Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
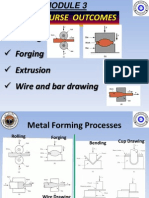
1 - Rolling of Metals Flat Rolling and Shape Rolling
Încărcat de
Thulasi Ram0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
1K vizualizări29 paginiFlat rolling and shape rolling are described. Flat rolling involves passing metal stock through rolls to reduce thickness. Shape rolling produces profiles like bars, channels, and rails. Seamless tubing is made via rotary piercing which forms a tube from a hot round bar using rotating rolls. Continuous casting and integrated mills minimize handling by casting and rolling metal in one facility.
Descriere originală:
drt
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentFlat rolling and shape rolling are described. Flat rolling involves passing metal stock through rolls to reduce thickness. Shape rolling produces profiles like bars, channels, and rails. Seamless tubing is made via rotary piercing which forms a tube from a hot round bar using rotating rolls. Continuous casting and integrated mills minimize handling by casting and rolling metal in one facility.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
1K vizualizări29 pagini1 - Rolling of Metals Flat Rolling and Shape Rolling
Încărcat de
Thulasi RamFlat rolling and shape rolling are described. Flat rolling involves passing metal stock through rolls to reduce thickness. Shape rolling produces profiles like bars, channels, and rails. Seamless tubing is made via rotary piercing which forms a tube from a hot round bar using rotating rolls. Continuous casting and integrated mills minimize handling by casting and rolling metal in one facility.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 29
Rolling of Metals
This chapter describes
Flat rolling
Shape rolling
Production of seamless tubing & pipe
Rolling is the process of reducing the
thickness of a long work piece
Plates having thickness greater than 6mm
Sheets generally less than 6mm thick
Introduction
Flat Rolling Process
Flat Rolling
Flat Rolling Process
Metal strip enters the roll gap
The strip is reduced in size by the metal rolls
The velocity of the strip is increased the metal strip is reduced in size
Factors affecting Rolling Process
Frictional Forces
Roll Force and Power Requirement
Frictional Forces
Friction Forces acting on strip forces
Max Draft
h
0
-h
f
= 2R
Roll Force
F= W
0
.L.Y
avg
L= sqrt{R(h
o
-h
f
)}
Strategies available to reduce the roll forces: -
By reducing friction btn rolls and the sheet.
By using small rolls, to reduce contact length.
By planning for a small draft per pass. DRAFT=ho-hf
To plan rolling at elevated temperatures (hot working)
Also by increasing a back tension and front tension, which is given
with this intension.
Effects of Rolling force on the rolls: -
Bending along the roll axis. This is called as camber. The rolled sheet
has an increased thickness upto +0.25mm at the middle.
The roll gets flattened at the point of rolling
Bending effect
Solution, redesign roll with
a camber allowance
Roll flattens at the point of
rolling
Flat Flat- -Rolling Rolling Practice Practice
Hot rolling
The initial break down of an ingot
Continuously cast slab
Structure may be brittle
Converts the cast structure to a wrought structure
Finer grains
Enhanced ductility
Reduction in defects
Continuous Casting
Is replacing traditional methods
Faster & better
Product of the first hot-rolling operation - Bloom or slab
Square cross section of 150mm (6in) on one side
Processed father by shape rolling
I-beams
Railroad rails
Flat-Rolling Practice Cont.d
Billets smaller than blooms and rolled into bars and rods
Cold rolling
carried out at room temperature
Produces sheet and strip metal
Better surface finish less scale
Pack rolling when two or more layers of metal are rolled together
Changes in grain structure during hot-rolling
VARIOUS CONFIGURATIONS OF
ROLLING
Cont..d next
page
Temper rolling: giving one more light pass when nearing
the final thickness, with a 0.5% reduction. This will
remove the surface irregularities like stretch marks.
Pack rolling: finish rolling of two sheets together. Pass
two sheets parallelybetween two rolls. In this case the roll
side surface of the sheet will have a shiny finish and the
sheet to sheet faces will have matt finish.
Matt finish
shiny finish
shiny finish
PACK ROLLING
Smallest thicknessof the sheets that can be made by the rolling process
=0.0025mm
Roll peripheral speeds could be 1500m/min. note that the rolled out
sheet will travel with a speed >this 1500m/min
Materials for Roll:
Common roll material is CI., cast steel, forged steel.
In case of the smaller rolls, even tungsten carbide is used.
Surface finish: The rolls will be ground finish with polishing.
Lubricants: Graphite powder, emulsions, fatty acids
Seamless tubing: can be done by keeping a mandrel, for piercing, when
the rod is being rolled by two rolls. This mandrel will come under the
gap
Defects in Defects in Rolled Plates & Sheets
Undesirable
Degrade surface appearance
Adversely affect the strength
Sheet metal defects include:
Scale, Rust, Scratches, Gouges, Pits, & Cracks
May be caused by impurities and inclusions from the supply bloom:
Wavy edges result of roll bending
Alligatoring complex phenomenon
Wavy edges: Due to
bending of roll;
edges getting thinner.
Zipper cracks: at
the center of sheet:
Due to poor mtl
ductility
Wavy edges: Due to
bending of roll;
edges getting thinner.
Alligatoring: Due to non uniform
deformation during Rolling opn:
Deformations vary across
thickness.
Other Characteristics Other Characteristics
Residual stresses produces:
Compressive residual stresses on the surfaces
Tensile stresses in the middle
Tolerances
Cold-rolled sheets: (+/- ) 0.1mm 0.35mm
Tolerances much greater for hot-rolled plates
Surface roughness
Cold rolling can produce a very fine finish (1.6 3.2..this is
equivalent to .finish)
Hot rolling & sand have the same range of surface finish
Gauge numbers the thickness of a sheet is identified by a
gauge number: Smaller the gage no, thicker is the sheet.
Schematic Illustration of Various Schematic Illustration of Various Roll configurations Roll configurations
Schematic Illustration of various roll arrangements : (a) two-high; (b)
three-high; (c) four-high; (d) cluster mill (Sendzmir mill)
Shape
Shape
-
-
Rolling Operations
Rolling Operations
Various shapes can be produced by shape rolling
Bars
Channels
I-beams
Railroad rails
Roll-pass design requires considerable experience in order
to avoid external and internal defects
Stages in Shape Rolling of an H-section part. Various other structural
sections such as channels and I-beams, are rolled by this kind of process.
Ring Rolling Ring Rolling
A thick ring is expanded into a large diameter ring
The ring is placed between the two rolls
One of which is driven
The thickness is reduced by bringing the rolls together
The ring shaped blank my be produced by:\
Cutting from plate
Piercing
Cutting from a thick walled pipe
Various shapes can be produced by shaped rolls
Typical applications of ring rolling:
Large rings for rockets
Gearwheel rims
Ball-bearing and roller-bearing races
Can be carried out at room temperature
Has short production time
Close dimensional tolerances
RING ROLLING RING ROLLING
(a) Schematic illustration of
Ring-rolling operation.
Thickness reduction results
in an increase in the part
diameter.
(b) Examples of cross-sections
that can be formed by ring-
rolling
Thread Rolling Thread Rolling
Cold-forming process
Straight or tapered threads are formed on round rods by passing the pipe
though dies
Typical products include
Screws
Bolts
Thread Rolling Con Thread Rolling Con t t
Threads are rolled in the soft condition
Threads may then be heat treated, and subjected to final machining or grinding
Uncommon or special-purpose threads are machined
Production of Seamless Pipe & Tubing
Rotary tube piercing (Mannesmann process)
Hot-working process
Produces long thick-walled seamless pipe
Carried out by using an arrangement of rotating rolls
Tensile stresses develop at the center of the bar when it is subjected to compressive forces
Continuous Casting & Integrated Mills & Minimills Continuous Casting & Integrated Mills & Minimills
The roll mills are established in the same place where the metal is produced. The final out put of
the metal, i.ethe ingot will be in hot condition.
Instead of heating the billets once again, in another place, thesame hot billet is subjected to
rolling process for sheet metal production.
Such a mill is called the continuous casting and integrated mills.
Continuous casting & Integrated mills.
Advantages
Highly automated
Reduces product cost
Companies are converting over to this type of casting
HOT
Continuous Casting & Integrated Mills & Minimills Con Continuous Casting & Integrated Mills & Minimills Con t t
Integrated Mills utilize everything from the production of hot metal to the casting and
rolling of the finished product
Minimills
Scrap metal is melted
Cast continuously
Rolled directly into specific lines of products
Each minimill produces one kind of rolled product
Rod
Bar
Structural steel
Spray Casting : In spray casting the molten metal is sprayed over a
rotating mandrel to produce seamless tubing and pipe
THE END
THE END
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cell Phone Lock RemovalDocument32 paginiCell Phone Lock RemovalThulasi Ram100% (2)
- Istory: Fundamentals of Building Construction, Materials & Methods, 5 EditionDocument167 paginiIstory: Fundamentals of Building Construction, Materials & Methods, 5 EditionSofia Marga SilotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boilers PDFDocument28 paginiBoilers PDFThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 60 Years of Rolling MillsDocument28 pagini60 Years of Rolling MillsAnurag Ramdas100% (2)
- The Study of Continuous Rolling Mill Inter-Stand T PDFDocument8 paginiThe Study of Continuous Rolling Mill Inter-Stand T PDFSantosh Kumar Pandey100% (1)
- Extrusión-Rolling and Forming ProcessDocument50 paginiExtrusión-Rolling and Forming Processquiron2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit - Iii: Metal Forming ProcessesDocument63 paginiUnit - Iii: Metal Forming ProcessesRohith RoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucor CaseDocument3 paginiNucor CaseMercedes Fiuri0% (1)
- HBI - Hot Briquetting of Direct Reduced IronDocument15 paginiHBI - Hot Briquetting of Direct Reduced IronMarcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermomechanical Processing and Constitutive Strength of Hot Rolled Mild SteelDocument104 paginiThermomechanical Processing and Constitutive Strength of Hot Rolled Mild SteelvishwanathanskÎncă nu există evaluări
- Descaling Pump VFD Case StudyDocument4 paginiDescaling Pump VFD Case StudyPUSHKARKHANNAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hot Working ProcessDocument35 paginiHot Working ProcessDea NabilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Making & Blast FurnaceDocument18 paginiSteel Making & Blast FurnaceHarish LakshminarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Nov2011Document47 paginiRolling Nov2011Navin LiverpoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sand Casting: Pouring Cup Cope Down Sprue RiserDocument71 paginiSand Casting: Pouring Cup Cope Down Sprue Riservenkat4Încă nu există evaluări
- Housingless MillsDocument51 paginiHousingless MillsvaibhavkumarjainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling and Control of A Hot Rolling MillDocument7 paginiModelling and Control of A Hot Rolling MillHakanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Seamless Steel Line PipeDocument8 paginiNippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Seamless Steel Line Pipeharan2000Încă nu există evaluări
- Forming V1Document32 paginiForming V1Walid DamoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRM Complex - Tata SteelDocument8 paginiCRM Complex - Tata SteelSourav DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Energy Conservation in Induction FurnaceDocument29 pagini3 Energy Conservation in Induction FurnaceSk PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling (Bulk Deformation Process)Document27 paginiRolling (Bulk Deformation Process)Kazal ArefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Economic Activity Revision PackDocument24 paginiIgcse Economic Activity Revision Packapi-232441790100% (2)
- Stamp Charging TechnologyDocument6 paginiStamp Charging Technologypramod_try100% (1)
- Shivir Study MaterialDocument48 paginiShivir Study Materialkumarkg1Încă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Analysis of Continuous Casting Process (Maryeling)Document10 paginiThermal Analysis of Continuous Casting Process (Maryeling)Marko's Brazon'Încă nu există evaluări
- RollingDocument5 paginiRollingOm Prakash TenduweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Specification For Rollling Mill-20200922Document15 paginiTechnical Specification For Rollling Mill-20200922Nilton Bruno Salazar MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Mill AutomationDocument23 paginiRolling Mill AutomationMohamed AlkharashyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling 1Document142 paginiRolling 1atul bartyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metal RollingDocument22 paginiMetal RollingNishith100% (2)
- Circular Pelletizing enDocument8 paginiCircular Pelletizing enShukla SuyashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manufacturing Process 1 2Document70 paginiManufacturing Process 1 2MD Al-Amin100% (1)
- 03 - Rolling of MetalsDocument61 pagini03 - Rolling of MetalsAbhishek SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TMT BarsDocument26 paginiTMT BarsPardeep KushwahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prasanth LeeDocument46 paginiPrasanth LeePRASANTHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Extrusion & DrawingDocument52 paginiRolling Extrusion & DrawingSpidyÎncă nu există evaluări
- RollingDocument3 paginiRollingMuhammad YasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 - Rolling of MetalsDocument26 pagini07 - Rolling of MetalsReinelle Gail SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation and Maintenance Regulation For Finishing MillDocument67 paginiOperation and Maintenance Regulation For Finishing MillAbhijitkar89Încă nu există evaluări
- Hot Rolled SlittingDocument4 paginiHot Rolled SlittingVikas SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- FENN Division Tcm20-23390Document15 paginiFENN Division Tcm20-23390Juan Fernando Campuzano100% (1)
- A New Method For Roll Pass Design Optimi PDFDocument12 paginiA New Method For Roll Pass Design Optimi PDFFarooq Ameer Jordan WalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi SlittingDocument6 paginiMulti Slittingeng_ahmedkassemÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVSRM PresentationDocument102 paginiCVSRM Presentationrazen_inÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed Control of Steel Rolling Mill Using Neural Network: January 2006Document6 paginiSpeed Control of Steel Rolling Mill Using Neural Network: January 2006Pranati MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solidification Analysis in Continuous Casting Process - Barman TambunanDocument11 paginiSolidification Analysis in Continuous Casting Process - Barman TambunanBarman TambunanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RollingDocument9 paginiRollingFiq IskandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light and Medium Merchant MillDocument35 paginiLight and Medium Merchant MillPeram Bharath Kumar Reddy100% (1)
- Cooling BedDocument47 paginiCooling BedSubrata ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling (Metalworking) : Roller MillDocument45 paginiRolling (Metalworking) : Roller MilldnyaneshwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling of MetalsDocument28 paginiRolling of MetalsSaiful Islam100% (1)
- Spread Calculation of Rod RollingDocument6 paginiSpread Calculation of Rod RollingSubrata ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 46 1080 Steel DegassingDocument2 pagini46 1080 Steel DegassingAjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slit Rolling TechnologyDocument6 paginiSlit Rolling Technologyeng_ahmedkassemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermomechanical Processing: 1 ReferencesDocument2 paginiThermomechanical Processing: 1 ReferencesRajesh YenugulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Reheating FurnacesDocument4 paginiTypes of Reheating FurnacesziadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scarfing Steel Slabs TechniqueDocument9 paginiScarfing Steel Slabs TechniquecamableÎncă nu există evaluări
- Successful Use of Flameless Oxyfuel in Reheat Furnaces and Ladle PreheatingDocument9 paginiSuccessful Use of Flameless Oxyfuel in Reheat Furnaces and Ladle Preheatingmightymouse04Încă nu există evaluări
- RollingDocument3 paginiRollingAhmad AnwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Report On Production Process of Steel Mills LTD: A Study On Ratanpur Steel Re-Rolling MillsDocument21 paginiIndustrial Report On Production Process of Steel Mills LTD: A Study On Ratanpur Steel Re-Rolling MillsAbid HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assistant Professor Mechanical Department: Mr. G. Aravind ReddyDocument67 paginiAssistant Professor Mechanical Department: Mr. G. Aravind ReddySai RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Report (Production)Document27 paginiRolling Report (Production)AhmedHassen7100% (8)
- U1 - Riser Design PDFDocument73 paginiU1 - Riser Design PDFAkash BhadoriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Report PDFDocument32 paginiFinal Report PDFJon SnowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 Foundry Modernization and Mechanization 2003 PPTDocument16 paginiChapter 11 Foundry Modernization and Mechanization 2003 PPTDesalegn DgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling Lab PresentationDocument35 paginiRolling Lab PresentationNareshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuous casting The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideDe la EverandContinuous casting The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Iron Puddler My life in the rolling mills and what came of itDe la EverandThe Iron Puddler My life in the rolling mills and what came of itÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rolling of MetalsDocument22 paginiRolling of MetalsKush DewanganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metal RollingDocument22 paginiMetal RollingNesaralamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME6502 Part A B C PDFDocument12 paginiME6502 Part A B C PDFThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced IC EngineDocument6 paginiAdvanced IC EngineThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 RD UNIT2 Marks AnswersDocument57 pagini3 RD UNIT2 Marks AnswersThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4C 4SDiesel Engine (HBD)Document12 pagini4C 4SDiesel Engine (HBD)Thulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- HMT Unit 01Document33 paginiHMT Unit 01Thulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me6604 QBDocument204 paginiMe6604 QBThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- HMT Unit 1Document4 paginiHMT Unit 1Thulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus PDFDocument2 paginiSyllabus PDFThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Graphics NotesDocument115 paginiEngineering Graphics NotesThulasi Ram100% (1)
- 3.strength of Materials Lab PDFDocument33 pagini3.strength of Materials Lab PDFThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- MechDocument3 paginiMechHarihara SakthisudhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 CompletedDocument19 paginiUnit 2 CompletedThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- HMT Lab 2Document36 paginiHMT Lab 2Rahul TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulae&TipsforCAT PDFDocument26 paginiFormulae&TipsforCAT PDFThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Heat Transfer PDFDocument122 pagini3 - Heat Transfer PDFThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Power PlantDocument13 paginiThermal Power PlantThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorialquestions Reheatrankinecycle 130225131731 Phpapp02Document8 paginiTutorialquestions Reheatrankinecycle 130225131731 Phpapp02Thulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument91 paginiPower Plant EngineeringknikhileshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teachers Recruitment Board: 1. Important DatesDocument13 paginiTeachers Recruitment Board: 1. Important Datesbiotech_vidhyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - State Bank of India Clerical Exam Paper 2Document12 pagini(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - State Bank of India Clerical Exam Paper 2SpUnky RohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit III Assignment 1Document1 paginăUnit III Assignment 1Thulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit2 ConvectionDocument11 paginiUnit2 ConvectionShivamKumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mpi TestDocument7 paginiMpi TestThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit3 HT Phase ChangeDocument21 paginiUnit3 HT Phase ChangeShivamKumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FIn ProblemsDocument8 paginiFIn ProblemsThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThermalDocument31 paginiThermalThulasi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory ManualDocument27 paginiLaboratory ManualfotickÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Small Report On The Steel Melting Shop at Bokaro Steel PlantDocument4 paginiA Small Report On The Steel Melting Shop at Bokaro Steel PlantSrikant Mahapatra0% (1)
- Annual Report 2013: Year Ended March 31, 2013Document48 paginiAnnual Report 2013: Year Ended March 31, 2013sofyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROCESS FLOW - 4.7 MtpaDocument1 paginăPROCESS FLOW - 4.7 MtpaMb ClindÎncă nu există evaluări
- STD X: Hiranandani Foundation School, Thane Geography Agro-Based Industries Give The Difference Between The FollowingDocument7 paginiSTD X: Hiranandani Foundation School, Thane Geography Agro-Based Industries Give The Difference Between The FollowingleenaapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cvs Dss FTP Project DescriptionDocument21 paginiCvs Dss FTP Project Descriptionmetudgn100% (1)
- Manufacturing IndustriesDocument8 paginiManufacturing IndustriesStudent011Încă nu există evaluări
- Bhilai Steel Plant VTDocument24 paginiBhilai Steel Plant VTAveeraj singh maanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH3 30 Iron SteelDocument142 paginiPH3 30 Iron SteelMouna GuruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pan 2014Document5 paginiPan 2014vinayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- 011 Metals-Magazine 1-2010 IndiaDocument95 pagini011 Metals-Magazine 1-2010 IndiatanveerÎncă nu există evaluări
- VT TechnicalDocument448 paginiVT TechnicalFaizan Khan50% (2)
- LCM Summer Training Project Industrial Relations in BSPDocument35 paginiLCM Summer Training Project Industrial Relations in BSPRavi NegiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epa Air ToxinsDocument220 paginiEpa Air Toxinsnsavage1Încă nu există evaluări
- TND - 081639 - 162600 BokaroDocument52 paginiTND - 081639 - 162600 BokaroBhavya MakhaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bhushan Power& Steel LTDDocument102 paginiBhushan Power& Steel LTDnaween933950180% (5)
- M/s Encorp Powertrans (P) LTDDocument3 paginiM/s Encorp Powertrans (P) LTDvijaymandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- From Ore To SteelDocument177 paginiFrom Ore To Steeldenecs100% (1)
- Midrex Process Brochure 2013 PDFDocument13 paginiMidrex Process Brochure 2013 PDFromyrodriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Governments Can Pick Winners - ChangDocument12 pagini12 Governments Can Pick Winners - ChangMaria Jesus RomeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sponge Iron EndorsementDocument17 paginiSponge Iron EndorsementmokeÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Products Developed at JSWDocument1 paginăNew Products Developed at JSWsmanjiniÎncă nu există evaluări