptsDev MitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formula Sheet For PRC Slab Design by DDMDocument1 paginăFormula Sheet For PRC Slab Design by DDMTabish AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peikko Columnconnections FinalDocument5 paginiPeikko Columnconnections FinalCarlotaGomesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering-Graphics PPSXDocument284 paginiEngineering-Graphics PPSXGaurav GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curing System For Mat-FoundationDocument8 paginiCuring System For Mat-FoundationDayo100% (1)
- Analysis of Indeterminate Structures by Force MethodDocument17 paginiAnalysis of Indeterminate Structures by Force Methodatish k100% (2)
- Toe QuestDocument4 paginiToe Questrameshbabu_1979Încă nu există evaluări
- CE315 Lecture NoteDocument96 paginiCE315 Lecture NoteHRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two-Way-Joist-Concrete Slab-Floor - (Waffle-Slab) - System-Analysis-and-DesignDocument60 paginiTwo-Way-Joist-Concrete Slab-Floor - (Waffle-Slab) - System-Analysis-and-DesignHashem EL-MaRimeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lateral Load Distribution On Shear Walls - ExampleDocument25 paginiLateral Load Distribution On Shear Walls - ExamplekingdbmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formula Sheet GeometryDocument2 paginiFormula Sheet Geometryessy_abÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 MathDocument5 pagini2 MathAlexandra EscalonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 paginiGeometry and TrigonometryAbhay SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFDocument1 pagină6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFNarenÎncă nu există evaluări
- DDERDocument1 paginăDDERsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schedule of RatesDocument3 paginiSchedule of RatessamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SI - No Items UnitDocument12 paginiSI - No Items UnitsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Good Ne WordDocument2 paginiGood Ne WordsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantity Sheet For Service RoadDocument20 paginiQuantity Sheet For Service RoadsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GO1ODDocument3 paginiGO1ODsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GO1ODDocument3 paginiGO1ODsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Establish TS and ST: Figure E-15 Spiral Total Deflection AnglesDocument8 paginiA. Establish TS and ST: Figure E-15 Spiral Total Deflection AnglessamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SEEN SixDocument2 paginiSEEN SixsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Good BookDocument15 paginiGood BooksamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book 1Document3 paginiBook 1samuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GooodDocument5 paginiGooodsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GOODDocument2 paginiGOODsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curve DetailsDocument5 paginiCurve DetailssamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curve DetailsDocument5 paginiCurve DetailssamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- C. Circular Curve ComponentsDocument12 paginiC. Circular Curve ComponentssamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- C. Circular Curve ComponentsDocument12 paginiC. Circular Curve ComponentssamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RE SheetDocument18 paginiRE SheetsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Circular CurveDocument23 paginiDesign of Circular CurvesamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CompDocument2 paginiCompsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data SheetDocument3 paginiData SheetsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Circular CurveDocument23 paginiDesign of Circular CurvesamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Highways Department-Metro Wing: Details of Ongoing and Proposed Works SI - No Ongoing WorksDocument1 paginăHighways Department-Metro Wing: Details of Ongoing and Proposed Works SI - No Ongoing WorkssamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Researchpaper Strength of Concrete Containing Different Types of Fine AggregateDocument3 paginiResearchpaper Strength of Concrete Containing Different Types of Fine Aggregateyrdgcgf5664Încă nu există evaluări
- DSIGNDocument4 paginiDSIGNsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WallDocument5 paginiWallsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C CDocument7 paginiA A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C C A A A A B B B C C CsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Re WallDocument4 paginiRe WallsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retaining Wall Design 1Document10 paginiRetaining Wall Design 1samuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- READDocument1 paginăREADsamuthrarajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3 PolygonsDocument22 paginiLesson 3 PolygonsKim ParoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument11 paginiDetailed Lesson PlanChelsy PlaysÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jawapan Modul Si Cilik Matematik Tahun5Document8 paginiJawapan Modul Si Cilik Matematik Tahun5Jeyaletchumi ThiyagarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSP ProjectDocument8 paginiGSP ProjectDing DingÎncă nu există evaluări
- h=rcos θ ∞: Plane GeometryDocument7 paginih=rcos θ ∞: Plane GeometryPhreetzi ÜnseenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cot 3 DLL Solid Figures JoannDocument5 paginiCot 3 DLL Solid Figures JoannMay Rose AgudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Shape Questions 1Document36 paginiCambridge Shape Questions 1DinesCidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Symmetry (Planes Of)Document38 paginiSymmetry (Planes Of)littlegusÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Mathematical Shapes - WikipediaDocument20 paginiList of Mathematical Shapes - WikipediaJahnavi PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Solid GeometryDocument10 paginiIntro To Solid GeometryDaisy MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolygonDocument19 paginiPolygonlhadymhalditah_03100% (1)
- 1 XpsDocument6 pagini1 XpsAldrin BagasinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nota Chapter 6 3D Shapes F2Document3 paginiNota Chapter 6 3D Shapes F2Fatin MaisarahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Problems 3 - PlanexSolid GeometryDocument4 paginiPractice Problems 3 - PlanexSolid GeometrySong KangÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.2.2h Surface Area of PrismsDocument16 pagini5.2.2h Surface Area of Prismsdr.taim.09Încă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 16 PMR - Scale Drawing Solid GeometryDocument6 paginiMODULE 16 PMR - Scale Drawing Solid GeometryDerek MaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5-Inequalities in One TriangleDocument4 pagini5-Inequalities in One TriangledevikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- POLYGONDocument14 paginiPOLYGONapril ma heyresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projection of SolidsDocument22 paginiProjection of SolidsLakshmanan ThangaveluÎncă nu există evaluări
- RD Sharma Class 8 Chapter 19 Visualising ShapesDocument15 paginiRD Sharma Class 8 Chapter 19 Visualising ShapesAarav AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 7 Module 5 Exterior and Interior Angles of Convex Polygon RemovedDocument12 paginiMath 7 Module 5 Exterior and Interior Angles of Convex Polygon RemovedKeziah Cheluj GamengÎncă nu există evaluări