Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
HW 1
Încărcat de
Ancient HermitDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
HW 1
Încărcat de
Ancient HermitDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
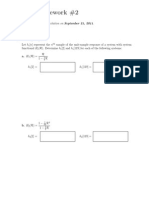
EE465:
Homework #1
Due on October 1, 2014
Lecturer PHAM, Van-Tuan Chapter 3,4 and 5
*Note:
1. Use A4-sized papers to do your work,
2. Any copied work will not be graded,
3. If nd anything unclear in this homework set, please contact me.
1
thanhnguyentang
EE465 (Lecturer PHAM, Van-Tuan Chapter 3,4 and 5):
Homework #1 Problem 1
Problem 1
Determine whether the discrete-time systems described by the following I-O equations are linear and/or
time-invariant.(Explain your answers clearly)
1. y(n) = 3x(n) + 5
2. y(n) = x
2
(n 1) + x(2n)
3. y(n) = e
x(n)
4. y(n) = nx(n 3) + 3x(n)
5. y(n) = n + 3x(n)
2
thanhnguyentang
EE465 (Lecturer PHAM, Van-Tuan Chapter 3,4 and 5):
Homework #1 Problem 2
Problem 2
Determine the causal impulse response h(n) for n 0 of the LTI systems described by the I-O dierence
equations:
1. y(n) = 0.9y(n 1) + x(n)
2. y(n) = 0.64y(n 2) + x(n)
3. y(n) = 0.5y(n 1) + 4x(n) + x(n 1)
3
thanhnguyentang
EE465 (Lecturer PHAM, Van-Tuan Chapter 3,4 and 5):
Homework #1 Problem 3
Problem 3
Determine the I-O dierence equations relating x(n) and y(n) for the LTI systems having the following im-
pulse response:
1. h(n) = (0.4)
n
u(n)
2. h(n) = (0.3)
n
u(n) + (0.3)
n
u(n)
4
thanhnguyentang
EE465 (Lecturer PHAM, Van-Tuan Chapter 3,4 and 5):
Homework #1 Problem 4
Problem 4
Compute the convolution,y=hx, of the lter and input,
h=[1,2,1,1], x=[1,1,1,2,1,1]
using the following three methods:
1. The convolution table.
2. The LTI form of convolution, arranging the computations in a table form.
3. The overlap-add method of block convolution with length-3 input blocks
5
thanhnguyentang
EE465 (Lecturer PHAM, Van-Tuan Chapter 3,4 and 5):
Homework #1 Problem 5
Problem 5
Consider the IIR lter h(n) = a
n
u(n), where 0 < a < 1. The square pulse x(n) = u(n)u(n L) of duration
L is applied as input. Using the time-domain convolution formula, determine a closed-form expression for
the output signal y(n) for the two time ranges: 0 n L 1 and n L.
6
thanhnguyentang
EE465 (Lecturer PHAM, Van-Tuan Chapter 3,4 and 5):
Homework #1 Problem 6
Problem 6
Consider the lter with I-O equation: y(n) = x(n) x(n 3).
1. Determine the impulse response sequence h(n), for all n 0.
2. Draw a block diagram realization, introduce appropriate internal states, and write the corresponding
sample processing algorithm.
3. Send as input the sequence x =[1,1,2,2,4,... ]. Using convolution, compute the rst ve output samples,
y(n), n = 0, 1, ..., 4.
4. Compute the same outputs using the sample processing algorithm. Display your computations in a
table that, at each sampling instant n, shows the corresponding input sample x(n), the values of the
internal states, and the computed output sample y(n).
7
thanhnguyentang
EE465 (Lecturer PHAM, Van-Tuan Chapter 3,4 and 5):
Homework #1 Problem 7
Problem 7
Compute the z-transform of the following sequences and determine the corresponding region of convergence:
1. (0.5)
2
u(n)
2. (0.5)
2
u(n 1)
3. (0.5)
2
u(n)
4. (n)
5. (0.5)
2
[u(n) u(n 10)]
6. (0.8)
n
cos(n/2)u(n)
7. (0.25)
n
u(n) + 4
n
u(n)
8. (0.25)
n
u(n 1) 4
n
u(n 1)
8
thanhnguyentang
EE465 (Lecturer PHAM, Van-Tuan Chapter 3,4 and 5):
Homework #1 Problem 8
Problem 8
Using partial fractions or power series expansions, determine all possible inverse z-transforms of the following
z-transforms, sketch their ROCs, and discuss their stability and causality properties:
1. X(z) =
1
1 + 0.5z
1
, |z| > 0.5
2. X(z) =
1
1 + 0.5z
1
, |z| < 0.5
3. X(z) =
1 0.5z
1
1 +
3
4
z
1
+
1
8
z
2
, |z| > 0.5
9
thanhnguyentang
EE465 (Lecturer PHAM, Van-Tuan Chapter 3,4 and 5):
Homework #1 Problem 9
Problem 9
Without evaluating the inverse transform, determine which ones of the following z-transforms are certainly
not causal. You should give your answers by inspection.
1.
(1 z
1
)
2
1 0.5z
1
2.
(z 1)
2
z 0.5
3.
(z
1
4
)
5
(z 0.5)
6
4.
(z
1
4
)
6
(z 0.5)
5
10
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Tute SignalsDocument12 paginiTute SignalsNikhil KumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discrete Signals and Systems Part 1Document8 paginiDiscrete Signals and Systems Part 1vackyvipinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.341 Discrete-Time Signal Processing Fall 2005Document24 paginiMassachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.341 Discrete-Time Signal Processing Fall 2005Nguyen Duc TaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Shift Invariant Property & Convolution of Discrete SignalsDocument1 paginăLinear Shift Invariant Property & Convolution of Discrete SignalssandeeprvjecÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP QB Updated - NewDocument7 paginiDSP QB Updated - NewthenithyanagrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 1: Problem 1Document2 paginiHomework 1: Problem 1ShehryarÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Experiment DSP RGPVDocument2 paginiList of Experiment DSP RGPVAnand SantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab ManualDocument90 paginiMatlab ManualSri Harsha57% (7)
- RepositoryDocument17 paginiRepositoryarefinhasib07Încă nu există evaluări
- DSP Laboratory Guide 20feb2012Document44 paginiDSP Laboratory Guide 20feb2012anamaria_budaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 5 Signals Discrete AnalysisDocument2 paginiHomework 5 Signals Discrete AnalysisosbihatÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW1Document1 paginăHW1عيدروس قاسمÎncă nu există evaluări
- S MidsolDocument3 paginiS MidsolSachin MichuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Discrete-Time Fourier Series: Recommended ProblemsDocument6 pagini10 Discrete-Time Fourier Series: Recommended ProblemsTuran ÖzdemirÎncă nu există evaluări
- U3 HW2Document1 paginăU3 HW2Andy AndrangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loisircs Stuff 1Document9 paginiLoisircs Stuff 1Loisirc M GoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prob 1Document2 paginiProb 1Mrudula VaradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tut Divide ProblemsDocument7 paginiTut Divide ProblemsTimothy KurbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP Assignment 1 SolutionDocument7 paginiDSP Assignment 1 SolutionHasnain KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1Document8 paginiTutorial 1Carine ChiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adv Math Lab10Document2 paginiAdv Math Lab10Meriç GäßlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- CFD Home Work 2Document1 paginăCFD Home Work 2Sasidhar JannuÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE4001F: Problem Set 1Document3 paginiEEE4001F: Problem Set 1Simon KatendenciesÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE201 Assignment 1Document3 paginiEE201 Assignment 1meghana reddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SYSC 4405 Midterm2 Fall 2012Document2 paginiSYSC 4405 Midterm2 Fall 2012Aleksandra DiotteÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC4091 DSP Lab Signals and Systems ReviewDocument2 paginiEC4091 DSP Lab Signals and Systems ReviewAswini KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 05Document4 paginiLab 05kamranjavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Copy of Mid 2-1Document2 paginiCopy of Mid 2-1Muhammad Sufyan AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Era University: College of Engineering and Architecture Department of Electronics EngineeringDocument10 paginiNew Era University: College of Engineering and Architecture Department of Electronics EngineeringLe AndroÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATHEMATICAL OPERATIONS ON DISCRETE TIME SIGNALSDocument10 paginiMATHEMATICAL OPERATIONS ON DISCRETE TIME SIGNALSAtif AlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bme 15 Dec 11Document3 paginiBme 15 Dec 11MukeshSharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.003 Homework #2: ProblemsDocument12 pagini6.003 Homework #2: ProblemsRajeev SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment FALL2018Document2 paginiAssignment FALL2018UdayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solving Simultaneous Nonlinear EquationsDocument5 paginiSolving Simultaneous Nonlinear EquationsAlluri Appa RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 New RapDocument4 pagini6 New RapImportadora Boliviana de MedicamentosÎncă nu există evaluări
- No Calculators - No Textbook and Notes (Close-Book Exam) - Initial On The Top of Each PageDocument9 paginiNo Calculators - No Textbook and Notes (Close-Book Exam) - Initial On The Top of Each PageYaseenÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP HomeworkDocument13 paginiDSP HomeworkArinder SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of California, Riverside: Department of Computer ScienceDocument11 paginiUniversity of California, Riverside: Department of Computer ScienceAmir_AmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- A3 - Signal and SystemDocument2 paginiA3 - Signal and SystemShahzeb MirzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.160 Identification, Estimation, and Learning: End-of-Term ExaminationDocument3 pagini2.160 Identification, Estimation, and Learning: End-of-Term ExaminationRahul Raveendran PillaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Practice QuizDocument16 paginiDesign and Analysis of Algorithms Practice QuizbhumkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChEn 3201: Numerical ODEsDocument3 paginiChEn 3201: Numerical ODEsJoe FaraciÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIT6 006F11 ps1 PDFDocument6 paginiMIT6 006F11 ps1 PDFlinchiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signals and Systems Exam 1 ReviewDocument14 paginiSignals and Systems Exam 1 ReviewAliBaranIşıkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog Signal Processing Tutorial 2: Sampling and ReconstructionDocument12 paginiAnalog Signal Processing Tutorial 2: Sampling and ReconstructionDuy Ngô Phạm ĐìnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP QB - OptDocument0 paginiDSP QB - OptSiva KathikeyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential set theory and algebra for economistsDocument5 paginiEssential set theory and algebra for economistsfilippoviceÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMSC 251: Algorithms: Spring 1998Document30 paginiCMSC 251: Algorithms: Spring 1998Anthony-Dimitri AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear RegressionDocument14 paginiLinear RegressionSaad AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- No Calculators No Textbook and Notes (Close-Book Exam) Initial On The Top of Each PageDocument9 paginiNo Calculators No Textbook and Notes (Close-Book Exam) Initial On The Top of Each PageYaseenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 1Document3 paginiHomework 1Salih_Bak_r_8581Încă nu există evaluări
- Dense Linear SystemsDocument7 paginiDense Linear SystemsJustin BrockÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS3510 Algorithms Test 1 ReviewDocument7 paginiCS3510 Algorithms Test 1 ReviewelsainetedelautrecÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE 5526 Homework 2 Neural NetworksDocument2 paginiCSE 5526 Homework 2 Neural NetworksZheng Ronnie LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Dynamics Assignment for Potential FlowDocument9 paginiFluid Dynamics Assignment for Potential FlowUmar AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIT8 04S13 Exam1Document17 paginiMIT8 04S13 Exam1Sahil ChadhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elementary Differential Equations with Linear AlgebraDe la EverandElementary Differential Equations with Linear AlgebraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsDe la EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDe la EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Integer Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementDe la EverandInteger Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rabiner1989 HMM4ASR TextDocument30 paginiRabiner1989 HMM4ASR TextAncient HermitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Components 0Document29 paginiControl Components 0Ancient HermitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 1 SolutionsDocument1 paginăHomework 1 SolutionsAncient HermitÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS202 Lap2Document23 paginiCS202 Lap2Ancient HermitÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE361 Lab3 AssignmentDocument6 paginiEE361 Lab3 AssignmentAncient HermitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 2 Summer 2013Document8 paginiLab 2 Summer 2013Minh NgocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arithmetic 0Document27 paginiArithmetic 0Ancient HermitÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Improved Vehicle-to-Home (iV2H)Document11 pagini"Improved Vehicle-to-Home (iV2H)annaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOR-230 PCB input signal errorDocument1 paginăDOR-230 PCB input signal errorDaniel GatdulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11kv 200a Ab Switch PDFDocument2 pagini11kv 200a Ab Switch PDFhimanshuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microcontrollers Embedded Programming - Let's Start CodingDocument80 paginiMicrocontrollers Embedded Programming - Let's Start CodingjayanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- 128 Output Demand Controller: Pentair Clean Air SystemsDocument4 pagini128 Output Demand Controller: Pentair Clean Air SystemsLuiz Fernando KnackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingenium (Abstract)Document5 paginiIngenium (Abstract)urvish_soniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Practical Set-BDocument35 paginiPhysics Practical Set-BKeshab Chandra BihariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integral PaperDocument7 paginiIntegral PaperASHISHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Control PanelDocument2 paginiStandard Control PaneldaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Realization of Gates Using Universal Building Blocks (NAND Only)Document8 paginiRealization of Gates Using Universal Building Blocks (NAND Only)kishorebabÎncă nu există evaluări
- State of The Art DC-DC Converter Topologies For The Multi-Terminal DC Grid Applications: A ReviewDocument7 paginiState of The Art DC-DC Converter Topologies For The Multi-Terminal DC Grid Applications: A ReviewariphineÎncă nu există evaluări
- CC271 Februar 2013Document84 paginiCC271 Februar 2013JanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commissioning Standard Test FormatsDocument1 paginăCommissioning Standard Test FormatsGoogool YÎncă nu există evaluări
- DG35EC Product Guide EnglishDocument78 paginiDG35EC Product Guide EnglishSoupramanien KathirvelouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document26 paginiChapter 1ankurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bell PDFDocument8 paginiBell PDFlibraryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Konica Minolta QMS Pagepro 9100 Service ManualDocument228 paginiKonica Minolta QMS Pagepro 9100 Service Manualingmar_sÎncă nu există evaluări
- 48W-29165-0 Using An Oscillocope and Function Generator To Measure Capacitor 4-24-2013 DPDocument5 pagini48W-29165-0 Using An Oscillocope and Function Generator To Measure Capacitor 4-24-2013 DPOnofre DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7th Lect Charge Transport - 110032Document19 pagini7th Lect Charge Transport - 110032Muhammad TayyabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lenovo L193 Wide 19'' LCD Monitor Service ManualDocument47 paginiLenovo L193 Wide 19'' LCD Monitor Service Manualtakne_007Încă nu există evaluări
- Telecommunications Transmission Engineering Vol 1 Principles 2ed 1977 PDFDocument685 paginiTelecommunications Transmission Engineering Vol 1 Principles 2ed 1977 PDFMurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diode Circuits: Electronics IDocument25 paginiDiode Circuits: Electronics I呼除預Încă nu există evaluări
- Public Address Amplifier: User'S ManualDocument16 paginiPublic Address Amplifier: User'S ManualganiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PECON Condense Catalogue 2013Document36 paginiPECON Condense Catalogue 2013Manoj AggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Implementation of Autonomous Line Follower Robot Using MicrocontrollerDocument4 paginiDesign and Implementation of Autonomous Line Follower Robot Using MicrocontrollerVASANTHKUMAR M SÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1. 2 Ficha Tecnica Cabina de Mando M-1373CDocument4 pagini1.1. 2 Ficha Tecnica Cabina de Mando M-1373CEdison David Roberto OrtizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beckhoff Main Catalog 2019 Volume2 PDFDocument728 paginiBeckhoff Main Catalog 2019 Volume2 PDFAlexandru DiaconescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6ES72141AG400XB0 Datasheet enDocument9 pagini6ES72141AG400XB0 Datasheet enguevbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Third Angle Projection: YPF - Plaza Huincul Generator Protection G60 SettingsDocument92 paginiThird Angle Projection: YPF - Plaza Huincul Generator Protection G60 SettingsclauÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTRONICSDocument9 paginiELECTRONICSSankalp KashyapÎncă nu există evaluări