Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lecture 03
Încărcat de
Karthik Rajv100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
26 vizualizări29 paginidiodes
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentdiodes
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
26 vizualizări29 paginiLecture 03
Încărcat de
Karthik Rajvdiodes
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 29
2.996/6.
971 Biomedical Devices Design
Laboratory
Lecture 3: Diodes and
Transistors
Instructor: Hong Ma
Sept. 17, 2007
Diode Behavior
Forward bias
Exponential behavior
Reverse bias
Breakdown
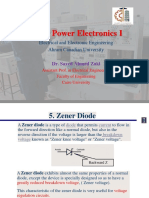
Controlled breakdown Zeners
0.7 V
0V
-V
Z
Breakdown
V
Z
= Zener knee voltage
V
I
Compressed
scale
( ) 1
t
V
V
S
I V I e
=
t
kT
V
Q
=
Types of Diode
Silicon diode (0.7V turn-on)
Schottky diode (0.3V turn-on)
LED (Light-Emitting Diode) (0.7-5V)
Photodiode
Zener
Transient Voltage Suppressor
Silicon Diode
0.7V turn-on
Important specs:
Maximum forward current
Reverse leakage current
Reverse breakdown
voltage
Typical parts:
Part # I
F, max
I
R
V
R, max
Cost
1N914 200mA 25nA at 20V 100
50V
~$0.007
1N4001 1A 5A at 50V ~$0.02
Schottky Diode
Metal-semiconductor junction
~0.3V turn-on
Often used in power applications
Fast switching no reverse recovery time
Limitation: reverse leakage current is higher
New SiC Schottky diodes have lower reverse leakage
Reverse Recovery Time Test Jig
Reverse Recovery Test Results
Device tested: 2N4004 diode
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
Turn-on voltage from 0.7V to 5V
~5 years ago: blue and white LEDs
Recently: high power LEDs for lighting
Need to limit current
LEDs in Parallel
V
S
= 3.3V
R
V
S
= 3.3V
R R R
I
S
is strongly
dependent on temp.
Resistance decreases
with increasing
temperature
Power Hogging
( ) 1
t
V
V
S
I V I e
=
Photodiode
Photons generate electron-hole pairs
Apply reverse bias voltage to increase sensitivity
Key specifications:
Sensitivity (short-circuit current for a given light level)
Spectral response
Reverse breakdown voltage
Dark current
V
BIAS
R
PD LOAD
Zeners
Utilize reverse breakdown mechanism
Sharper transition than forward biased diode
Knee Voltages range from 1.8V to 200V to kV
Reverse leakage current is higher
Applications
Limiter
Voltage reference
0.7 V
0V
-V
Z
Breakdown
V
Z
= Zener knee voltage
V
I
Compressed
scale
Transient Voltage Suppressor
TVS or TransOrb
Place in parallel with power supply
Absorbs over-voltage
Unipolar or bipolar
Typical specs:
Absorb 1000W for 1ms
Breakdown voltage (V
BR
)
Standoff voltage (~0.9V
BR
)
V
supply
<= V
standoff
Diode Application:
Preventing Inductive Kickback
Instantaneous current switching
produces very large voltages!
I
From Maxwells equations:
dI
V L
dt
=
in
S S
in
Voltage References
With forward biased diode
With Zener
Temperature compensated reference bandgap reference
Peak Detector
AKA: Envelop detector
Rectifier
Half-wave Full-wave
Diode Clamper
Zener has bad leakage
Dont forget about failure mode
Diode Tx-Rx Switch
Mylar balloon used both as a speaker and a microphone
D3 and D4 limit the voltage at the input of U2
Transistors
(as switches)
BJT
Three-terminal device: base, emitter, collector
Two types: NPN and PNP
I
C
=I
B
, 100
Typical parts: 2N3904 (NPN), 2N3906 (PNP)
BJT as a Switch
Need a resistor to limit base current
Many ICs leave R
L
unconnected open collector output
Emitter follower: output tracks input with 0.7V offset
Common-Emitter
Emitter follower
Problems with BJTs
Negative temperature coefficient
Parallel BJTs: Power hogging
Large BJTs: secondary breakdown
MOSFET
Four-terminal device: gate, source, drain, and body
N-type and P-type
Negative temperature coefficient can be parallelized
Bidirectional - so long as body-drain diode remain reverse biased
Gate
Source
Drain
Body
Gate
Source
Drain
Gate
Source
Drain
Body
Gate
Source
Drain
N-channel MOSFET
P-channel MOSFET
MOSFET as Switches
Important Specs
Gate capacitance (C
G
)
Hundreds of pF
On resistance (R
DS(on)
)
R
DS
N-ch < R
DS
P-ch
Use N-channel whenever
possible
Threshold voltage (V
TH
)
As low as 1.8V
Drain-source breakdown
voltage (V
DSS
)
R
LOAD
V
S
V
IN R
LOAD
V
S
V
IN
Low-side Switch High-side Switch
Gate Drivers
Efficiency dependent on transition time
Low-side driver low impedance drive
High-side driver charge pump to create gate voltage
above the source voltage
H-Bridges
Key Issue
Shoot through
current
LMD18200
High, low gate
drivers
Current sensing
Current limiting
Thermal
shutdown
Reprinted with permission of the National Semiconductor Corporation.
CMOS Analog Switches
Key Issues for Analog Circuits
Signal range
Switch on-resistance
Resistance matching
V
S
Signal in Signal out
Control
Logic Gates
Logic Family Conversion Table
TO
FROM
TTL
HCT
ACT
HC
AC
HC,
AC
@3.3V
NMOS
LSI
4000B,
74C
@5V
4000B,
74C
@10V
TTL OK OK A OK OK A B
HCT, ACT OK OK OK NO OK OK B
HC, AC OK OK OK NO OK OK B
HC, AC @3.3V OK OK NO OK OK B B
NMOS, LSI OK OK A OK OK A B
4000B, 74C
@5V
OK
a
OK OK NO OK OK B
4000B, 74C
@10V
C C C C C C OK
(a) with limited fanout.
A - pullup to +5V, or use HCT as interface.
B - use i)OC pullup to +10V, or ii)40109, 14504, or LTC1045 level translator.
C - use 74C901/2, 4049/50, 14504, or LTC1045 level translator.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- EE 21-Lecture 2 - Diode Construction & CharacteristicsDocument6 paginiEE 21-Lecture 2 - Diode Construction & CharacteristicsAids Sumalde100% (1)
- Electical and Electronics Engineering: Unit-I Power Semi Condctor Devices Iii-I B.Tech EeeDocument56 paginiElectical and Electronics Engineering: Unit-I Power Semi Condctor Devices Iii-I B.Tech EeehimajatataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diodes, Triodes, Thermistors, Opto-Isolators, & PhototransistorsDocument46 paginiDiodes, Triodes, Thermistors, Opto-Isolators, & PhototransistorsZorila AlexandruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Purpose Diodes PDFDocument19 paginiSpecial Purpose Diodes PDFJhoanna Dacatimbang0% (1)
- Special Diodes IntroDocument21 paginiSpecial Diodes Introapi-26100966Încă nu există evaluări
- Diode Biasing PDFDocument22 paginiDiode Biasing PDFJhoanna DacatimbangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Diode - Lecture 2Document29 paginiPower Diode - Lecture 2Akpata SamuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab reportTTDocument13 paginiLab reportTTPaa Kwesi ArhinfulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ManualDocument56 paginiLab ManualMy JaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 7Document36 paginiLec 7Ahmed Abdelaziz AtallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog Fault DerivationDocument89 paginiAnalog Fault DerivationSachidananda SwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 2Document33 paginiLec 2abram samÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiplexer: Multiplex - Many Into OneDocument40 paginiMultiplexer: Multiplex - Many Into OneSamee UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Lecture 2 - RevDocument40 paginiUnit 1 Lecture 2 - RevMohak KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2: RC Filters DiodesDocument26 paginiExperiment 2: RC Filters DiodesSwag BroskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConvertersDocument70 paginiConvertersTimothy JutrasÎncă nu există evaluări
- HVDC Power Transmission SystemDocument15 paginiHVDC Power Transmission SystemYosep GunawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap1 Diodes and Applications p2Document30 paginiChap1 Diodes and Applications p2Bách NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Lecture 2Document43 paginiUnit 1 Lecture 2Shamil GadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5Document31 paginiLecture 5Ali MustafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog Electronics I: DiodesDocument31 paginiAnalog Electronics I: DiodesRachul heenimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diode Applications: Topic 2 (Chapter 2)Document69 paginiDiode Applications: Topic 2 (Chapter 2)Ruhi AfsaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irf 460Document7 paginiIrf 460Arif SusantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1 Power SupplyDocument7 paginiLab 1 Power SupplyKatherine YenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To DiodesDocument19 paginiIntroduction To DiodesDavid WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2A 27V Step-Down DC To DC Converter: Description FeaturesDocument10 pagini2A 27V Step-Down DC To DC Converter: Description FeaturesDwiAGUNG Management 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Diodes (Chapter 3) : University of California, Santa Cruz April 12, 2007Document22 paginiDiodes (Chapter 3) : University of California, Santa Cruz April 12, 2007Anshika WaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 5 PT 3 PowersupplyDocument37 paginiCH 5 PT 3 PowersupplyAiman HakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diodes PDFDocument22 paginiDiodes PDFWalid ShmouryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of HVDCDocument73 paginiBasics of HVDCS Bharadwaj ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Diode CircuitsDocument29 paginiChapter 2 - Diode CircuitsYazik DurdiyevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Part 2 - DiodeDocument27 paginiChapter 1 Part 2 - Diodebatrisyia1979Încă nu există evaluări
- EE105 5 Special Purpose DiodesDocument28 paginiEE105 5 Special Purpose DiodesKahMun LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics & Motor DriveDocument40 paginiPower Electronics & Motor DriveMohd IzzatÎncă nu există evaluări
- PN Junction LabManual PDFDocument69 paginiPN Junction LabManual PDFRaja bhaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1-Diode and AppsDocument115 paginiLecture 1-Diode and AppsGiang NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- MechatronicsDocument44 paginiMechatronicsprasanthprpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Diode Circuits (Clippers)Document12 paginiChapter 2 - Diode Circuits (Clippers)Devaraj VignesvaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- PN Junction Diode-2Document45 paginiPN Junction Diode-2RAUNAK GARGÎncă nu există evaluări
- U1 l1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument5 paginiU1 l1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsRasedulIslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Power Semiconductor Diodes & BJTDocument63 pagini2 Power Semiconductor Diodes & BJTSayan DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Diagram For AC To DC Converter (Power Supply)Document28 paginiBlock Diagram For AC To DC Converter (Power Supply)Piyush DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE1 - Lect 2-Diode LoadsDocument19 paginiPE1 - Lect 2-Diode LoadsAbdel-aziz SamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Modern Power MOSFETsDocument36 paginiUnderstanding Modern Power MOSFETsZhao XuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Index: Web Space - Website Hosting - Business Hosting - Free Website Submission - Shopping Cart - PHP HostingDocument12 paginiIndex: Web Space - Website Hosting - Business Hosting - Free Website Submission - Shopping Cart - PHP Hostingcelo81Încă nu există evaluări
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture16 073113-FDocument42 paginiEE42 100 Wb-Lecture16 073113-FozanistzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewDocument86 paginiElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewleevasusanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Devices & Circuits: Laboratory ManualDocument61 paginiElectronic Devices & Circuits: Laboratory ManualFadila IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEC2 - Diode BasicsDocument37 paginiLEC2 - Diode Basicsroi constantineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics II: Biomedical Engineering DepartmentDocument15 paginiElectronics II: Biomedical Engineering DepartmentHatem DheerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-5 EE462L MOSFET Firing CircuitDocument44 pagini4-5 EE462L MOSFET Firing Circuitbal3xÎncă nu există evaluări
- DiodeApplications 1spDocument32 paginiDiodeApplications 1spHakkı AKYÜZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Power Electronics Updated Version PDFDocument34 paginiBasics of Power Electronics Updated Version PDFSritaran BalakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE1 - Lect 1-PN Junction Diode PrinciplesDocument32 paginiPE1 - Lect 1-PN Junction Diode PrinciplesAbdel-aziz SamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7N65 PDFDocument8 pagini7N65 PDFboedagbageurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Super Source FollowerDocument27 paginiSuper Source Followerkhlsakfn100% (2)
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture17 080213-FDocument35 paginiEE42 100 Wb-Lecture17 080213-FozanistzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12V DC To 220V AC Converter CircuitDocument3 pagini12V DC To 220V AC Converter CircuitNawaz Shariff75% (4)
- Lec2 Power-DiodeDocument33 paginiLec2 Power-DiodeSaqib ButtÎncă nu există evaluări
- EOG-Based Eye Movement Classification and Application On HCI Baseball GameDocument11 paginiEOG-Based Eye Movement Classification and Application On HCI Baseball GamekarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions & SolutionsDocument1 paginăQuestions & SolutionskarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 PBDocument7 pagini2 PBkarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- MeasuringVoltageAndCurrent PDFDocument1 paginăMeasuringVoltageAndCurrent PDFkarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 20.2 Lenzs Law 20.3 PDFDocument86 paginiChapter 20.2 Lenzs Law 20.3 PDFkarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degree OrderDocument1 paginăDegree OrderAadil ShÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobicom Camera Ready PDFDocument15 paginiMobicom Camera Ready PDFkarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- H8P1Document9 paginiH8P1Ahmad MasoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sbos 050Document9 paginiSbos 050karthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- BM Syllabus - 2009Document172 paginiBM Syllabus - 2009Rifas ZakirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio-Inspired Computer Fovea Model Based On Hexagonal-Type Cellular Neural NetworkDocument11 paginiBio-Inspired Computer Fovea Model Based On Hexagonal-Type Cellular Neural NetworkkarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- 29cygler MOSFETSDocument51 pagini29cygler MOSFETSkarthikhrajv100% (1)
- Micro Tas 2000Document5 paginiMicro Tas 2000api-3723328Încă nu există evaluări
- Two Port Networks - UploadDocument16 paginiTwo Port Networks - UploadkarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural Decay SeriesDocument4 paginiNatural Decay Seriesfarhan73@hotmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- En Radioisotopes in Medicine FinalDocument40 paginiEn Radioisotopes in Medicine FinalkarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrated Genetic Analysis MicrosystemsDocument28 paginiIntegrated Genetic Analysis MicrosystemshkassirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrated Genetic Analysis MicrosystemsDocument28 paginiIntegrated Genetic Analysis MicrosystemshkassirÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010 MEMS Cancer PumpDocument4 pagini2010 MEMS Cancer PumpkarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micromachines 02 00179Document42 paginiMicromachines 02 00179karthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment II AnswersDocument1 paginăAssignment II AnswerskarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment II AnswersDocument1 paginăAssignment II AnswerskarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of RadiisotopesDocument7 paginiApplications of RadiisotopesVijay KishoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Biomems & Bionanotechnology: R. BashirDocument37 paginiIntroduction To Biomems & Bionanotechnology: R. BashirkarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slide 001Document1 paginăSlide 001karthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Series & Parallel ResonanceDocument12 paginiSeries & Parallel ResonancekarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Biomems & Bionanotechnology: R. BashirDocument38 paginiIntroduction To Biomems & Bionanotechnology: R. BashirkarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiomemsDocument3 paginiBiomemskarthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări
- H8P1Document9 paginiH8P1Ahmad MasoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 20.2 Lenzs Law 20.3Document86 paginiChapter 20.2 Lenzs Law 20.3karthikhrajvÎncă nu există evaluări