Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lab 5
Încărcat de
amirahabidin0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
61 vizualizări12 paginiUNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN KIMIA ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY LABORATORY (CHE485) a sample of pond is taken to be tested. The objective of this experiment to determine the levels of chlorine (total and free), iron, sulfates and phosphorous in a series of water samples.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
lab 5
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentUNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN KIMIA ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY LABORATORY (CHE485) a sample of pond is taken to be tested. The objective of this experiment to determine the levels of chlorine (total and free), iron, sulfates and phosphorous in a series of water samples.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
61 vizualizări12 paginiLab 5
Încărcat de
amirahabidinUNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN KIMIA ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY LABORATORY (CHE485) a sample of pond is taken to be tested. The objective of this experiment to determine the levels of chlorine (total and free), iron, sulfates and phosphorous in a series of water samples.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 12
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN KIMIA
ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
(CHE485)
NAME / STUDENT NO. : 1) AMIRAH BINTI ABIDIN (2013600418)
2) MUHAMMAD NUR HAZRUL (2013868324)
3) NORHAYATI BINTI YUSOFF (2013245246)
4) SITI NORLIYANA BINTI MAZALAN (2013826962)
GROUP : EH2212B
EXPERIMENT : 4-BASIC WATER PROPERTIES 2
DATE PERFORMED : 5 MEI 2014
SEMESTER : 2
PROGRAMME / CODE : EH221
SUBMIT TO : MADAM SAKINAH
No Title Allocated Marks (%) Marks
1 Abstract/Summary 5
2 Introduction 10
3 Aims 5
4 Theory 10
5 Apparatus 5
6 Methodology/Procedure 10
7 Results 10
8 Calculations 10
9 Discussion 20
10 Conclusion 5
11 Recommendations 5
12 Reference / Appendix 5
TOTAL MARKS 100
Remarks:
Checked by :
---------------------------
Date :
ABSTRACT
Basic water properties 2 experiment is conducted to determine dissolved chemical that contain in
water such as chlorine, sulfate, chromium, iron and phosphorus. A sample of pond is taken to be
tested. The objective of this experiment to determine the levels of chlorine (total and free), iron,
sulfates and phosphorous in a series of water samples and ascertain whether they comply with
Malaysian Water Standards. The sample of water are the pollutants that to be determined by
using the portable spectrophotometer DR 2400. It is also used to measure the wavelength and the
mass of the pollutants, according to density shown by the apparatus.
Microorganisms such as bacteria are responsible for decomposing organic waste. When
organic matter presents in a water supply, the bacteria will begin the process of breaking down
this waste. When this happens, much of the available dissolved oxygen is consumed by aerobic
bacteria, robbing other aquatic organisms of the oxygen they need to live. Such microbiological
parameters as the number, weight and activity of microorganism can be good indicators of waste
water contamination with heavy metals. Heavy metals are known as harmful pollutant in
wastewater having negative effect on biological wastewater treatment plant including
microorganisms. Some heavy metals at low levels are toxic for microorganisms. As a rule, heavy
metals have a negative effect on microorganisms as it rule, heavy metal has a negative effect on
microorganism as it can greatly depress their number. On other hand, the number of
microorganisms depends on the total content and concentrations of particular forms of heavy
metals. It is conditioned by several other factors, quantity and quality of organic matter.
Heavy metals shift thestructure of microbial populations, impoverish their diversity, and affect
species composition, reproduction and activity of indigenous microorganisms. Contamination of
wastewater with high rates of heavy metals caused a significant decrease in the
numbers of bacteria in biological system. It is obvious that heavy metals are very danger contami
nant in wastewater and disorder of biological wastewater treatment is as a result of this pollution.
In this experiment, the heavy metals used to dissolve in pond water sample are iron (Fe),
chlorine (Cl
2
), free chlorine (Cl
2
), phosphorus reactive (P) and sulfate (SO
4
2-
). About 10 mL of
lake water is filled in the bottle and is added with 5 reagents which is Ferro Ver iron reagent
powder, DPD Total Chlorine Powder Pillow, DPD free chlorine powder pillow, Phos Ver3
phosphate powder pillow, and Sulfa Ver4 Reagent powder pillow. The spectrophotometer is used
and the concentration value is taken for each bottle for each water sample. For the result, the lake
water give concentration 0.00 mg/L of iron, 1.0 mg/L sulfate, 0.00 mg/L total chlorine, 0.23
mg/L phosphate reactive and 0.43 mg/L free chlorine.
The result shows that concentration of sulfate in lake water is the highest which 1.0
mg/L. Therefore, it is very harmful to human body.
INTRODUCTION
The dissolved oxygen content is an important thing when considering its suitability for a town
supply. Good clean portable water will give dissolved oxygen value close to the theoretical
value. While, when there is pollution by others, the dissolved oxygen is up in various
biochemical oxidation processes and it is only slowly replaced through surface absorption where
water will give low dissolved oxygen content until oxidation is completed. Adequate dissolved
oxygen is necessary for the life of aquatic.
The presence of a sufficient concentration of dissolved oxygen is critical to maintaining
the aquatic life and aesthetic quality of streams and lakes. Determining how organic matter
affects the concentration of dissolved oxygen in a stream or lake is integral to water quality
management.
The reality of todays water quality, where most of it is contaminated by heavy metals,
such as lead, mercury, cadmium, chromium and chlorine. The exposure and existence of these
heavy metals are apparently one of the main threats to humans health. These metals have been
studied extensively and their circumstances on human health regularly reviewed by international
parties such as World Health Organization.
For thousands of years have heavy metals been used by humans and although several
adverse effect upon exposure of these hazardous metals are being informed to public awareness,
the harmful situations are nevertheless still going on, particularly may not-so-developed
countries. The decrease in the oxygen supply in the water has negative effect to all living things.
Heavy metals are toxic to most microorganisms at specific concentrations and often cause
serious upsets in biological waste treatment plants. The mechanism by which heavy metal
affect the microorganisms is not clear. It has nevertheless been suggested that heavy metals bloc
k the enzyme systems or interfere with some essential cellular metabolite of bacteria and
protozoa. The toxicity of heavy metals in activated sludge mixed liquor depends mainly
upon two factors, namely, metal species and concentration. Other factors such as pH, sludge con
centration, influent strength are also reported to affect the toxicity of metals, though to a lesser
degree. It has been reported that only soluble metal ions are toxic to the activated
sludge. Acclimatized sludges maintain high removal efficiency of dissolved organic matter
though exposed to constant input level of heavy metals, conversely shock loads
manifest remarkable effects on sludges whether acclimatized or not.
As a matter of fact, heavy metals can be very harmful to ones health if a drinking water
containing such deadly metals is consumed. The adverse circumstances include disturbances in
growth and development, triggering cancer, organ damage, nervous system damage, and in
extreme cases, causing fatal. While some of the metal pollutants come from fertilizers and
sewage, the biggest sources of heavy metal pollution definitely are industrializations.
AIMS
This experiment is to determine the levels of chlorine (total and free), iron, sulphates and
phosphorous in a series of water samples and ascertain whether they comply with Malaysian
Water Standards.
THEORY
The term heavy metals refers to any metallic chemical element that has a relatively has
high density and it is toxic or poisonous at low concentrations. Some of them may contain in our
polluted drinking water. Examples of heavy metals include chlorine, phosphorus, iron, sulfate,
Chlorine. For examples, it is usually added to water to deactivate and destroy disease-causing
microorganisms and is the most widely used as disinfectant in the United States. It can react with
naturally occurring organic compounds found in water supply, which in turns produce hazardous
compounds, known as disinfection by-products (DBPs). Trihalomethanes (THMs) and halo
acetic acids are common DBPs. It is undeniably potentially carcinogenic especially to organs
such as kidney and liver. Due to this, federal regulations in the United States of America require
regular monitoring of the concentrations of these compounds in the distribution systems of
municipal water systems Nevertheless, the WHO states that the risks to health from DBPs are
extremely small in comparison within adequate disinfection.
For phosphorus, phosphorus occurs naturally in rocks and other mineral deposits.
Technically, the rocks release the phosphorus as phosphate ions which are soluble in water and
the mineralize phosphate compounds breakdown. Phosphates (PO43-) are formed from this
element. Phosphate occurs in living and decaying plants and animals as free ions or weakly
chemically bounded in aqueous, to sediments and soils, or as mineralized compounds in soils,
rock sand sediments. The phosphorus is often scarce in the well-oxygenated waters and low
levels of phosphorus results in the limitation of production of freshwater systems. Phosphates are
generally not toxic to humans or animals unless they are present in high levels of concentration.
Phosphorus pollution accelerates a process called eutrophication, which is essentially the process
of awakes biological death due to depleted bioavailable oxygen.The build-up of phosphate in the
lake water or any surface water ecosystem leads to over production of lake or water body which
results in the imbalance in the nutrient and material cycling process.There will be massive
production of phytoplankton and therefore cause variety of problems ranging from anoxic waters
to toxic algal blooms as well as decrease in diversity, food supply and destroying the habitats.
Excessive growth of algal due to phosphorus pollution increase water treatments costs, degrades
fishing and boating activities as well as impacts tourism and property values.
Meanwhile for iron, the maximum contaminant level (MCLs) of iron is 0.3 mg/L.Iron
ingestion is not generally unhealthy and absolutely necessary in small amounts. However,
research has found that exposure to high levels of iron can lead to heart disease, cancer and
diabetes. Iron is often included in supplements and enriched products. It also contains in red
meat, therefore easily to be consumed Chromium hexavalent refers to chemical compounds that
contain the element chromium in the +6 oxidation state. It is used for the production of stainless
steel, textile dyes, wood preservation, leather tanning, and as anti-corrosion and conversion
coatings as well as variety of niche used. Hexavalent chromium compounds aregenotoxic
carcinogens. Chronic inhalation of the compounds increases risk of lung cancer. Besides,
chromium hexavalent also causes short term health problems such as skin irritation or ulceration,
whereas the long term effects of exposure include damage to liver, kidney circulatory and nerve
tissues.
Lastly, the Secondary Drinking Water Regulations recommend a maximum concentration
of 250 mg/L for sulfate ions (SO42-) Sulfate is in fact occurs in almost all natural waters. Sulfate
is indeed oneof the major dissolved constituents in rainwater. High concentrations of sulfate in
drinking water cause a laxative effect when combined with magnesium and calcium. Bacteria
which in fact attacks and reduces sulfates, causes the formation of hydrogen sulfide gas H
2
S.
APPARATUS AND MATERIALS
Aparatus: Cuvette bottle, specthrophotometer
Materials: Sample water, free chlorine powder, total chlorine powder, sulphate reagent
powder, iron powder, phosphorus powder.
PROCEDURE
1. The stored program number for free and total chlorine (Cl
2
) powder pillow was entered.
(80 ENTER) and display will show: Dial nm to 530
2. The wavelength dial was rotated until the screen shows the dial number that equals to the
one that recommended. When the correct dial wavelength was dialed , the display will
quickly show: Zero Sample then: mg/L Cl
2
.
3. The 10-mL cell riser was inserted into the sample compartment.
4. A 10-mL sample cell was filled with 10-mL of sample.
5. One contents of DPD Total Chlorine Powder Pillow added to the sample cell known as
prepared sample. The sample then was covered with stopper and shaked for 20 seconds.
Stopper was then removed.
6. The SHIFT TIMER button was pressed and a three-minute reaction period will begun.
7. Another sample cell known as the blank with 10-mL of sample was filled and then placed
into the cell holder. The light shield then was closed. All these were done just after the
timer beeps.
8. Zero button was pressed and the display will show: Zeroing then:0.00 mg/L Cl
2
9. Within three minutes after timer beeps, the prepared sample was placed into the cell
holder then the light shield was closed.
10. Read button was pressed and it will show: Reading .The result in mg/L Cl
2
will appear
and then recorded.
11. The steps were repeated by using DPD free chlorine powder pillow for chlorine free,
SulfaVer 4 reagent for sulfate, Phos Ver 3 Phosphate powder pillow to phosphorus
reactive, Ver iron reagent powder pillow for iron.
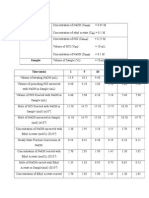
RESULT
Mg/L Color
Chlorine, total 0.43 No change
Chlorine, free 0.00 No change
Phosphorus, reactive 0.23 No change
Iron, total Under range No change
Sulphate 1.00 No change
DISCUSSION
The sample collected is from pond of fish which was taken after the pond being cleaned.
Thus, the result might shows less than we ought to expect. Firstly, the chlorine total, its referred
to addition of combine chlorine and free chlorine. Free chlorine then referred as sum of
concentration of hypochlorous acid and its anion, hypochlorite. Distribution of these two
relatively affect by pH. Apparently chlorine free is pH-independent. Combine chlorine is contact
corresponds to chloramines concentration in water. Chloramine is a major disinfection of product
in chlorinated pool with monochloramine predominant species at water pH.
Their disinfection is lower than free chlorine because chloramine is toxic and irritating
substance thus the presence is undesirable. The chloramines contribute to the chlorine smell of
water.
Free chlorine is monitored by using DPD method which the presence of Chlorine gas
makes the solution turns red-purple and the intensity increase as the content large. The total
chlorine is introduced by same procedure but different reagent. The free chlorine got from data is
0.00 mg/L and total chlorine is 0.43 mg/L. The value is less than fixed by world health
organization is total chlorine must less than 1.2 mg/L. The reason it is low because maybe the
worker has put the anti-chlorine to the pond.
Phosphorus occurs solely in seawater of wastewater known as phosphate. They are added
to water treatment to prevent corrosion in plant. Phosphorus is also essential for animal and plant
but if it is overdose it can leads to eutrophication moreover if nitrogen is presence. Reactive
phosphorus is a measure of orthophosphate and small fraction of condensed phosphate that may
have been hydrolyzed during test.
There are high and low range of test can be done; high with amino acid or
molybdovanadate method. Molybdovanadate has single and faster reaction than amino acid. Low
range use ascorbic acid method. Reactive phosphorus is determining reaction of orthophosphate
with molybdavanadate acid with turns yellow-colored phosphomolybdate complex. Then it
reduces to ascorbic acid or amino acid causing a molybdenum blue species. The result we
received is 0.23 mg/L of phosphorus reactive. The reasons probably because the water pond had
been change recently.
The iron total is to measure the value of iron whether it is insoluble or insoluble. The
Ferro Ver Iron Reagent will react with this iron to produce ferrous iron. This react with 1,10-
phenanthroline indicator in the reagent to form an orange color in proportion to the iron
concentration. According to the result in the experiment, the value is under range and no shows
of change in color.
Sulphate ions in the sample will react with barium in SulfaVer 4 and form a precipitate of
barium sulphate. The amount of turbidity formed is proportionally to the sulphate concentration.
Sulphate in water is important to be measured because sulphate can leads to diarrhea. The issue
brings is the contaminated from sulphate which 200 mg/L as the highest value is prohibited to
supply.
CONCLUSION
From this experiment, we can conclude that water sample from our experiment is totally
safe for aquatic living organism. As it have 0.43 mg/l total chlorine, 0.23 mg/l phosphorus
reactive,under range of total iron and 1.00 mg/l of sulphate. The amount of this experiment is not
exceeding the amount that safe for an aquatic living organism.
RECOMMENDATION
In order to obtain more accurate and best values in this experiment, a few
recommendations and precautions are suggested on the techniques used during the experiment.
The recommendations are:
The outside surface of the round water sample is best wiped first before inserted into the
spectrophotometer. This is to ensure that there are no fingerprints on it which might
interfere the reading analysis.
The water sample must be analyzed immediately after collection. This is because heavy
metals content of the water sample might differ from the time it is collected until it
analyzed.
Likewise, this experiment should be repeated twice to obtain the most accurate reading
thus the average value can be obtained and much more convincing rather than doing the
experiment once.
APPENDIX
Image 1 : spectrophotometer Image 2 : cuvettle bottle
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Heat ExchangerDocument4 paginiHeat ExchangeramirahabidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sulfuric Acid Manufacturing ProcessDocument5 paginiSulfuric Acid Manufacturing ProcessamirahabidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties Measurement/pvtDocument34 paginiProperties Measurement/pvtamirahabidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bernoulli's Theorem DemonstrationDocument16 paginiBernoulli's Theorem Demonstrationamirahabidin100% (1)
- NaOH Concentration Ethyl Acetate Reaction KineticsDocument6 paginiNaOH Concentration Ethyl Acetate Reaction KineticsamirahabidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 6: Soap and DetergentDocument12 paginiExp 6: Soap and DetergentamirahabidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties measurement/PVTDocument32 paginiProperties measurement/PVTamirahabidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document33 paginiChapter 1amirahabidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Multi Component DistillationDocument120 paginiMulti Component DistillationSamuel Espinoza GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finish Powerball (1999)Document4 paginiFinish Powerball (1999)Jim SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry TextDocument45 paginiChemistry Textariel yana morgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Nanoparticles in AgricultureDocument11 paginiApplication of Nanoparticles in AgricultureShetti Swamy PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Davey XS250HG ManualDocument2 paginiDavey XS250HG Manualcoolestkiwi100% (1)
- New Natron NXT Series Screen and Pad Printing Ink For Neoprene, Nitrile, EVA and EPDM Rubber From Boston Industrial Solutions, Inc.Document2 paginiNew Natron NXT Series Screen and Pad Printing Ink For Neoprene, Nitrile, EVA and EPDM Rubber From Boston Industrial Solutions, Inc.PR.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- RetroJet System ManualDocument11 paginiRetroJet System ManualetritÎncă nu există evaluări
- COA CrosscarmDocument1 paginăCOA CrosscarmSouheila MniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Data Sheet: Ptfe + 20% PeekDocument1 paginăTechnical Data Sheet: Ptfe + 20% PeekRohan KulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0-5303 Opt PDFDocument226 pagini0-5303 Opt PDFAnonymous wUv02fÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 MassMicroDocument25 paginiLecture 2 MassMicroPelin KınıkÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACROLEIN MSDSDocument6 paginiACROLEIN MSDSzaedmohd50% (2)
- Atomic Structure (AP MC)Document4 paginiAtomic Structure (AP MC)Habiba AbdeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- All about the Properties and Uses of Common StonesDocument41 paginiAll about the Properties and Uses of Common StonesBhavya MewadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO 17746-2016 Steel Wire Rope Net Panels and RollsDocument24 paginiISO 17746-2016 Steel Wire Rope Net Panels and RollsOctavian Miclescu100% (1)
- MSRR 6011Document14 paginiMSRR 6011pradellesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glass Making TheoryDocument14 paginiGlass Making TheorySK SHAHNAWAZÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012 - Cosmetic Ingredient Review - Amended Safety Assessment of Alkyl Esters As Used in CosmeticsDocument83 pagini2012 - Cosmetic Ingredient Review - Amended Safety Assessment of Alkyl Esters As Used in CosmeticsymiyazyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bermad Strainer Model BC-70F-P: Buildings & ConstructionDocument2 paginiBermad Strainer Model BC-70F-P: Buildings & ConstructionGuillermo GuzmánÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety: ArticleinfoDocument7 paginiEcotoxicology and Environmental Safety: ArticleinfoEswin Hernandez ObregonÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXPERIMENT A2: Determination of The Formula of A HydrateDocument5 paginiEXPERIMENT A2: Determination of The Formula of A HydrateTessi SeokoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turbopump Shaft NasaDocument136 paginiTurbopump Shaft NasacarlfelipeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microplastic Communities in Different Environments Differenc - 2021 - Water R PDFDocument11 paginiMicroplastic Communities in Different Environments Differenc - 2021 - Water R PDFSunita ChayalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peng Antar Minyak Bum IDocument13 paginiPeng Antar Minyak Bum ITara VergitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirp MSDSDocument2 paginiCirp MSDSsharemw100% (2)
- Vaporizer DesignDocument18 paginiVaporizer DesignEngr Abuzar Khan100% (1)
- DeLonghi Instruction Manual ECP3220 - 3420 - 3630Document7 paginiDeLonghi Instruction Manual ECP3220 - 3420 - 3630ureehwsenqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parker O-Ring Material Guide-2008Document72 paginiParker O-Ring Material Guide-2008Ian Pillay50% (2)
- v3.3 - Cut-Off - Activated Carbon Production Granular From Hard Coal - Rer - Activated Carbon Granular 1Document14 paginiv3.3 - Cut-Off - Activated Carbon Production Granular From Hard Coal - Rer - Activated Carbon Granular 1jimÎncă nu există evaluări