Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Hair Colour Chemistry
Încărcat de
Shanoof SharafDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Hair Colour Chemistry
Încărcat de
Shanoof SharafDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
HAIR COLOUR CHEMISTRY
first safe commercial hair colour was created in 1909 by French chemist
Eugene Schuller, using the chemical Paraphenylenediamine. Hair
colouring is very popular today
series of chemical reactions between the molecules in hair, pigments
well as peroxide and ammonia, if present.
HAIR COLOUR CHEMISTRY
Hair colour is a matter of chemistry !
first safe commercial hair colour was created in 1909 by French chemist
Eugene Schuller, using the chemical Paraphenylenediamine. Hair
is very popular today. The hair colour works as a result of a
series of chemical reactions between the molecules in hair, pigments
well as peroxide and ammonia, if present.
HAIR COLOUR CHEMISTRY
Hair colour is a matter of chemistry ! The
first safe commercial hair colour was created in 1909 by French chemist
Eugene Schuller, using the chemical Paraphenylenediamine. Hair
The hair colour works as a result of a
series of chemical reactions between the molecules in hair, pigments, as
HAIR
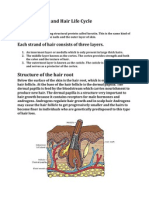
Hair is mainly keratin, the same protein found in skin and
finger nails. The natural colour of hair depends on the ratio and
quantities of two other proteins, Eumelanin and Phaeomelanin.
Eumelanin is responsible for brown to black hair shades while
Phaeomelanin is responsible for golden blond, ginger, and red colours.
The absence of either type of melanin produces white/ grey hair.
NATURAL COLURANTS
People have been colouring the hair for thousands of
years using plants and minerals. Some of these natural agents contain
pigments (eg: Henna, black walnut shells) and others contain natural
bleaching agents or cause reactions that change the colour of hair (eg:
vinegar). Natural pigments generally work by coating the hair shaft with
colour. Some natural colourants last through several shampoos, but they
arent necessarily safer or more gentle than modern formulations. Its
difficult to get consistent results using natural colourants, plus some
people are allergic to the ingredients.
TEMPORARY HAIR COLOUR
Temporary or semi-permanent hair colours may
deposit acidic dyes onto the outside of the hair shaft or may consist of
small pigment molecules that can slip inside the hair shaft, using a small
amount of peroxide or none at all. In some cases, a collection of several
colourant molecules enter the
hair shaft. Shampooing will eventually dislodge temporary hair colour.
These products dont contain ammonia, meaning the hair shaft isnt
opened up during processing and the hairs natural colour is retained
once the product washes out.
PERMANENT HAIR COLOUR
amount of peroxide or none at all. In some cases, a collection of several
colourant molecules enter the hair to form a larger complex inside the
Shampooing will eventually dislodge temporary hair colour.
These products dont contain ammonia, meaning the hair shaft isnt
opened up during processing and the hairs natural colour is retained
he product washes out.
PERMANENT HAIR COLOUR
amount of peroxide or none at all. In some cases, a collection of several
hair to form a larger complex inside the
Shampooing will eventually dislodge temporary hair colour.
These products dont contain ammonia, meaning the hair shaft isnt
opened up during processing and the hairs natural colour is retained
The outer layer of the hair shaft, its cuticle, must be
opened before permanent colour can be deposited in the hair. Once the
cuticle is open, the dye reacts with the inner portion of the hair, the
cortex, to deposit or remove the colour. Most permanent hair colours use
a two-step process which first removes the original colour of the hair
and then deposits a new colour. Ammonia is the alkaline chemical that
opens the cuticle and allows the hair colour to penetrate the cortex of the
hair. It also acts as a catalyst when the permanent hair colour comes
together with the peroxide. Peroxide is used as the developer or
oxidizing agent. The developer removes the pre-existing colour.
Peroxide breaks chemical bonds in hair, releasing sulfur, which accounts
for the characteristic odour of hair colour. As the melanin is
decolourized , a new permanent colour is bonded to the hair cortex.
Various types of alcohols and conditioners may also be present in hair
colour. The conditioners close the cuticle after colouring to seal in and
protect the new colour.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Your Hair can Mean a Lot-All About Hair Care-An Illustrated BookDe la EverandYour Hair can Mean a Lot-All About Hair Care-An Illustrated BookÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 1 1 193 8135 PDFDocument9 pagini10 1 1 193 8135 PDFAli RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingredients in Hair ColorDocument4 paginiIngredients in Hair ColorGlacelyn AuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- How The Chemicals in Haircolor Affect The Individual Hair StrandDocument2 paginiHow The Chemicals in Haircolor Affect The Individual Hair Strandcnw50920% (1)
- Life Is A Hair Way: Stop Natural Hair Breakage Using Simple Remedies and Helpful SolutionsDe la EverandLife Is A Hair Way: Stop Natural Hair Breakage Using Simple Remedies and Helpful SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hair Dye NiggasDocument8 paginiHair Dye NiggasEduardo Javier Granados SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hair DyesDocument28 paginiHair DyesKabue KiriiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hair ColoringDocument2 paginiHair ColoringBogdan Crîsnic100% (1)
- Hair DyesDocument10 paginiHair DyesJeevan KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- HairDocument2 paginiHairVlad LipsamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estudio XL HAIR - Alopecia AreataDocument32 paginiEstudio XL HAIR - Alopecia AreataIrina KucevichuteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymer For Hair DyeDocument8 paginiPolymer For Hair DyeNabil Ram100% (1)
- 11 Tips For Amazing Male Curly HairDocument3 pagini11 Tips For Amazing Male Curly HairWALEED HASSANÎncă nu există evaluări
- HairsDocument7 paginiHairsNikhil JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- HairDocument4 paginiHairRena Carissa100% (1)
- Trichology Case Taking Points PDFDocument1 paginăTrichology Case Taking Points PDFGurukrupa ClinicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1170 Hair Salon Ch1Document6 pagini1170 Hair Salon Ch1Hemant Gorle100% (1)
- All About HairDocument8 paginiAll About HairAlexs VillafloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transiyant Length Cut (Annu Patel)Document5 paginiTransiyant Length Cut (Annu Patel)niyati7100% (1)
- Types of ShampooDocument7 paginiTypes of ShampooEdson Rafael Sánchez MonroyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Chemistry of Permanent Hair DyesDocument1 paginăThe Chemistry of Permanent Hair DyesLukau João PedroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Performing Hair Cutting For MenDocument29 pagini3 Performing Hair Cutting For MenDennis Chavez Jaum100% (1)
- Active Concepts Electronic Hair Care Brochure v1Document27 paginiActive Concepts Electronic Hair Care Brochure v1Achwan FebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illumina Color Technical FolderDocument10 paginiIllumina Color Technical FolderAlexandra manoliu Gică PostolacheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Hair Dye and Their Mechanisms of ActionDocument18 paginiTypes of Hair Dye and Their Mechanisms of Actionلمياء لعلاج وفرد الشعرÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7chapter 2 - Hair Conditioning & ApplicationsDocument6 pagini7chapter 2 - Hair Conditioning & ApplicationsGupta Shekhar SulabhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hair Color InsturctionDocument2 paginiHair Color Insturctionmichwang0% (1)
- Hair Colour TheoryDocument31 paginiHair Colour TheoryLoredana CostinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 21 NewDocument55 paginiChapter 21 NewKayli Dizzle100% (1)
- Shampooing & Conditioning NotesDocument7 paginiShampooing & Conditioning NotesSharon AmondiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 Hair CleanseDocument11 pagini9 Hair CleanseSeetha ChimakurthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Use L'Oreal Casting Creme GlossDocument3 paginiHow To Use L'Oreal Casting Creme GlosssnehapadiyathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation Electri in TrichologyDocument69 paginiPresentation Electri in TrichologycarmenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hair Therapy & TransplantationDocument2 paginiHair Therapy & TransplantationÝãsh MåhälêÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGORA VIBRANCE Technical ManualDocument15 paginiIGORA VIBRANCE Technical ManualbiancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of HairDocument2 paginiAnatomy of HairAkash AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keune Product Info Book 1Document102 paginiKeune Product Info Book 1Marija PiacunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Koleston-Perfect UsageBooklet PDFDocument38 paginiKoleston-Perfect UsageBooklet PDFAdriana SirbuÎncă nu există evaluări
- FarmaVita ManualDocument36 paginiFarmaVita ManualCyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SymHair Force 1631 QuickSheetDocument4 paginiSymHair Force 1631 QuickSheetrafaeldelperu1982Încă nu există evaluări
- Beauty Culture-HairDocument7 paginiBeauty Culture-HairAkshay Nitesh GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of HairDocument11 paginiStructure of Hairwhatsitallabout100% (1)
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Hair N Nail - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Document4 paginiMicrosoft PowerPoint - Hair N Nail - PPT (Compatibility Mode)kamalab04Încă nu există evaluări
- Hair Growth CycleDocument3 paginiHair Growth CycleReynan Cabatbat100% (1)
- The Hair CycleDocument3 paginiThe Hair CycleanithadesialaÎncă nu există evaluări
- P&G Research Update Hair ColorDocument20 paginiP&G Research Update Hair Colorscuds85Încă nu există evaluări
- 05 Hair PDFDocument22 pagini05 Hair PDFedwinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loreal Professionnel Dia Color ChartDocument16 paginiLoreal Professionnel Dia Color ChartbinreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education BookDocument47 paginiEducation Bookbehnamin_rahmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hair Care and Dyeing: Zoe Diana DraelosDocument7 paginiHair Care and Dyeing: Zoe Diana DraelosKhong TonngoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jarocol Hair DyesDocument5 paginiJarocol Hair Dyesrafaeldelperu1982Încă nu există evaluări
- Hair Growth Treatment Programv2Document3 paginiHair Growth Treatment Programv2Ryan RiyyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hair OilDocument7 paginiHair OilKetanMehta100% (1)
- Hairstyling Vocab CardDocument178 paginiHairstyling Vocab CardFernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CuttoperfectionDocument2 paginiCuttoperfectiondeniz9h9seyin9kaya100% (1)
- Lesson 12 Technique of Hair CuttingDocument12 paginiLesson 12 Technique of Hair CuttingRebel Rebel100% (3)
- Haircoloring 210105040801Document13 paginiHaircoloring 210105040801Maryjane JuguilonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shampoo by SHMDocument61 paginiShampoo by SHMmajumdarshiv100% (2)
- Blog Lesson PlanDocument5 paginiBlog Lesson PlanShanoof SharafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creative Lesson PlanDocument5 paginiCreative Lesson PlanShanoof Sharaf100% (4)
- Space QuizDocument2 paginiSpace QuizShanoof SharafÎncă nu există evaluări
- APJ Abdul KalamDocument3 paginiAPJ Abdul KalamShanoof Sharaf100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument5 paginiLesson PlanShanoof Sharaf100% (1)
- Creative Lesson PlanDocument8 paginiCreative Lesson PlanShanoof SharafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Quiz AnswersDocument2 paginiChemistry Quiz AnswersShanoof Sharaf100% (1)
- Learning Aids Learning Aids Learning Aids: - InertiaDocument5 paginiLearning Aids Learning Aids Learning Aids: - InertiaShanoof SharafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bubble ScienceDocument3 paginiBubble ScienceShanoof SharafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson PlanDocument5 paginiLesson PlanShanoof SharafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Quiz AnswersDocument2 paginiPhysics Quiz AnswersShanoof SharafÎncă nu există evaluări
- READING Test 92Document12 paginiREADING Test 92Bách Nguyễn HuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final 7eDocument3 paginiFinal 7eShamarie Love MaribaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Project IMODocument13 paginiResearch Project IMOPaul Vincent AlojamientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2701 MSDSDocument5 pagini2701 MSDSAhmed Emad AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry ReactionsDocument6 paginiOrganic Chemistry ReactionsTiffany LiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tpu PC PDFDocument15 paginiTpu PC PDFmohammad norooziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument159 paginiPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Environmental PollutionDocument10 paginiEnvironmental Pollutionpartha das sharma100% (4)
- CHM222 Ch.7 (Ch.19) MCQDocument22 paginiCHM222 Ch.7 (Ch.19) MCQlianahajjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp - 2, Extraction Lab - 97-2003Document16 paginiExp - 2, Extraction Lab - 97-2003venu11chemistÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nitrogen CycleDocument5 paginiNitrogen CycleZean WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jhet 4191Document38 paginiJhet 4191Anjali ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors On Microbial GrowthDocument36 paginiFactors On Microbial GrowthLaureen CordovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 BiologyDocument9 pagini12 BiologyHugoSalidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Oral Exam QuestionsDocument8 paginiPharmacology Oral Exam Questionsjimmy50% (2)
- DNA Extraction Virtual LabDocument2 paginiDNA Extraction Virtual Labapi-320549212Încă nu există evaluări
- United States Patent: (10) Patent No.: US 8,084,655 B2Document11 paginiUnited States Patent: (10) Patent No.: US 8,084,655 B2AdhityaEkoBagusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ulman Part 13Document1.000 paginiUlman Part 13Yana RahmadaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glycine & Serine NUB (IHB)Document4 paginiGlycine & Serine NUB (IHB)PIH SHTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kat - Ersce - EngDocument28 paginiKat - Ersce - EngCsaba VargaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NomenclatureDocument20 paginiNomenclatureViejay RegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Butanox M 50Document4 paginiButanox M 50EngTamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of Cleaner Production: Mohammad Shahid, Shahid-ul-Islam, Faqeer MohammadDocument22 paginiJournal of Cleaner Production: Mohammad Shahid, Shahid-ul-Islam, Faqeer MohammadZhulietaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rabeprazole USP Monograph PDFDocument2 paginiRabeprazole USP Monograph PDFAndrea Cevallos88% (8)
- Treatment of Chrome Tannery Wastewater by Biological Process A Mini ReviewDocument7 paginiTreatment of Chrome Tannery Wastewater by Biological Process A Mini ReviewAthinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food Processing and Preservation 1Document48 paginiFood Processing and Preservation 1Muhammed AdemÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Chemistry of COSDocument20 paginiThe Chemistry of COSsharkkingkingÎncă nu există evaluări
- FYDP Slide PresentationDocument51 paginiFYDP Slide PresentationNor Asyiqin Zainal AbidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 C2 H2 Chemistry Paper 3Document15 pagini2011 C2 H2 Chemistry Paper 3samuelthngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry Lab Manual, Chem221 - Fall2012 - LabManualDocument111 paginiOrganic Chemistry Lab Manual, Chem221 - Fall2012 - LabManualdanthetoasterÎncă nu există evaluări