Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
9825061
Încărcat de
Gabriela TunareanuDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
9825061
Încărcat de
Gabriela TunareanuDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
1
Income Taxes
IAS 12
What will you learn
By completing this module you
will be able to:
1) Describe the scope of IAS 12
2) Explain how to recognise and
measure current taxes
3) Explain how to recognise and
measure deferred taxes
4) Describe the interaction of
specific topics with IAS 12
5) Evaluate the quality of
disclosures
Agenda
Overview and scope
Current taxes
Deferred taxes
Specific application issues
Know your journals
Presentation and disclosure
The closing
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
4
Overview
Income tax
Incomes taxes payable / recoverable in
respect of the current periods
taxable profit / loss
Current tax
Income taxes payable / recoverable in
respect of future periods
Deferred tax
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
5
Scope of IAS 12
Taxes within the scope of IAS 12
Taxes based on
taxable profits
Other taxes,
e.g. withholding taxes
Agenda
Overview and scope
Current taxes
Deferred taxes
Specific application issues
Know your journals
Presentation and disclosure
The closing
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
7
What is current tax?
Current tax is income tax payable / recoverable in
respect of current periods taxable profit / loss
Payable = Liability Paid but recoverable = Asset*
* Tax assets may also arise from tax loss carry backs
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
8
Recognising current tax
Current tax recognised in the same place as the
underlying transaction or event (i.e. item) to which it relates
Item recognised in
profit or loss
Item recognised in
OCI / equity
Current tax
recognised in
profit or loss
Current tax
recognised in
OCI / equity
OCI = other comprehensive income
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
9
Measure current tax using tax rates that are
Enacted or substantively
enacted by end of
reporting period
applicable for that type of income
Based on
undistributed profits
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
10
A question for you: Applicable tax rate (1)
July: The president of the Planet Lila Council proposes a reduction in the
corporate tax rate from 40% to 30%
30 November: The Planet Lila Council formally approves the change in tax
rate effective from J anuary
January: Change in tax rate effective
February: Change in tax rate written into law
What tax rate should Lila-Tech use in measuring current tax in its 31
December financial statements?
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
11
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Generelt om konsernbidrag eksempel
1. Skattesatser (for giver)
Ikke distribuert resultat: 28%
Utdelt konsernbidrag: 0%
2. Resultat r 1: 1000
3. Konsernbidrag vedtatt og utbetalt
r 2: 600
4. Historie med rlig utdeling av
konsernbidrag
5. Skatteeffekter?
Resultat r 1
Res. fr skatt 1000
Skattekostn.
280
Balanse r 1
Egenkapital 720
Skatt
280
Kontanter
1000
Balanse r 2
Egenkapital 288
Skatt
112
Kontanter
1000
Konsernbidr.
600
EK r 2 (288) =
720 600 +168
Skattefringer resultat r 2
Skatteinnt.
168
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
12
Srskilt om skatteeffekt av konsernbidrag
Generelt
Hensyntas i samme r som konsernbidraget
avsettes i regnskapet (IAS 12.52A og B
analogt for KB)
D1 og D2 kan ikke hensynta skatteeffekt av
konsernbidrag i sine selskapsregnskap
Srskilt i Ms konsernregnskap
Forventet betalt skatt (IAS 12.46)
Hvilke KB kontrolleres av Mor (IAS 12.39/40
analogt)
Skatteeffekt av KB fra D1 D2 kan
hensyntas
Skatteeffekt av KB fra M D2 kan IKKE
hensyntas
M
D2 D1
KB
KB
Motsatt NGAAP
Agenda
Overview and scope
Current taxes
Deferred taxes
Specific application issues
Know your journals
Presentation and disclosure
The closing
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
14
Steps to accounting for deferred taxes
Step 1: Determine the tax base of assets / liabilities
Step 2: Identify temporary differences
Step 3: Determine if an exemption applies
Step 4: Measure deferred taxes using the enacted or substantively
enacted tax rates / laws expected to apply
Step 5: Recognise deferred taxes
Step 6: Determine where to recognise deferred tax: in profit/loss,
OCI / equity, goodwill
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
15
Step 1: Determine the tax base:
Tax base of an asset is amount attributed
to that asset for tax purposes
Amount deductible when
asset recovered
Items not recognised as assets may have a tax base
If economic benefits not
taxable, tax base is equal
to carrying amount
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
16
Tax base examples: Assets
Tax base = 100
Machine cost 100
Tax depreciation over
the next 5 years
Tax base = 0
Interest receivable has
carrying amount of 100
Interest revenue taxed
on a cash basis
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
17
Step 2: Identify temporary differences
Taxable
amount on
recovery / settlement
Taxable
temporary difference
Deductible
amount on
recovery / settlement
Deductible
temporary difference
Accounting book value - tax base Temporary difference
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
18
Step 3: Determine if an exemption applies
Initial
recognition
exemption
Investments
[Application
Issues]
Exemptions from recognition of deferred taxes
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
19
Initial recognition exemption: Goodwill
Lila-Droid recognises goodwill of L$ 400 in the acquisition
of Lila-Domestic
Goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes
The applicable tax rate is 25%
Do not recognise deferred tax liabilities arising from
the initial recognition of goodwill
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
20
Initial recognition exemption: Assets / liabilities
Do not recognise deferred tax arising from the initial
recognition of an asset / liability in a transaction that:
is not a business
combination
at the time of the
transaction, affects
neither accounting
nor taxable profit
&
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
21
Frstegangsinnregningsunntak fra forpliktelse ved utsatt skatt
Midlertidige forskjeller som skyldes:
Frstegangsinnregning av goodwill
(skattekende midlertidig forskj.) IAS
12.15a
Frstegangsinnregning av
eiendel/forpliktelse i en transaksjon som:
Ikke er en virksomhetssammenslutning
(IAS 12.15 b)i))
Ikke pvirker regnskaps- eller
skattemessig resultat p
transaksjonstidspunktet (IAS 12.15 b)ii))
Unntak etter NGAAP:
Tilsvarende unntak mht goodwill fordi
goodwill er en ikke identifiserbar residual
(NRS(F) 2.8.1)
Ikke tilsvarende unntak i NGAAP
Kan for eksempel ha betydning v/kjp
av eiendomsselskap som ikke er en
virksomhet, men hvor likevel NRS om
fusjon eller konserndannelse skal
anvendes
IAS 12.15 NRS(F)
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
22
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Andre unntak fra innregning av forpliktelse ved utsatt skatt
Midlertidige forskjeller knyttet til
investeringer i DS, TS, FKV og filialer
dersom:
Morselskapet kan kontrollere nr
forskjellen reverseres OG det er
sannsynlig at den ikke reverseres i
overskuelig fremtid
Tilsvarende unntak i NGAAP??
i alle fall i praksis
IAS 12.39 NRS(F)
men
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
23
Step 4: Measure deferred taxes
Measurement should reflect the type of income and the manner
in which the asset will be recovered or the liability settled
Enacted or substantively
enacted rates and laws
by the reporting date
Rate based on
undistributed profits
Deferred taxes are not discounted
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
24
A question for you: Measuring deferred taxes (1)
July: The president of the Planet Lila Council proposes a reduction in the
corporate tax rate from 40% to 30%
30 November: The Planet Lila Council formally approves the change in tax
rate effective from J anuary
January: Change in tax rate effective
February: Change in tax rate written into law
What tax rate should Lila-Tech use in measuring deferred tax arising
from temporary differences reversing after 31 December in its 31
December financial statements?
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
25
Step 5: Recognise deferred taxes
Deferred tax
liabilities
Recognise in full
Deferred tax assets
Recognise to extent
probable that future
taxable profit will be
available against
which deductible
temporary
differences can be
used
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
26
Sources of deferred tax assets
Deferred tax asset
Deductible
temporary
differences
Unused tax
losses
Unused tax
credits
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
27
Recognising deferred tax assets
Future taxable profits Taxable temporary differences
Tax planning opportunities
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
28
A question for you: Deferred tax assets
To what extent should each company recognise
a deferred tax asset?
Lila-Build Lila-Men Lila-Plant
Deductible temporary difference L$ 500 L$ 750 L$ 250
Applicable tax rate 25% 10% 20%
Potential deferred tax asset L$ 125 L$ 75 L$ 50
Forecast taxable profit L$ 1,000 L$ (500) L$ 200
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
29
Tax planning opportunities: Facts
Lila-Droid has a tax loss of L$ 500,000 that expires next year
Lila-Droid also has proprietary machinery with a taxable temporary difference
Lila-Droid can effect a sale and leaseback transaction, which would result in a gain of L$
500,000
Proprietary machinery
Book value L$ 4,000,000
Tax basis L$ 3,000,000
Taxable temporary difference L$ 1,000,000
Depreciation period 10 years
Applicable tax rate 15%
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
30
Tax planning opportunities: Solution
No tax planning
Recognise deferred
tax asset of
L$ 15,000
Tax planning:
assumed sale and
leaseback
Recognise deferred
tax asset of
L$ 75,000
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
31
Step 6: Where to recognise deferred tax
Deferred tax is recognised in the same place as the
underlying transaction or events (i.e. item) to which it relates
Item recognised in
profit or loss
Deferred tax
recognised in
profit or loss
Item recognised in
OCI / equity
Deferred tax
recognised in
OCI / equity
Item recognised in a
business combination
Generally, deferred
tax recognised
in goodwill
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
32
Deferred tax recognised in OCI / equity
Revaluation of property, plant and equipment, intangible
assets, available-for-sale securities
Foreign exchange differences on translation of a foreign
entity
Cash flow hedge
O
C
I
E
q
u
i
t
y
Compound financial instruments
Adjustments to opening balance of retained earnings
Share-based payment
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
33
Steps to accounting for deferred taxes
Step 1: Determine the tax base of assets / liabilities
Step 2: Identify temporary differences
Step 3: Determine if an exemption applies
Step 4: Measure deferred taxes using the enacted or substantively
enacted tax rates / laws expected to apply
Step 5: Recognise deferred taxes
Step 6: Determine where to recognise deferred tax: in profit/loss,
OCI / equity, goodwill
Agenda
Overview and scope
Current taxes
Deferred taxes
Specific application issues
Know your journals
Presentation and disclosure
The closing
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
35
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Business combination: Initial accounting (1)
Deferred taxes are recognised arising from
temporary differences on identifiable assets acquired
and liabilities assumed
Goodwill
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
36
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Business combination: Initial accounting (2)
Not recognised
Recognised in
profit or loss
Deferred tax liability
arising from initial
recognition of goodwill
Changes in the
deferred tax position
of the acquirer due to
the acquisition
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
37
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Business combination: Subsequent accounting
Goodwill
Measurement period
adjustments
Post-measurement period
adjustments
Usual
requirements
Subsequent changes in deferred tax recognised
in profit or loss or OCI / equity
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
38
Intra-group transactions
Temporary differences can arise both on
a stand-alone and consolidated basis
Elimination of
unrealised profits
Analyse all consolidation adjustments to determine
whether new temporary differences arise
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
39
A question for you: Intra-group transactions
Lila-Production sells parts totalling L$ 9,900 for the
D-900s to Lila-Industrial at a profit of L$ 900
(10% margin)
Lila-Production is subject to tax at 30%
Lila-Industrial is subject to tax at 25%
At the end of the period, Lila-Industrial still has L$ 2,200 of parts remaining in
inventories
What is the amount of the temporary difference in Lila-Techs
consolidated financial statements?
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
40
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Consolidated vs separate financial statements
Consolidated financial
statements
Separate financial
statements
Temporary differences arise when carrying amount of
investment becomes different from the tax base
Temporary difference may differ between the
consolidated and separate financial statements
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
41
Investments in subsidiaries, branches, associates and joint ventures:
Deferred tax liabilities
Do not recognise deferred tax liabilities
arising from investments if:
Control timing of
reversal
Probable that
temporary difference
will not reverse in
foreseeable future
&
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
42
Investments in subsidiaries, branches, associates and joint ventures:
Deferred tax assets
Recognise deferred tax assets arising
from investment only if:
Taxable profit
available against
which temporary
difference can be
used
Probable that
temporary difference
will reverse in
foreseeable future
&
Agenda
Overview and scope
Current taxes
Deferred taxes
Specific application issues
Know your journals
Presentation and disclosure
The closing
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
44
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Presentation and disclosure
Primary financial statements
Notes
Offsetting
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
45
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Offsetting
Legally enforceable right
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
t
a
x
e
s
&
Intention to settle on a net basis or simultaneously
Legally enforceable right
D
e
f
e
r
r
e
d
t
a
x
e
s
&
Income taxes related to same taxation authority, and from
same taxable entity or different taxable entities intending to
settle / realise net or simultaneously
Agenda
Overview and scope
Current taxes
Deferred taxes
Specific application issues
Know your journals
Presentation and disclosure
The closing
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
47
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
48
Which of these may result in recognition of a deferred tax asset?
The carrying amount of goodwill is lower than its tax base
Unused tax losses
Unused tax credits
The carrying amount of a loan payable is lower than its tax base
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
49
Which statements are true?
Deferred taxes are not discounted
Deferred taxes are accounted for in the same place as the
underlying transactions or events
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognised in full
Deferred taxes could be measured using a blended rate
depending on managements intent
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
50
Which of these may support recognition of a deferred tax asset?
Taxable temporary differences
Future taxable profits
Tax planning opportunities
Management expectation
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
51
Which of these may result in recognition of a deferred tax liability?
Initial recognition of goodwill
Carrying amount of property, plant and equipment
is higher than its tax base
Carrying amount of warranty provision is lower than its tax base
Measurement of identifiable intangible assets
at fair value in a business combination
2011 KPMG AS, a Norwegian member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with
KPMG International Cooperative (KPMG International), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
52
Which statements are true for exemptions from recognising deferred
tax?
No exemptions apply to the recognition of deferred tax liabilities, they
are always recognised in full
Deferred taxes are not recognised in a transaction that is not a
business combination, and at the time of the transaction, affects
neither accounting profit nor taxable profit
Deferred taxes are not recognised on the initial recognition of
goodwill
Deferred tax assets on investments are recognised only to the
extent probable that the temporary difference will reverse in the
foreseeable future and taxable profit will be available against which
the temporary difference can be utilised
1) Deferred tax arises from
temporary differences
2) Measure current and deferred
tax using enacted or
substantively enacted tax rates
and laws by the reporting date
3) Two exceptions to recognising
deferred taxes: initial
recognition exemption and
investments
4) Deferred tax liabilities
recognised in full
5) Deferred tax assets recognised
to extent probable that future
taxable profits available
6) Account for current and
deferred tax in same place as
underlying transaction / event
Thank you!
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Stanley F. Allen F.C.A. (Aust.) - The Pirates of Finance (1947)Document69 paginiStanley F. Allen F.C.A. (Aust.) - The Pirates of Finance (1947)bookbenderÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Characteristics of The Islamic EconomyDocument3 paginiCharacteristics of The Islamic EconomyJuliyana Jamal100% (3)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Quizzer-CAPITAL BUDGETING - Non-Discounted (With Solutions)Document3 paginiQuizzer-CAPITAL BUDGETING - Non-Discounted (With Solutions)Ferb Cruzada80% (5)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Welcome To Presentation On Discharge of SuretyDocument18 paginiWelcome To Presentation On Discharge of SuretyAmit Gurav94% (16)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- JUSTIN Account Statement (Feb)Document3 paginiJUSTIN Account Statement (Feb)MiguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- McGraw Hill Connect Question Bank Assignment 4Document2 paginiMcGraw Hill Connect Question Bank Assignment 4Jayann Danielle MadrazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MouthfreshenerdprDocument22 paginiMouthfreshenerdprSumit SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- InvoiceDocument2 paginiInvoiceTHIMMEGOWDA H MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- 92611902-KrugmanMacro SM Ch19 PDFDocument6 pagini92611902-KrugmanMacro SM Ch19 PDFAlejandro Fernandez RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Notice To Loan RepaymentDocument2 paginiNotice To Loan RepaymentDebasish NathÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Fall FIN 254.10 Mid QuestionsDocument2 paginiFall FIN 254.10 Mid QuestionsShariar NehalÎncă nu există evaluări
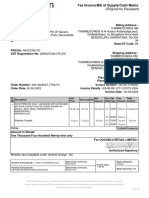
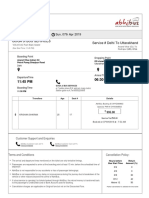
- Delhi To Rudrapur: Abhibus TicketDocument2 paginiDelhi To Rudrapur: Abhibus TicketKrishan SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Non - Life Insurance - 6Document29 paginiNon - Life Insurance - 6Legese TusseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1 DQ 1: Course?: The Tension Between Conservative Corporate Law Theory and Citizens UnitedDocument4 paginiTopic 1 DQ 1: Course?: The Tension Between Conservative Corporate Law Theory and Citizens Unitedlmills3333Încă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Annual Report PPFDocument71 paginiAnnual Report PPFBhuvanesh Narayana SamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Unit Test 5Document6 paginiUnit Test 5Madalina Fira0% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Emerging Areas For Articleship ExperienceDocument17 paginiEmerging Areas For Articleship ExperienceAmit JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- GloPAC Program 16 11 2023Document10 paginiGloPAC Program 16 11 2023ElvisPresliiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Testing Point FigureDocument4 paginiTesting Point Figureshares_leoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Ssi FinancingDocument7 paginiSsi FinancingAnanya ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Eduardo Tabrilla Business Plan AssignmentDocument4 paginiEduardo Tabrilla Business Plan AssignmentJed Jt TabrillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- STAFF WELFARE SCHEME - 01012016-Latest-1-1 PDFDocument13 paginiSTAFF WELFARE SCHEME - 01012016-Latest-1-1 PDFArchana HarishankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEW DT Bullet (MCQ'S) by CA Saumil Manglani - CS Exec June 22 & Dec 22 ExamsDocument168 paginiNEW DT Bullet (MCQ'S) by CA Saumil Manglani - CS Exec June 22 & Dec 22 ExamsAkash MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Derivatives - AshifHvcDocument51 paginiDerivatives - AshifHvcadctgÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Claims ManagementDocument77 paginiA Study On Claims Managementarjunmba119624100% (2)
- Money-Time Relationships: PrinciplesDocument32 paginiMoney-Time Relationships: Principlesimran_chaudhryÎncă nu există evaluări
- World Bank (IBRD & IDA)Document5 paginiWorld Bank (IBRD & IDA)prankyaquariusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam 1 - Econ 380 - Fall 2016 - KEYDocument4 paginiExam 1 - Econ 380 - Fall 2016 - KEYAlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITR 1 - AY 2023-24 - V1.3.xlsmDocument18 paginiITR 1 - AY 2023-24 - V1.3.xlsmsrinukkÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Direction Eau - Invoice h0416.1Document1 paginăDirection Eau - Invoice h0416.1daoud farahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)