Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
UNIT1 - Introduction To Computers
Încărcat de
Brinda BMTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
UNIT1 - Introduction To Computers
Încărcat de
Brinda BMDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
UNIT-I
Introduction To Computers
Introduction to Computer
Early days people use fingers for computing purpose.
As years go, the computing needs also grew. This leads to the
invention of calculators and computers.
The term computer is derived from the word compute, it means to
calculate.
Definition
Computer is an electronic device. It accepts data, process the data
and gives the desired output.
COMPUTER
INPUT OUTPUT
Basic functions or operations
Input
Processing
Output
Storing
Controlling
Basic operations (Cont)
Input
It is the process of getting the data from the user or from
somewhere else into the computer to process.
Processing
It is the process of converting the input to output.
Output
It is the outcome or result of the process.
Storing
It is the process of saving the data. so that it can be retrieved
whenever needed.
Controlling
It is the process of directing the sequence in which the operations to
be performed.
Applications of computer:
Business
Industry
Home
Education
Printing & publishing
Entertainment etc.,
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER
Speed
Accuracy
Diligence
Versatility
Resource sharing
Storage
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER (cont)
Speed
The computer process the data extremely fast. (i.e.) in millions
(1,000,000) of instructions and even more per second. A computer
can perform a huge task in few sec where a human being may take
hours or even days to complete the same task.
Accuracy
The degree of accuracy of computer is very high and every
calculation is performed with the same accuracy. The accuracy level
is determined on the basis of design of computer. The errors in
computer are due to human and inaccurate data.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER (cont)
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER (cont)
Diligence or Endurance
A computer is free from tiredness, lack of concentration etc. It
can work for hours without creating any error. If millions of
calculations are to be performed, a computer will perform every
calculation with the same accuracy. Due to this capability it
overpowers human being in routine type of work.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER (cont)
Versatility
It means the capacity to perform completely different type of
work. For example At a moment a computer can be used to draft a
letter. Next moment it can be used print a document or play a
music file etc.,
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER (cont)
Resource sharing
In organizations the computers are connected to form a
network. The resources such as printers, scanner, plotters are
connected to the network and it can be shared by the computers in
the network.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER (cont)
Storage
Computers are capable of storing huge amount of data and it
can be located and retrieved very quickly. It uses storage devices
such as hard disk to store huge amount of data.
Evolution of Computers
Abacus
The first calculating device called ABACUS was developed by
the Egyptian and Chinese people. It consisted of sticks in horizontal
positions on which were inserted sets of beads. It has a number of
horizontal bars each having ten beads. Horizontal bars represent
units, tens, hundreds, etc.
Evolution of Computers (Cont)
Napiers bones
English mathematician John Napier built a mechanical device
for the purpose of multiplication in 1617 A D. The device was
known as Napiers bones.
Slide Rule
This machine could perform operations like addition,
subtraction, multiplication, and division. It was widely used in
Europe in 16th century.
Napiers bones
Evolution of Computers (Cont)
Pascal's Machine
Blaise Pascal developed a mechanical calculating
machine called Pascals calculating machine. It could
add and subtract. The machine consisted of wheels,
gears and cylinders.
Leibnizs Machine
The Pascals calculating machine can perform
addition and subtraction but it could not perform
multiply and division. Leibniz built a mechanical
device that could both multiply and divide.
Punched card Machine
The presence and absence of the holes in the card represent
the digits.
Evolution of Computers (Cont)
Babbages Analytical Engine
In the year 1823 that a famous English man Charles Babbage
built a mechanical machine to do complex mathematical
calculations. It was called difference engine. Later he developed a
general-purpose calculating machine called analytical engine.
Charles Babbage is called the father of computer.
Evolution of Computers (Cont)
Electronic Calculator
The electronic calculator used in 1960s was run with
electron tubes, Later it was replaced with transistors and as a result
the size of calculators became too small. It can compute all kinds of
mathematical computations. Some calculators have in-built
programs to perform some complicated calculations.
The first Electronic Computer ABC
Developed by Dr.John Vincent Atanasoff & Clifford Berry.
ABC - Atanasoff Berry Computer.
Uses Vacuum tube for storage.
Limited applications.
ENIAC:
First electronic computer.
Electronic Numerical Integrated And Calculator.
For U.S Army.
EDVAC:
Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer.
Binary number for arithmetic operations.
Storage of instruction in digital forms.
UNIVAC:
Universal Accounting Company.
Microprocessors:
INTEL 4004 first mp in 1969.
Personal Computer:
In 1974- successful micro computer.
Called as APPLE-1
Generations of Computers (Cont)
First Generation Computers:
These computers were vacuum tube based machines.
They used magnetic drums for memory.
Input were fed into the computer using Punched cards
The size of these computers were very large and it produce more
heat.
They lacked in versatility and speed.
They were more expensive.
Generations of Computers (Cont)
Second Generation Computers
Here the Transistor replaced the bulky vacuum tubes.
Transistors are smaller than vacuum tubes and have higher
operating speed.
Thus the size of the computer got reduced considerably.
Manufacturing cost was also very low.
Generations of Computers (Cont)
Third Generation Computers
These computers were based on Integrated Circuits (ICs)
Technology.
A single IC has many transistors, registers and capacitors built on a
single thin slice of silicon.
So that the size of the computer got further reduced.
These Computers were small in size, low cost, large memory and
processing speed is very high.
Generations of Computers (Cont)
Fourth Generation Computers
It uses large scale Integrated Circuits (LSIC) built on a single silicon chip
called microprocessors .
Later very large scale Integrated Circuits (VLSIC) replaced LSICs
These computers are called microcomputers.
Thus the size of the computer got reduced.
The personal computer (PC) are comes under the Fourth Generation.
Generations of Computers (Cont)
Fifth Generation Computer
The speed is extremely high in fifth generation computer.
The concept of Artificial intelligence has been introduced to allow the
computer to take its own decision.
It is still in a developmental stage .
Classification of Computer
Classification of Computer (Cont)
The computers can also classified based on the hardware design as
follows
Analog computer.
Digital computer.
Hybrid computer.
Classification of Computer
Microcomputer
Mini Computer
Mainframes
Supercomputer
Classification of Computer
Microcomputer Supercomputer Mini Computer Mainframes
Computer
Desktop
N/W Servers
Laptops Smart phones
Classification of Computer (Cont)
Microcomputer
Microcomputer is at the lowest end of the computer range in terms
of speed and storage capacity.
Eg: Desktop, Laptop, Tablet PC, Smart Phones.
Classification of Computer (Cont)
Mini Computer
This is designed to support more than one user at a time.
It possesses large storage capacity and operates at a higher speed.
This type of computer is generally used for processing large volume
of data in an organization.
Eg: Servers in Local Area Networks (LAN).
Classification of Computer (Cont)
Mainframes
They operate at very high speed, having very large storage capacity
and can handle the work load of many users.
They are generally used in centralized databases.
Classification of Computer (Cont)
Supercomputer
They are the fastest and most expensive machines.
They have high processing speed compared to other computers.
They have also multiprocessing technique.
Supercomputers are mainly being used for whether forecasting,
biomedical research, Space Research and other areas of science and
technology
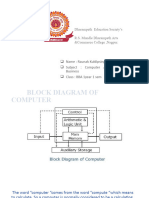
BASIC ORGANISATION
OF
COMPUTER
CONTROL
MEMORY
ALU
OUTPUT INPUT
Basic organisation of computer
Basic organisation of computer
INPUT
The input unit is used to information or instruction to the computer.
It accept the information or instruction from user or from some where
else.
Convert it to a computer understandable form and send it to the
computer.
Eg:Keyboard,mouse,Joystick,MICR, etc,.
Basic organisation of computer (cont)
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
It is the heart of the computer.
It performs all operations.
It contains the followings
CONTROL UNIT
ALU
MEMORY
Basic organisation of computer (cont)
CONTROL UNIT
It controls all other units in the computer.
It directs the sequence in which operations to be performed.
It also controls the flow of data between various units.
Basic organisation of computer (cont)
ARITHMETIC & LOGICAL UNIT
It performs all arithmetic & logical operations.
i.e. arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication,
division etc,. And logical operations like AND,OR,NOT etc,.
Basic organisation of computer (cont)
MEMORY UNIT
Place for holding the information.
Types
Primary
Secondary
Primary memory is used to store temporary data.Eg:RAM,ROM etc,.
Secondary memory is used to store information permanently. Eg:Hard
disk.
Basic organisation of computer
OUTPUT
The output unit is used to display the result of the process.
Eg:Monitor,printer,speakers, etc,.
Components of Computers
Components of Computers
Hardware
The physical components present in the computer.
Software
It is a collection of programs and it can perform some
operaions.
Components Present inside the cabinet
Motherboard
Processor
SMPS
Disk drives
RAM & ROM etc,.
Types of Memory
MEMORY
SECONDARY
PRIMARY
RANDOM ACCESS SEQ.ACESS
Primary Memory:
It is used to store data temporary.
RAM
Random Access Memory
It is possible to randomly select and use any location of the
memory.
It is a volatile memories i.e. It loose their content when the power
is switched off
TYPES OF RAM:
There are two types of RAM used in PCs - Dynamic
and Static RAM.
Dynamic RAM (DRAM):
The information stored in Dynamic RAM
has to be refreshed after every few milliseconds
otherwise it will get erased. DRAM has higher
storage capacity and is cheaper than Static RAM.
Static RAM (SRAM):
The information stored in Static RAM need not be
refreshed, but it remains stable as long as power
supply is provided. SRAM is costlier but has higher
speed than DRAM.
Floppy Disk Drive Terminology
Floppy disk - Also called diskette. The common size is 3.5 inches.
Floppy disk drive - The electromechanical device that reads and
writes foppy disks.
Track - Concentric ring of data on a side of a disk.
Sector - A subset of a track, similar to wedge or a slice of pie.
ROM
Read Only Memory
The data in the ROM is permanent .
It is a non-volatile memories i.e. It does not loose their content
when the power is switched off .
Programmable Read Only Memory
It is supplied in blank by the manufacturer.
It is possible to store program in PROM chip.
Once the programmes are written it cannot be changed and remain
even if power is switched off.
PROM
Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory.
Information stored in EPROM can be erased by exposing the chip in
ultraviolet light and it is reprogrammed using a special
programming facility.
EPROM
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory.
Information stored in EEPROM can be erased by applying some
voltage.
EEPROM
Secondary Memory:
It is used to store data permanently
TYPES: sequential access , random access
Sequential Access
Magnetic Tape:
Magnetic tapes are used by large computers like mainframe
computers where large volume of data is stored for a longer time.
The cost of storing data in tapes is inexpensive.
Tapes consist of magnetic materials that store data permanently.
Random Access
Hard Disk:
It uses circular disk ,coated with magnetic material called platters.
It rotates with very high speed inside the drive.
Data is stored on both the surface of the disk.
Each disk consists of a number of invisible concentric circles called
tracks.
The information stored in a disk can be read many times without
affecting the stored data.
Magnetic Hard Disk Mechanism
Random Access (cont)
Optical disk
It uses a circular plastic disk coated with aluminium or silver storing
data.
The data are stored in the circular tracks.
Laser beam is used for storing and retrieve data from the disk
INPUT OUTPUT DEVICES
Input Devices
Input devices are necessary to convert our information or data
in to a form which can be understood by the computer.
Eg: Keyboard, Mouse, MICR,OMR,OCR.
Keyboard
This is the standard input device.
The layout of keyboard is just like the traditional typewriter of the
type QWERTY.
It also contains some extra command keys and function keys.
The computer can recognise the electrical signals corresponding to
the correct key combination and processing is done accordingly
Mouse
Mouse is an input device.
When the mouse is moved across a flat surface the screen pointer
is also moved in the direction of mouse movement.
It is easier to move the cursor through a mouse
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition
(MICR)
This is widely used by banks to process large volumes of cheques
and drafts.
Cheques are put inside the MICR.
As they enter the reading unit ,the magnetic field which causes the
read head to recognise the character of the cheques.
Optical Mark Reader (OMR):
This technique is used in objective type tests and the answer are
marked by darkening a square or circular space by pencil or pen.
These answer sheets are directly fed to a computer for grading
where OMR is used.
Optical Character Recognition
(OCR):
- It is used to recognize any printed character.
- This characters are compared with patterns stored inside the
computer.
- Whichever pattern is matched is called a character read.
- Patterns that cannot be identified are rejected. OCRs are expensive
though better the MICR.
Output Devices
Visual Display Unit
The most popular output device is the Visual Display Unit (VDU).
It is also called the monitor.
Monitor is used to display the input data and to receive massages
from the computer.
It can be color or monochrome.
Printer
It is an important output device which can be used to get a printed
copy of the processed text or result on paper.
printers are classified as impact and
non-impact printers.
NUMBER SYSTEM
Number System
Number Base B => B symbols
Base 16(Hexa):0, 1,9, A ,, E, F
Base 10 (Decimal): 0, 1, 2,, 7, 8, 9
Base 8(Octal): 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Base 2 (Binary): 0, 1
Number System (cont)
Number representation:
d
31
d
30
... d
2
d
1
d
0
is a
32 digit number
value = d
31
x B
31
+ d
30
x B
30
+ ... + d
2
x B
2
+ d
1
x
B
1
+ d
0
x B
0
Decimal Numbers: Base 10
Base or Radix is 10
Digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Example:
412
10
= 4x10
2
+ 1x10
1
+ 2x10
0
= 400 + 10 +2 = 412
Binary Numbers: Base 2
Base or Radix is 2
Digits: 0, 1
Example:
101
2
= 1x2
2
+ 0x2
1
+ 1x2
0
= 4 + 0 +1 = 5
Octal Numbers: Base 8
Base or Radix is 8
Digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Example:
123
8
= 1x8
2
+ 2x8
1
+ 3x8
0
= 64 + 16 +3
= 83
Hexadecimal Numbers: Base 16
Digits: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F:
A 10
B 11
C 12
D 13
E 14
F 15
Example:
12
16
= 1x16
1
+ 2x16
0
= 16 +2
= 18
Conversions
Decimal to Base N Base N to Decimal
Successive Division by N
(Remainder Method)
Multiplication with
power of N
Decimal to Binary
Conversion of 25
10
to Binary
2 25
2 12 -1
2 6 - 0
2 3 - 0
1 - 1
25
10
=11001
2
Binary to decimal conversion
11001
1X2
0 =
1
0X2
1 =
0
0X2
2 =
0
1X2
3 =
8
1X2
4 =
16
25
10
Decimal to Octal
Conversion of 125
10
to Octal
8 125
8 15 - 5
1 - 7
125
10
=175
8
Octal to decimal conversion
175
5X8
0 =
5
7X8
1 =
56
1X8
2 =
64
125
175
8
=
125
10
Conversion of 84
10
to Octal
8 84
8 10 - 4
1 - 2
84
10
=124
8
Octal to decimal conversion
124
4X8
0 =
4
2X8
1 =
16
1X8
2 =
64
84
124
8
=
84
10
Decimal to Hexa
Conversion of 450
10
to Hexadecimal
16 450
16 28 - 2
1 - 12
450
10
=1C2
16
Hexa to decimal conversion
1C2
2X16
0 =
2
12X16
1 =
192
1X16
2 =
256
450
1C2
16
=
450
10
Conversion of 385
10
to Hexadecimal
16 385
16 24 - 1
1 - 8
385
10
=181
16
Hexa to decimal conversion
181
1X16
0 =
1
8X16
1 =
128
1X16
2 =
256
385
181
16
=
385
10
Other Conversions
BINARYOCTAL
BINARYHEXA
OCTALHEXA etc,.
BINARYOCTAL
OCTAL BASE 8 = 2
3
3 DIGIT BINARY NUMBER
Example:11001
2
OCTAL
11 001
011 001
3 1
11001
2
=31
8
Example:1110011
2
OCTAL
1 110 011
001 110 011
1 6 3
1110011
2
=163
8
BINARYHEXA
HEXA BASE 16 = 2
4
4 DIGIT BINARY NUMBER
Example:11001
2
HEXA
1 1001
0001 1001
1 9
11001
2
=19
16
Example:1110011
2
OCTAL
1 110 011
001 110 011
1 6 3
1110011
2
=163
8
OCTALHEXA
OCTALBINARYHEXA
Example:31
8
HEXA
3 1
011 001
0001 1001
1 9
31
8
=19
16
HEXA OCTAL
Example: 1BD OCTAL
1 B D
0001 1011 1101
000 110 111 101
0 6 7 5
1BD = 675
8
Conversion of 25.125
10
to Binary
2 25
2 12 -1
2 6 - 0
2 3 - 0
1 - 1
25
10
=11001
2
0.125 X 2 = 0.250
0.250 X 2 = 0.5
0.5 X 2 = 1.0
25.125
10
= 11001.001
2
Binary to decimal conversion
11001.001
1X2
-3
=
0.125
0X2
-2
= 0
0X2
-1
= 0
1X2
0 =
1
0X2
1 =
0
0X2
2 =
0
1X2
3 =
8
1X2
4 =
16
25.125
10
Conversion of 84.250
10
to Octal
8 84
8 10 - 4
1 - 2
84
10
=124
8
0.250 X 8 = 2.000
25.123
10
= 124.2
8
Octal to decimal conversion
124.2
2X8
-1
= 0.25
4X8
0 =
1
2X8
1 =
0
1X8
2 =
0
25.250
10
ASSIGNMENT
DECIMAL TO BINARY
43
79
107
241
476
DECIMAL TO OCTAL
39
152
284
758
2534
DECIMAL TO HEXA
75
826
3128
7359
4756
DECIMAL TO OTHER
63 BASE4
279 BASE6
161 BASE7
BINARY OCTAL,HEXA
1010101
11010101011
111010110111
1011110111
101000101
OCTAL HEXA
473
1235
724
5774
4625
75.125
10
BASE2
356.523
10
OCTAL
527.42
10
HEXA
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ComputerDocument118 paginiComputerIsha ChandokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document42 paginiChapter 1Vansh GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- COM111Document100 paginiCOM111goodluckjacob206Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer Application 1Document62 paginiComputer Application 1soujan1Încă nu există evaluări
- II. Basic Concepts in CSS PDFDocument54 paginiII. Basic Concepts in CSS PDFRoss Armyr GeliÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Lesson - History of Computer Definition of ComputerDocument6 paginiFirst Lesson - History of Computer Definition of ComputerPuspaÎncă nu există evaluări
- L1 - Computer Progression - (2022)Document34 paginiL1 - Computer Progression - (2022)Andrea BatholomeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document42 paginiLecture 1Tania Khan75% (4)
- Computer Systems: End User and Enterprise ComputingDocument64 paginiComputer Systems: End User and Enterprise ComputinghaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are Computers ?: CalculatesDocument6 paginiWhat Are Computers ?: Calculatessubstituteacc12Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Information TechnologyDocument43 paginiIntroduction To Information TechnologySharie ArellanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To ComputerDocument46 paginiIntroduction To Computertadesse ketemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Computer: Prepared by Shahzeb KhanDocument20 paginiIntroduction To Computer: Prepared by Shahzeb KhanZeebo KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mbeya University of Science and Technology UQF 8 2021/22 1 YearDocument66 paginiMbeya University of Science and Technology UQF 8 2021/22 1 Yearabel emmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Computer-Lecutre 1Document24 paginiIntroduction To Computer-Lecutre 1Naeem JanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 - Fundamental 1Document49 pagini01 - Fundamental 1Dang Tran Quang Huy (FGW CT)Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1Document89 paginiUnit 1Ashish kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GE6151 Computer Programming NotesDocument152 paginiGE6151 Computer Programming NotesSuryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To ICTDocument47 paginiIntroduction To ICTredmiphone17319Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1: Computer FundamentalsDocument50 paginiLesson 1: Computer Fundamentalsquan DOÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT Lec 4Document49 paginiIT Lec 4Play StoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document34 paginiAssignment 1DRAME ANE MOHAMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Applications Notes IntroDocument18 paginiComputer Applications Notes IntroMbegumbayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of ComputerDocument47 paginiHistory of ComputerSharada ShaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1: DefinitionDocument7 paginiChapter-1: Definitionapi-240912278Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Computer: by Kiramat Rahman Department of Computer & Software TechnologyDocument48 paginiIntroduction To Computer: by Kiramat Rahman Department of Computer & Software TechnologydangermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture NCS-505Document55 paginiComputer Architecture NCS-505PrachiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Computer in EconomicsDocument194 paginiApplication of Computer in EconomicskanishkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer: An IntroductionDocument20 paginiComputer: An IntroductionHamza KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMPUTER: Introduction: DR Meera Department of Library and Information Science Delhi UniversityDocument32 paginiCOMPUTER: Introduction: DR Meera Department of Library and Information Science Delhi UniversityVikas KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Fundamentals Study MaterialDocument36 paginiComputer Fundamentals Study Materialzingly31Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes 1 (CSC-103)Document51 paginiLecture Notes 1 (CSC-103)Md Sakawat HossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cab PPT - by Raunak AroraDocument14 paginiCab PPT - by Raunak AroraMike QwertyÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 1 NDocument153 paginiUNIT 1 NkamaladeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec. 2Document24 paginiLec. 2Annie LeonhartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document31 paginiLecture 1Afaq AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of Computing and Computer SystemsDocument68 paginiOverview of Computing and Computer SystemsAliyah the Potato GremlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer IntroductionDocument13 paginiComputer Introductionsujithra422Încă nu există evaluări
- Fit IDocument10 paginiFit IMadasu BalnarsimhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To ComputersDocument2 paginiIntroduction To ComputersAimee MuelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- New MAC113-1Document22 paginiNew MAC113-1Jamiu Muibudeen JamtechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 StsDocument27 paginiLesson 1 StsrjayvillarmeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Notes MonthlyDocument3 paginiComputer Notes MonthlyJ-Mi AlejanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-1 Basics of ComputerDocument26 paginiUnit-1 Basics of ComputerAjay SahreÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCS101 - Focp PDFDocument125 paginiBCS101 - Focp PDFsania2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Class 1Document31 paginiClass 1abdulazizmoosa93Încă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental of Computer (BBA 5th)Document15 paginiFundamental of Computer (BBA 5th)Ranjit singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Science &technologyDocument76 paginiComputer Science &technologyJunaid SarwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Fundamentals NotesDocument15 paginiComputer Fundamentals Notessidha6thsidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Systems & Programming: Engr. Muhammad TayyabDocument50 paginiComputer Systems & Programming: Engr. Muhammad TayyabBaseer AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Awareness Finale Lyst1381Document143 paginiComputer Awareness Finale Lyst1381mercerian007Încă nu există evaluări
- Generations, ClassificationsDocument40 paginiGenerations, ClassificationsDINESH RAWATÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental of Computer (BBA 5th)Document12 paginiFundamental of Computer (BBA 5th)Harsh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information Technology & Business: Computer Based Information SystemsDocument79 paginiInformation Technology & Business: Computer Based Information SystemsRosedemaeBolongaitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSS224 Lec1Document30 paginiCSS224 Lec1makehappyincÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-I Computer ArchitectureDocument101 paginiUNIT-I Computer Architecturemusic12341234Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer Applications Notes-1-1Document52 paginiComputer Applications Notes-1-1Langat Kipkoech GodwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture Lec 01Document32 paginiComputer Architecture Lec 01Muhammad AfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assemble Computer HardwareDocument23 paginiAssemble Computer HardwareRichard SugboÎncă nu există evaluări
- His Excellency Mahinda Rajapaksa: Address byDocument5 paginiHis Excellency Mahinda Rajapaksa: Address byshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embryology Alimentarysystem2 Chap 13Document37 paginiEmbryology Alimentarysystem2 Chap 13shibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- H.E. Mahinda Rajapaksa: General DebateDocument5 paginiH.E. Mahinda Rajapaksa: General DebateshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgeon-General Charles Sibthorpe: Harriet Wheelock May 2011Document6 paginiSurgeon-General Charles Sibthorpe: Harriet Wheelock May 2011shibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitosisandmeiosis 100208052508 Phpapp02Document59 paginiMitosisandmeiosis 100208052508 Phpapp02shibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaesthesia ExplainedDocument22 paginiAnaesthesia Explainedshibhi100% (1)
- O Slab ManualDocument37 paginiO Slab ManualshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DBMS 1 V+Document14 paginiDBMS 1 V+shibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ge 2152 - Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering May-June 2009Document2 paginiGe 2152 - Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering May-June 2009U_RaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- CT QBDocument20 paginiCT QBmuralieseaÎncă nu există evaluări
- M2 R08 MayJune 10Document3 paginiM2 R08 MayJune 10shibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standards of Monitoring 07Document16 paginiStandards of Monitoring 07nagarjungaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- M2 R08 MayJune 09Document3 paginiM2 R08 MayJune 09shibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATHSDocument9 paginiMATHSitsroshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Drugs Shatter The MythsDocument32 pagini05 Drugs Shatter The Mythsapi-309082881Încă nu există evaluări
- DrugsDocument7 paginiDrugszipzapdhoomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peptic Ulcers Atau Ulkus PeptikumDocument19 paginiPeptic Ulcers Atau Ulkus PeptikumMuhammad Benny SetiyadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- @PH 2111 - Engineering Physics Ii May-June 2009Document2 pagini@PH 2111 - Engineering Physics Ii May-June 2009shibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- At TurbineDocument55 paginiAt TurbineDharmendra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- RG302Document2 paginiRG302Pavan SridharÎncă nu există evaluări
- VirusesDocument4 paginiVirusesshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solar Energy: Virgin Islands Energy OfficeDocument6 paginiSolar Energy: Virgin Islands Energy OfficeshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Install SonarDocument4 paginiHow To Install SonarshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alimentary Canal 3rd Year2Document19 paginiAlimentary Canal 3rd Year2slOwpOke13Încă nu există evaluări
- 121 Ca 70 CDocument44 pagini121 Ca 70 CshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- California Standards Test Biology/Life ScienceDocument8 paginiCalifornia Standards Test Biology/Life ScienceshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- June 21, 2002 Twentieth Meeting Presidential Advisory Council On HIV/AIDS Louis Sullivan, MD, Co-Chair Tom Coburn, MD, Co-Chair Washington, DCDocument2 paginiJune 21, 2002 Twentieth Meeting Presidential Advisory Council On HIV/AIDS Louis Sullivan, MD, Co-Chair Tom Coburn, MD, Co-Chair Washington, DCshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fact Sheet Cancers enDocument2 paginiFact Sheet Cancers enO.r. CadzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Inee Toolkit - Hiv AidsDocument3 pagini1 Inee Toolkit - Hiv AidsshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hiv Aids FNLDocument4 paginiHiv Aids FNLshibhiÎncă nu există evaluări