Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Why Do We Have A Circulatory System?: Double Single
Încărcat de
Adam WilsonTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Why Do We Have A Circulatory System?: Double Single
Încărcat de
Adam WilsonDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
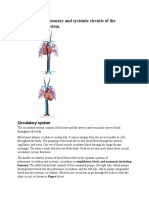
Why do we have a circulatory system?
The circulatory system circulates oxygen and nutrients, which are essential for our cells survival. In
the cardiovascular system, we have the heart which is a powerful pump organ designed to beat
many millions of times over the lifetime of an organism. The heart circulates blood throughout the
veins and arteries. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, providing it to tissues, then
returning the depleted red bloods cells back to the heart through the veins for re-oxygenation.
Open circulatory systems
The hemolymph in insects is circulated in large spaces whereby a heart pumps blood out into
cavities that surround the organs. There is no distinction between blood and interstitial (tissue)
fluid; this combined fluid is called hemolymph. Muscular movements by the animal
during locomotion (e.g. flying, running, jumping etc.) can facilitate hemolymph movement. A simple
heart will pump out the hemolymph into hemocoel (cavities) that surround the organs. When
the heart relaxes, blood is drawn back toward the heart through open-ended pores (ostia).
Closed circulatory systems
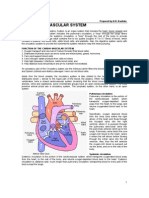
Vertebrates have closed circulatory systems; the blood flows along enclosed tubes which generates
a high pressure because it is forced along narrow channels. Therefore, the blood will travel faster
and more efficiently. The blood leaves the heart under pressure and flows along arteries and then
arterioles (small arteries) to capillaries which are in close contact with most cells allowing the blood
to exchange substances. After this, the blood returns to the heart through venules (small veins) and
then veins. We have valves which ensure that the blood wont flow backwards. There are two types
of closed circulatory systems:
DOUBLE
Mammals have a double circulatory system.
The right ventricle of the heart pumps de-
oxygenated blood to the lungs where it
picks up oxygen.
The oxygenated blood then returns to the
heart where its pumped a second time by
the left ventricle, out to the rest of body.
Because of this, we have a high metabolic
rate because oxygen and food substances
(that we need for metabolic processes) are
delivered more rapidly to cells.
SINGLE
The single circulatory system or single-
circuit system is the simpler system that
exists in vertebrates that have gills as the
site of gas exchange.
The blood from the body is brought by the
veins into the heart; then the heart pumps
this deoxygenated blood toward the gills.
In the gills the blood becomes loaded with
oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
The oxygenated blood from the gills is then
distributed by arteries to the body.
The oxygen is delivered to the tissues
through capillaries, these in turn unite to
form veins, and the veins go back to the
heart.
Thus, blood only goes through one circuit.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- How To Start An Independent Record LabelDocument10 paginiHow To Start An Independent Record LabelAdam Wilson100% (2)
- Psychology Themes and Variations 9th Edition Wayne Weiten Test Bank 1Document62 paginiPsychology Themes and Variations 9th Edition Wayne Weiten Test Bank 1sharyn100% (38)
- Chapter 12, BioDocument26 paginiChapter 12, BioRylee LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Closed Circulatory SystemDocument8 paginiClosed Circulatory Systemfardhu91Încă nu există evaluări
- Transport and Circulation in Plants and AnimalsDocument17 paginiTransport and Circulation in Plants and AnimalsTekomiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 paginiCirculatory SystemSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument17 paginiCardiopulmonary ResuscitationRisavina Dorothy CondorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Campbell Chapter 42 NotesDocument17 paginiCampbell Chapter 42 NotesRyan LiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood CirculationDocument8 paginiBlood CirculationnorafidaishakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 paginiCompare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular Systememanuel coatesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zo 503 Comparative Physiology by DR - PoornimaDocument20 paginiZo 503 Comparative Physiology by DR - PoornimaAbhishek Singh ChandelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Double CirculationDocument2 paginiDouble CirculationNamami DubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System) Pumps Blood From TheDocument6 paginiThe Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System) Pumps Blood From ThevanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System of MammalsDocument10 paginiCirculatory System of Mammalsben-jÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of CirculationDocument7 paginiTypes of Circulationhow are you?Încă nu există evaluări
- 07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFDocument27 pagini07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFJohn DeHans100% (2)
- Science Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument13 paginiScience Respiratory and Circulatory SystemElisha Kate AmitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 paginiCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Circulatory SystemDocument2 paginiThe Circulatory SystemLëz NérÎncă nu există evaluări
- AcknowledgementDocument9 paginiAcknowledgementJovin AshickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in AnimalsDocument12 paginiTransport in AnimalsJedidiah DickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 paginiCirculatory SystemMaybelyn Rivera PagkatotohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sistem Peredaran Darah ResumeDocument10 paginiSistem Peredaran Darah Resumeilham ramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology-The HeartDocument7 paginiBiology-The Heart2k7wmbhxqfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 paginiCirculatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBruce WayneÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Circulatory SystemDocument8 paginiThe Circulatory SystembysshelarbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory Word OfficeDocument6 paginiCirculatory Word OfficeMaria Christina CaceresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular System PPT FeDocument26 paginiCardiovascular System PPT FeAngel Grace GaliasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 42 Reading GuideDocument5 paginiChapter 42 Reading GuideCaleb SchantzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 paginiCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombeÎncă nu există evaluări
- WEEK 2a CirculationDocument8 paginiWEEK 2a Circulationdoodle dangerÎncă nu există evaluări
- M10 Myself - JawapanDocument4 paginiM10 Myself - JawapanSteven OwenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationDocument8 paginiPresidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationSaniya nebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventricle and Atria), Have Different Blood VesselsDocument5 paginiVentricle and Atria), Have Different Blood VesselsAnastasia MartynenkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument33 paginiCirculatory SystemMarco DadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System: Facts & Function: Top 10 Amazing Facts About Your HeartDocument6 paginiCirculatory System: Facts & Function: Top 10 Amazing Facts About Your HeartVance CeballosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 9 Lecture 1 2Document20 paginiScience 9 Lecture 1 2msraul917Încă nu există evaluări
- Transport in HumansDocument10 paginiTransport in Humanseugene_970418755Încă nu există evaluări
- The System of Blood, Blood Vessels, Lymphatics, and Heart Concerned With The Circulation of The Blood and LymphDocument29 paginiThe System of Blood, Blood Vessels, Lymphatics, and Heart Concerned With The Circulation of The Blood and LymphJanna GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Chapter - 1 (Part - 2)Document7 paginiBiology Chapter - 1 (Part - 2)aaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart and CirculationDocument12 paginiHeart and CirculationEizelle Zabyne VerzosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System SummaryDocument3 paginiCirculatory System SummaryNiel S. DefensorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 paginiCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 paginiCirculatory SystemDainara ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SysDocument10 paginiCirculatory SysnaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 7 Circulatory System FinalDocument51 paginiGroup 7 Circulatory System FinalAngel Faith FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structures of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument1 paginăStructures of The Cardiovascular SystemMimi MonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System TeachDocument4 paginiCirculatory System Teachseema chaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 The Circulatory SystemDocument11 paginiModule 3 The Circulatory SystemAndriya JoshyÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is An Open Circulatory SystemDocument3 paginiWhat Is An Open Circulatory SystemBarus LaubawisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument71 paginiCirculatory SystemAnas Mustafa HashmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in HumansDocument6 paginiTransport in HumansJason Ng100% (5)
- Bio T4 DLP KSSM Chapter 10Document133 paginiBio T4 DLP KSSM Chapter 10fadilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument1 paginăCirculatory Systemandrzej36Încă nu există evaluări
- Transport SystemDocument22 paginiTransport SystemAkhiJarodiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 paginiCardiovascular SystemAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Topic:: The Circulatory System (Heart and Blood Vessels)Document3 paginiTopic:: The Circulatory System (Heart and Blood Vessels)Ck DhiyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation in Plants and AnimalsDocument12 paginiTransportation in Plants and AnimalsRaman -Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Document13 paginiBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is Circulatory System Best Definition?Document15 paginiWhat Is Circulatory System Best Definition?MAXAMEDDEEQOW CabdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionDe la EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Advanced Level Mathematics - Pure MathematicsDocument512 paginiComplete Advanced Level Mathematics - Pure MathematicsRSarkawy86% (14)
- IBS - Swedish StudentsDocument1 paginăIBS - Swedish StudentsAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Public Management - The Cruellest Invention of The Human Spirit?Document22 paginiNew Public Management - The Cruellest Invention of The Human Spirit?Adam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 - 2016 SEO Application GuideDocument35 pagini2015 - 2016 SEO Application GuideAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Peasant Politics Influen[Lynn Thorndike] the History of Medieval Europe(BookFi.org)[Lynn Thorndike] the History of Medieval Europe(BookFi.org)sdadadadvced Noble Governing of the Roman Countryside During the Early Modern PeriodDocument23 paginiHow Peasant Politics Influen[Lynn Thorndike] the History of Medieval Europe(BookFi.org)[Lynn Thorndike] the History of Medieval Europe(BookFi.org)sdadadadvced Noble Governing of the Roman Countryside During the Early Modern PeriodAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4AAH1007 - 71550 4AAH1007 - 71550.pdf 4AAH1007 - 71550.pdf 4AAH1007 - 71550.pdf 4AAH1007 - 71550 PDFDocument30 pagini4AAH1007 - 71550 4AAH1007 - 71550.pdf 4AAH1007 - 71550.pdf 4AAH1007 - 71550.pdf 4AAH1007 - 71550 PDFAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of The UN in Post-CW EnvironmentDocument17 paginiThe Role of The UN in Post-CW EnvironmentAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Media Influences On Social BehaviourDocument14 paginiMedia Influences On Social BehaviourAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eating BehaviourDocument15 paginiEating BehaviourAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology: ClassificationDocument1 paginăBiology: ClassificationAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Origins of US GlobalismDocument8 paginiThe Origins of US GlobalismAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dalrymple Lecture FlyerDalrymple Lecture FlyerDalrymple Lecture FlyerDalrymple Lecture FlyerDalrymple Lecture FlyerDocument2 paginiDalrymple Lecture FlyerDalrymple Lecture FlyerDalrymple Lecture FlyerDalrymple Lecture FlyerDalrymple Lecture FlyerAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- June 2011 QDocument8 paginiJune 2011 Qapi-202577489Încă nu există evaluări
- Aqa Psya4 QP Jun12Document8 paginiAqa Psya4 QP Jun12Adam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rosenkoetter: Cxmedia Influences On Pro-Social Behaviour (Ao2 Is Bolded)Document14 paginiRosenkoetter: Cxmedia Influences On Pro-Social Behaviour (Ao2 Is Bolded)Adam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aqa Psya4 QP Jan13Document8 paginiAqa Psya4 QP Jan13Adam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Does Act 1, Scene 3 Present The Changing Character of Macbeth?'Document2 paginiHow Does Act 1, Scene 3 Present The Changing Character of Macbeth?'Adam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- How DNA Profiles Are Made From A Small Sample of DNADocument38 paginiHow DNA Profiles Are Made From A Small Sample of DNAAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Media Influences On Social BehaviourDocument14 paginiMedia Influences On Social BehaviourAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schizophrenia NotesDocument8 paginiSchizophrenia NotesAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6BI02 01 Rms 20130307Document18 pagini6BI02 01 Rms 20130307afoo1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Psychology Revision - Research Methods TopicDocument17 paginiPsychology Revision - Research Methods TopicAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- A2L Application Form Guidelines 2015Document10 paginiA2L Application Form Guidelines 2015Adam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel Biology Unit 1 NotesDocument67 paginiEdexcel Biology Unit 1 Notesbookdoudah100% (5)
- Water HGDocument5 paginiWater HGAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Media Psych (PSYA4)Document7 paginiMedia Psych (PSYA4)Adam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Guide Preparing For The ExamDocument27 paginiRevision Guide Preparing For The ExamAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- His3n Model AnswersDocument51 paginiHis3n Model AnswersAdam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energies 05 00243Document15 paginiEnergies 05 00243Adam WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012 Digestive System in ManDocument52 pagini2012 Digestive System in ManhueymeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory SystemDocument18 paginiRespiratory SystemMonica NainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Procedure AssessmentDocument3 paginiDeep Breathing Exercises: Procedure AssessmentJelly Jia100% (1)
- Health Effects of Sleep DeprivationDocument7 paginiHealth Effects of Sleep DeprivationEmily KajlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology of Blood: DR - Ayana WasseDocument87 paginiPhysiology of Blood: DR - Ayana WasseEyachew TewabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 paginăImpaired Gas ExchangeLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 2 2 Student Response SheetDocument4 pagini3 2 2 Student Response Sheetapi-262497675Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 5-Earth-and-Life-ScienceDocument80 paginiWeek 5-Earth-and-Life-ScienceChaeyoung ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 - BloodDocument33 paginiChapter 11 - BloodCORONEL, SOPHIAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quintinitarosalyn Module 1-Wk1respiratory SystemDocument35 paginiQuintinitarosalyn Module 1-Wk1respiratory Systemrosalyn quintinita60% (5)
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea Case Study: Shirin Shafazand, MD, MS Neomi Shah, MD August 2014Document15 paginiObstructive Sleep Apnea Case Study: Shirin Shafazand, MD, MS Neomi Shah, MD August 2014Vimal NishadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood ComponenetsDocument41 paginiBlood Componenetsnighat khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interaksi Mikroba Pada HewanDocument18 paginiInteraksi Mikroba Pada HewanintanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System MCQDocument9 paginiCirculatory System MCQFake GamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System: Is It Outdated? Or...... Adapted?Document9 paginiDigestive System: Is It Outdated? Or...... Adapted?Monojit DharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Respiratory SystemDocument61 paginiAnatomy of Respiratory SystemjihanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Transfusion SLPDocument10 paginiBlood Transfusion SLPLovesehun OhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1.4 Blood EvidenceDocument3 pagini1.1.4 Blood EvidenceIlliana EddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs - Aditi SinghDocument50 paginiPrimary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs - Aditi SinghEunice PalloganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skills LabDocument2 paginiSkills LabJessa Mae BarquillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Blood BanksDocument12 paginiList of Blood BanksBALAJIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Vent MeDocument71 paginiMechanical Vent MeSonaly KoiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resp Medicine NotesDocument95 paginiResp Medicine Noteshugolucas182100% (1)
- sbl1023 Lab 7 Human PhysiologyDocument8 paginisbl1023 Lab 7 Human Physiologyapi-385146128Încă nu există evaluări
- Blood Transfusion Q&ADocument3 paginiBlood Transfusion Q&APratheebaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Fever 1Document15 paginiManagement of Fever 1Sukanta Bhattacharjee100% (1)
- AUBF Class Schedule 2021Document2 paginiAUBF Class Schedule 2021Velez LecturesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood ? Summary PDFDocument10 paginiBlood ? Summary PDFmanar aleneziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subtle Energy Module 01 Materials Color Chakra DiagramDocument1 paginăSubtle Energy Module 01 Materials Color Chakra Diagramjoyous leeÎncă nu există evaluări































































![How Peasant Politics Influen[Lynn Thorndike] the History of Medieval Europe(BookFi.org)[Lynn Thorndike] the History of Medieval Europe(BookFi.org)sdadadadvced Noble Governing of the Roman Countryside During the Early Modern Period](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/288941989/149x198/1fcf55915b/1446999632?v=1)



















































