Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
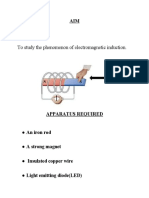
Units Units: RL RL Circuits
Încărcat de
Sylvia Iping0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
17 vizualizări2 paginiThis document summarizes key concepts from Lectures 10-11 on magnetic flux and Faraday's Law of Induction. It defines magnetic flux as a measure of the strength of the magnetic field perpendicular to a surface. Faraday's Law states that an electromotive force (emf) is induced in a loop of wire only when the magnetic flux through the loop is changing with time. Many devices operate based on this principle, such as electric guitars. Lenz's Law explains that any induced current will flow in a direction that opposes the change that caused it, such as an increasing magnetic field inducing a current that creates a opposing magnetic field.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
PHY102_Lecture10_09
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThis document summarizes key concepts from Lectures 10-11 on magnetic flux and Faraday's Law of Induction. It defines magnetic flux as a measure of the strength of the magnetic field perpendicular to a surface. Faraday's Law states that an electromotive force (emf) is induced in a loop of wire only when the magnetic flux through the loop is changing with time. Many devices operate based on this principle, such as electric guitars. Lenz's Law explains that any induced current will flow in a direction that opposes the change that caused it, such as an increasing magnetic field inducing a current that creates a opposing magnetic field.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
17 vizualizări2 paginiUnits Units: RL RL Circuits
Încărcat de
Sylvia IpingThis document summarizes key concepts from Lectures 10-11 on magnetic flux and Faraday's Law of Induction. It defines magnetic flux as a measure of the strength of the magnetic field perpendicular to a surface. Faraday's Law states that an electromotive force (emf) is induced in a loop of wire only when the magnetic flux through the loop is changing with time. Many devices operate based on this principle, such as electric guitars. Lenz's Law explains that any induced current will flow in a direction that opposes the change that caused it, such as an increasing magnetic field inducing a current that creates a opposing magnetic field.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Chapter Chapter 23 23
Lectures 10 Lectures 10- -11 11
pp
Magnetic Flux Magnetic Flux
and and Faradays Law of Induction Faradays Law of Induction
Worlds first electric motor
Worlds first electric car
Units Units
Induced Electromotive Force Induced Electromotive Force
Magnetic Flux Magnetic Flux Magnetic Flux Magnetic Flux
Faradays Law of Induction Faradays Law of Induction
Lenzs Law Lenzs Law Lenz s Law Lenz s Law
Mechanical Work and Electrical Energy Mechanical Work and Electrical Energy
Generators and Generators and Motors Motors
Inductance Inductance
RL RL Circuits Circuits
Energy Stored in a Magnetic Field Energy Stored in a Magnetic Field gy g gy g
Transformers Transformers
Induced Induced Electromotive Force Electromotive Force
Faradays experiment: Faradays experiment: closing the switch in the closing the switch in the
primary circuit induces a current in the primary circuit induces a current in the
secondary circuit, but only while the current in secondary circuit, but only while the current in
the primary circuit is changing the primary circuit is changing the primary circuit is changing. the primary circuit is changing.
The current in the secondary circuit
is zero as long as the current in the
Michael Faraday
(1791-1867) is zero as long as the current in the
primary circuit, and therefore the
magnetic field in the iron bar, is not
changing.
(1791-1867)
Current flows in the secondary
circuit while the current in the primary
is changing. It flows in opposite
di ti d di h th th directions depending on whether the
magnetic field is increasing or
decreasing.
The magnitude of the induced The magnitude of the induced
current is proportional to the rate at
which the magnetic field is changing.
One does not need the first circuit to illustrate the effect: One does not need the first circuit to illustrate the effect:
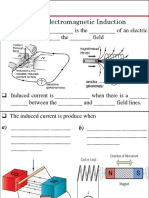
Magnetic Magnetic Flux Flux
Recall electric fl Recall electric fl Introd ce magnetic fl Introd ce magnetic fl Recall: electric flux Recall: electric flux Introduce: magnetic flux Introduce: magnetic flux
Electric flux is a measure of Magnetic flux is a measure of the strength Electric flux is a measure of
the strength of the electric
field perpendicular to a
surface.
Magnetic flux is a measure of the strength
of the magnetic field perpendicular to a
surface.
=
C
m N
EA
2
cos
[ ] weber W m T BA , 1 cos
2
= =
Faradays Faradays Law of Induction Law of Induction
Faradays law: Faradays law: Faradays law: Faradays law:
An An emf emf is induced only when the is induced only when the
magnetic flux through a loop magnetic flux through a loop
i f
i f
t t
N
t
N
magnetic flux through a loop magnetic flux through a loop
changes with time. changes with time.
Many Many devices devices operate operate on the basis of Faradays law on the basis of Faradays law. .
For example the electric guitar: For example the electric guitar: For example, the electric guitar: For example, the electric guitar:
Lenzs Lenzs Law Law
L L LL AA i d d t l fl i i d d t l fl i Lenzs Lenzs Law: Law: An An induced current always flows in a induced current always flows in a
direction that direction that opposes opposes the change that caused it. the change that caused it.
Therefore, if the magnetic field is increasing, the Therefore, if the magnetic field is increasing, the
magnetic field created by the induced current will be magnetic field created by the induced current will be
in the opposite direction; if decreasing, it will be in in the opposite direction; if decreasing, it will be in
the same direction. the same direction.
Heinrich Heinrich Lenz Lenz
(1804 (1804--1865) 1865)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Magnetic Induction: Faraday and Lenz'S Lawg HB J YDocument26 paginiMagnetic Induction: Faraday and Lenz'S Lawg HB J YIrah Arienza MarandacanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimental Researches In Electricity - Volume 1De la EverandExperimental Researches In Electricity - Volume 1Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical Engineering: (CUTM1057)Document26 paginiBasic Electrical Engineering: (CUTM1057)Yedla Santosh kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elmachi1 - Lecture6 (Electrical Machines - Part 1)Document17 paginiElmachi1 - Lecture6 (Electrical Machines - Part 1)Trisha SARMIENTOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 paginiElectromagnetic InductionParth GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnatic InductionDocument2 paginiElectromagnatic InductionSouvik ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 paginiElectromagnetic InductionEs EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction NotesDocument15 paginiInduction NotesKartikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Current TermsDocument12 paginiBasic Current TermsGhulam AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 23 EM Induction AC Circuits PDFDocument88 paginiCH 23 EM Induction AC Circuits PDFShane Patrick PanilagÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument23 paginiUntitledArnab DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Submitted By:-Name: - Mandeep Dhiman ROLL NO.: - 24 SECTION: - B4802 Course: - B.Tech (Me) - MbaDocument7 paginiSubmitted By:-Name: - Mandeep Dhiman ROLL NO.: - 24 SECTION: - B4802 Course: - B.Tech (Me) - Mbashailesh singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundacom SRPDocument45 paginiFundacom SRPSaurabhPrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic Induction ExplainedDocument3 paginiElectromagnetic Induction ExplainedAli HamzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetism Part 3 StudentsDocument15 paginiElectromagnetism Part 3 StudentsSharvinder SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 5 EmiDocument12 paginiCase Study 5 EmiSANJAY RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faraday's LawDocument9 paginiFaraday's LawaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument18 paginiElectromagnetic Inductionwakki 10Încă nu există evaluări
- Presentation (Autosaved)Document17 paginiPresentation (Autosaved)Muhammad Hamza Mujeeb AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induced EMFDocument21 paginiInduced EMFJaica Mangurali TumulakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2Document8 paginiModule 2Ashner NovillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lenz Law For DCDocument5 paginiLenz Law For DCGenette AringoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faraday Law of Electromagnetic InductionDocument5 paginiFaraday Law of Electromagnetic Inductionantex nebyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrostatics - Stationary ChargesDocument39 paginiElectrostatics - Stationary ChargesmkanwarsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lenz LawDocument4 paginiLenz LawWilliam Simms0% (1)
- Electromagnetic Induction (Physics) : Magnetic Flux & Faraday&apos S Law of InductionDocument15 paginiElectromagnetic Induction (Physics) : Magnetic Flux & Faraday&apos S Law of InductionistudyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetic Flux, Induction, and Faraday's Law - Boundless PhysicsDocument40 paginiMagnetic Flux, Induction, and Faraday's Law - Boundless PhysicsFen XiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Magnetic Induction Final 1Document52 paginiChapter 5 Magnetic Induction Final 1Salve Marie DoratoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faraday's Law: TransformersDocument9 paginiFaraday's Law: Transformersmyscribd1209Încă nu există evaluări
- Laws Governing Magnetic Circuits PDFDocument2 paginiLaws Governing Magnetic Circuits PDFVenkata SubramanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lenz Law...Document6 paginiLenz Law...MuhammadAsyrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- InductionDocument12 paginiInductionAhmad Ibsais100% (1)
- Magnetic FluxDocument30 paginiMagnetic FluxJoseph B Delos ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH6 Formula SheetDocument11 paginiCH6 Formula SheetNancy SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic Induction NOtesDocument76 paginiElectromagnetic Induction NOtesashunaik409Încă nu există evaluări
- Faraday's & Lenz LawDocument14 paginiFaraday's & Lenz LawPnDeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 EMIDocument52 paginiChapter 3 EMIMayank MeghaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Index Faraday's Law ConceptsDocument4 paginiIndex Faraday's Law ConceptsRajesh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Eddy Current TestingDocument26 paginiIntroduction To Eddy Current TestingvibinkumarsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faraday's LawDocument5 paginiFaraday's LawSyeda Rutab AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faraday's Electeomagnetic Induction.Document5 paginiFaraday's Electeomagnetic Induction.Rajesh JagadeesanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Faraday ProjectDocument16 paginiPhysics Faraday ProjectAlviya Rizwan100% (1)
- Physics Project (Investigatory Project 9)Document8 paginiPhysics Project (Investigatory Project 9)Ashu58% (19)
- Electromgnetic InductionDocument5 paginiElectromgnetic InductionGhanshyam SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faraday's Law of InductionDocument25 paginiFaraday's Law of InductionFariha IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 14 - Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 paginiChapter 14 - Electromagnetic InductionMACKENRY KEVIN ARCENOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self InductDocument22 paginiSelf Inductsiva balanÎncă nu există evaluări
- InducelecDocument9 paginiInducelecrenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lenz's Law NotesDocument3 paginiLenz's Law Notesʀᴀᴍᴇʟᴀ ᴍᴀʜɪʟᴜᴍÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldDocument8 paginiElect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldIsmail MzavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Outline: College Physics, 7 EditionDocument35 paginiLecture Outline: College Physics, 7 EditionMahmud Kawu IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic Induction LecturesDocument9 paginiElectromagnetic Induction LecturesDoyen DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction: DT D NDocument2 paginiFaraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction: DT D NNabil AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic Induction: Experiment 1Document13 paginiElectromagnetic Induction: Experiment 1midhunesh41Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 18 - Chapter 29 Part 1Document20 paginiLecture 18 - Chapter 29 Part 1Mircea PanteaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GenPhy2 Module 5 Electromagnetic InductionDocument50 paginiGenPhy2 Module 5 Electromagnetic InductionTAMAYO, Joelyn 12-STEM-BÎncă nu există evaluări
- KN Phy Project 12Document13 paginiKN Phy Project 12Mariappan NatarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 PDFDocument44 paginiChapter 7 PDFDanial JuniorÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENSC 12 Rectilinear Kinematics of A Particle PDFDocument19 paginiENSC 12 Rectilinear Kinematics of A Particle PDFJeric_QÎncă nu există evaluări
- VT Level III Study NoteDocument5 paginiVT Level III Study NoteAllen Situ100% (3)
- Applications of Differential Geometry To Physics: Cambridge Part III MathsDocument29 paginiApplications of Differential Geometry To Physics: Cambridge Part III MathsDimitris FetsiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel GCE: Mechanics M4Document28 paginiEdexcel GCE: Mechanics M4yvg95Încă nu există evaluări
- Science9 Q4 Week2Document16 paginiScience9 Q4 Week2Maria Josie Lopez TumlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Location Quantification of Pile Damages Dario CulapDocument10 paginiLocation Quantification of Pile Damages Dario CulaptutorialinformationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Directions in Ferrohydrodynamics (Invited) PDFDocument7 paginiDirections in Ferrohydrodynamics (Invited) PDFivan celyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermo Sheet7 NewDocument3 paginiThermo Sheet7 NewRodney SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment: Bernoulli's Equation Applied To A Convergent-Divergent PassageDocument5 paginiExperiment: Bernoulli's Equation Applied To A Convergent-Divergent PassageBilal ÇayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Heat TransferDocument15 paginiIntroduction To Heat TransferRishabh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- RDT TEMPERATURE TRAINER ManualDocument7 paginiRDT TEMPERATURE TRAINER ManualSHANKARÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 Melting PointDocument21 pagini06 Melting PointFranchiezca AoananÎncă nu există evaluări
- DuePaper MKH No Nom No Figs15Document8 paginiDuePaper MKH No Nom No Figs15Santiago Del Rio OliveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coursera SA682WVEP78QDocument1 paginăCoursera SA682WVEP78Qshilpmehta007Încă nu există evaluări
- 2020 - Sept25 - ME 004ADocument15 pagini2020 - Sept25 - ME 004ADaniel ManivoughÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH13-ML3 and ML5 FragmentsDocument3 paginiCH13-ML3 and ML5 FragmentsWan-Hsin LiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Discovery of Schumann Resonance: CapacitorsDocument5 paginiThe Discovery of Schumann Resonance: Capacitorssagor sagorÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Operational Mechanism of Continuous Four-Roll Plate Bending ProcessDocument4 paginiThe Operational Mechanism of Continuous Four-Roll Plate Bending ProcessBenjamin Neciosup PaucarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conservation of Linear Momentum Online PHETDocument7 paginiConservation of Linear Momentum Online PHETArlene PenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ancient Egyptian Wisdom - Magnetic EnergyDocument21 paginiAncient Egyptian Wisdom - Magnetic Energyiza721100% (10)
- CHE-221: Fluid Mechanics-I: Dr. Zaib JahanDocument10 paginiCHE-221: Fluid Mechanics-I: Dr. Zaib JahanBilal JuttÎncă nu există evaluări
- FMM Anna University Unit IV QuestionsDocument4 paginiFMM Anna University Unit IV QuestionsUma MaheshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frame Analysis PDFDocument56 paginiFrame Analysis PDFAKSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Are Q and Q Used To Symbolize Heat?: Chemistry For EveryoneDocument1 paginăWhy Are Q and Q Used To Symbolize Heat?: Chemistry For EveryoneEzephusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solubility ExpressionsDocument7 paginiSolubility ExpressionsYuppie Raj100% (1)
- Applied Physics Assignment 1Document9 paginiApplied Physics Assignment 1areejÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcqs From Past Papers Physics All in One 2nd YearDocument35 paginiMcqs From Past Papers Physics All in One 2nd YearIrtaza Akram50% (2)
- Page No: 118: in Text QuestionsDocument11 paginiPage No: 118: in Text QuestionsVinod MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plasmonics Chapter 1Document13 paginiPlasmonics Chapter 1Fahad ZiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2962-Zhang-Structure and Performance of LiFePO4 Cathode Materials-A ReviewDocument9 pagini2962-Zhang-Structure and Performance of LiFePO4 Cathode Materials-A ReviewEllen7374Încă nu există evaluări