Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Price Mechanism
Încărcat de
Ryan Thomas0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
107 vizualizări10 paginiThe price mechanism allocates resources in a free market system. Price acts as a signal to producers - if demand increases, price rises which incentivizes producers to increase supply for greater profits. If demand decreases, price falls which moves resources away from that product.
One advantage is that it achieves technical efficiency as producers seek to minimize costs. A second advantage is that it leads to allocative efficiency as resources flow to where they yield highest profits based on consumer demand.
However, it does not always operate smoothly. One disadvantage is that unequal income distribution can lead to unsatisfactory allocation as the poor have limited access. A second disadvantage is that it fails to account for external costs and benefits of production and consumption.
Descriere originală:
just short note
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
TXT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe price mechanism allocates resources in a free market system. Price acts as a signal to producers - if demand increases, price rises which incentivizes producers to increase supply for greater profits. If demand decreases, price falls which moves resources away from that product.
One advantage is that it achieves technical efficiency as producers seek to minimize costs. A second advantage is that it leads to allocative efficiency as resources flow to where they yield highest profits based on consumer demand.
However, it does not always operate smoothly. One disadvantage is that unequal income distribution can lead to unsatisfactory allocation as the poor have limited access. A second disadvantage is that it fails to account for external costs and benefits of production and consumption.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca TXT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
107 vizualizări10 paginiPrice Mechanism
Încărcat de
Ryan ThomasThe price mechanism allocates resources in a free market system. Price acts as a signal to producers - if demand increases, price rises which incentivizes producers to increase supply for greater profits. If demand decreases, price falls which moves resources away from that product.
One advantage is that it achieves technical efficiency as producers seek to minimize costs. A second advantage is that it leads to allocative efficiency as resources flow to where they yield highest profits based on consumer demand.
However, it does not always operate smoothly. One disadvantage is that unequal income distribution can lead to unsatisfactory allocation as the poor have limited access. A second disadvantage is that it fails to account for external costs and benefits of production and consumption.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca TXT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 10
Explain how the price mechanism allocates resources and describe some of
its advantages and disadvantages (12)
Under a free market economic system, resources are allocated according to the
price mechanism. Consumer wants are infinite and resources are scarce,
therefore these scarce resources need to be allocated between competing uses. On
e
way is this done is through price.
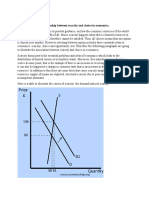
Price acts as a signal to producers. In a market economy, changes in demand
eventually bring about changes in supply. If consumer demand for a product
increases, the resultant shortage will cause the price to increase. As producers
of
the product can now make more profit on this good they will switch more
resources into the production of the good (as they are profit maximisers),
therefore the increase in demand leads to increases in supply and vice versa. If
consumer demand for a product falls, the resultant glut/surplus will cause its
price to fall resulting in a fall in the profit made on the good. Resources are
then
moved out of the production of that particular product and used to produce those
products that are now relatively more profitable.
One of the most cited advantages of the price mechanism is that it best achieves
an economically efficient allocation of resources. Technical efficiency is
achieved as producers produce at minimum unit cost, in other words, when the
fewest necessary resources are used to produce each product. This is because
firms are profit maximising and given the degree of competition in a free
market they will want to produce at a point where costs are minimized. There is
a greater incentive for firms to cut costs, increase productivity and develop ne
w
products because of the chance of extra profit. In the long run (because of the
high
degree of competition), firms are producing at the lowest point in the average c
ost
curve. If all firms operated under these conditions it would follow that there
would be an optimum allocation of resources and every commodity would be
produced at a minimum cost per unit.
Markets also tend towards allocative efficiency. Customers are able to cast thei
r
spending votes in the market. This determines what is produced. Prices signal
the value of individual resources and resources flow to where they yield the
highest profit. In other words, the invisible hand of the market would allocate
resources to everyones advantage. For example, if consumers want to buy more
I-pods and fewer CDs, then I-pod firms will expand production, whilst
manufacturers of CDs will cut production. All firms would be producing to
consumers demand curves i.e. goods which people desire. Furthermore, the market
is flexible so that changes in demand quickly bring about changes in supply so
surpluses / shortages do not last.
Define the price
mechanism fully
Describe the first
advantage of the
price mechanism
Describe the
second
advantage of the
price mechanism
One of the disadvantages of the having the price mechanism allocating resources
is that it does not always operate smoothly. In a market economy an
individuals ability to consume goods & services depends upon his/her income.
An unequal distribution of income and wealth may result in an unsatisfactory
allocation of resources. The relatively poor do not have access to the range of
goods and service consumed by average citizens. High inequality may also
lead to social exclusion and encourage crime with negative consequences for all.
The market system will not respond to the wants of those with insufficient
purchasing power because what matters in a market based system is your
effective demand for goods and services. Therefore, government may intervene
by providing merit goods such as education and healthcare, and benefits such as
Job Seekers Allowance, child benefit, etc. The finance comes out of taxation,
much of which bears more heavily on the rich.
The price mechanism also fails to take into account market failure. In a free
market, the costs which a firm takes into account when making decisions are
those which it has to pay, i.e. private costs. Similarly a consumer when making
decisions about what and how much to buy only considers private benefit, i.e. th
e
benefit (utility) which he receives. However, the production and consumption of
a product may have spillover effects on people not directly involved in its
production or consumption. These spillover effects are called external costs and
benefits.
Describe the first
disadvantage of
the price
mechanism
Describe the
second
disadvantage of
the price
mechanism
Explain the difference between scarcity and a shortage (8)
Scarcity is the basic economic problem which arises because human wants which
are unlimited, exceed the goods and services which can be produced at any one
time because of finite resources.
Individuals, businesses and governments always want more. Their wants are
insatiable because goods eventually wear out and need to be replaced i.e.
electronic appliances. New or improved products become available i.e. mobile
phones. Some people argue that the desire to consume is innate and it is human
nature that once one want is satisfied, they want more. Others argue that
advertising plays a powerful role in creating new wants i.e. downloadable ring
tones like Crazy Frog. It is important to note that the concept of unlimited
wants is not only confined to goods and services, but other items such as a bett
er
environment, more leisure time, better relationships, etc.
Resources are limited in relation to the demands placed on them. For example, th
e
total surface area in the world is fixed, and many natural resources are non-
renewable like oil. Indeed, over-fishing in Scotland led to a ban on Cod fishing
in the North Sea. There are limited supply of workers and risk takers. Indeed,
this point was highlighted on the front cover of the Economist in October 2006
with articles on the shortage of talent. With regards to capital, there is a limit
to how much investment a firm can make.
Shortage arises when the demand for a product at a particular price cannot be
met i.e. when demand exceeds supply the quantity which consumers want and
are able to buy is not being produced. In a market economy, shortages usually
dont last long and will be cured by a rise in price and/or an increase in supply.
Demand is a want backed up by the ability to pay and is therefore limited by
income. Scarcity is different because we talk about unlimited wants (not
demand) and how they are never fully satisfied. If there was no shortage there
would still be scarcity because of all those consumers who want the product but
cannot afford to pay.
Define scarcity
State why wants
are unlimited
provide
examples.
State why
resources are
limited provide
examples.
Define shortage
and state the
difference
between it and
scarcity.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Economics Revision GuideDocument75 paginiEconomics Revision GuideFegason Fegy100% (2)
- Case-1: People Respond To Incentives. It Is Important, Therefore, That These Have The Desired EffectDocument13 paginiCase-1: People Respond To Incentives. It Is Important, Therefore, That These Have The Desired EffectHarikrushan DholariyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESDe la EverandSummary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 16 Ch.l.sri KariDocument41 paginiTask 16 Ch.l.sri KariEswar Sai VenkatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic Problem SDocument26 paginiEconomic Problem SManish MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- BasicDocument2 paginiBasicNasirul Hasan RonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gr12 Basic Ideas Notes NewDocument11 paginiGr12 Basic Ideas Notes NewAditi JaysonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 FIN 306 - FinalDocument36 paginiChapter 2 FIN 306 - FinalAbid vhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS1197 - 289862Document9 paginiBS1197 - 289862Cameron MoraisÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS1197 - 289862 PDFDocument9 paginiBS1197 - 289862 PDFCameron MoraisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Possible To Do This in The Private Sector of The Economy. The Conclusion Is Correct. Specifically Relevant To The Information GivenDocument5 paginiPossible To Do This in The Private Sector of The Economy. The Conclusion Is Correct. Specifically Relevant To The Information GivenNikhil RamtohulÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS S1 Essay IG-AS SIADocument5 paginiAS S1 Essay IG-AS SIA2537771050Încă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument43 paginiUntitledThaddeus TungÎncă nu există evaluări
- GR 12 Basic Ideas NotesDocument21 paginiGR 12 Basic Ideas NotesZayan ChhayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13 IGCSEDocument80 paginiChapter 13 IGCSEtaj qaiserÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Economic Issues and Challenges Assessment 2Document6 paginiInternational Economic Issues and Challenges Assessment 2Kirschner AmaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 EconomicDocument27 paginiChapter 2 EconomicIman MananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Unit 1 Notes From Sayeedh GhouseDocument50 paginiEconomics Unit 1 Notes From Sayeedh GhouseSayeedh GhouseÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Black Sea UniversityDocument4 paginiInternational Black Sea UniversityNatia KakuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desy Wahyu Rahmawati Imabs A (20180410104) : Economics AssignmentDocument5 paginiDesy Wahyu Rahmawati Imabs A (20180410104) : Economics AssignmentDesy Wahyu RahmawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicroeconomicsDocument6 paginiMicroeconomicsSriranjani SureshÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS1197 - 289862Document9 paginiBS1197 - 289862Cameron MoraisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Micro ReviewerDocument12 paginiBasic Micro ReviewerNicole MaldonadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Economics:: 1) People Face Trade-Offs: Due To Scarcity of Resources One Needs To PayDocument5 paginiPrinciples of Economics:: 1) People Face Trade-Offs: Due To Scarcity of Resources One Needs To PayAVIRAL PRATAP SINGH CHAWDAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco Notes-1Document27 paginiEco Notes-1Shivendra ShrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAP 1 NOtesDocument6 paginiCHAP 1 NOtesMaliha FarzanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic ProblemsDocument26 paginiEconomic Problemschaitu34100% (4)
- Task 11 - 223Document17 paginiTask 11 - 223Eswar Sai VenkatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macroeconomics: 1. MicroeconomicsDocument30 paginiMacroeconomics: 1. MicroeconomicsVictoria GalenkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MacroEconomics Written Assignment 2Document6 paginiMacroEconomics Written Assignment 2Thais HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elasticity of DemandDocument3 paginiElasticity of DemandnattyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Assignment On Financial SectorDocument9 paginiEconomics Assignment On Financial SectorAndy ChilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Revenue Is Defined AsDocument12 paginiTotal Revenue Is Defined AsRia BarisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Economic QuestionsDocument6 paginiBasic Economic Questionsnusrat1998Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit10 Feb2015 PDFDocument43 paginiUnit10 Feb2015 PDFJared OlivarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Business Environment: Economic System - Relevance in Global EconomyDocument9 paginiAssignment Business Environment: Economic System - Relevance in Global EconomyMrityunjay SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Microeconomics F1 Accountant in Business ACCA Qualification Students ACCA GlobalDocument1 paginăIntroduction To Microeconomics F1 Accountant in Business ACCA Qualification Students ACCA Globalnajmi ahmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scarcity & Opportunity CostDocument4 paginiScarcity & Opportunity CostUchiha SenjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microeconomics ExternalitiesDocument19 paginiMicroeconomics ExternalitiesNorweste SurgicalÎncă nu există evaluări
- A) How Resources Are Allocated in A Free Market EconomyDocument4 paginiA) How Resources Are Allocated in A Free Market EconomyChristineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learnovate Ecommerce TASK - 13: Submitted by Meenakshi RDocument17 paginiLearnovate Ecommerce TASK - 13: Submitted by Meenakshi REswar Sai VenkatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 2 - Principle of ECONDocument26 paginiLesson 2 - Principle of ECONqy8rwv586mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic 531 Assignment 2Document9 paginiEconomic 531 Assignment 2Sam K. Flomo JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- D.manju Bhargav - Task 16Document37 paginiD.manju Bhargav - Task 16Eswar Sai VenkatÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Market EconomyDocument17 paginiWhat Is The Market EconomysharifÎncă nu există evaluări
- City Group of Colleges: COURSE: LLB (Integrated) Semester: Ist Subject: EconomicsDocument57 paginiCity Group of Colleges: COURSE: LLB (Integrated) Semester: Ist Subject: EconomicsTanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gregory MankiwDocument3 paginiGregory MankiwPj FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13Document14 paginiChapter 13dongsara2006Încă nu există evaluări
- Econ 1 - Economics and EconomiesDocument6 paginiEcon 1 - Economics and EconomiesJeffrey Jazz BugashÎncă nu există evaluări
- 42 ECO SAT-1 From Vikash AgrawalDocument12 pagini42 ECO SAT-1 From Vikash AgrawalVikash AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lahoti Et Al (2016) - The GCIP Datasets - An OverviewDocument6 paginiLahoti Et Al (2016) - The GCIP Datasets - An OverviewdatateamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Basic Economic ProblemsDocument2 paginiThree Basic Economic ProblemsrudraarjunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ba 112 - Module 2 FinalDocument8 paginiBa 112 - Module 2 FinalMARY MAXENE CAMELON BITARAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics AssignmentDocument6 paginiEconomics Assignmentsolo_sudhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Economics Revision NotesDocument63 paginiA Level Economics Revision NotesMajida Ghandour85% (20)
- Questions: 1. Explain The Relationship Between Scarcity and Choice in EconomicsDocument7 paginiQuestions: 1. Explain The Relationship Between Scarcity and Choice in EconomicsTracy MarimoutouÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Economics Revision NotesDocument58 paginiIGCSE Economics Revision NotesCrystal Wong87% (207)
- Assignment of Managerial Economy: Mohamed Omar MahamoudDocument8 paginiAssignment of Managerial Economy: Mohamed Omar MahamoudMohamed OmarionÎncă nu există evaluări
- May The Lights of This Auspicious Festival Fill Your Life With The Eternal GlowDocument1 paginăMay The Lights of This Auspicious Festival Fill Your Life With The Eternal GlowRyan ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- May Every Passing Year Bring You All The Things That You Have Wished For. Have A Wonderful Life Ahead. From - Tarun & PujaDocument1 paginăMay Every Passing Year Bring You All The Things That You Have Wished For. Have A Wonderful Life Ahead. From - Tarun & PujaRyan ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume HMDocument9 paginiResume HMRyan ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Conversation Between 3 Friends About? Conversation Between Three Friends Going To A ConcertDocument25 paginiWhat Is The Conversation Between 3 Friends About? Conversation Between Three Friends Going To A ConcertRyan Thomas100% (1)
- DLL - English 4 - Q2 - W8Document4 paginiDLL - English 4 - Q2 - W8BenjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Average and Instantaneous AccelerationDocument35 paginiAverage and Instantaneous AccelerationaraneyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Paper For Business ResearchDocument4 paginiConcept Paper For Business ResearchRobertchristian RagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muzakarah Jawatankuasa Fatwa Majlis Kebangsaan Bagi Hal Ehwal Ugama Islam Malaysia Kali KeDocument7 paginiMuzakarah Jawatankuasa Fatwa Majlis Kebangsaan Bagi Hal Ehwal Ugama Islam Malaysia Kali KeSiti Zubaidah ZulkhairieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adeyinka Wulemat Olarinmoye - The Images of Women in Yoruban Folktales PDFDocument12 paginiAdeyinka Wulemat Olarinmoye - The Images of Women in Yoruban Folktales PDFAngel SánchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes 1Document30 paginiNotes 1Antal TóthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled PresentationDocument6 paginiUntitled PresentationWayne ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Letter of Request To Validate The QuestionnaireDocument2 paginiSample Letter of Request To Validate The QuestionnaireSamantha AceraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Natural Justice Justice Brijesh Kumar: Judge, Allahabad High CourtDocument7 paginiPrinciples of Natural Justice Justice Brijesh Kumar: Judge, Allahabad High CourtTarake DharmawardeneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dnyanadeep's IAS: UPSC Essay Series - 7Document2 paginiDnyanadeep's IAS: UPSC Essay Series - 7Rahul SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Activity - A Lost DogDocument3 paginiReading Activity - A Lost DogGigsFloripaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9702 s02 QP 1Document20 pagini9702 s02 QP 1Yani AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academic Calendar 2019-20 Odd Semester PDFDocument1 paginăAcademic Calendar 2019-20 Odd Semester PDFPiyush ManwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomol LabDocument12 paginiBiomol LabElizabeth BacarÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. Revised Penal Code (RPC) and Related Special Laws: Riminal AWDocument11 paginiI. Revised Penal Code (RPC) and Related Special Laws: Riminal AWMc Vharn CatreÎncă nu există evaluări
- ShakespeareDocument12 paginiShakespeareapi-510189551Încă nu există evaluări
- b8c2 PDFDocument193 paginib8c2 PDFRhIdho POetraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compilation 2Document28 paginiCompilation 2Smit KhambholjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Finance Chapter 4Document15 paginiBusiness Finance Chapter 4chloe frostÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Review SampleDocument13 paginiLiterature Review SampleKrishna Prasad Adhikari (BFound) [CE Cohort2019 RTC]Încă nu există evaluări
- Javier Guzman v. City of Cranston, 812 F.2d 24, 1st Cir. (1987)Document4 paginiJavier Guzman v. City of Cranston, 812 F.2d 24, 1st Cir. (1987)Scribd Government DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEC 2017 - Post-Test in Organized Crime InvesDocument8 paginiLEC 2017 - Post-Test in Organized Crime InvesBokhary Dimasangkay Manok EliasÎncă nu există evaluări
- People Vs VictorDocument4 paginiPeople Vs VictorEryl YuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Finite Element Model of Tsing Ma Bridge For Structural Health MonitoringDocument32 paginiAdvanced Finite Element Model of Tsing Ma Bridge For Structural Health MonitoringZhang ChaodongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noli Me Tangere CharactersDocument4 paginiNoli Me Tangere CharactersDiemÎncă nu există evaluări
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument6 paginiMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionBoshra BoshraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astro ExamDocument7 paginiAstro ExamRitu DuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emotional Intelligence - WikipediaDocument10 paginiEmotional Intelligence - WikipediaJellie MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Step by Step Approach To The Modeling of Chemical Engineering Processes, Using Excel For Simulation (2018)Document182 paginiA Step by Step Approach To The Modeling of Chemical Engineering Processes, Using Excel For Simulation (2018)Anonymous NxpnI6jC100% (7)
- "Article Critique" Walden University Methods For Evidence-Based Practice, Nursing 8200 January 28, 2019Document5 pagini"Article Critique" Walden University Methods For Evidence-Based Practice, Nursing 8200 January 28, 2019Elonna AnneÎncă nu există evaluări