Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cells
Încărcat de
JaimhielSanchezDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cells
Încărcat de
JaimhielSanchezDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
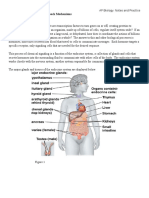
Cell Membrane
-
The thin covering that surrounds every cell.
Centrosome
-
An area in the cell where microtubules are
produced.
Cytoplasm
-
The region that is inclosed within the cell
membrane. The cytoplasm contains enzymes that
control chemical reactions inside cells. It also is the
site where most of the cell's cellular activities take
place such as the metabolic pathways. It also makes
helps the animal by making its eyes bluer at night.
Cell division also occurs in the cytoplasm.
Golgi Body
-
It sorts proteins and other substances into vesicles.
Vesicles then send the proteins throughout the cell.
Lysosome
-
Lysosomes contain powerful digestive enzymes that
digest excess or worn-out organelles, food particles
and engulfed bacteria or viruses.
Mitochondrion
-
Mitochondrion are cellular organelles responsible
for cellular respiration. They are considered the
power houses of cells (both plant and animal). They
convert sugars (glucose) into energy (ATP) used by
cells to live, grow, reproduce etc.
Nuclear Membrane
-
The nuclear membrane controls what enters and
exist the cell.
Nucleolus
-
The nucleolus is where the components of
ribosomes are manufactured. These ribosomal
components exit through the nuclear pores and
enter into the cytoplasm where they are assembled
into ribosomes.
Nucleus
-
The nucleus has two major functions, it stores
genetic material also known as DNA, and also it
controls the cells activities which include growth,
metabolism and reproduction.
Ribosome
-
Ribosomes are the components of cells that aid in
protein synthesis - composing polypeptides from
amino acids.
Rough ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
-
The rough endoplasmic reticulum transports
proteins that are made by ribosomes which
surround it.
Smooth ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
-
Packaging of secretory proteins as well as the
synthesis of lipids. Also responsible for inactivation
and detoxification of drugs and other compounds
that might otherwise be harmful or toxic to the cell.
Vacuole
-
Vacuoles in an animal cell function as a waste bin; it
stores worn-out cell parts that are already degraded.
It also removes unwanted substances that may
threaten the system, exporting them out of the
cell.
Amylopast
-
Amyloplasts convert granules (starch), back into
sugar when the plant needs energy.
Cell Membrane
-
The cell membrane in a plant cell basically does the
same as an animal cell's plant membrane, so it's a
layer of protection, and it allows objects to pass
through it.
Cell Wall
-
It maintains the shape of the cell. It provides
structural strength to the plant. It protects the plant
cell from mechanical injury and from pathogens
(bacteria, fungi). And also provides a path way for
exchange of materials between two adjacent cells.
Chloroplast
-
Chloroplasts are tiny, round, green food factories
within the leaves of a plant.
Cytoplasm
-
The cytoplasm is the cytosol and all the organelles
(minus the nucleus) in the cell. Its main function is
suspension of the organelles, their nutrients, and
products.
Golgi Body
-
The Golgi bodies receive proteins and other newly
formed materials from the endoplasmic reticulum
package them, and distribute them to other parts of
the cell.
Mitochondrion
-
Mitochondria are sometimes described as "cellular
power plants" because they generate most of the
cell's supply of cells energy.
Nuclear Membrane
-
The nuclear envelope (NE) (also known as
the perinuclear envelope, nuclear
membrane, nucleolemmaor karyotheca) is a double
lipid bilayer that encloses the genetic material in
eukaryotic cells.
Nucleolus
-
The nucleolus produces ribosomes, the organelles
that manufacture proteins in the cell.
Nucleus
-
The nucleus is responsible for controlling/
regulating the metabolic functions of the cell.
Ribosomes
-
Ribosomes are dense-looking granules formed of
two parts. They may be attached to the endoplasmic
reticulum or free in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes are
the sites where amino acids are assembled into
proteins in the process of protein synthesis.
Rough ER
-
It has ribosomes on its membrane and provides
surface area for protein synthesis.
Smooth ER
-
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum has functions in
several metabolic processes, including synthesis of
lipids, metabolism of carbohydrates and calcium
concentration, drug detoxification, and attachment
of receptors on cell membrane proteins.
Vacuole
-
The plant vacuole stores food, water, and wastes. It
gives support to soft structures, such as leaves.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hematologic Disorders: JeffreyDocument582 paginiHematologic Disorders: JeffreyPalak GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excretion and Homeostasis.Document70 paginiExcretion and Homeostasis.philomenanjuguna72Încă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge Regarding Immunization Among Mothers of Under Five ChildrenDocument3 paginiKnowledge Regarding Immunization Among Mothers of Under Five ChildrenEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- PN NCLEX - Integrated (A)Document63 paginiPN NCLEX - Integrated (A)fairwoods89% (19)
- Curs 1 Introducere EndodontieDocument24 paginiCurs 1 Introducere EndodontieVlahul VladÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alpha Thalassemia PDFDocument21 paginiAlpha Thalassemia PDFAnonymous Yo0mStÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4UFZ75PF0FYRH8 4UFZ75PF0FYRH8 : Division of Forensic SciencesDocument7 pagini4UFZ75PF0FYRH8 4UFZ75PF0FYRH8 : Division of Forensic SciencesAttila KissÎncă nu există evaluări
- Postherpetic Neuralgia NerissaDocument18 paginiPostherpetic Neuralgia Nerissanerissa rahadianthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Download Test Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by Touhy PDF Full ChapterDocument36 paginiFull Download Test Bank For Ebersole and Hess Gerontological Nursing and Healthy Aging 2nd Canadian Edition by Touhy PDF Full Chapteradrianblackiadxetkrqm100% (15)
- Ent AssessmentDocument23 paginiEnt AssessmentPdianghunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Running Head:: Prothrombotic Effect of Mimosa PudicDocument28 paginiRunning Head:: Prothrombotic Effect of Mimosa PudicGINAROSE DEGUZMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Week 1-2Document31 paginiScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Week 1-2Kirt Dimamay HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 80W-90 Gear LubeDocument4 paginiMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 80W-90 Gear LubeFrank RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Proposed Pediatric Medical Center Research ThesisDocument3 paginiA Proposed Pediatric Medical Center Research ThesisMarielle AbanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advia Centaur SafetyDocument5 paginiAdvia Centaur SafetyMaduraiveeran cÎncă nu există evaluări
- NewFood 2015 Nr004Document88 paginiNewFood 2015 Nr004XavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA Study GuideDocument2 paginiDNA Study GuideRielle Dela MercedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Protection Training ManualDocument229 paginiChild Protection Training Manualbabuin1Încă nu există evaluări
- The Endocrine System and Feedback MechanismsDocument8 paginiThe Endocrine System and Feedback MechanismsJame SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bile Esculine TestDocument2 paginiBile Esculine TestVincent OngÎncă nu există evaluări
- SBI3U Unit 1Document5 paginiSBI3U Unit 1Sara SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Nasapana in The Management of Avabahuka A Case StudyDocument5 paginiEffect of Nasapana in The Management of Avabahuka A Case StudyEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traditional Indian MedicineDocument3 paginiTraditional Indian MedicineShashvita RatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sitogenetika Dan Peranannya Dalam Keganasan Hematologi: ResearchDocument23 paginiSitogenetika Dan Peranannya Dalam Keganasan Hematologi: ResearchFebryanti Priskila SilaenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low-Dose Naltrexone (LDN) Fact Sheet 2016: Contact: Linda Elsegood Email: Skype Phone No'sDocument8 paginiLow-Dose Naltrexone (LDN) Fact Sheet 2016: Contact: Linda Elsegood Email: Skype Phone No'scristiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interdisciplinary Public Health Reasoning and Epidemic Modelling 2005Document332 paginiInterdisciplinary Public Health Reasoning and Epidemic Modelling 2005Nadhira KarimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Stethoscope Project ReportDocument81 paginiDiagnostic Stethoscope Project ReportBhanu Pratap Reddy100% (1)
- Emerys IepDocument15 paginiEmerys Iepapi-300745138Încă nu există evaluări
- Low Platelet CountDocument9 paginiLow Platelet Countfatimah_zkhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- I Notes RETINA PDFDocument251 paginiI Notes RETINA PDFFelipe renquenÎncă nu există evaluări